Hosting: options, comparisons, user statistics
Surprisingly, from the abundance of articles on the topic of hosting on the Internet, there are hardly a dozen where the topic is disclosed in a language accessible to all. Often, even professionals and experienced users note that in the majority of descriptions “hell will break a leg”, especially on the websites of companies offering this service. What can we say about those who do not understand digital technologies, but want to use them in their business with an understanding of at least the basics.
We want to correct the situation and tell lucidly for those who are interested at any level of preparation for the question what hosting opportunities are today, how they differ, what are the advantages of some over others and what are the user statistics in Russia and abroad. The article is intended for a wide range of readers from neophytes to advanced users (therefore, explanations of terms well known to experienced users are often given in brackets).
First, let’s introduce a little bit of those who do not understand the topic of the article and indicate what hosting is and who needs it.
Hosting(hosting) is a service provided by companies hosting providers (hosters), which consists in placing information resources of users on their (companies) servers. The functionality of the server depends on the installed software, which, in turn, depends on the operating system. Hostings are distinguished by the presence of certain services, the ability to support various technologies, programming languages and scripts. They also differ in quantitative and qualitative limitations (disk space, number of sites, channel bandwidth, etc.). User access to their data is implemented through a personal account. Processing requests to customer information resources is carried out in real time 24/7. The hosting service includes technical support, security and data backup.
Information resources (here) are sites of various functionalities: online stores, corporate sites, Internet portals, information and news sites, web services. They consist of an abundance of digital data:
The need for such a remote location is dictated by the fact that a lot of this data that grows over time cannot be stored and processed on the personal computer of the owner of an information resource - the volumes are too large, the machine’s capacities are not enough. To use your computer as a server, you need a redundant array of independent disks (Redundant Array of Independent Disks, RAID) or a very large storage device (SSD), a powerful outgoing channel to the Internet, a licensed server operating system and the knowledge to use it all . But the main thing is that it costs a lot of money. Therefore, there are physical and virtual servers that hosting providers rent out. These are: VPS / VDS, dedicated servers, shared hosting, cloud hosting.
It’s worth starting with it, because the rest of the host services are virtual analogues of a dedicated server.
A dedicated server (dedicated server) is a real physical server (bare-metal server), which the hosting company provides the client with for rent. It is important that the hoster allocates the server to the client as a whole for inseparable use, that is, all server resources, all its hardware are used by only one tenant. It is possible to flexibly configure the system and optimize it "for yourself", including installing software. Due to full ownership, a dedicated server is the most expensive hosting service.
It is a powerful computer rack-mounted with other similar servers and a switch. Server racks are localized in host data centers or individual data centers (that is, owned by the company for its business purposes; in this case, we are not talking about dedicated servers, since no one rents them out - the machines are the property of the company and are simply called servers) .
A dedicated server is required to host projects that either require powerful computing resources, or cannot be adjacent to other projects or their components (for example, a complex business application, or a database, or a network game site), or require direct access to equipment.
Shared hosting (shared hosting) is the provision of a lease of one physical server to several tenants at once. Its hardware capacities are distributed among all users. In order to avoid uneven distribution of machine capacities (processor power, disk and RAM) and their shortage during peak loads, some hosters limit server resources for individual user scripts (a script file or a program with a script to automate some site processes). There is no “customization" setting - everyone uses the same software that the provider installs. Suitable for small and uncomplicated projects. This is the cheapest type of hosting.
VPS (Virtual Private Server) and VDS (Virtual Dedicated Server) are essentially the same thing. These are virtual servers that emulate the operation of a physical server and are provided by the hoster for rent to the client with maximum privileges: installation of the operating system and software, root access (rights of the main administrator). The client receives dedicated server hardware resources for use with full management and control, but perhaps not all available on the machine. That is, on the same physical server several virtual servers are running for different clients, but on each of them the administrator (customer) can work the same as on a separate physical machine, while the rent is significantly lower than for a dedicated server.
VPS Virtualization of such a server is carried out within the operating system (containerization) using special technologies ( FreeBSD Jail , Parallels Virtuozzo Containers , iCore Virtual Accounts , OpenVZ and others). The client can work in a personal isolated software environment with superuser privileges, but cannot change the operating system itself or its kernel. There are also various restrictions based on the hoster's policy (for example, continuous availability of server resources).
