Low, high, last. GLC - the fifth element of the Lakhta Center
We are often asked the question - will there be more skyscrapers in Lakhta? High-altitude area, like Moscow City or Defense? One can see that next construction site is gaining momentum next to the Lakhta Center. Perhaps behind her blue fence lies the birth of a new, even more incredible super-skyscraper?
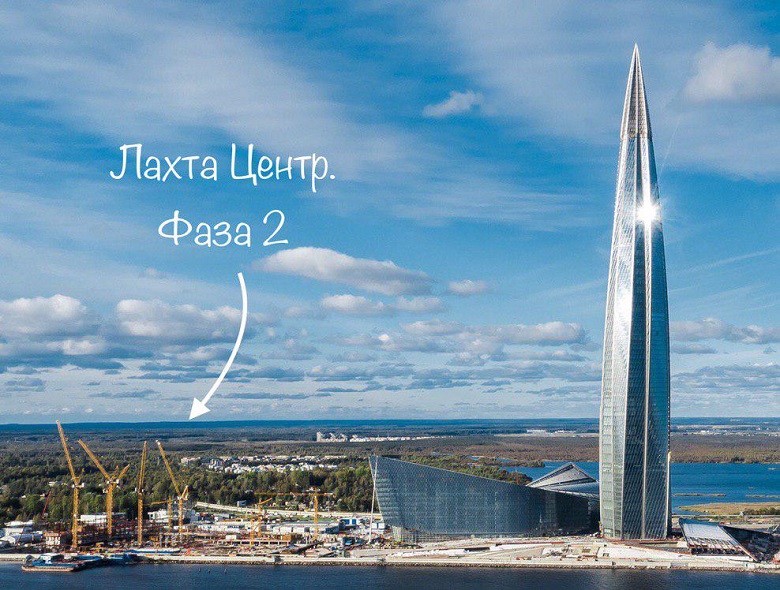

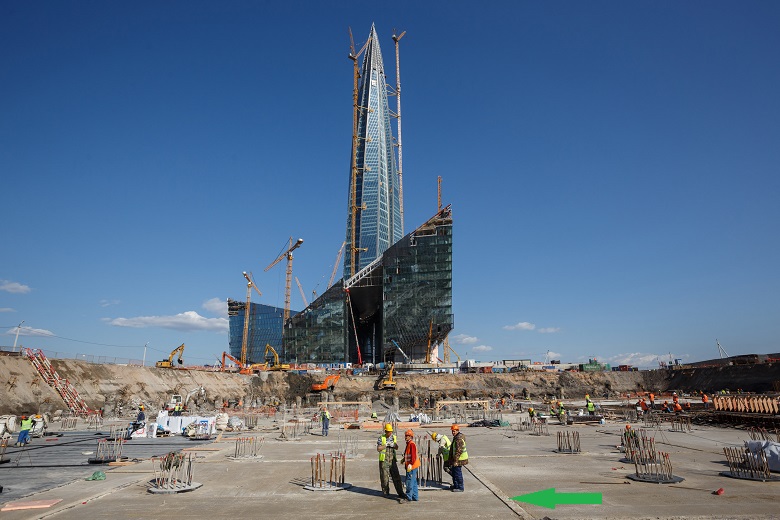
Yes, indeed, from last year, geotechnicians and concrete workers, reinforcers and surveyors, crane operators and designers - all again put under the gun. The best construction forces have been thrown at the construction of the final facility of the Lakhta Center complex. And, like any finale, this construction site intrigues the imagination. Let's see what is there?
Builders call the new facility simply and intelligibly - “Lakhta-2”.

The official name is GLC, almost a rebus. Its decoding - “Complex of buildings and structures” does not add anything to understanding. The building is just one.
And the meaning is unexpected. That was the name of the corporate residence of Gazprom in Moscow - and here the St. Petersburg headquarters was named in honor and memory. From corporations you do not expect sentimentality, but sometimes it happens.
The GLC becomes the final facility of the Lakhta Center. A tower, a multifunctional building, an arch of the main entrance and a stylobate have already been commissioned. GLC is the second and final phase.

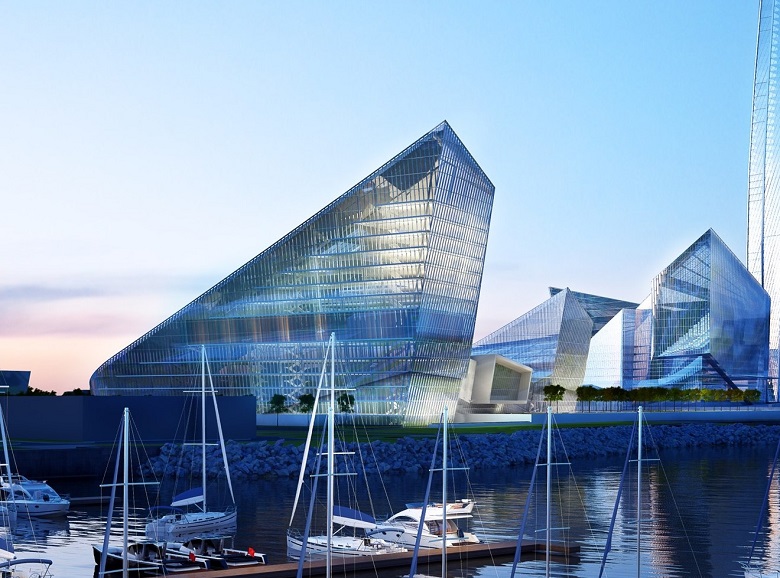
The GLC is made in an easily recognizable style, but the beginner has something to add to the architectural concept. The fifth element, continuing the axis of the MFZ, balances the tower horizontally. It turns out a complete and proportional architectural ensemble, making the Baltic coast of the Baltic recognizable.
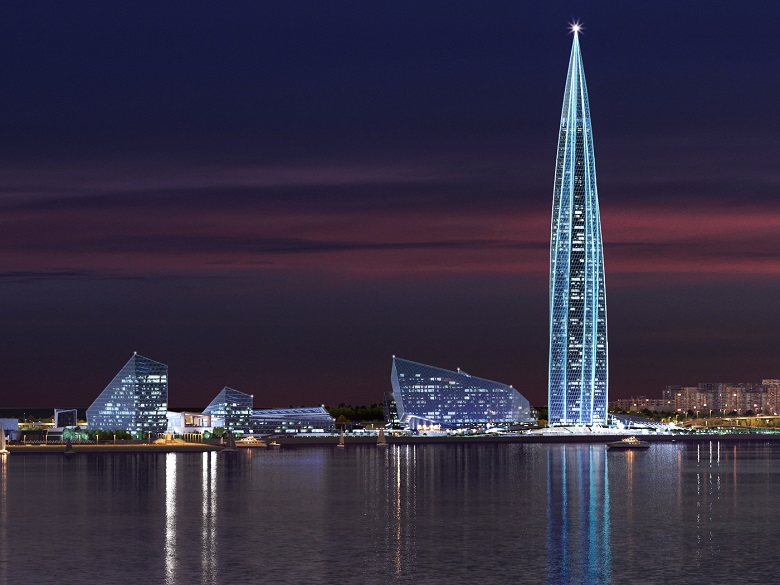

The object itself is a building divided into two buildings by a covered courtyard and united by a common stylobate.
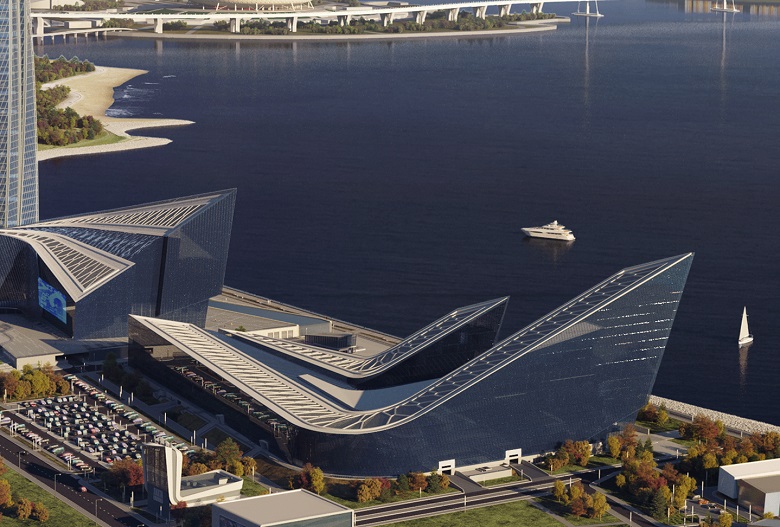

Number of storeys - variable, from 2 to 13 floors with a peak at 85 meters. Even according to the most loyal estimates, it does not reach a skyscraper, but due to the extended low-rise part, it sends greetings to the camp of supporters of low headquarters "like Apple". The area of the object is more than 150 thousand m2. With the commissioning of the GLC, the Lakhta Center footage has crossed the half-million line. The complex, with its 572 thousand m2, will go into the category of the largest headquarters in the world.
The main parameters of the GLC are similar to the Multifunctional building of the Lakhta Center, but the differences are obvious.

At the KZS there is an extended low-rise part, like an “atrium” roof “recessed” between the buildings, an “island” in the center of the courtyard - there will be a kind of MCC - a dispatch center. All this seems like a beautiful architectural variation, but in fact the background is more complex than aesthetics.
The GLC stands on two sites at once due to the small territorial interspersing within the boundaries of the main spot of development.
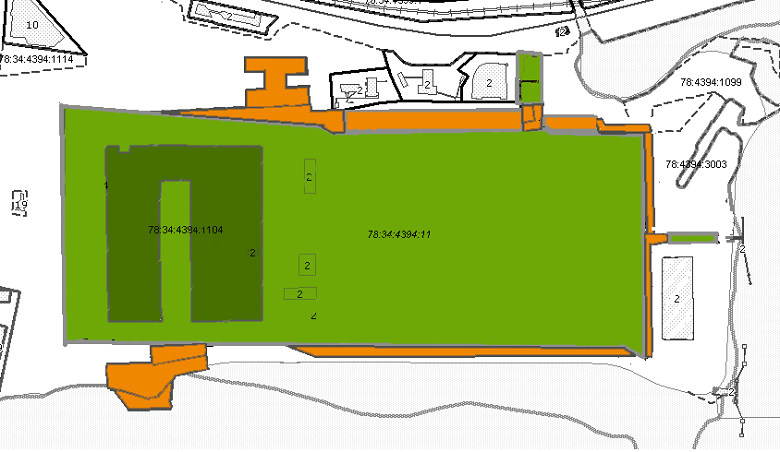
The historically formed cadastral collision could lead to a dead end: the high-rise regulations of “autonomy” are standard 27 meters versus 500 meters on the main part of the site. But, due to the different heights of the GLC and the skill of architects, the building was able to fit into the constraint without compromising on functionality and aesthetics. It was as if it went under the “glass ceiling” in order to then go upward at a turn to the harbor, to observe high-altitude regulations, but to remain itself is part of the recognizable Lakhta Center complex.

