How to combine the advantages of a laptop and a desktop computer? Analysis of the problem and solutions
At the moment, laptops and personal computers are very different from each other. Under the system unit of a stationary computer, as a rule, it is understood as a "tower" mainly of the midi-tower standard, weighing 15-20 kilograms (or more), which occupies a huge space under the table. To move the system unit from place to place, as a rule, a lot of effort is required.
A laptop is a solution of small weight and size, mobile, which you can work with at home, in the office, on vacation, and even on the way from one place to another. In addition, all the peripherals that need to be connected to the system unit are built into the laptop. Unfortunately, laptops are almost always significantly inferior in performance to desktop computers, and if they are not inferior, they have a very high price compared to the "big brother". But, probably, the most unpleasant thing is that it is almost impossible to make a laptop “for you”, choose those components that are relevant to you today in terms of speed, performance, price and appearance, and after a couple of years if you want to change these components to more modern ones.
So. Is it possible to combine the advantages of a laptop and a desktop computer, and, if possible, then what needs to be done?
To begin, let's say that in this post we will not talk about portable monitors, mice and other peripherals. In this post we will talk almost entirely about the computer case. What should be the case and what components should it contain in order to provide high performance with a relatively compact size, as well as the ability to assemble a computer as it is seen by the end user?
At the moment, solutions are beginning to appear that partially answer this question. The most popular and affordable solutions include, for example, SilverStone rvz01 ( rvz02 ) and Node 202from Fractal Design. However, it is worth recognizing that such computers took more disadvantages both from laptops and from personal computers than advantages: a computer assembled in such cases does not turn out to be very compact (the volume of both cases is more than 10 liters), while at the same time performance.
I want solutions that would not be much inferior to either laptops or personal computers. In other words, I want compact and high-performance systems. Is it possible to achieve this? Let's try to find a way to a solution.
Of course, to make a case that would accommodate all the full-fledged components of a "large computer" will fail. But we set ourselves the goal of developing a case that would be more efficient than the popular compact cases described above.
goal: Design of the case, allowing you to assemble a high-performance computer that can be carried in a laptop bag.
PS of course, this is not about a thin ultrabook case with a diagonal of 13 ". But the bag for the proposed solution should be comfortable enough. I will present my vision of the" comfortable "bag a little later, but first we’ll examine the standard accessories to understand, but from what will we “assemble” the computer?