VDS Virtualization of this type of server is carried out at the hardware level. This is the physical allocation of machine resources, or rather the emulation of its physical elements using special technologies (VMWare , LDoms , KVM , Microsoft Hyper-V , XEN ). The client not only receives CPU, disk space and memory resources for permanent use, but can also install another operating system and make modifications to it up to changing BIOS settings.
This type of host service is gaining popularity in the world due to the price / quality ratio. First of all, quality is understood as the breadth of possibilities for managing your hosted projects and the simplicity of scalability of allocated resources. In addition to the owners or system administrators of sites, developers are especially fond of it for the actual development and testing of new software. And the VPS / VDS hosting business helps reduce costs.
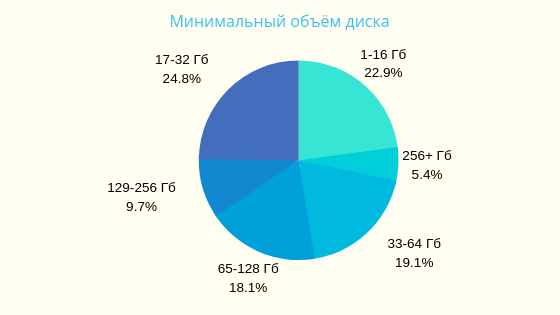
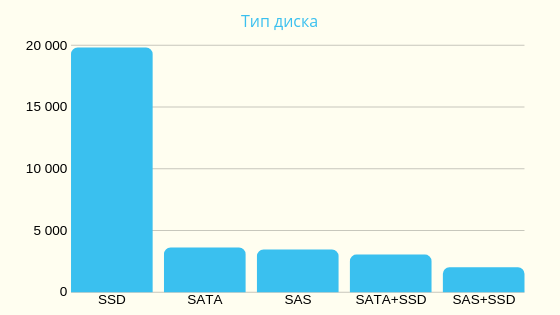
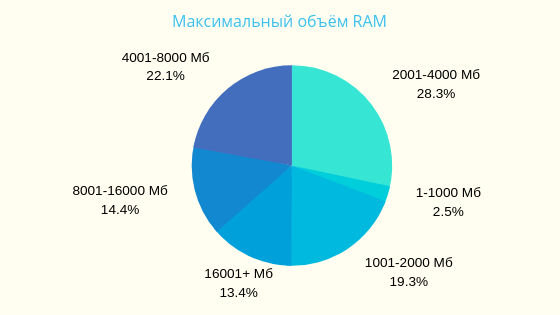
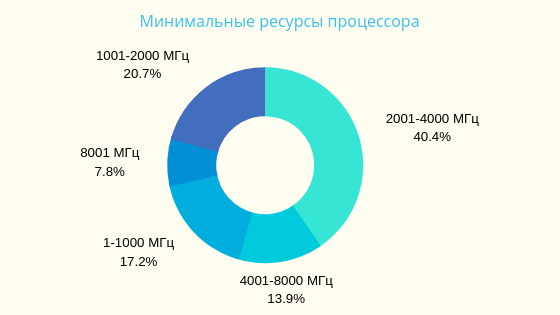
Based on search queries of 500,000 Russian users in 2017 on the site poiskvps.ru


According to J'son & Partners Consulting, the turnover of Russian hosting companies in the IaaS segment approximately coincides with the costs of Russian companies for Western hosting services.
Cloud hosting uses cloud resources to deploy sites, mobile applications, and even entire "offices in the cloud" ( virtual office ). Unlike other types of hosting, this does not happen on one local server, but on several physical and virtual servers connected to a cluster, to which data storage systems ( SANs ) connected to the network are added . When renting, the user pays only for the resources actually used, which can be quickly scaled or turned off depending on the needs. Moreover, the payment is hourly, that is, you can configure the consumption of resources in the daytime and at night. Settings can be adjusted automatically through the application. This flexibility is the main advantage of cloud hosting.
The cloud model is gaining popularity largely due to the development of BaaS (Backend-as-a-Service - backend as a service) and IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service - infrastructure as a service). We will not delve into its description, since this is beyond the scope of the article. We can only say that the developers are attracted to it by the versatility of the cross-platform backend for any project, and business owners - the reliability of backups and the convenience of teamwork on projects. Suitable for large and fast-growing projects, companies with seasonal fluctuations in demand.
