Android will offer European users a browser and search engine of choice
Back in 2009, the European Commission recognized that Microsoft was abusing its monopoly position in the operating system market by supplying its Internet Explorer browser with Windows. The American corporation was forced to show a special window with a choice of browser. So it looked in 2010:
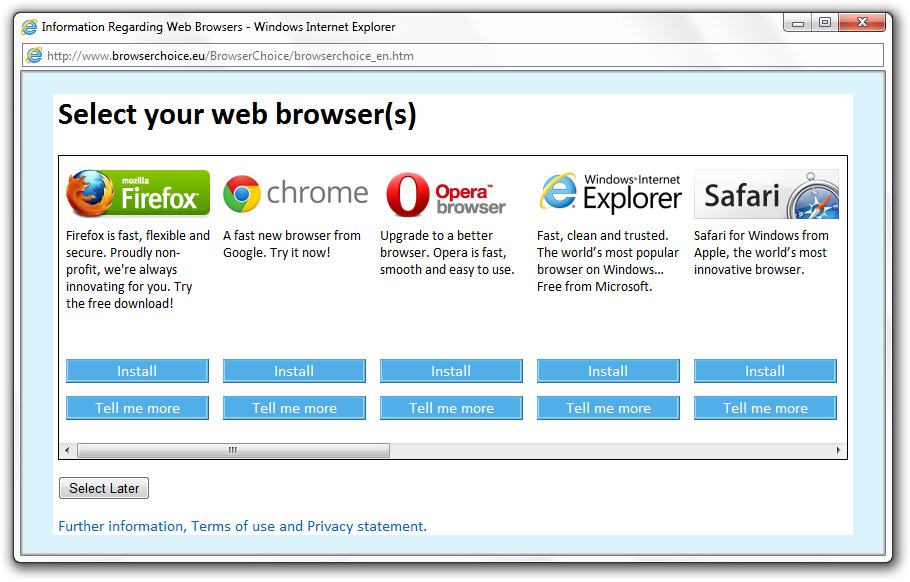
Almost 10 years have passed - and now the story repeats itself, but with the Android operating system. Following the EU’s “recommendation”, Google also decided to offer new European users an Android browser and a search engine of their choice.
The last stage of the confrontation between Google and the European Union began in July last year, when European authorities finedthe company for a record $ 5.05 billion (4.34 billion euros) for violating antitrust laws in Europe. Commission chairman Margret Vestager accused the company of three violations:
Google has still not paid a fine and filed an appeal in a lawful manner, which may take several years.
At the same time, the company responded: in October, it announced, which will separately sell licenses for the Google Apps package and for search with a browser. That is, one license for an application package, including Google Play, Gmail, YouTube and maps. Another license is available for companies that want to preinstall Google Search and the Chrome browser. Thus, phone manufacturers get more freedom to use competing services, which is what the European Commission sought. For example, you can now use the Google Apps package with a third-party browser. Or vice versa - Google search and Chrome browser, but without a package of branded applications. The company did not say how much it would charge for licenses. According to rumors, the cost reaches $ 40 for each device .
Now in this story, a new turn: Google has voluntarily decided to offer users of Android a browser and a search engine of their choice. Users of new Android devices in Europe will see the corresponding window: “We have always tried to give people the best and fastest answers - whether directly from Google or from a wide range of specialized websites and application providers that exist today,” a Google press release said. “These recent changes demonstrate our ongoing commitment to acting openly and principally.”
Android is the most popular mobile operating system in the world, which is installed on more than 80% of smartphones. Google says it runs on more than 24,000 different types of devices. Using Android has allowed companies like Samsung to compete with Apple’s iPhone without having to create their own software. By providing Android for free for any device manufacturer to use and modify, Google is simultaneously promoting its Google Apps application suite.
It is obvious that the proceedings of Google with the European Commission will continue for a long time. Moreover, the latter was not limited only to the aforementioned fine of 4.34 billion euros for violating antitrust laws. Today it became known that another fine of 1.49 billion euros was imposed on Google"For illegal practices in search advertising that reinforce its dominant position in the market." This was also reported by the same chairman of the commission Margret Westagher on her twitter.