We note once again that we are going to build a housing that involves the replacement of components and assembly "for themselves." Therefore, the concept of the case will be built around things that do not change much over the years, and not relative to specific models of specific processors (power supplies, video cards), more powerful analogues of which will be released within one year after this publication.
First, let's talk about things that are more or less obvious to everyone who has ever assembled a compact case:
All the things stated above, of course, are quite obvious to computer builders in small cases.
At the very beginning of the article, I talked about two massive enclosures that are most suitable for assembling Mini ITX systems. Now we turn to the existing solutions, much less massive, which have a volume of less than 10 liters, and at the same time allow you to fit all of the above components. Such solutions, as a rule, are based on two formats:
1) slim-desktop. An example is the Dr.Zaber Sentry case .
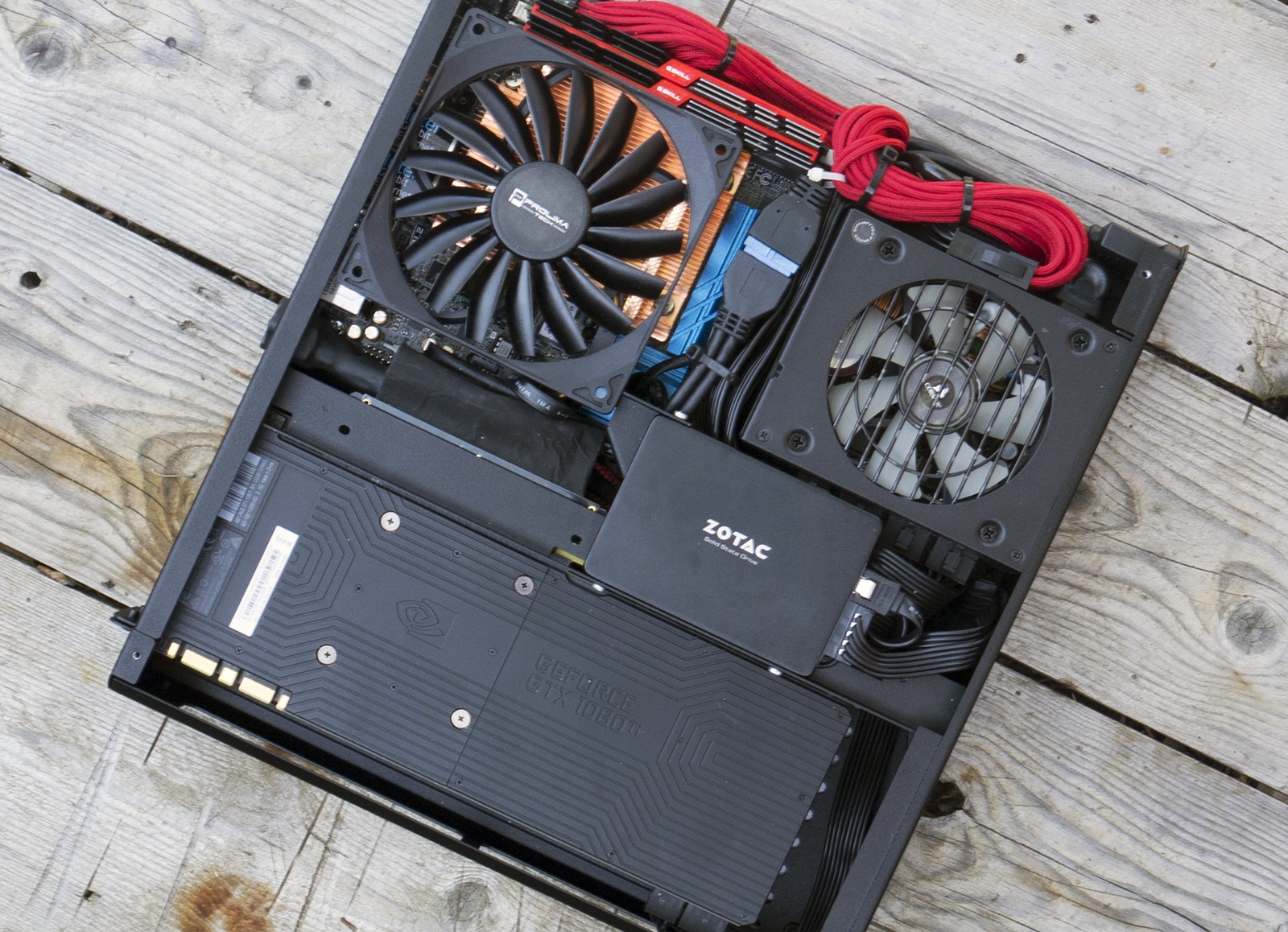
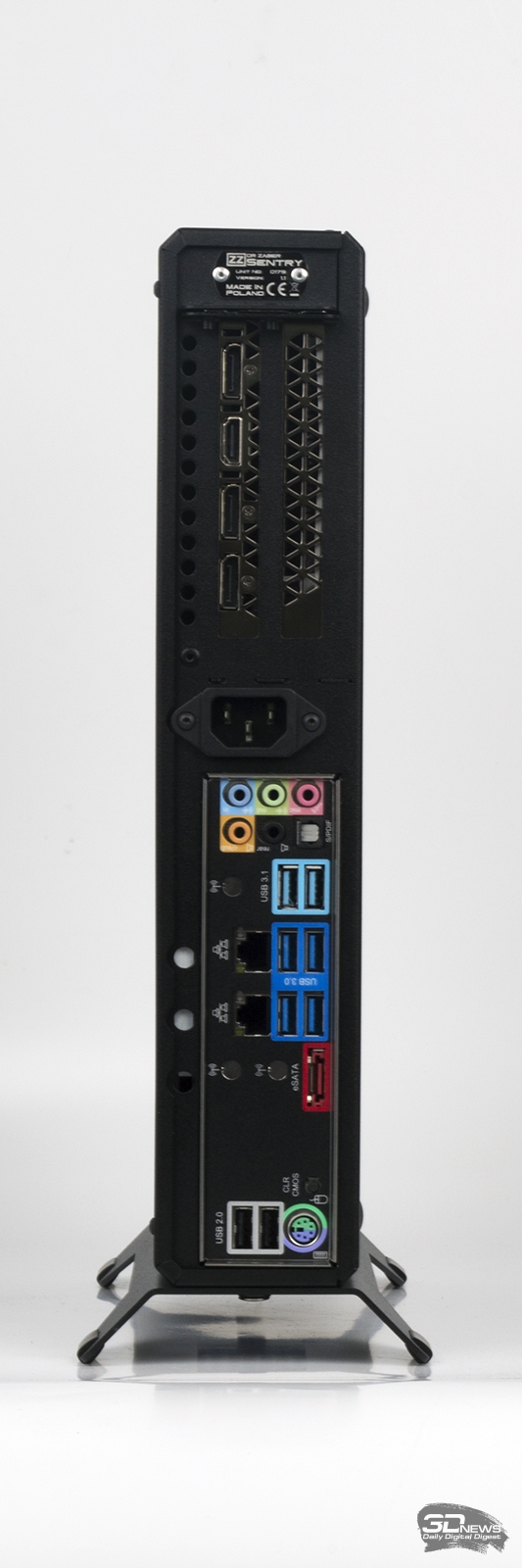


In this format, all components are located in the same plane. This principle of component placement guarantees the smallest possible thickness, and it is limited in the thickness of the SFX power supply in enclosures such as Dr.Zaber Sentry.
2) The group has not yet received a name, but is rapidly gaining popularity. We will call her by the name of the most famous representative of Dan-a4 . Unlike slim-desktop, the video card is placed in a different plane relative to the motherboard and power supply. Thus, the body becomes a little thicker, but at the same time less tall, that is, more “cubic”.
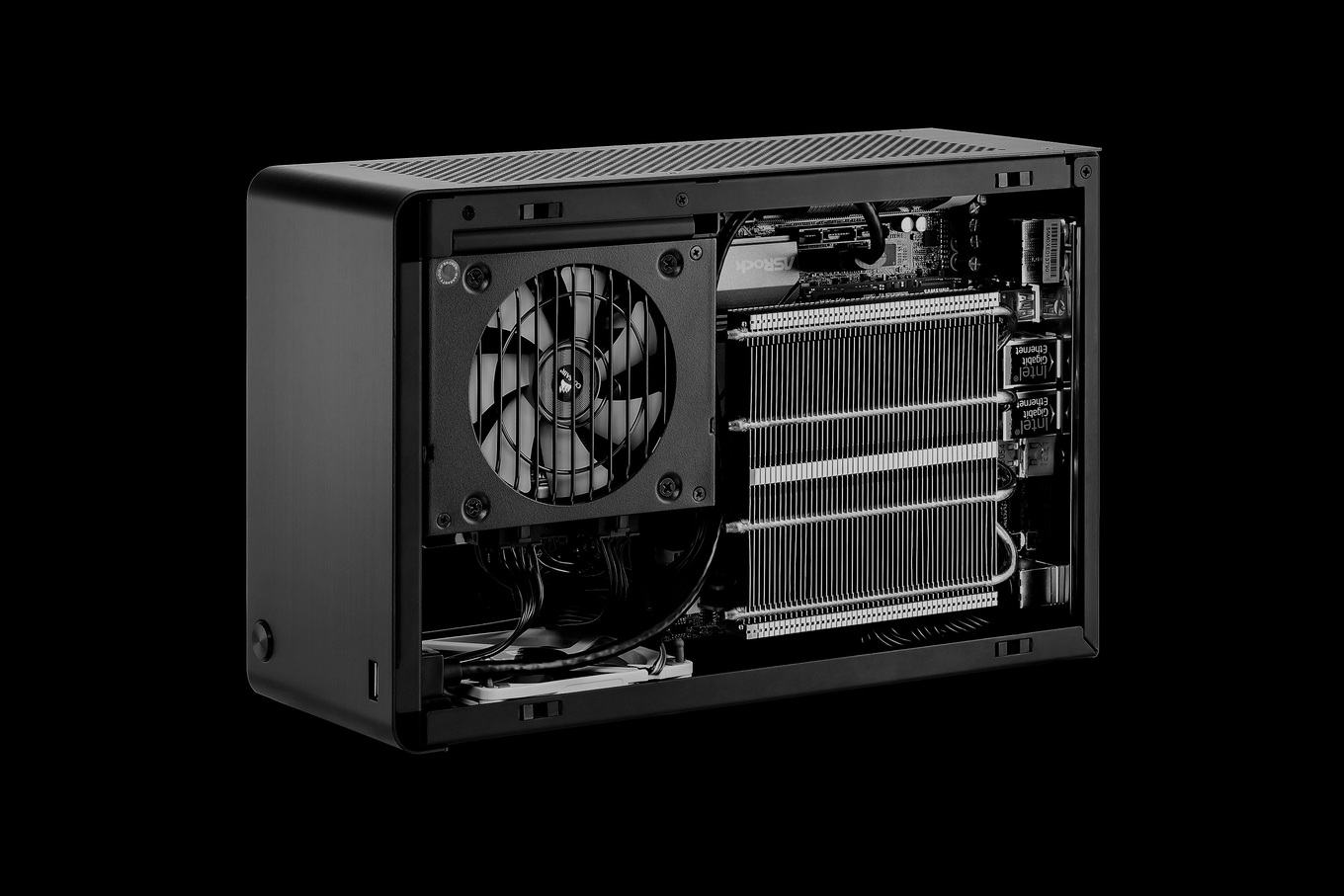
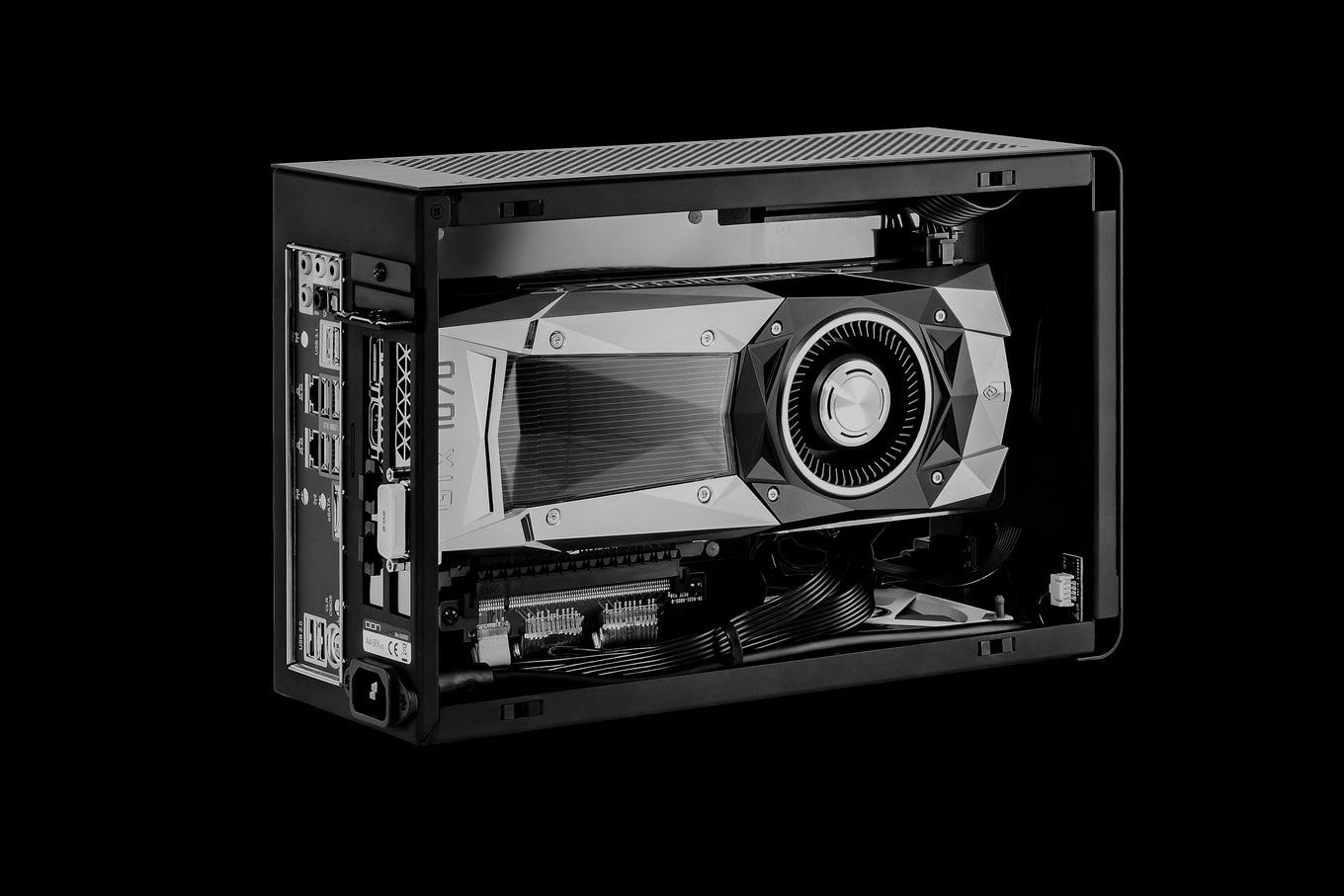


Let's talk about the main problem of these buildings, which does not allow call such solutions good for high performance assemblies
Cooling
That one that has a different format is having problems cooling their components. By and large, this is the only drawback of mini-systems: a lot of heat is generated, and there is nowhere to remove it. Enthusiasts make the most diverse decisions in such assemblies: downvoltage with lower frequencies, rejection of high-performance components, various add-ons over the case, often spoiling its entire appearance, and a host of others, each of which raises big questions.
We will go over several options for ensuring sufficient cooling:
We decided on the main list of components.
We give an example of assembly in the Dan-A4 form factor. Among a number of cases, I like this one most . For this case, there is a separately purchased expansion compartment that allows you to install a CBO. Let us show an example of assembly in this building with a serviced CBO:
In this assembly, after some setbacks and component replacement, it was possible to maintain stable processor operation during overclocking to 5 GHz for all cores. The video card also accelerated quite well. In general, the results shown in this assembly turned out to be very close to the maximum that could be obtained with this processor and video card. That is, the cooling system has performed well.