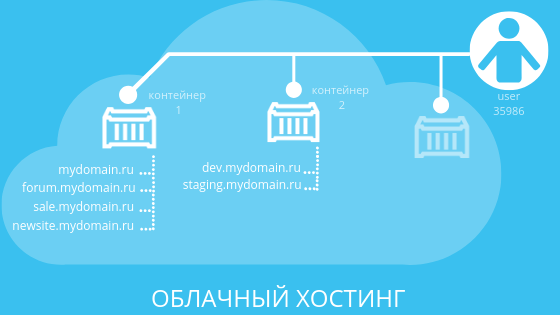
In the cloud, sites are located in isolated environments - containers. For example, working versions of sites can be located in one container, and test versions in another. The processes and possible malfunctions in the work of sites both inside containers and between containers do not affect the other sites in any way. An unlimited number of projects can be placed inside a separate container.
Source: iKS-Consulting, 2016.
Source: iKS-Consulting, 2018.

Summarizing, we note: choosing a hosting provider, focus not only on the promised information from his site and reviews - ask him questions! Until fire safety in the data center is ensured. Remember the scalability of projects - what your site is now can be very different from what it will be in 2 years. Having decided on the type of hosting, follow our recommendations from the sections "selection criteria" that are in each block.


We want to correct the situation and tell lucidly for those who are interested at any level of preparation for the question what hosting opportunities are today, how they differ, what are the advantages of some over others and what are the user statistics in Russia and abroad. The article is intended for a wide range of readers from neophytes to advanced users (therefore, explanations of terms well known to experienced users are often given in brackets).
First, let’s introduce a little bit of those who do not understand the topic of the article and indicate what hosting is and who needs it.
Hosting(hosting) is a service provided by companies hosting providers (hosters), which consists in placing information resources of users on their (companies) servers. The functionality of the server depends on the installed software, which, in turn, depends on the operating system. Hostings are distinguished by the presence of certain services, the ability to support various technologies, programming languages and scripts. They also differ in quantitative and qualitative limitations (disk space, number of sites, channel bandwidth, etc.). User access to their data is implemented through a personal account. Processing requests to customer information resources is carried out in real time 24/7. The hosting service includes technical support, security and data backup.
Information resources (here) are sites of various functionalities: online stores, corporate sites, Internet portals, information and news sites, web services. They consist of an abundance of digital data:
- text, graphic, photo, video files
- code files
- database management systems
- CRM-systems (software for managing relationships with customers, suppliers and employees within the company)
- CMS-systems designed to manage site content (WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, MODX, OpenСart)
- applications
The need for such a remote location is dictated by the fact that a lot of this data that grows over time cannot be stored and processed on the personal computer of the owner of an information resource - the volumes are too large, the machine’s capacities are not enough. To use your computer as a server, you need a redundant array of independent disks (Redundant Array of Independent Disks, RAID) or a very large storage device (SSD), a powerful outgoing channel to the Internet, a licensed server operating system and the knowledge to use it all . But the main thing is that it costs a lot of money. Therefore, there are physical and virtual servers that hosting providers rent out. These are: VPS / VDS, dedicated servers, shared hosting, cloud hosting.
What is a dedicated server
It’s worth starting with it, because the rest of the host services are virtual analogues of a dedicated server.
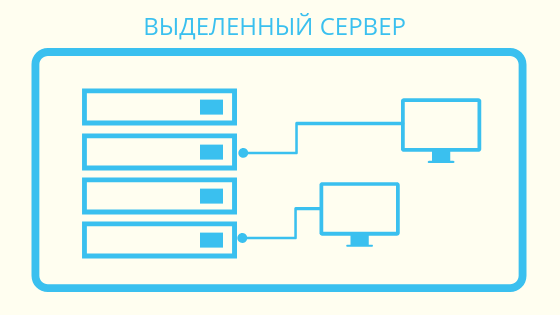
A dedicated server (dedicated server) is a real physical server (bare-metal server), which the hosting company provides the client with for rent. It is important that the hoster allocates the server to the client as a whole for inseparable use, that is, all server resources, all its hardware are used by only one tenant. It is possible to flexibly configure the system and optimize it "for yourself", including installing software. Due to full ownership, a dedicated server is the most expensive hosting service.
It is a powerful computer rack-mounted with other similar servers and a switch. Server racks are localized in host data centers or individual data centers (that is, owned by the company for its business purposes; in this case, we are not talking about dedicated servers, since no one rents them out - the machines are the property of the company and are simply called servers) .