***
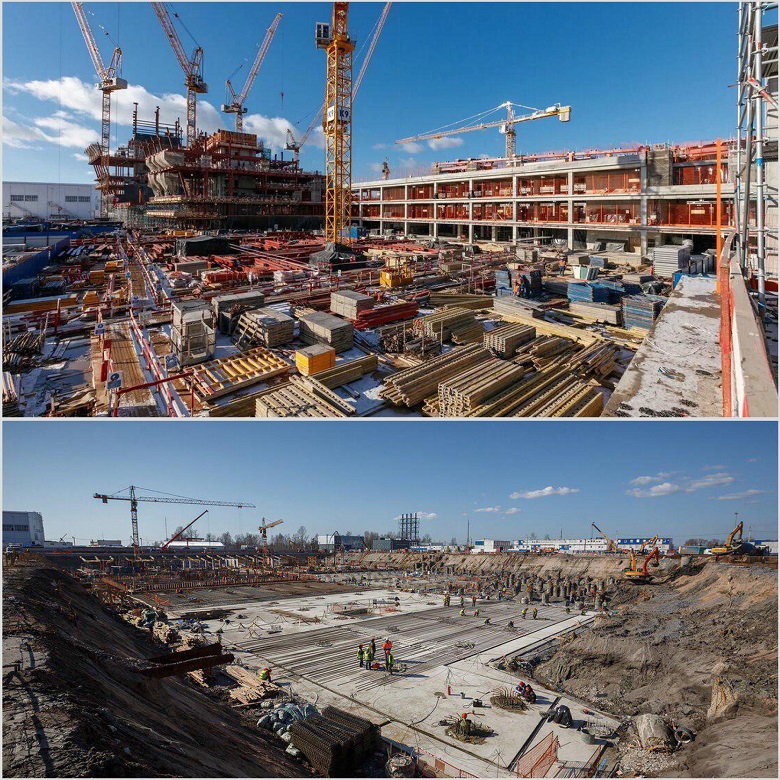

The difference in the photo is only a year. Speed is one of the main characteristics of this construction site. Powerful handicap - already familiar soils, compounding materials, organizational and technological schemes and techniques. However, no one canceled the negative factors. The main force majeure, the weather, is still valid.
Irina Anisimova, Development Director of IFC Lakhta Center JSC:
The zero cycle started in the summer of 2017. Experience has shown that the installation of a pile field before excavating a pit is the best option in local soil conditions. Piles work as anchors and keep the soil from moving, which keeps it compacted and reduces subsequent settlement of buildings. So the primacy of piles is not discussed.
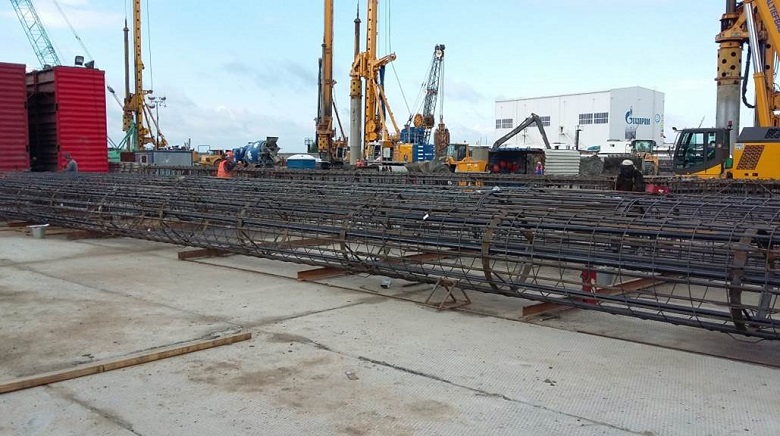
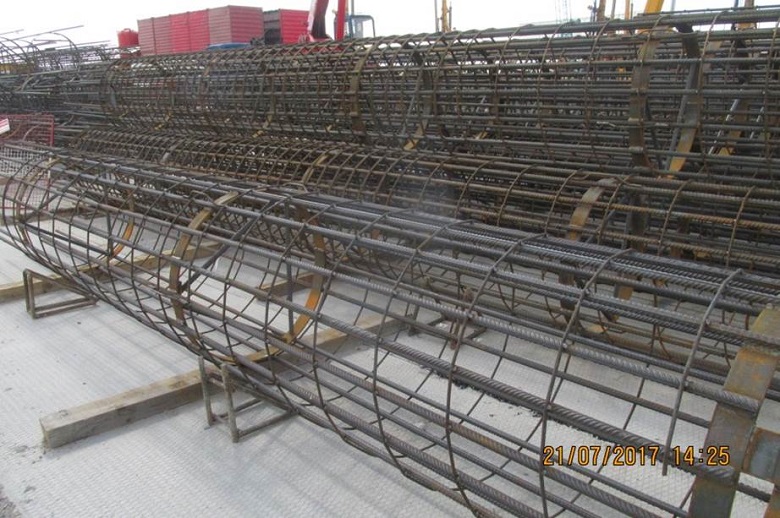


Armored carcasses of bored piles
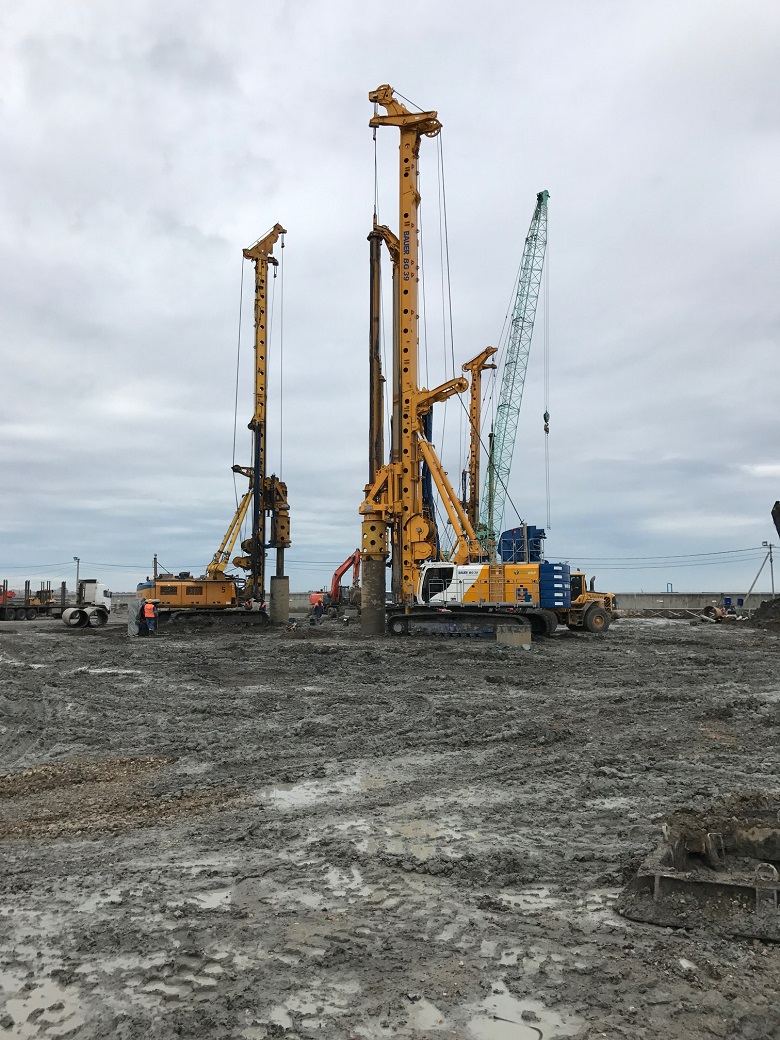

Drilling of wells for installation of piles is protected by casing so that water from the upper layers of the soil does not get into the well
Already by November, builders are completing the construction of the pile field by installing more than 1400 bored piles with a diameter of mainly 1180 mm and a laying depth of 35 m.
Digging a pit is always a struggle with soil pressure. On the Lakhta coast to the minus 4 m mark, the pressure in the soil rises to 2399 kN / l.m. If you don’t do anything with this, but just dig, you can’t avoid pushing into the walls of the pit.
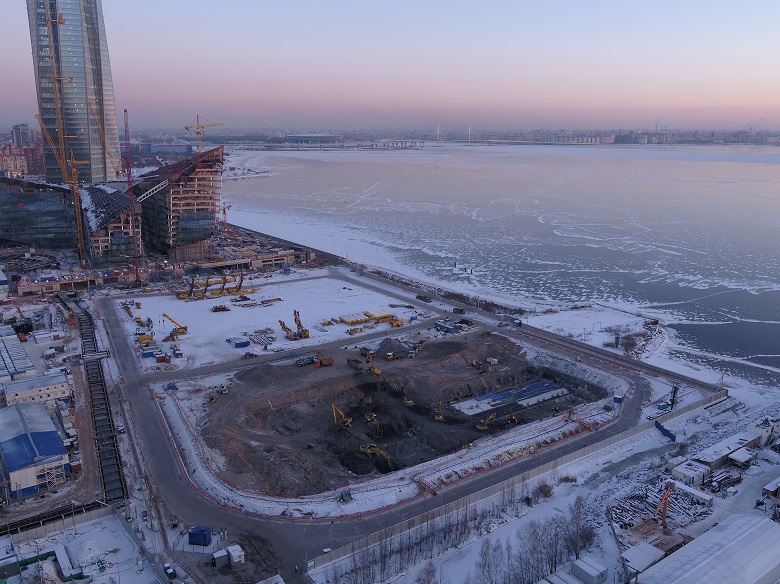
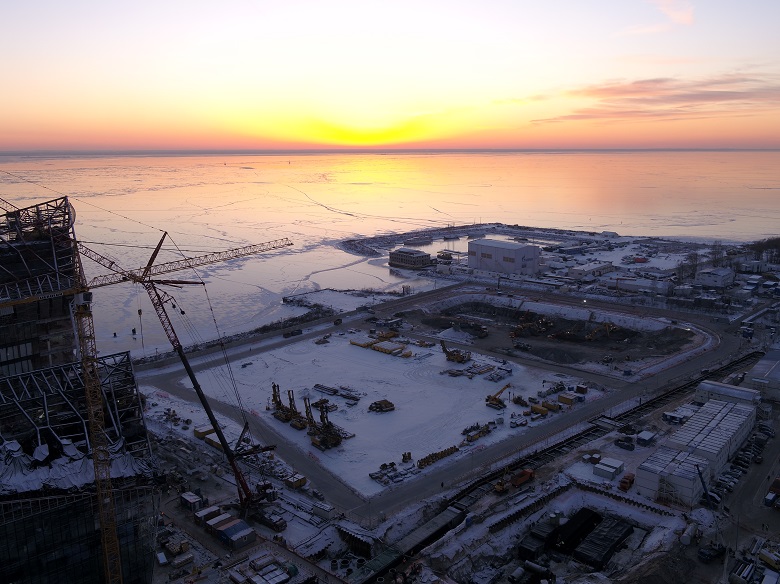


The beginning of the excavation of the excavation pit of the KZS. Winter 2018, project archive
Builders solve this problem in different ways - for example, in the foundation pit of the tower the walls were closed with reinforced concrete spacer discs.