Together with an additional compartment, the dimensions of the case were 245 * 140 * 322 mm, which gives a volume of just over 11 liters. You can carry such a thing in a backpack. But I want something even more compact. You can’t put such a case in a case, because its width is 140 millimeters.
Now we give an example of assembly inside the Dr.Zaber Sentry case. The dimensions of this case are 340 * 66 * 310, that is, the volume is less than 7 liters. It can be carried in a bag.
The assembly will be with a non-top video card on a shortened printed circuit board, but at the same time with a maintenance-free CBO.
As you can see, after assembly, there is very little space left inside. You can assemble a case with a top-end graphics card, but then it will not be possible to install a liquid cooling system.
To understand what the case should be like, let's once again list all its main components, pointing out important features. This time I will mention some specific models that were relevant at the time of publication, mentioning some of their features, but I believe that the features mentioned will remain or will not change much in models that will be released within a few years after publication.
At the beginning of the article, we set the goal of placing the computer in a laptop bag. Due to the thickness of the power supply, thin bags will not work. The approximate dimensions of a thick 17.3 "laptop bag are: length - 400-460 millimeters, width 280-380 centimeters, thickness - 70-120 millimeters.
I have two laptop bags. Both are thick. One of them is very large, about 480x390x110, and, frankly, it’s not very convenient for daily use. Too big. The second is about 390x310x90. Comfortable, you can carry it at least every day (unless, of course, you are not a girl). I would very much like to make a computer case that fits in something like that.
So. To begin with, we will consider only four main components - a motherboard, a video card, a power supply and a radiator. All the rest, "then we shall smack somewhere."
The radiator, along with the fans, as we have already discussed, must be located separately to ensure air access. The power supply must also be separate, otherwise the case will be thicker than 65 millimeters. But the motherboard and the video card can intersect, but not in the area of the “plugs” of the rear panel, since the parameters of the plug of the motherboard are 158.75 ± 2 mm by 44.45 ± 2 mm, and the plugs of the video card are 107 ± 3 mm by 41 ± 3 mm.
I will give several options for placing the main 4 components in such cases. I ask readers to add a little imagination to present the missing components. And the remaining components, in fact, are few. Hard drive or SSD 2.5 "in size, if any. Cables, adapters, risers. Two fans - they will be installed on the radiator. As well as CBO elements (pump, fittings and tubes)
Option 1 I

tried to keep the proportions in the image, but I warn you: it will be wrong to make "centimeter-long conclusions" regarding the location of certain parts of various components.
The video card partially covers the motherboard. “Is there enough room to install fittings and hoses?” Firstly, it is a matter of the fittings and hoses themselves, and secondly, it will be necessary to test.