A dedicated server is required to host projects that either require powerful computing resources, or cannot be adjacent to other projects or their components (for example, a complex business application, or a database, or a network game site), or require direct access to equipment.
▍ Criteria for choosing a dedicated server
- The current and planned number of visitors to the resource. On average, a typical dedicated server for a Russian company (without performance optimization) can withstand 2,000-300,000 hosts per day (unique visitors).
- Static or updatable project. There are sites with a large daily visit (about 30,000 hosts), but with a relatively rare addition of new voluminous data, without the use of complex filters for visitors to select - they do not require large capacities: thematic collective blogs, forums. And there are, for example, large online stores or online cinemas with frequent updating of the database, selection tools from a huge list of goods, constant loading of items from the warehouse - they need huge capacities.
- Platform. As we said above, a set of features and supported services depends on the chosen operating system. Moreover, some providers do not provide a choice of OS (mostly foreign) - this must be taken into account initially.
- Feature set. Not all services included in the rental package may be needed. However, each of them adds value. It is advisable to understand what is really necessary for the project and what is not.
- The ability to scale. Because increasing server capacities in the future is more economical than acquiring a new machine configuration, a more productive server solution.
What is shared hosting?
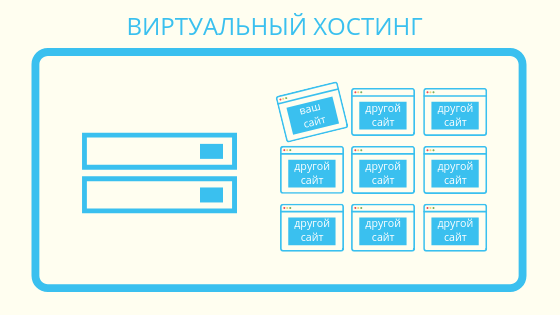
Shared hosting (shared hosting) is the provision of a lease of one physical server to several tenants at once. Its hardware capacities are distributed among all users. In order to avoid uneven distribution of machine capacities (processor power, disk and RAM) and their shortage during peak loads, some hosters limit server resources for individual user scripts (a script file or a program with a script to automate some site processes). There is no “customization" setting - everyone uses the same software that the provider installs. Suitable for small and uncomplicated projects. This is the cheapest type of hosting.

▍ Criteria for choosing a shared hosting
- Limitations of server resources by the hoster affecting server performance - the amount of disk space, RAM and CPU (processor power).
- The number of sites, databases, FTP accounts, mailboxes and more.
- The operating system used - it depends on which software will support the functionality of the site or services.
What are VPS and VDS
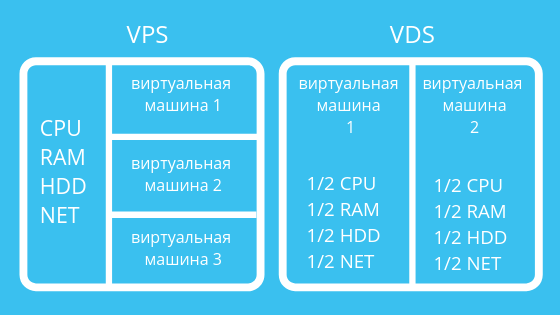
VPS (Virtual Private Server) and VDS (Virtual Dedicated Server) are essentially the same thing. These are virtual servers that emulate the operation of a physical server and are provided by the hoster for rent to the client with maximum privileges: installation of the operating system and software, root access (rights of the main administrator). The client receives dedicated server hardware resources for use with full management and control, but perhaps not all available on the machine. That is, on the same physical server several virtual servers are running for different clients, but on each of them the administrator (customer) can work the same as on a separate physical machine, while the rent is significantly lower than for a dedicated server.
▍Difference between VPS and VDS
VPS Virtualization of such a server is carried out within the operating system (containerization) using special technologies ( FreeBSD Jail , Parallels Virtuozzo Containers , iCore Virtual Accounts , OpenVZ and others). The client can work in a personal isolated software environment with superuser privileges, but cannot change the operating system itself or its kernel. There are also various restrictions based on the hoster's policy (for example, continuous availability of server resources).
VDS Virtualization of this type of server is carried out at the hardware level. This is the physical allocation of machine resources, or rather the emulation of its physical elements using special technologies (VMWare , LDoms , KVM , Microsoft Hyper-V , XEN ). The client not only receives CPU, disk space and memory resources for permanent use, but can also install another operating system and make modifications to it up to changing BIOS settings.