Spacer system: temporary disks on the walls of the foundation pit of the Lakhta Center tower. Summer 2013
GLC has a relatively simpler spacer system. A reinforced concrete wall in the soil with a width of 800 mm is made - this is to protect against water in the upper layers of the soil. Along it, a metal beam was launched along the perimeter, to which spacers were welded - pipes with a diameter of 1.2 meters to hold the external walls of the foundation pit "in the design position" - that is, without deflection inward.
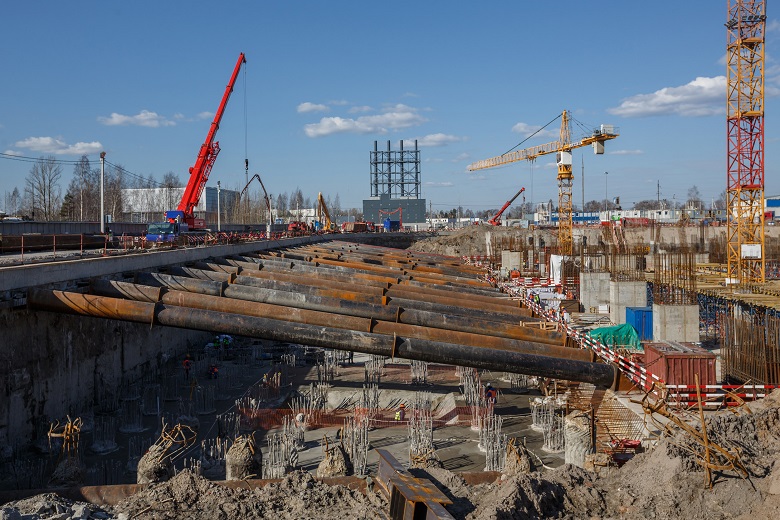


KZS spacer system
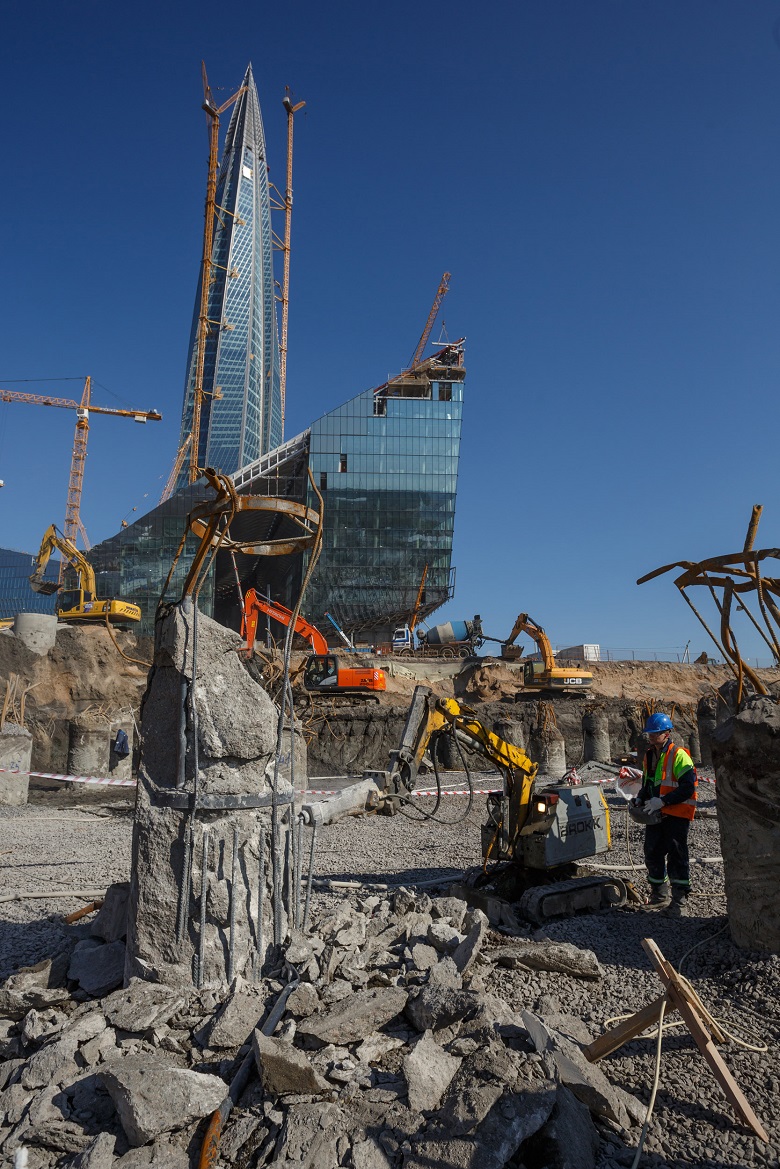
By spring 2018, the landscape at the bottom of individual sections of the pit resembles Easter Island.
Like stone statues, the heads of piles rise.

They have to cut down.
When pouring piles, heavy concrete displaces upward bentonite mortar and sludge - particles of drilled soil, which sometimes remain at the bottom of the pile well. There, right above, there is rubble, which temporarily clogged the mouth of a newly made pile. Therefore - such a “terminator" comes here, drills and cuts off the pile "heads".
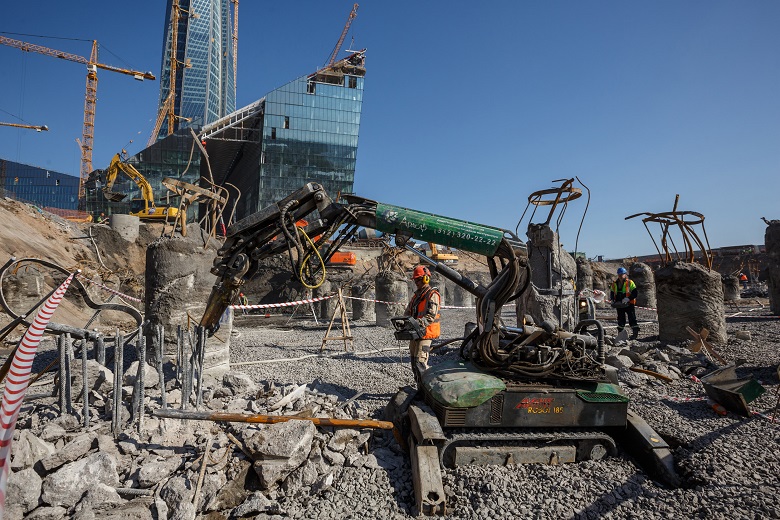

“Terminator” works remotely - the operator with the control panel is at a respectful distance and in full protective ammunition.

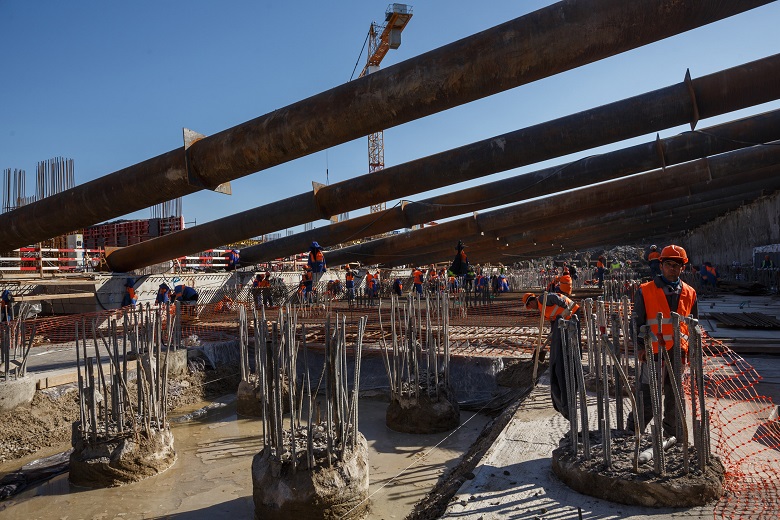
KZS relies on a slab grillage - a slab into which the pile heads are reinforcedly tied and monolithic. Long foundation - a whole concrete field of 4.2 hectares.

Pouring this at a time will not work, and it is not necessary. The foundation is concreted with gripping parts. The foundation plate itself will be a monolithic structure. But a little higher - at the stylobate level, in several places they will make expansion joints - narrow sections filled with an elastic insulator. Such seams make parts of the extended building more independent of each other during subsequent settlement and prevent plate deformation.