If we take the standard RAM without a radiator (the highest element of the main part of the motherboard) - the standard height of the RAM strips is 31.25 mm, plus the thickness of the slots themselves, plus a small margin for the back of the motherboard.
So. The proportions of the case with this arrangement of components will be as follows:
Thickness: 64-75 millimeters.
Length: 170 (motherboard) + 125 (power supply) + 120 (radiator CBO) + 15-45 (margin) = 430-460 millimeters.
Width: 170 (motherboard) + 107 (video card) + 10-30 (stock) = 287-307 millimeters.
As a result, the volume will fluctuate between 7.9-10.6 liters.
I’ll give you a couple of options:

In these options, you can optimize the volumes of the final building even more, but you have to face a number of design issues, from the shape of the connector to the water block of the video card and ending with the ability to lay risers and power cables. However, if a positive answer is found to these questions, then the dimensions of the case will be further optimized. In particular, even the dimensions of the aforementioned Dr.Zaber Sentry are theoretically achievable in the last picture. In practice, this, of course, is unlikely, the body will be larger. However, it seems to me that achieving the main goal - to fit the case into the parameters of a laptop bag - is quite realistic.
Now let's evaluate the cost of the components:
Cooling
This is the bulk of the spending. We will write in details:
Waterblock for a processor
Simple (at prices beginning in 2019) start at about 2,000 rubles for cheap Chinese, and starting at 3,000 rubles for water blocks from decent manufacturers. Waterblocks of full coverage (cooling the processor itself + power system) are more expensive, while quite rare. For example, in the evopc store , the water block on the Z370I Strix motherboard is presented in a single copy and costs 8800 rubles.
Water block on the video card
There are also simple ones installed on the video core itself. Prices for such solutions - from about 3,000 rubles for cheap, for 4,000 rubles - decent. Waterblocks of full coverage for video cards are much more common. The cost for the latest generation of video cards for decent models starts from about 8,000 rubles.
Radiator
Prices for thin 240 mm radiators range from two to six thousand rubles.
Fans
prices for 120 mm fans - from 600 to 3,000 rubles per fan.
Pump
Prices of good pumps start from 3000 rubles
Tubes and fittings
As I already wrote, most likely, for such decisions it will be necessary to manufacture fittings and tubes themselves. However, what is the price to lay? Let's estimate about 3-4 thousand rubles, especially since some finished sets of pipes and fittings on the market cost about the same.
Cooling other elements
In my opinion, a very dubious thing. Why cool, for example, the RAM bar, if its consumption is 1.25 volts? How much heat can be generated there? Unless for the interests of modding. Well, or simply for the reason "why not?"
Housing
I think that such a case can cost relatively little in only one case: in the case of mass implementation. In this case, you can probably count on the prices of the “bare case”, without specific elements that roughly coincide with the Fractal Design Node 202 and SilverStone rvz02. Otherwise, you should rather focus on the price of Dan-a4 and Dr.Zaber Sentry cases, which are sold over two hundred dollars apiece.
In the remaining elements, the case will not differ much from the slim desktop counterparts.
This solution is by no means intended for “ultra-cheap assemblies”, therefore we will make two comparative “assemblies”. In the first we will select the components of the average budget and make a comparison with similar performance solutions in different segments. In the second there will be top-end components.
The first build is based on the rtx 2060 / gtx 1070, similar in performance.
The main opponent in both price categories will be quite popular and having many different implementations of MSI Trident. Regarding the components of this “ready-made solution”, we will assemble all the others.
Assembly 1:
Processor - i7 8700
Video card - gtx 1070 (we will take rtx 2060, for greater objectivity also MSI)
Storage capacity - 1000 + 256 GB (we will take Toshiba L200 Slim + samsung 970 evo plus)
RAM capacity - 16 GB ( we will take two 8 GB Samsung strips)
The motherboard is unknown (we will take the MSI B360I GAMING PRO AC)
The power supply is external (we will take the Corsair SF450)
We assume that in this case the cost of our cooling system together with the cost of the case will be "budget", in the amount of not more than 25 thousand rubles.
Two other rivals are the assembly in the Dr.Zaber Sentry case, which will have a smaller volume, and the assembly in the midi-tower case, which will have a significantly lower cost.
Dimensions of "our case" are approximate. In the same way as the midi-tower cases, since there are a lot of such cases, and they are not very different from each other
It seems to me that even in this price segment the assembly has a right to exist. However, this case is still oriented to a different assembly.
Assembly 2:
Processor - i9 9900K
Video card - gtx 2080ti (we will take the MSI GeForce RTX 2080 Ti sea hawk ek x)
storage
capacity - 2000 + 512 GB (we will take the Toshiba L200 Slim + Samsung 970 pro) RAM capacity - 32 GB (we we’ll take two 16 GB Samsung strips)
The motherboard is unknown (we will take the ASUS ROG STRIX Z390-I GAMING - it has a fully-covered water
block ) Power supply - 650 watts SFX (we will take the Corsair SF600)
We assume that in this case the cost of our cooling system along with the cost of the case will be expensive. Given that the water block is already in the video card, we will lay the cost of the remaining elements of the cooling system no more than 40 thousand rubles.
Two other rivals are the assembly in the GHOST S1 MkII case, and the assembly in the midi-tower case with simpler components, which will have a significantly lower cost.
In this price category, there are no longer any cases that are more compact and could provide a decent cooling system. If you manage to maintain reasonable prices, then such a proposal would be very good from many points of view.
Unfortunately, professional systems have nothing to compare with, otherwise such a comparison could be made.
Summarize. Even with modern components, you can create a compact enough productive solution so that this solution is completely mobile. This solution will combine the advantages of a modern computer. But the article is called “the problems of combining the advantages of a laptop and a computer”, and the advantages of a laptop were far from fully realized. After all, the laptop has a screen and a keyboard, a battery for battery life, and the thickness of the gaming (or working) laptop is only 2-3 centimeters!
If we talk about the screen and keyboard, then there are already quite compact portable monitors powered by one USB Type C connector. The same goes for the keyboard.
But what about the battery life? Unfortunately, everything is a bit more complicated here. Indeed, modern uninterruptible power supplies are enough for a personal computer relatively briefly to ensure the operation of a stationary computer, despite the fact that they are much more powerful than a laptop battery. To ensure autonomous operation of a stationary computer, there must be some conceptual solutions, such as energy-saving cores, built-in processors and video cards, fans that turn off in this mode, and so on.
The motherboard could already be used in the Thin mini-ITX format, but, unfortunately, such motherboards are currently very specific and not suitable for organizing powerful systems: almost never, with the exception of single instances, do not support the PCI-E x16 slot , there is not a single motherboard on powerful chipsets, etc. It is understandable - such boards are supposed to be in very thin compact cases, which means that you cannot install any sufficiently powerful air coolers on them. But the water block requires a much smaller volume. I am sure that as soon as there is an understanding that compact systems can and should be assembled “on the water”, Thin Mini-ITX boards with water blocks will appear
Let's move on to the video card. Reducing its thickness to one expansion slot is obviously not a problem. Just think, we lose one connector for connecting a monitor. Shortening the circuit board a little harder, but possible. In the 10th generation of video cards from Nvidia, the powerful Zotac 1080 TI Arctic Storm Mini graphics card was released, the length of which was only 212 mm. This video card is in no way inferior to the longer video cards, which were also liquid-cooled. This means that you can definitely reduce the length of the video card while maintaining performance in the presence of a water block, the question is how much.