European Commission clarifiedthat a fine has been imposed because since 2006 Google has entered into contracts with third-party sites, prohibiting Google competitors from placing their ads in the search results of these resources. This is considered an abuse of a dominant position in the online advertising market. A corresponding investigation began in 2016. “All violations are recorded in contractual obligations that Google imposed on its partners - owners of websites,” Margrethe Westager emphasized. In addition, Google used other illegal practices, abusing its monopoly position in the search and online advertising market, including placing it in the first positions in the search results of its partners, and also paid manufacturers of mobile devices and operating systems to include pre-installed applications Google search.
For Google, this is the third antitrust penalty from the European Commission in the last two years:
This is probably not the end.

Almost 10 years have passed - and now the story repeats itself, but with the Android operating system. Following the EU’s “recommendation”, Google also decided to offer new European users an Android browser and a search engine of their choice.
The last stage of the confrontation between Google and the European Union began in July last year, when European authorities finedthe company for a record $ 5.05 billion (4.34 billion euros) for violating antitrust laws in Europe. Commission chairman Margret Vestager accused the company of three violations:
- Google undermines competition in the Android device market by integrating its search engine and applications into the operating system.
- Google restricts manufacturers to use alternative versions of Android, blocking access to their services.
- The company paid major manufacturers and mobile networks to set Google search as their default product.
Google has still not paid a fine and filed an appeal in a lawful manner, which may take several years.
At the same time, the company responded: in October, it announced, which will separately sell licenses for the Google Apps package and for search with a browser. That is, one license for an application package, including Google Play, Gmail, YouTube and maps. Another license is available for companies that want to preinstall Google Search and the Chrome browser. Thus, phone manufacturers get more freedom to use competing services, which is what the European Commission sought. For example, you can now use the Google Apps package with a third-party browser. Or vice versa - Google search and Chrome browser, but without a package of branded applications. The company did not say how much it would charge for licenses. According to rumors, the cost reaches $ 40 for each device .
Now in this story, a new turn: Google has voluntarily decided to offer users of Android a browser and a search engine of their choice. Users of new Android devices in Europe will see the corresponding window: “We have always tried to give people the best and fastest answers - whether directly from Google or from a wide range of specialized websites and application providers that exist today,” a Google press release said. “These recent changes demonstrate our ongoing commitment to acting openly and principally.”
Android is the most popular mobile operating system in the world, which is installed on more than 80% of smartphones. Google says it runs on more than 24,000 different types of devices. Using Android has allowed companies like Samsung to compete with Apple’s iPhone without having to create their own software. By providing Android for free for any device manufacturer to use and modify, Google is simultaneously promoting its Google Apps application suite.
It is obvious that the proceedings of Google with the European Commission will continue for a long time. Moreover, the latter was not limited only to the aforementioned fine of 4.34 billion euros for violating antitrust laws. Today it became known that another fine of 1.49 billion euros was imposed on Google"For illegal practices in search advertising that reinforce its dominant position in the market." This was also reported by the same chairman of the commission Margret Westagher on her twitter.
European Commission clarifiedthat a fine has been imposed because since 2006 Google has entered into contracts with third-party sites, prohibiting Google competitors from placing their ads in the search results of these resources. This is considered an abuse of a dominant position in the online advertising market. A corresponding investigation began in 2016. “All violations are recorded in contractual obligations that Google imposed on its partners - owners of websites,” Margrethe Westager emphasized. In addition, Google used other illegal practices, abusing its monopoly position in the search and online advertising market, including placing it in the first positions in the search results of its partners, and also paid manufacturers of mobile devices and operating systems to include pre-installed applications Google search.
For Google, this is the third antitrust penalty from the European Commission in the last two years:
- $ 2.7 billion for abuse in the search engine market (2017);
- $ 5 billion for Android restrictions (2018);
- $ 1.69 billion for abuse of a dominant position in the online advertising market (2019).
This is probably not the end.