Preparation for concreting the grips, spring 2018

In the photo - a technological seam between the grips of the slab grillage
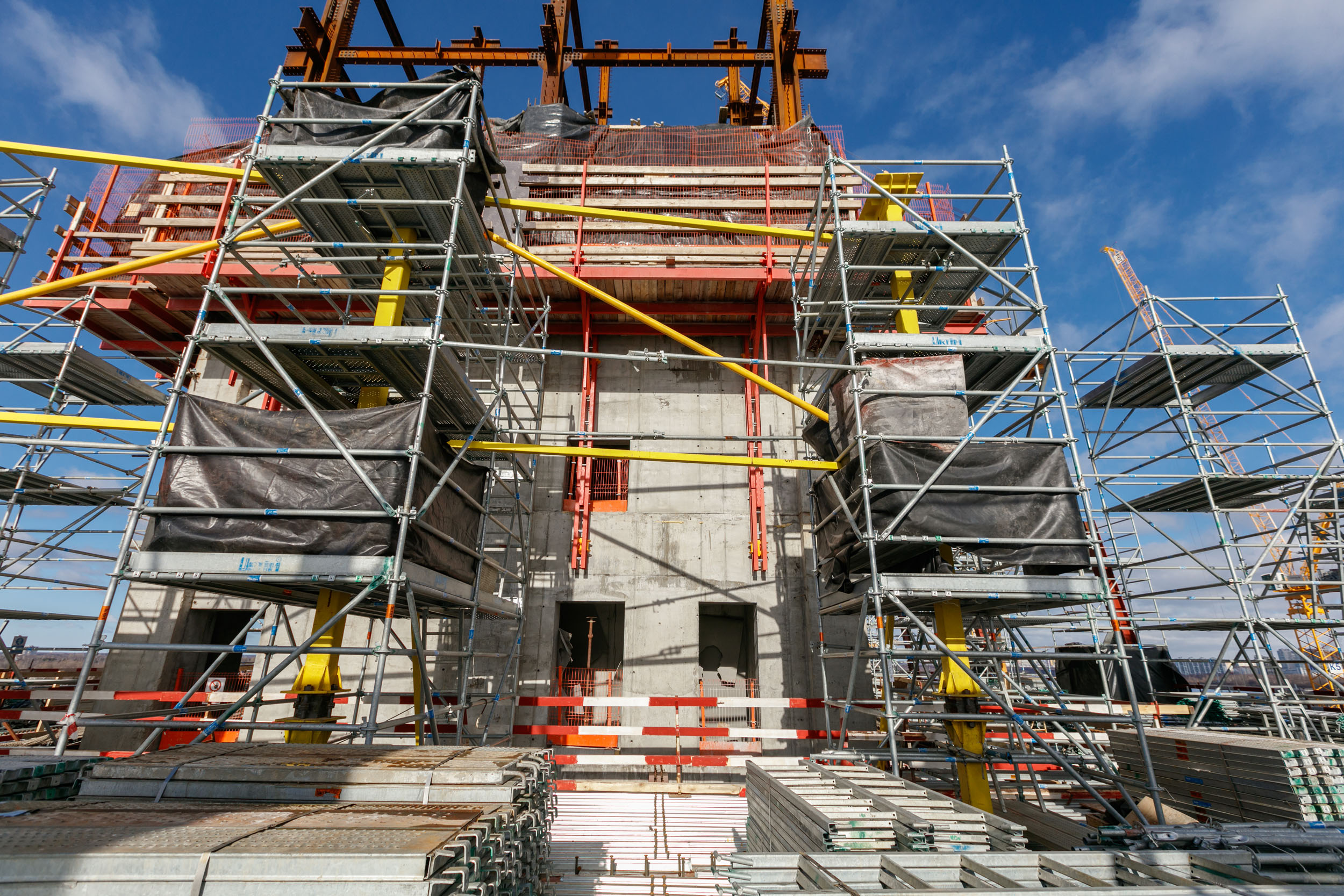
Ready foundation plate:

Releases of reinforcement from it become the basis for the armoframe of future walls in the stylobate. The plate is buried - minus the first and minus the second floors of the building
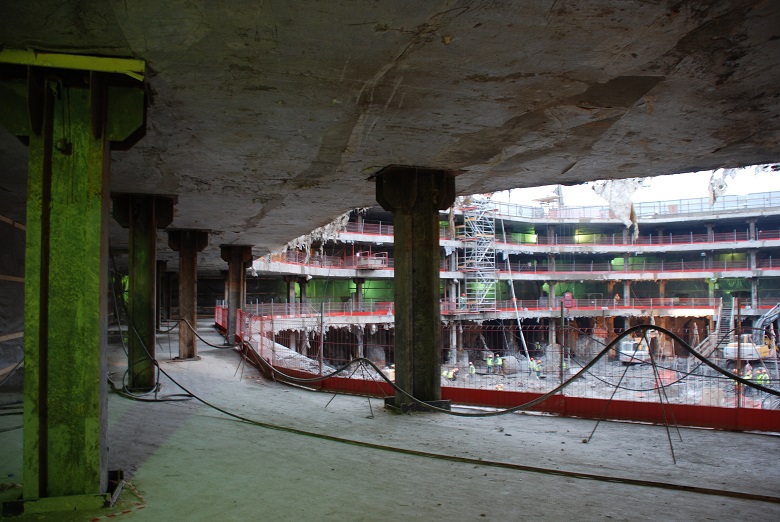
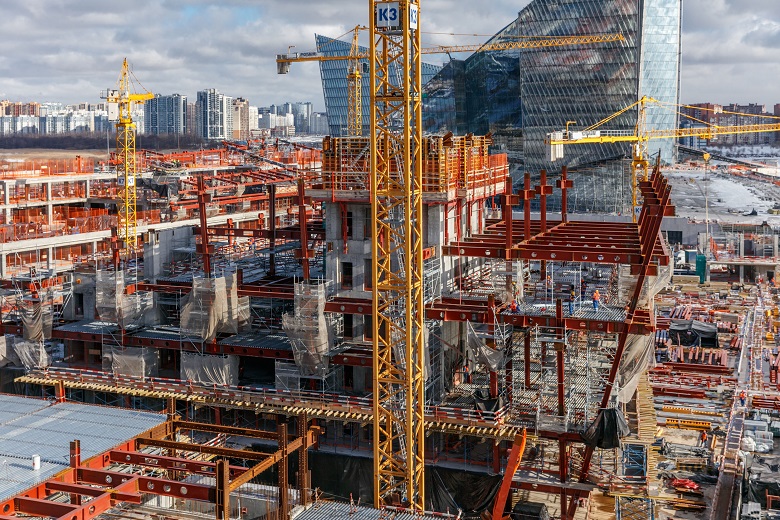
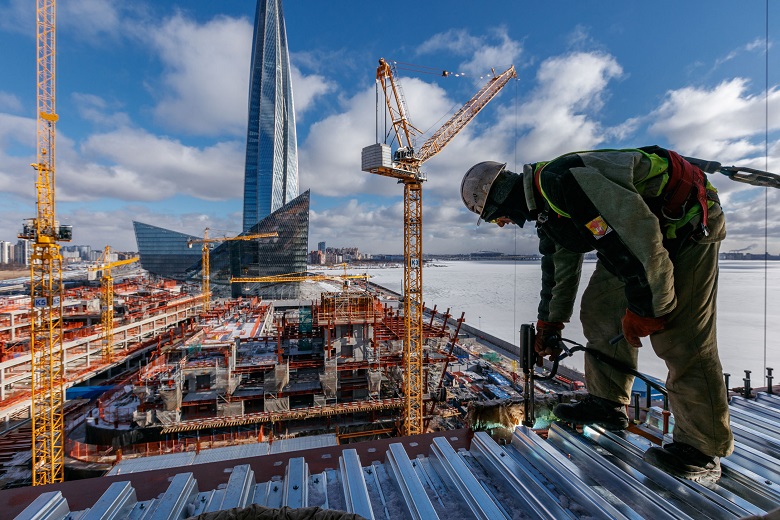
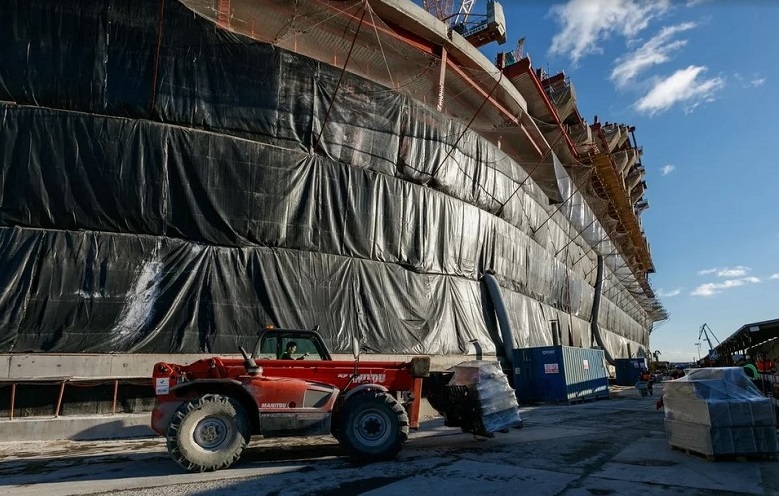
To date, builders are in the process of climbing. Now the construction avant-garde is metalworkers, working at around 10 floors. The face of the GLC is becoming more readable.
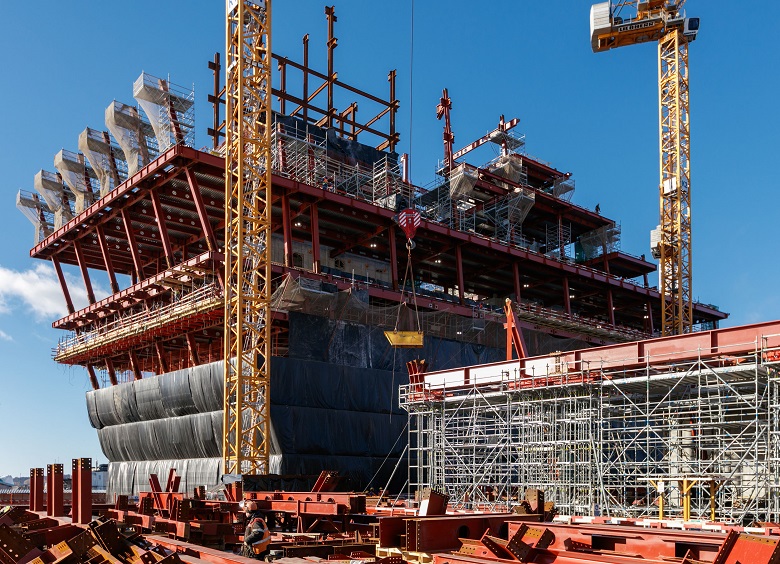

GLC, March 2019

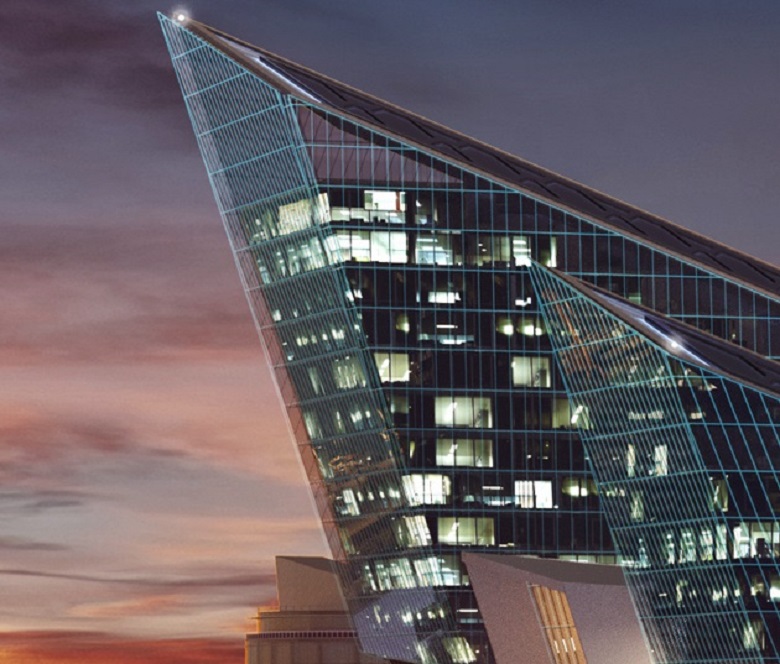
Visualization of GLC
The main difficulty of the GLC in terms of ensuring the stability of its above-ground part is the length of the building and the presence of large-span spaces inside it.
The solution is based, of course, on reinforced concrete stiffness cores, which simultaneously form lift and stairwells.