The same applies to the power supply, and the CBO radiator along with the fans. In my opinion, we need new standards for the elements of a personal computer. At one time, Intel Corporation proposed the ATX standard, now a modern standard should be proposed that allows computers to be assembled in miniature enclosures.
In my opinion, while maintaining an advanced level of performance without application, the dimensions of a system unit of about 320 * 240 * 35 are quite achievable. That is, in this case, “Full PC performance in a laptop-sized case” will be achieved.
A laptop is a solution of small weight and size, mobile, which you can work with at home, in the office, on vacation, and even on the way from one place to another. In addition, all the peripherals that need to be connected to the system unit are built into the laptop. Unfortunately, laptops are almost always significantly inferior in performance to desktop computers, and if they are not inferior, they have a very high price compared to the "big brother". But, probably, the most unpleasant thing is that it is almost impossible to make a laptop “for you”, choose those components that are relevant to you today in terms of speed, performance, price and appearance, and after a couple of years if you want to change these components to more modern ones.
So. Is it possible to combine the advantages of a laptop and a desktop computer, and, if possible, then what needs to be done?
To begin, let's say that in this post we will not talk about portable monitors, mice and other peripherals. In this post we will talk almost entirely about the computer case. What should be the case and what components should it contain in order to provide high performance with a relatively compact size, as well as the ability to assemble a computer as it is seen by the end user?
At the moment, solutions are beginning to appear that partially answer this question. The most popular and affordable solutions include, for example, SilverStone rvz01 ( rvz02 ) and Node 202from Fractal Design. However, it is worth recognizing that such computers took more disadvantages both from laptops and from personal computers than advantages: a computer assembled in such cases does not turn out to be very compact (the volume of both cases is more than 10 liters), while at the same time performance.
I want solutions that would not be much inferior to either laptops or personal computers. In other words, I want compact and high-performance systems. Is it possible to achieve this? Let's try to find a way to a solution.
Of course, to make a case that would accommodate all the full-fledged components of a "large computer" will fail. But we set ourselves the goal of developing a case that would be more efficient than the popular compact cases described above.
goal: Design of the case, allowing you to assemble a high-performance computer that can be carried in a laptop bag.
PS of course, this is not about a thin ultrabook case with a diagonal of 13 ". But the bag for the proposed solution should be comfortable enough. I will present my vision of the" comfortable "bag a little later, but first we’ll examine the standard accessories to understand, but from what will we “assemble” the computer?
We note once again that we are going to build a housing that involves the replacement of components and assembly "for themselves." Therefore, the concept of the case will be built around things that do not change much over the years, and not relative to specific models of specific processors (power supplies, video cards), more powerful analogues of which will be released within one year after this publication.
First, let's talk about things that are more or less obvious to everyone who has ever assembled a compact case:
- Processors
If we do not talk about server solutions, then one processor in the computer is more than enough. - Video Cards
With video cards, everything is a little different. If we talk about the most resource-consuming games at maximum settings in maximum resolution, then FPS will sag. Moreover, this applies to any generation of video cards: that 980 TI, that 1080 TI, that 2080 TI. However, it is worth noting that, if you do not try to "unscrew all the settings to the maximum", then the FPS will be quite satisfactory. Regarding professionals, everything is a little more complicated, because professional tasks require significantly more resources. However, in general, if you make very small compromises and do not chase the "parrots in the benchmarks", then one top-level graphics accelerator is certainly enough. - RAM
As a rule, for dual-channel processors more than two RAM strips of the maximum possible size are enough (that is, in the days of DDR3 16GB were enough, 32 with DDR4 was enough, 64 with DDR5). For four-channel processors, everything is a little more complicated, since such processors are purchased for specific specific tasks. But overall, four slats should be enough.
As for the choice between DIMM and SO-DIMM, the tests show that the format of the bar does not matter. But in general, the choice of RAM is determined by the specific motherboard (I cited this paragraph to show: it is possible and necessary to abandon large and unnecessary DIMMs) - Data storage devices
There are two types of storage devices: HDD (hard drives) and SSD (solid state drives). SSDs are characterized by a higher data transfer rate, lower power consumption and lower noise level, however, they are inferior in the ratio “ruble per gigabyte” in the maximum memory capacity of the device, as well as in the service life and the ability to constantly overwrite information on the device. Therefore, at the moment, most users prefer to combine two types of devices in their computer: a hard disk (for organizing file storage) and a solid state drive (for fast operation of the system as a whole and some resource-intensive programs). However, many, not without reason, believe that modern solid-state drives are already good enough so that in the home, their shortcomings do not appear. Nonetheless, to organize the case, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of installing both SSD and HDD. To begin with - about the HDD. There are two form factors for HDD 2.5 "and 3.5". It is believed that the former are intended for laptops, the latter - for desktop computers. If you do not take the maximum volume of the device (which in domestic cases does not matter), then 2.5 "form factor hard drives are not inferior to 3.5" devices. They have approximately the same relative cost, heat less, have approximately the same speed of working with data. Even in server solutions, the choice is often made in favor of 2.5 "form factor devices. Adding the fact that the 2.5 device is physically smaller than 3.5", we get that the choice is obvious in a small package. There are two form factors for HDD 2.5 "and 3.5". It is believed that the former are intended for laptops, the latter - for desktop computers. If you do not take the maximum volume of the device (which in domestic cases does not matter), then 2.5 "form factor hard drives are not inferior to 3.5" devices. They have approximately the same relative cost, heat less, have approximately the same speed of working with data. Even in server solutions, the choice is often made in favor of 2.5 "form factor devices. Adding the fact that the 2.5 device is physically smaller than 3.5", we get that the choice is obvious in a small package. There are two form factors for HDD 2.5 "and 3.5". It is believed that the former are intended for laptops, the latter - for desktop computers. If you do not take the maximum volume of the device (which in domestic cases does not matter), then 2.5 "form factor hard drives are not inferior to 3.5" devices. They have approximately the same relative cost, heat less, have approximately the same speed of working with data. Even in server solutions, the choice is often made in favor of 2.5 "form factor devices. Adding the fact that the 2.5 device is physically smaller than 3.5", we get that the choice is obvious in a small package. If you do not take the maximum volume of the device (which in domestic cases does not matter), then 2.5 "form factor hard drives are not inferior to 3.5" devices. They have approximately the same relative cost, heat less, have approximately the same speed of working with data. Even in server solutions, the choice is often made in favor of 2.5 "form factor devices. Adding the fact that the 2.5 device is physically smaller than 3.5", we get that the choice is obvious in a small package. If you do not take the maximum volume of the device (which in domestic cases does not matter), then 2.5 "form factor hard drives are not inferior to 3.5" devices. They have approximately the same relative cost, heat less, have approximately the same speed of working with data. Even in server solutions, the choice is often made in favor of 2.5 "form factor devices. Adding the fact that the 2.5 device is physically smaller than 3.5", we get that the choice is obvious in a small package.
With SSDs, everything is about the same - M2 NVMIs are superior to 2.5 "SATA III in almost all respects, and in all other respects they are not much worse. - Power supply We
continue the trend of “destroying large old formats”: among all the power supply form factors on the market, only SFX and ATX are quite massive. And the first is enough to provide power to the assembly with one (even top-end) video card and one (even top-end) processor. - Motherboard To
summarize the trend. Motherboards in the mini-itx form factor (if we talk about the assembly with one processor and one video card) are quite massive and almost as good as their "large" counterparts. Sometimes they even allow you to set some records. Peripherals for a compact system are more than enough, and are represented in almost all possible sockets, including X- * 99, designed for powerful multi-core systems.
All the things stated above, of course, are quite obvious to computer builders in small cases.
At the very beginning of the article, I talked about two massive enclosures that are most suitable for assembling Mini ITX systems. Now we turn to the existing solutions, much less massive, which have a volume of less than 10 liters, and at the same time allow you to fit all of the above components. Such solutions, as a rule, are based on two formats:
1) slim-desktop. An example is the Dr.Zaber Sentry case .


In this format, all components are located in the same plane. This principle of component placement guarantees the smallest possible thickness, and it is limited in the thickness of the SFX power supply in enclosures such as Dr.Zaber Sentry.
2) The group has not yet received a name, but is rapidly gaining popularity. We will call her by the name of the most famous representative of Dan-a4 . Unlike slim-desktop, the video card is placed in a different plane relative to the motherboard and power supply. Thus, the body becomes a little thicker, but at the same time less tall, that is, more “cubic”.


Let's talk about the main problem of these buildings, which does not allow call such solutions good for high performance assemblies
Cooling
That one that has a different format is having problems cooling their components. By and large, this is the only drawback of mini-systems: a lot of heat is generated, and there is nowhere to remove it. Enthusiasts make the most diverse decisions in such assemblies: downvoltage with lower frequencies, rejection of high-performance components, various add-ons over the case, often spoiling its entire appearance, and a host of others, each of which raises big questions.
We will go over several options for ensuring sufficient cooling:
- Air cooling
Air-type cooling systems can provide a sufficient level of cooling for modern components. But let's immediately decide that we are not working with “air”. Air-type cooling systems, firstly, take up too large volumes. For example, processor coolers with a declared TDP of 150 watts occupy from one to four to five liters of volume, not to mention the fact that they need additional free space for air flow, and this place must be located inside the case. The situation is similar with video cards: top-end video cards, together with cooling systems, occupy a volume of one and a half liters or more, while with installed water blocks of full coverage - 0.5-0.7 liters. Secondly, the radiator of the water / liquid cooling system (hereinafter referred to as CBO) can be brought anywhere, to any part of the body. Finally, - Unattended NWO
Of course, an unattended NWO for the average user is much better than the unattended. It does not need to be filled, washed, selected components and assembled. However, it is impossible to make an unattended CBO suitable for all possible components: even several different processor sockets exist at the moment several dozen, and not all of them are compatible with each other. As regards video cards, it is still sadder: for the system to work well, the entire printed circuit board needs to be cooled, and the printed circuit boards for literally every video card are different from each other. In addition, there are other components that the end user may also wish to cool. - Serviced (custom) CBO
There remains the only option suitable for a laptop computer: serviced CBO
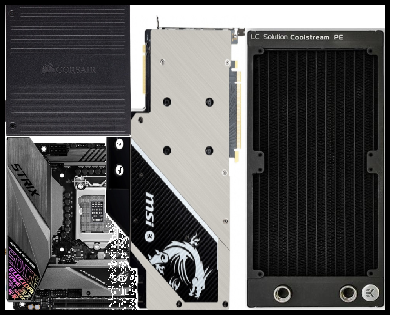
We decided on the main list of components.
We give an example of assembly in the Dan-A4 form factor. Among a number of cases, I like this one most . For this case, there is a separately purchased expansion compartment that allows you to install a CBO. Let us show an example of assembly in this building with a serviced CBO:
In this assembly, after some setbacks and component replacement, it was possible to maintain stable processor operation during overclocking to 5 GHz for all cores. The video card also accelerated quite well. In general, the results shown in this assembly turned out to be very close to the maximum that could be obtained with this processor and video card. That is, the cooling system has performed well.
Together with an additional compartment, the dimensions of the case were 245 * 140 * 322 mm, which gives a volume of just over 11 liters. You can carry such a thing in a backpack. But I want something even more compact. You can’t put such a case in a case, because its width is 140 millimeters.
Now we give an example of assembly inside the Dr.Zaber Sentry case. The dimensions of this case are 340 * 66 * 310, that is, the volume is less than 7 liters. It can be carried in a bag.
The assembly will be with a non-top video card on a shortened printed circuit board, but at the same time with a maintenance-free CBO.
As you can see, after assembly, there is very little space left inside. You can assemble a case with a top-end graphics card, but then it will not be possible to install a liquid cooling system.
To understand what the case should be like, let's once again list all its main components, pointing out important features. This time I will mention some specific models that were relevant at the time of publication, mentioning some of their features, but I believe that the features mentioned will remain or will not change much in models that will be released within a few years after publication.
- Processors
The most “gluttonous” processor of the mass segment today is the Intel core i9-9900K. According to hardwareluxx tests , its power consumption under load in acceleration to 5.1 GHz on all cores was 231 watts, although some other resources also received higher power consumption. If we talk about professional (but not server) solutions - then the leader of Ryzen Threadripper 2990WX. With overclocking to 4.25 GHz, this solution consumed 470 watts. However, usually no one overclocks professional solutions (a long processor life is more important), and without overclocking, the power consumption was just over 300 watts. Therefore, we assume that the processor will consume no more than 350 watts. - Video cards The
flagships of the last several generations, with a good cooling system in overclocking, consume within 300-350 watts. Obviously, in the coming years this limit will increase, but hardly much. We believe that potential limitations are 400 watts.
Now let's talk about the sizes that we will be laying for installing the video card. Since we decided that we will use a video card with a water block, we focus solely on video cards with a water block and do not assume the installation of a video card without a water block. Thanks to the water block, we will win a lot of extra space, so this solution is necessary. Given the growing popularity of waterblocks, this solution leaves a large selection of components and the possibility of an upgrade.
Without exception, all video cards with a water block have a thickness of about one slot, but use two expansion slots on the rear panel to connect interfaces. The length of such video cards is usually shorter than 300 mm. For the most part, manufacturers put the video card on a reference printed circuit board, which is even shorter (260-280 mm for top-end versions, 264 mm for RTX 2080 TI).
Keep in mind that the dimensions of the plugs for expansion slots are approximately 120 by 20.5 millimeters, however, the original height of the graphics cards is 107 mm with a slot size for graphic outputs of 16 mm. - Other elements
All other elements, including the motherboard, consume relatively little, especially considering the form factor in which it is impossible to use a huge amount of peripherals (HDD arrays, 5'25 devices, expansion slots, etc.). In general, if you make a margin of about 100 W for the rest of the periphery, then this is more than enough. - Power supply
At the time of this writing, there are options for SFX power supplies from several manufacturers at once with declared power of 600 watts or more. The Corsair SF750 became the record holder in this form factor (at the time of writing) . If we take the form factor a little more (SFX-L), then Silverstone SX-800LTI leads there .