Due to the length and division into GLC into blocks, there are fifteen such nuclei! They are the main ones in the perception of vertical and horizontal loads.


They play the role of the vertical communication arteries of the building. Inside - evacuation routes, security zones and elevators - 57 Kone cabins, including 9 that can be used to transport firefighters. The most lifting lift is designed for 3,250 kg. For comparison - in the tower the main heavy truck lifts up to 5,000 kg
In the meantime, the role of vertical transport is played by a construction hoist. Its installation is a sure sign of a grown building.

The structural scheme of the building is framed.
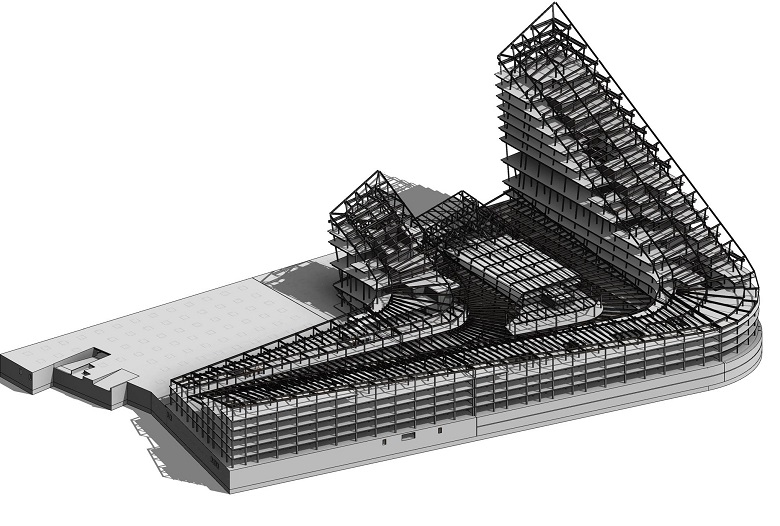
The frame is formed by longitudinal and cantilever beams made of high-strength steel of the Histar 460 brand. In areas of wide-span spaces - over 36 m without support in the form of columns, transverse and longitudinal trusses with rigid nodes are additionally installed.
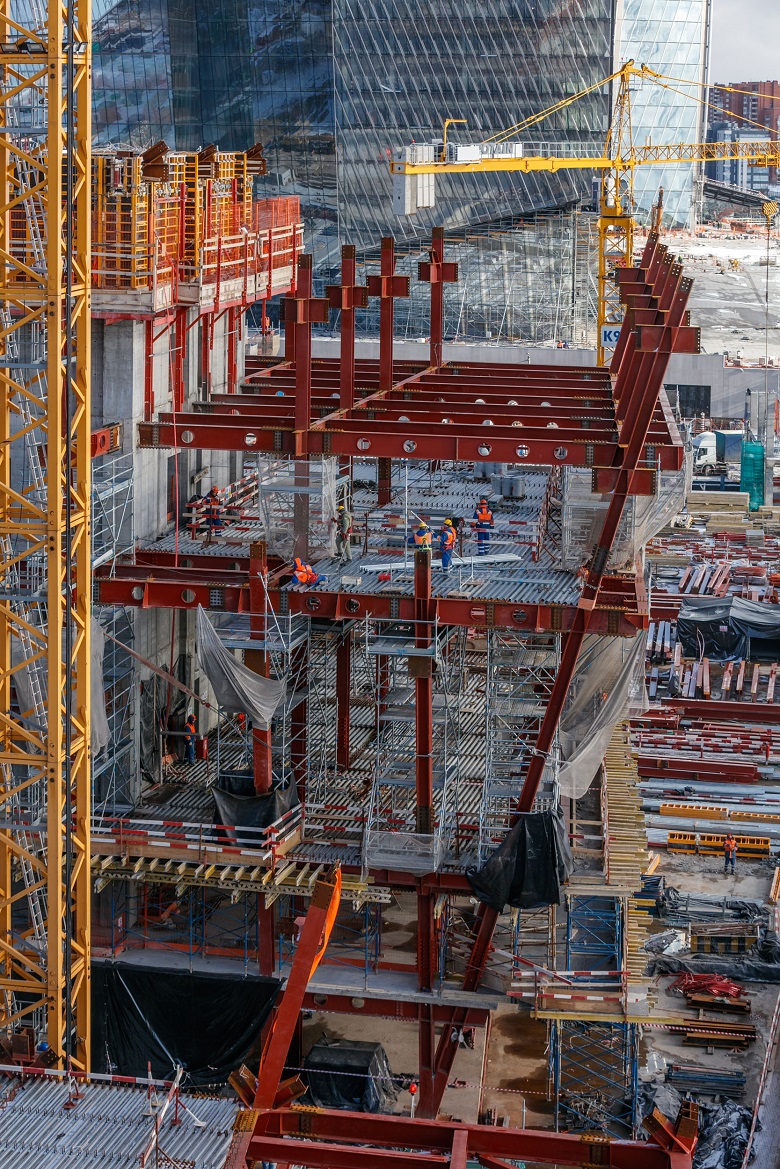
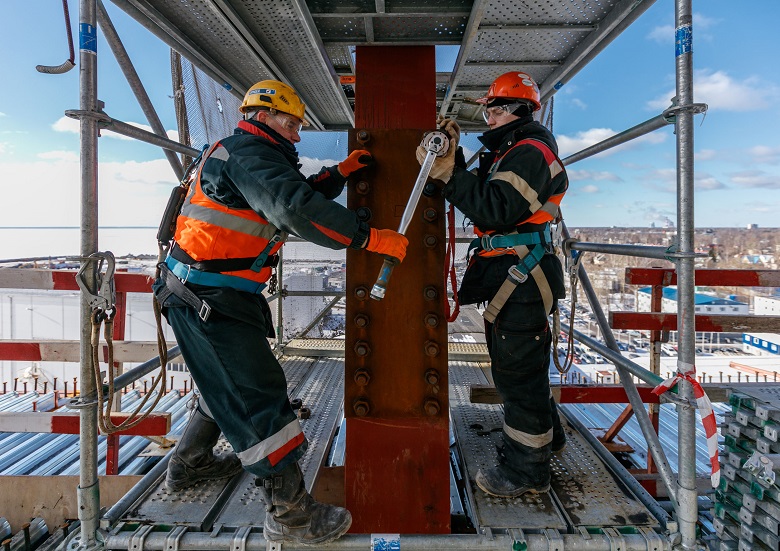
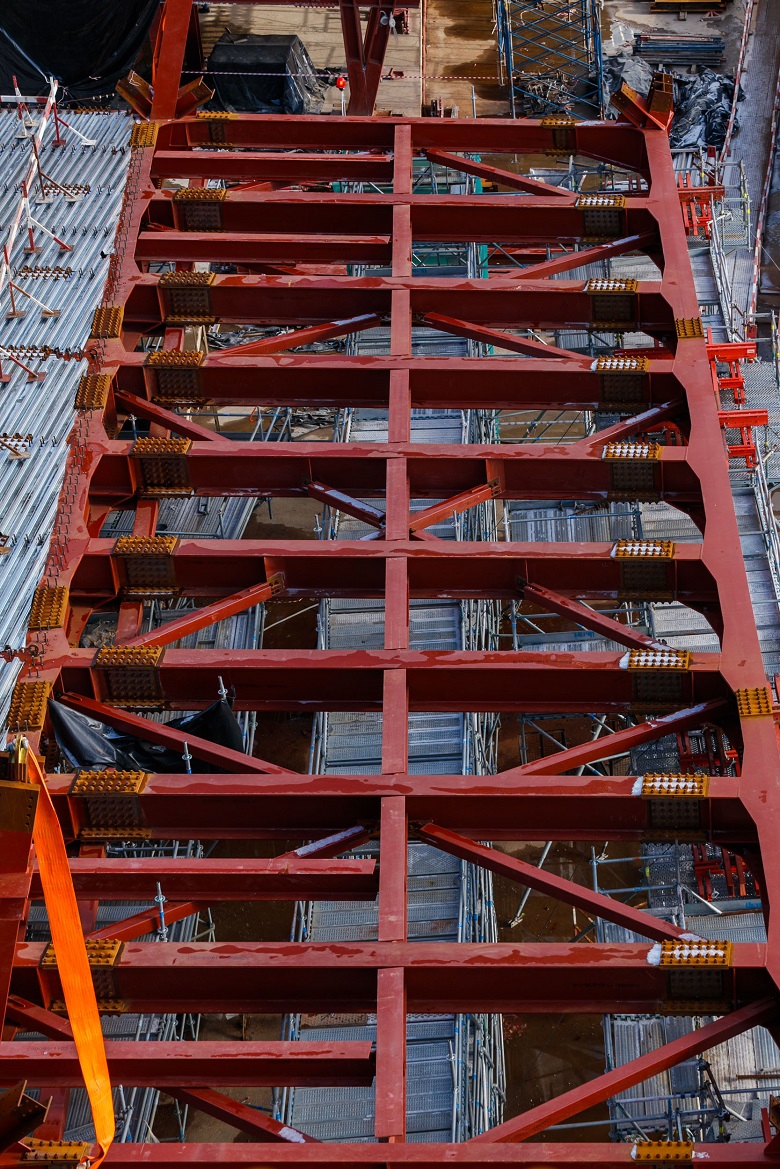



Interfloor ceilings - reinforced concrete according to the professional sheet. A profiled sheet is attached to the supporting beams with stud bolts, reinforcement is knitted, then the floor is concreted.
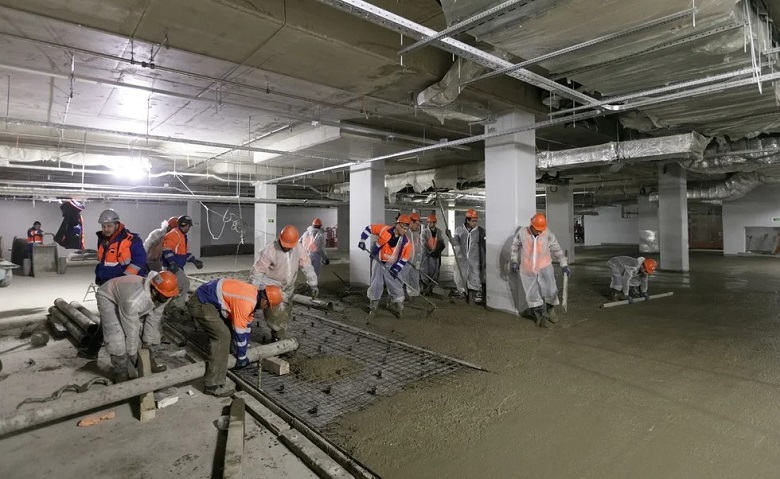



Facades of KZS - from multifunctional glass: metal spraying improves almost all consumer properties - energy efficiency, mechanical strength and others. This glass - plus a hundred points to aesthetics - it gives the effect of a continuous reflection of the environment - the bay, clouds, and so far mainly building realities.
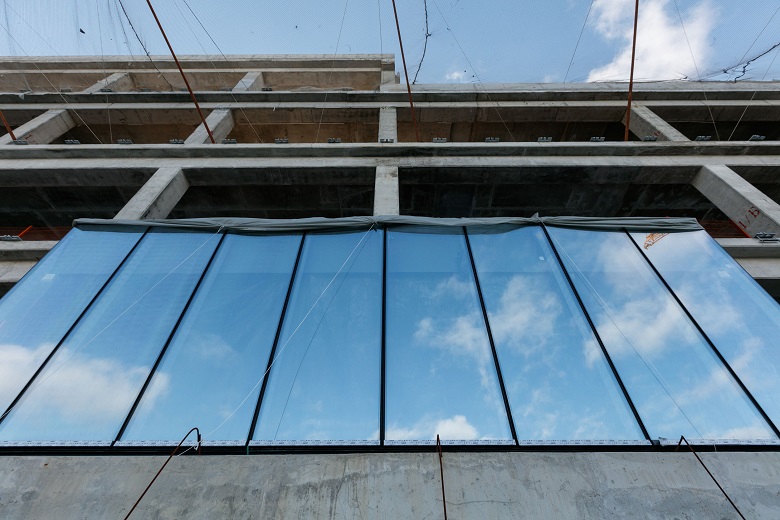
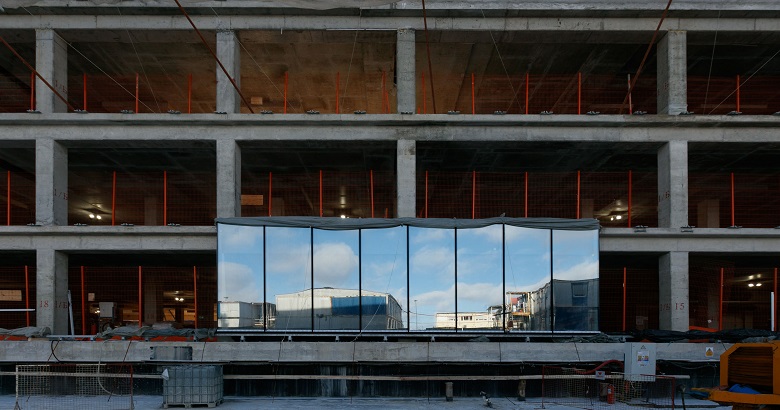


The care for those who will work behind the facade is sun-protection and a safe inner layer of tempered glass.
The glass module in a lightweight aluminum profile has dimensions 1500 * 4200 and covers the entire floor height without additional crossbars.
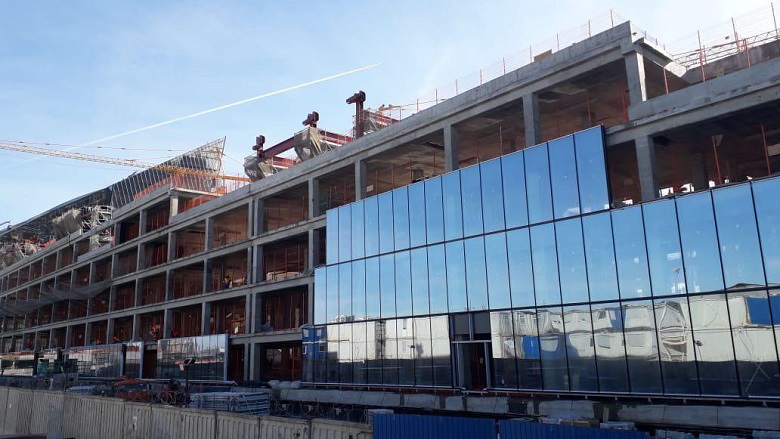

Double-glazed windows are hung on interfloor ceilings on brackets installed in increments of 1, 5 m. Mounts are fixed on one side and hinged on the other.

This provides some facade independence from temperature fluctuations in the rest of the building. Own expansion and contraction of glass are compensated by rubber sealant and non-hardening sealants.
In the curved sections of the facade, the glass will be cold-bent and also molded - that is, bent.

A double facade is planned in the end parts - the second glass wall will go a meter from the first, the half-timbered steel structure will serve as a support.

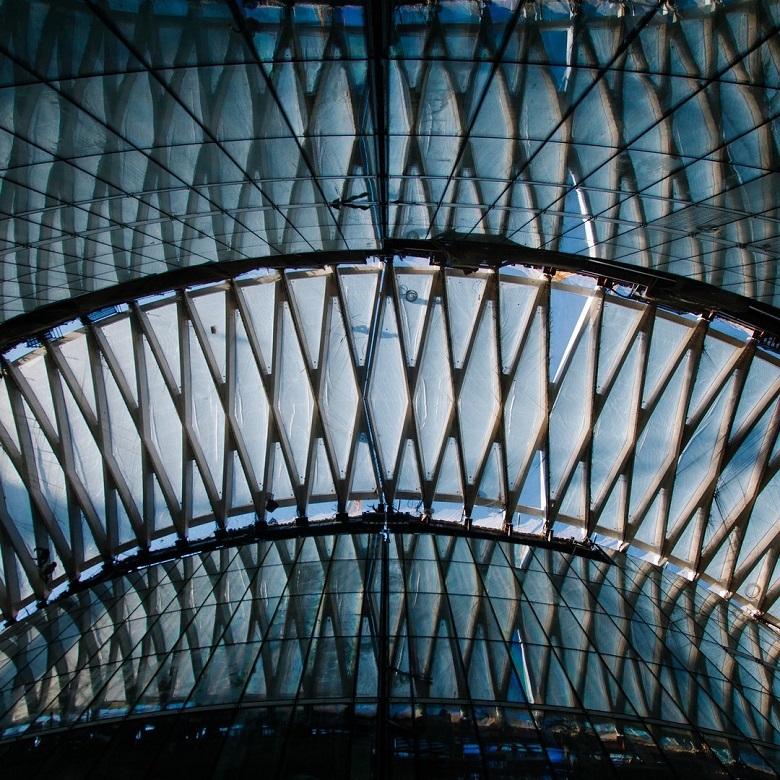
The most curious high point is, of course, the roof of the atrium. Here, as in MPF, instead of glazing, ETFE membranes will be used, forming a recognizable pattern.

From 4 polymer layers latched into a metal profile, cushions are formed, which are then pumped with air under a pressure of about 200 Pa. Here is what it looked like on the roof of the atrium of the MPF:

Pillows from ETFE in the initial state. Demonstration of the roof of the atrium of the MFZ Lakhta Center. Photo - spring 2018, archive

And after the air injection ... Demonstration on the example of the roof of the atrium of the MFZ Lakhta Center. Photos - summer 2018, archive
The membranes are light, their light transmittance exceeds the characteristics of the glass, and almost the only option for damage - puncture the pillow - does not pose any danger to those below. And in general it is unlikely to be noticeable due to the pneumatic pumping system.

Light transmittance of ETFE membranes as an example of the roof of the atrium of the MFZ Lakhta Center. Photo from the Lakhta Center art album The
roof of buildings is the place of work and rest of cranes for the facade service system of the KZS. In the parking position, cranes will hide on special platforms, and upon entering service, they will move along the “rails” laid on the roof.
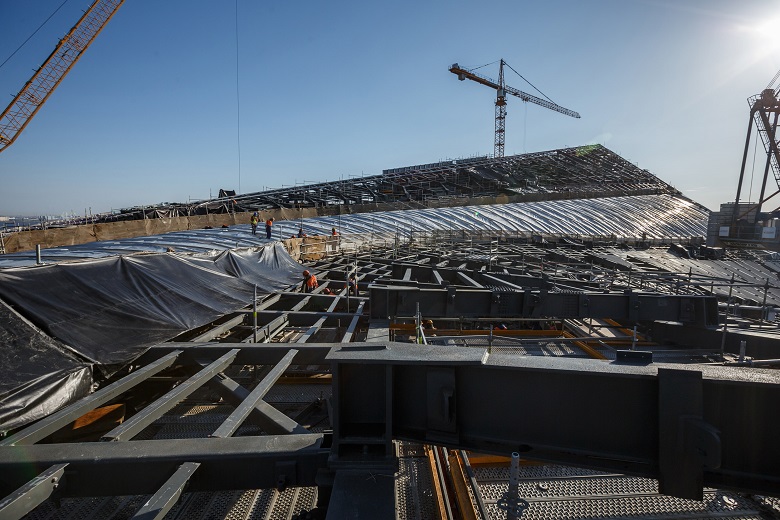

Inside the roof there are trellised flooring for the movement of specialists serving facades, parking spaces for SOF equipment, rails for moving cranes. Demonstration on the example of the roof of the atrium of the MFZ. Photos - spring, 2018, archive The
lower level of the GLC is also associated with transport.
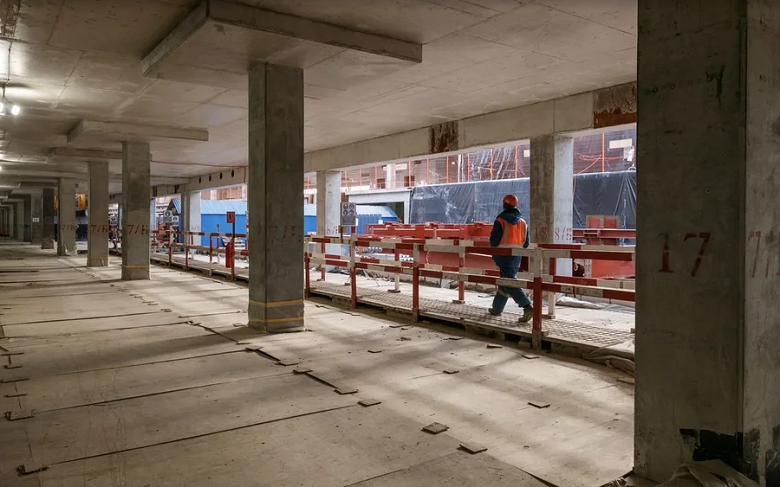
On the two underground floors of the stylobate, going almost to the borders of the site, there will be a parking lot, as well as a variety of technical rooms.