If you look at the restrictions set, obviously, these power supplies are a little inadequate. But this is if we are talking about a prospect in which powerful blocks in the SFX form factor will necessarily appear.
The SFX standard power supply unit has dimensions 125 * 100 * 63.5, the larger SFX-L - 125 * 130 * 63.5. This means that our case can never be thinner than 65 ± 1 mm. Let us dwell on this indicator and try to adhere to just such a thickness.
However, what exactly can and should be done is to replace the power cables. They took up too much space in the Dr.Zaber Sentry case. Manufacturers try to always make a margin in length, not knowing in advance what length the cables are needed. But, if we are talking about a specific case with a known arrangement of components - why not make the right length - Cooling
So, let's move on to the principles of the cooling system.
Heat exchanger - of course, heat exchangers with one fan will not be enough. For example, hardware labs statethat a thin two-section 240 mm heat exchanger is enough even to cool the processor and a bunch of two video cards. It is claimed that their heat exchanger can dissipate up to 750 watts of heat. The statement is, of course, controversial, but numerous tests show that a good 240 mm heat exchanger, even a thin one, is enough to cool the mass segment processor and top-end video card (both with overclocking and without it). Of course, the matter is also in the power of the pump and the fan speed, as well as in the conditions in which this heat exchanger will work. For example, fans should take air without hindrance.
The only possible solution when trying to install a heat exchanger in a thin casing is to install it on a through blow. That is, to make a special compartment in the case where nothing will be located, except for the radiator and the fans blowing it. Air will pass through the radiator and exit from the back of the case.
For a number of reasons, I want to use fans with a thickness of 25 millimeters.
Therefore, the thickness of the radiators should not exceed 40 millimeters, and most likely 35, so that anti-dust filters, vibration pads, etc. can be installed. There are a sufficient number of thinner radiators on the market, and they are quite productive, so 35 mm is not a problem.
Fans- They must be powerful enough at the same time to blow the heat exchanger well, and at the same time quiet, because they will not be hidden by anything. If you take market decisions, magnetic levitation fans are quite suitable.
Fittings and tubes . Let's pay attention to the video about the Dr.Zaber Sentry case. Fittings and tubes are not compact enough and take up too much space. They need to be reduced in size, and significantly - from such a solution, the cooling system will not lose in its performance, because the “bottlenecks” for the passage of fluid are by no means fittings and tubes, but radiators and water blocks. But the necessary place will be won. However, the fittings must be kept compatible with standard openings in water blocks, radiators, and pumps.
Storage tank- Most likely, it should not be placed in a case of this format. Firstly, it occupies a place in the case (which is already limited), and secondly, problems arise in moving this device. How to carry a case in which there is a tank? In this case, will air not get inside the circuit during operation? Or, on the contrary, will the liquid pour out of the circuit? However, there must be a way to fill the circuit / drain the fluid from the circuit if necessary (replacement of accessories or just maintenance), something like a pump with an external tank.
water pump- Of course, it is necessary, while separate from the water blocks, so that when replacing the processor (which will almost certainly be on the new socket) there is no need to change the pump. It is possible that the highest-performance pump (D5) is not compact enough for "our casing." However, tests show that even less efficient pumps (for example, a good DDC) are more than enough to cool one video card + one processor + circuit from one 240 mm radiator. Perhaps more compact pumps are suitable. - Motherboard The
size of the mini-ITX motherboard is 170x170 mm. The plug for the rear panel of the motherboard measures approximately 158.75 ± 2 mm by 44.45 ± 2 mm. At the same time, the dummy in the upper part of the motherboard starts almost immediately, and in the lower part it ends at the beginning of the PCI-E x16 slot, that is, leaving a good centimeter from the bottom.
At the beginning of the article, we set the goal of placing the computer in a laptop bag. Due to the thickness of the power supply, thin bags will not work. The approximate dimensions of a thick 17.3 "laptop bag are: length - 400-460 millimeters, width 280-380 centimeters, thickness - 70-120 millimeters.
I have two laptop bags. Both are thick. One of them is very large, about 480x390x110, and, frankly, it’s not very convenient for daily use. Too big. The second is about 390x310x90. Comfortable, you can carry it at least every day (unless, of course, you are not a girl). I would very much like to make a computer case that fits in something like that.
So. To begin with, we will consider only four main components - a motherboard, a video card, a power supply and a radiator. All the rest, "then we shall smack somewhere."
The radiator, along with the fans, as we have already discussed, must be located separately to ensure air access. The power supply must also be separate, otherwise the case will be thicker than 65 millimeters. But the motherboard and the video card can intersect, but not in the area of the “plugs” of the rear panel, since the parameters of the plug of the motherboard are 158.75 ± 2 mm by 44.45 ± 2 mm, and the plugs of the video card are 107 ± 3 mm by 41 ± 3 mm.
I will give several options for placing the main 4 components in such cases. I ask readers to add a little imagination to present the missing components. And the remaining components, in fact, are few. Hard drive or SSD 2.5 "in size, if any. Cables, adapters, risers. Two fans - they will be installed on the radiator. As well as CBO elements (pump, fittings and tubes)
Option 1 I

tried to keep the proportions in the image, but I warn you: it will be wrong to make "centimeter-long conclusions" regarding the location of certain parts of various components.
The video card partially covers the motherboard. “Is there enough room to install fittings and hoses?” Firstly, it is a matter of the fittings and hoses themselves, and secondly, it will be necessary to test.
If we take the standard RAM without a radiator (the highest element of the main part of the motherboard) - the standard height of the RAM strips is 31.25 mm, plus the thickness of the slots themselves, plus a small margin for the back of the motherboard.
So. The proportions of the case with this arrangement of components will be as follows:
Thickness: 64-75 millimeters.
Length: 170 (motherboard) + 125 (power supply) + 120 (radiator CBO) + 15-45 (margin) = 430-460 millimeters.
Width: 170 (motherboard) + 107 (video card) + 10-30 (stock) = 287-307 millimeters.
As a result, the volume will fluctuate between 7.9-10.6 liters.
I’ll give you a couple of options:


In these options, you can optimize the volumes of the final building even more, but you have to face a number of design issues, from the shape of the connector to the water block of the video card and ending with the ability to lay risers and power cables. However, if a positive answer is found to these questions, then the dimensions of the case will be further optimized. In particular, even the dimensions of the aforementioned Dr.Zaber Sentry are theoretically achievable in the last picture. In practice, this, of course, is unlikely, the body will be larger. However, it seems to me that achieving the main goal - to fit the case into the parameters of a laptop bag - is quite realistic.
Now let's evaluate the cost of the components:
Cooling
This is the bulk of the spending. We will write in details:
Waterblock for a processor
Simple (at prices beginning in 2019) start at about 2,000 rubles for cheap Chinese, and starting at 3,000 rubles for water blocks from decent manufacturers. Waterblocks of full coverage (cooling the processor itself + power system) are more expensive, while quite rare. For example, in the evopc store , the water block on the Z370I Strix motherboard is presented in a single copy and costs 8800 rubles.