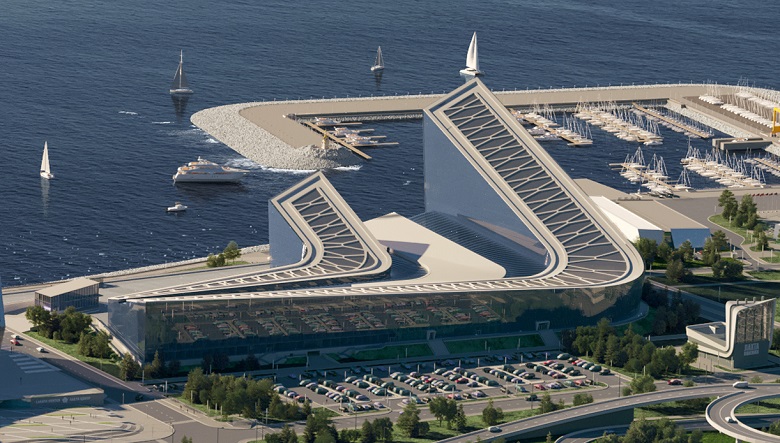
The stylobate roof will be exploitable - stone-paved paths, greenery and ponds are planned.
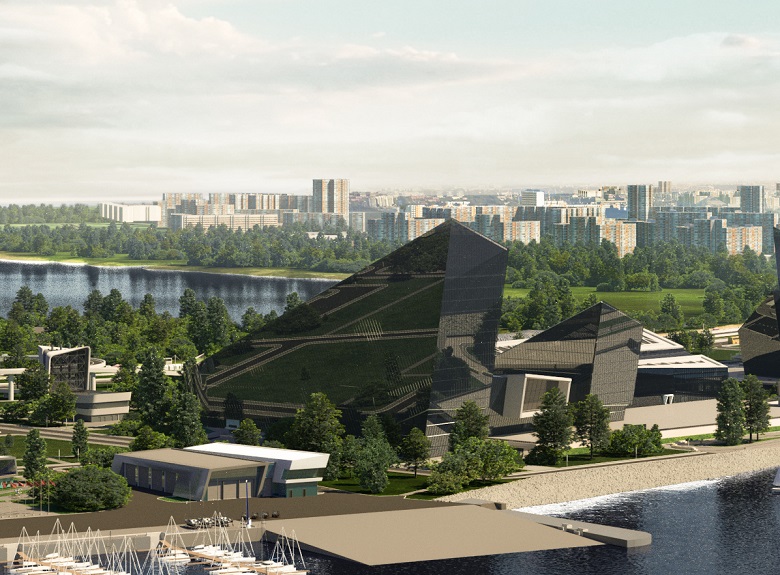

KZS with adjoining territory, visualization
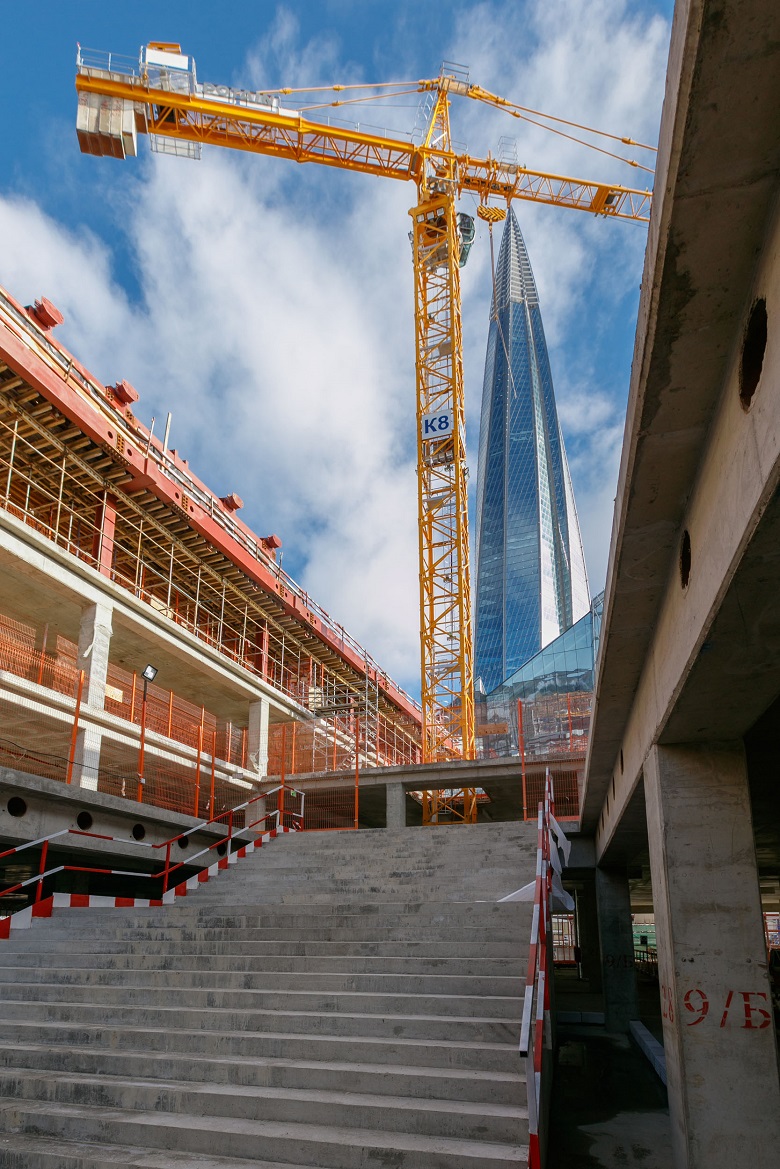

A staircase leading from the 1st floor to the gallery of the KZS courtyard
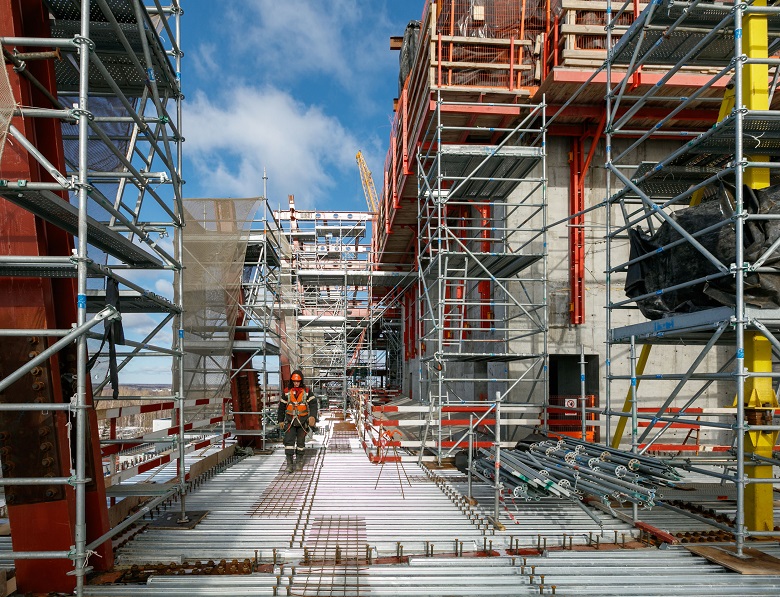
All work on the creation of a GLC is parallel - metal structures are installed at the top, concrete floors are poured below, even lower partitions are already plastering, communications are being pulled, and double-glazed windows are being installed.
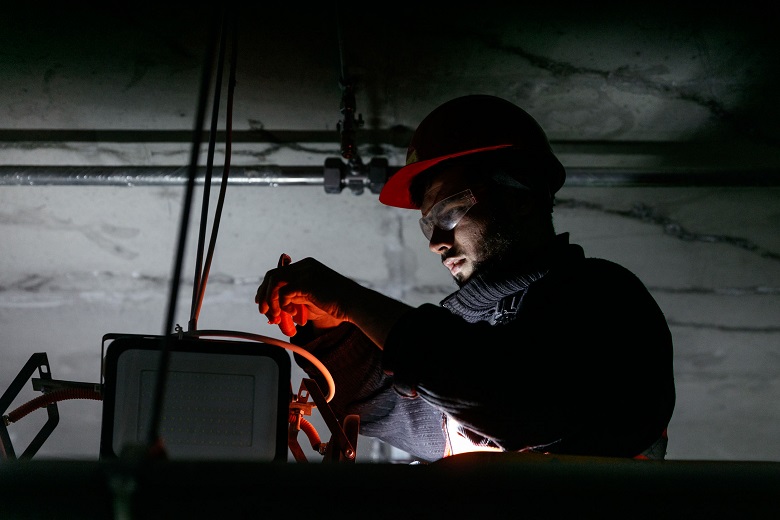

How electricians work, while there is still no light, there is
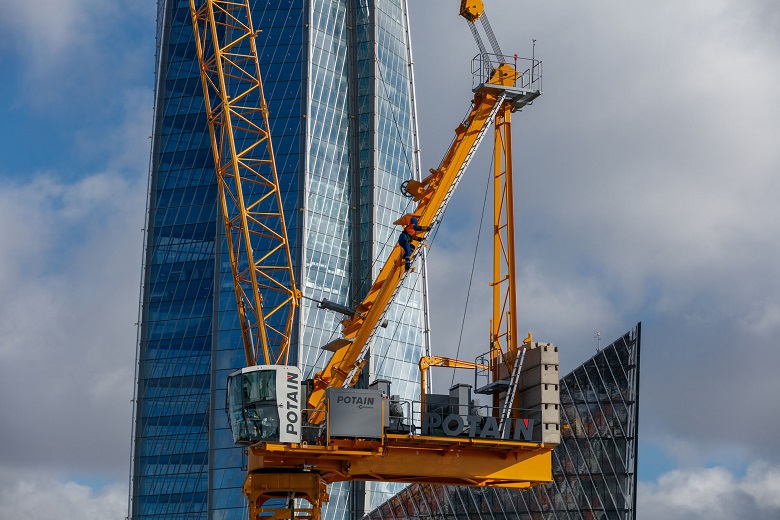

nothing stopping Service Engineers

Fencing all installation perimeters - signs of an inconspicuous but ubiquitous labor protection service

Surveyors are people without whom it is impossible to build complex geometry of the building.

Round-the-clock construction of the KZS
Once the work of some specialists is completed, here the workplace of others appears. In the rearguard - work in the underground parking lot - he seems ready to receive visitors.

Until this moment, there really is a little time left - the construction should be completed in the spring of 2021. This time, builders will forever leave this corner of the coast and the famous construction site in Lakhta.

***
Thank you for your help in preparing the material of the development director of IFC Lakhta Center JSC Irina Anisimova.

Yes, indeed, from last year, geotechnicians and concrete workers, reinforcers and surveyors, crane operators and designers - all again put under the gun. The best construction forces have been thrown at the construction of the final facility of the Lakhta Center complex. And, like any finale, this construction site intrigues the imagination. Let's see what is there?
PRO BUILDING
Why GLC?
Builders call the new facility simply and intelligibly - “Lakhta-2”.

The official name is GLC, almost a rebus. Its decoding - “Complex of buildings and structures” does not add anything to understanding. The building is just one.
And the meaning is unexpected. That was the name of the corporate residence of Gazprom in Moscow - and here the St. Petersburg headquarters was named in honor and memory. From corporations you do not expect sentimentality, but sometimes it happens.
Architectural Quintet
The GLC becomes the final facility of the Lakhta Center. A tower, a multifunctional building, an arch of the main entrance and a stylobate have already been commissioned. GLC is the second and final phase.

The GLC is made in an easily recognizable style, but the beginner has something to add to the architectural concept. The fifth element, continuing the axis of the MFZ, balances the tower horizontally. It turns out a complete and proportional architectural ensemble, making the Baltic coast of the Baltic recognizable.

High and low headquarters
The object itself is a building divided into two buildings by a covered courtyard and united by a common stylobate.

Number of storeys - variable, from 2 to 13 floors with a peak at 85 meters. Even according to the most loyal estimates, it does not reach a skyscraper, but due to the extended low-rise part, it sends greetings to the camp of supporters of low headquarters "like Apple". The area of the object is more than 150 thousand m2. With the commissioning of the GLC, the Lakhta Center footage has crossed the half-million line. The complex, with its 572 thousand m2, will go into the category of the largest headquarters in the world.
Gemini or not?
The main parameters of the GLC are similar to the Multifunctional building of the Lakhta Center, but the differences are obvious.

At the KZS there is an extended low-rise part, like an “atrium” roof “recessed” between the buildings, an “island” in the center of the courtyard - there will be a kind of MCC - a dispatch center. All this seems like a beautiful architectural variation, but in fact the background is more complex than aesthetics.
Territorial autonomy
The GLC stands on two sites at once due to the small territorial interspersing within the boundaries of the main spot of development.

The historically formed cadastral collision could lead to a dead end: the high-rise regulations of “autonomy” are standard 27 meters versus 500 meters on the main part of the site. But, due to the different heights of the GLC and the skill of architects, the building was able to fit into the constraint without compromising on functionality and aesthetics. It was as if it went under the “glass ceiling” in order to then go upward at a turn to the harbor, to observe high-altitude regulations, but to remain itself is part of the recognizable Lakhta Center complex.

***
HOW THE BUILDING IS GOING
Quickly

The difference in the photo is only a year. Speed is one of the main characteristics of this construction site. Powerful handicap - already familiar soils, compounding materials, organizational and technological schemes and techniques. However, no one canceled the negative factors. The main force majeure, the weather, is still valid.
Irina Anisimova, Development Director of IFC Lakhta Center JSC:
“... During a strong wind, cranes cannot work, and temperature swings increase the operating time. One day we fight with snow, the other with water and wind. It makes you watch all the time. ” (From an interview with the Paper portal)This is how the struggle continues, begun by St. Petersburg builders 300 years ago.
Excavation and piles - in reverse order
The zero cycle started in the summer of 2017. Experience has shown that the installation of a pile field before excavating a pit is the best option in local soil conditions. Piles work as anchors and keep the soil from moving, which keeps it compacted and reduces subsequent settlement of buildings. So the primacy of piles is not discussed.


Armored carcasses of bored piles

Drilling of wells for installation of piles is protected by casing so that water from the upper layers of the soil does not get into the well
Already by November, builders are completing the construction of the pile field by installing more than 1400 bored piles with a diameter of mainly 1180 mm and a laying depth of 35 m.
Under pressure
Digging a pit is always a struggle with soil pressure. On the Lakhta coast to the minus 4 m mark, the pressure in the soil rises to 2399 kN / l.m. If you don’t do anything with this, but just dig, you can’t avoid pushing into the walls of the pit.


The beginning of the excavation of the excavation pit of the KZS. Winter 2018, project archive
Builders solve this problem in different ways - for example, in the foundation pit of the tower the walls were closed with reinforced concrete spacer discs.

Spacer system: temporary disks on the walls of the foundation pit of the Lakhta Center tower. Summer 2013
GLC has a relatively simpler spacer system. A reinforced concrete wall in the soil with a width of 800 mm is made - this is to protect against water in the upper layers of the soil. Along it, a metal beam was launched along the perimeter, to which spacers were welded - pipes with a diameter of 1.2 meters to hold the external walls of the foundation pit "in the design position" - that is, without deflection inward.


KZS spacer system
Heads off
By spring 2018, the landscape at the bottom of individual sections of the pit resembles Easter Island.
Like stone statues, the heads of piles rise.

They have to cut down.
When pouring piles, heavy concrete displaces upward bentonite mortar and sludge - particles of drilled soil, which sometimes remain at the bottom of the pile well. There, right above, there is rubble, which temporarily clogged the mouth of a newly made pile. Therefore - such a “terminator" comes here, drills and cuts off the pile "heads".

“Terminator” works remotely - the operator with the control panel is at a respectful distance and in full protective ammunition.

Foundation
KZS relies on a slab grillage - a slab into which the pile heads are reinforcedly tied and monolithic. Long foundation - a whole concrete field of 4.2 hectares.

Pouring this at a time will not work, and it is not necessary. The foundation is concreted with gripping parts. The foundation plate itself will be a monolithic structure. But a little higher - at the stylobate level, in several places they will make expansion joints - narrow sections filled with an elastic insulator. Such seams make parts of the extended building more independent of each other during subsequent settlement and prevent plate deformation.

Preparation for concreting the grips, spring 2018

In the photo - a technological seam between the grips of the slab grillage
Ready foundation plate:

Releases of reinforcement from it become the basis for the armoframe of future walls in the stylobate. The plate is buried - minus the first and minus the second floors of the building
Spring walk on the construction site
To date, builders are in the process of climbing. Now the construction avant-garde is metalworkers, working at around 10 floors. The face of the GLC is becoming more readable.

GLC, March 2019

Visualization of GLC
Stability system for a very long building
The main difficulty of the GLC in terms of ensuring the stability of its above-ground part is the length of the building and the presence of large-span spaces inside it.
The solution is based, of course, on reinforced concrete stiffness cores, which simultaneously form lift and stairwells.

Due to the length and division into GLC into blocks, there are fifteen such nuclei! They are the main ones in the perception of vertical and horizontal loads.


They play the role of the vertical communication arteries of the building. Inside - evacuation routes, security zones and elevators - 57 Kone cabins, including 9 that can be used to transport firefighters. The most lifting lift is designed for 3,250 kg. For comparison - in the tower the main heavy truck lifts up to 5,000 kg
In the meantime, the role of vertical transport is played by a construction hoist. Its installation is a sure sign of a grown building.

The structural scheme of the building is framed.

The frame is formed by longitudinal and cantilever beams made of high-strength steel of the Histar 460 brand. In areas of wide-span spaces - over 36 m without support in the form of columns, transverse and longitudinal trusses with rigid nodes are additionally installed.



Interfloor ceilings - reinforced concrete according to the professional sheet. A profiled sheet is attached to the supporting beams with stud bolts, reinforcement is knitted, then the floor is concreted.



Facades in shades of the sea
Facades of KZS - from multifunctional glass: metal spraying improves almost all consumer properties - energy efficiency, mechanical strength and others. This glass - plus a hundred points to aesthetics - it gives the effect of a continuous reflection of the environment - the bay, clouds, and so far mainly building realities.


The care for those who will work behind the facade is sun-protection and a safe inner layer of tempered glass.
The glass module in a lightweight aluminum profile has dimensions 1500 * 4200 and covers the entire floor height without additional crossbars.

Double-glazed windows are hung on interfloor ceilings on brackets installed in increments of 1, 5 m. Mounts are fixed on one side and hinged on the other.

This provides some facade independence from temperature fluctuations in the rest of the building. Own expansion and contraction of glass are compensated by rubber sealant and non-hardening sealants.
In the curved sections of the facade, the glass will be cold-bent and also molded - that is, bent.

A double facade is planned in the end parts - the second glass wall will go a meter from the first, the half-timbered steel structure will serve as a support.

Extreme levels: above and below
The most curious high point is, of course, the roof of the atrium. Here, as in MPF, instead of glazing, ETFE membranes will be used, forming a recognizable pattern.

From 4 polymer layers latched into a metal profile, cushions are formed, which are then pumped with air under a pressure of about 200 Pa. Here is what it looked like on the roof of the atrium of the MPF:

Pillows from ETFE in the initial state. Demonstration of the roof of the atrium of the MFZ Lakhta Center. Photo - spring 2018, archive

And after the air injection ... Demonstration on the example of the roof of the atrium of the MFZ Lakhta Center. Photos - summer 2018, archive
The membranes are light, their light transmittance exceeds the characteristics of the glass, and almost the only option for damage - puncture the pillow - does not pose any danger to those below. And in general it is unlikely to be noticeable due to the pneumatic pumping system.

Light transmittance of ETFE membranes as an example of the roof of the atrium of the MFZ Lakhta Center. Photo from the Lakhta Center art album The
roof of buildings is the place of work and rest of cranes for the facade service system of the KZS. In the parking position, cranes will hide on special platforms, and upon entering service, they will move along the “rails” laid on the roof.

Inside the roof there are trellised flooring for the movement of specialists serving facades, parking spaces for SOF equipment, rails for moving cranes. Demonstration on the example of the roof of the atrium of the MFZ. Photos - spring, 2018, archive The
lower level of the GLC is also associated with transport.
On the two underground floors of the stylobate, going almost to the borders of the site, there will be a parking lot, as well as a variety of technical rooms.

The stylobate roof will be exploitable - stone-paved paths, greenery and ponds are planned.

KZS with adjoining territory, visualization

A staircase leading from the 1st floor to the gallery of the KZS courtyard
Trace to trace
All work on the creation of a GLC is parallel - metal structures are installed at the top, concrete floors are poured below, even lower partitions are already plastering, communications are being pulled, and double-glazed windows are being installed.

How electricians work, while there is still no light, there is

nothing stopping Service Engineers

Fencing all installation perimeters - signs of an inconspicuous but ubiquitous labor protection service

Surveyors are people without whom it is impossible to build complex geometry of the building.

Round-the-clock construction of the KZS
Once the work of some specialists is completed, here the workplace of others appears. In the rearguard - work in the underground parking lot - he seems ready to receive visitors.

Until this moment, there really is a little time left - the construction should be completed in the spring of 2021. This time, builders will forever leave this corner of the coast and the famous construction site in Lakhta.

***
Thank you for your help in preparing the material of the development director of IFC Lakhta Center JSC Irina Anisimova.