Water block on the video card
There are also simple ones installed on the video core itself. Prices for such solutions - from about 3,000 rubles for cheap, for 4,000 rubles - decent. Waterblocks of full coverage for video cards are much more common. The cost for the latest generation of video cards for decent models starts from about 8,000 rubles.
Radiator
Prices for thin 240 mm radiators range from two to six thousand rubles.
Fans
prices for 120 mm fans - from 600 to 3,000 rubles per fan.
Pump
Prices of good pumps start from 3000 rubles
Tubes and fittings
As I already wrote, most likely, for such decisions it will be necessary to manufacture fittings and tubes themselves. However, what is the price to lay? Let's estimate about 3-4 thousand rubles, especially since some finished sets of pipes and fittings on the market cost about the same.
Cooling other elements
In my opinion, a very dubious thing. Why cool, for example, the RAM bar, if its consumption is 1.25 volts? How much heat can be generated there? Unless for the interests of modding. Well, or simply for the reason "why not?"
Housing
I think that such a case can cost relatively little in only one case: in the case of mass implementation. In this case, you can probably count on the prices of the “bare case”, without specific elements that roughly coincide with the Fractal Design Node 202 and SilverStone rvz02. Otherwise, you should rather focus on the price of Dan-a4 and Dr.Zaber Sentry cases, which are sold over two hundred dollars apiece.
In the remaining elements, the case will not differ much from the slim desktop counterparts.
This solution is by no means intended for “ultra-cheap assemblies”, therefore we will make two comparative “assemblies”. In the first we will select the components of the average budget and make a comparison with similar performance solutions in different segments. In the second there will be top-end components.
The first build is based on the rtx 2060 / gtx 1070, similar in performance.
The main opponent in both price categories will be quite popular and having many different implementations of MSI Trident. Regarding the components of this “ready-made solution”, we will assemble all the others.
Assembly 1:
Processor - i7 8700
Video card - gtx 1070 (we will take rtx 2060, for greater objectivity also MSI)
Storage capacity - 1000 + 256 GB (we will take Toshiba L200 Slim + samsung 970 evo plus)
RAM capacity - 16 GB ( we will take two 8 GB Samsung strips)
The motherboard is unknown (we will take the MSI B360I GAMING PRO AC)
The power supply is external (we will take the Corsair SF450)
We assume that in this case the cost of our cooling system together with the cost of the case will be "budget", in the amount of not more than 25 thousand rubles.
Two other rivals are the assembly in the Dr.Zaber Sentry case, which will have a smaller volume, and the assembly in the midi-tower case, which will have a significantly lower cost.
Dimensions of "our case" are approximate. In the same way as the midi-tower cases, since there are a lot of such cases, and they are not very different from each other
| Comparison options | MSI Trident 3 | Our building | Dr. Zaber Sentry | midi tower assembly |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| approximate cost | 124000 | 113000 * | 108,000 | 85000 |
| Length | 346 | 400 * | 340 | 400 * |
| Height | 232 | 300 * | 310 | 400 * |
| Width | 71 | 65 * | 66 | 200 * |
| Volume | 5.7 | 7.8 * | 7.0 | 32.0 * |
It seems to me that even in this price segment the assembly has a right to exist. However, this case is still oriented to a different assembly.
Assembly 2:
Processor - i9 9900K
Video card - gtx 2080ti (we will take the MSI GeForce RTX 2080 Ti sea hawk ek x)
storage
capacity - 2000 + 512 GB (we will take the Toshiba L200 Slim + Samsung 970 pro) RAM capacity - 32 GB (we we’ll take two 16 GB Samsung strips)
The motherboard is unknown (we will take the ASUS ROG STRIX Z390-I GAMING - it has a fully-covered water
block ) Power supply - 650 watts SFX (we will take the Corsair SF600)
We assume that in this case the cost of our cooling system along with the cost of the case will be expensive. Given that the water block is already in the video card, we will lay the cost of the remaining elements of the cooling system no more than 40 thousand rubles.
Two other rivals are the assembly in the GHOST S1 MkII case, and the assembly in the midi-tower case with simpler components, which will have a significantly lower cost.
| Comparison options | MSI Trident X | Our building | GHOST S1 MkII | midi tower assembly |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| approximate cost | 275,000 * | 269,000 * | 265000 | 185,000 |
| Length | 396 | 400 * | 322 | 400 * |
| Height | 382 | 300 * | 245 | 400 * |
| Width | 129 | 65 * | 140 | 200 * |
| Volume | 19.5 | 7.8 * | 11.1 | 32.0 * |
In this price category, there are no longer any cases that are more compact and could provide a decent cooling system. If you manage to maintain reasonable prices, then such a proposal would be very good from many points of view.
Unfortunately, professional systems have nothing to compare with, otherwise such a comparison could be made.
Summarize. Even with modern components, you can create a compact enough productive solution so that this solution is completely mobile. This solution will combine the advantages of a modern computer. But the article is called “the problems of combining the advantages of a laptop and a computer”, and the advantages of a laptop were far from fully realized. After all, the laptop has a screen and a keyboard, a battery for battery life, and the thickness of the gaming (or working) laptop is only 2-3 centimeters!
If we talk about the screen and keyboard, then there are already quite compact portable monitors powered by one USB Type C connector. The same goes for the keyboard.
But what about the battery life? Unfortunately, everything is a bit more complicated here. Indeed, modern uninterruptible power supplies are enough for a personal computer relatively briefly to ensure the operation of a stationary computer, despite the fact that they are much more powerful than a laptop battery. To ensure autonomous operation of a stationary computer, there must be some conceptual solutions, such as energy-saving cores, built-in processors and video cards, fans that turn off in this mode, and so on.
The motherboard could already be used in the Thin mini-ITX format, but, unfortunately, such motherboards are currently very specific and not suitable for organizing powerful systems: almost never, with the exception of single instances, do not support the PCI-E x16 slot , there is not a single motherboard on powerful chipsets, etc. It is understandable - such boards are supposed to be in very thin compact cases, which means that you cannot install any sufficiently powerful air coolers on them. But the water block requires a much smaller volume. I am sure that as soon as there is an understanding that compact systems can and should be assembled “on the water”, Thin Mini-ITX boards with water blocks will appear
Let's move on to the video card. Reducing its thickness to one expansion slot is obviously not a problem. Just think, we lose one connector for connecting a monitor. Shortening the circuit board a little harder, but possible. In the 10th generation of video cards from Nvidia, the powerful Zotac 1080 TI Arctic Storm Mini graphics card was released, the length of which was only 212 mm. This video card is in no way inferior to the longer video cards, which were also liquid-cooled. This means that you can definitely reduce the length of the video card while maintaining performance in the presence of a water block, the question is how much.
The same applies to the power supply, and the CBO radiator along with the fans. In my opinion, we need new standards for the elements of a personal computer. At one time, Intel Corporation proposed the ATX standard, now a modern standard should be proposed that allows computers to be assembled in miniature enclosures.
In my opinion, while maintaining an advanced level of performance without application, the dimensions of a system unit of about 320 * 240 * 35 are quite achievable. That is, in this case, “Full PC performance in a laptop-sized case” will be achieved.