This type of host service is gaining popularity in the world due to the price / quality ratio. First of all, quality is understood as the breadth of possibilities for managing your hosted projects and the simplicity of scalability of allocated resources. In addition to the owners or system administrators of sites, developers are especially fond of it for the actual development and testing of new software. And the VPS / VDS hosting business helps reduce costs.

▍ VPS / VDS selection criteria
- Server configuration and hardware capacity. The speed of the hosted site depends on how much processor power (CPU), processor and random access memory (RAM) is allocated. The stability of the work depends on how well-known the brand of the proposed physical equipment for rent is.
- Operating system. The breadth of the spectrum of supported applications depends on it.
- Who will control the server? If the provider takes over the hosting management functions, it is a managed VPS (managed VPS), if you yourself are engaged in maintaining health and monitoring server performance, it is unmanaged VPS. It is logical that the unmanaged option is suitable for experienced administrators, and the managed one is suitable for business owners who are eager to delegate this occupation to professionals. The degree of control affects the tariff schedule.
- Uninterrupted and reliable operation. Uninterruptibility is characterized by such concepts as scalability (the ability to connect backup resources when the load is increased) and redundancy (actually reserving resources: how it is implemented by the host when there are problems with electricity, problems with the Internet provider, or overloading the physical server). Simply put, ask what disaster recovery measures the hoster uses. The reliability guaranteed by the hoster should be at least 99.95%. In addition to statements on the website of the service provider, which are not always true, it would be nice to read reviews about it on independent sites.
- Bandwidth Latitude. First you need to understand what bandwidth is needed for your projects. And then ask the hoster what its limitations are for this parameter, what is the fee for the additional latitude and whether there are quotas.
- Additional IP addresses. Not all hosters provide this service. However, it is often necessary: for each site or service on the VPS to have its own IP address, or for one site with different domains to have different IP addresses. Also, different IP addresses are needed to establish a secure connection using the SSL protocol .
- Server location The smaller the distance between the VPS and the location in which the audience of your site is concentrated, the better: faster access to users to the site (higher page response speed to a request), more opportunities to rise in search engine rankings.
- Responsive tech support. The whole side of your business related to the site depends on how quickly, smoothly and efficiently the hoster solves your problems, which you report to tech support. If the customer support is unsatisfactory, then you should not work with this hoster, even if the functionality and price of the host services are good.
- Money back guarantee. Hosters that take good care of customers have a so-called money back guarantee in case you do not like hosting. It is also good if there is a free trial period.
▍VPS usage statistics in charts
Based on search queries of 500,000 Russian users in 2017 on the site poiskvps.ru






According to J'son & Partners Consulting, the turnover of Russian hosting companies in the IaaS segment approximately coincides with the costs of Russian companies for Western hosting services.
What is cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting uses cloud resources to deploy sites, mobile applications, and even entire "offices in the cloud" ( virtual office ). Unlike other types of hosting, this does not happen on one local server, but on several physical and virtual servers connected to a cluster, to which data storage systems ( SANs ) connected to the network are added . When renting, the user pays only for the resources actually used, which can be quickly scaled or turned off depending on the needs. Moreover, the payment is hourly, that is, you can configure the consumption of resources in the daytime and at night. Settings can be adjusted automatically through the application. This flexibility is the main advantage of cloud hosting.
The cloud model is gaining popularity largely due to the development of BaaS (Backend-as-a-Service - backend as a service) and IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service - infrastructure as a service). We will not delve into its description, since this is beyond the scope of the article. We can only say that the developers are attracted to it by the versatility of the cross-platform backend for any project, and business owners - the reliability of backups and the convenience of teamwork on projects. Suitable for large and fast-growing projects, companies with seasonal fluctuations in demand.
In the cloud, sites are located in isolated environments - containers. For example, working versions of sites can be located in one container, and test versions in another. The processes and possible malfunctions in the work of sites both inside containers and between containers do not affect the other sites in any way. An unlimited number of projects can be placed inside a separate container.

▍Criteria for choosing a cloud hosting
- Availability of technology provided by the service
- The range of related services: not only the placement itself, but also access protection, backup services, support, load balancer, protection against DDoS attacks and others.
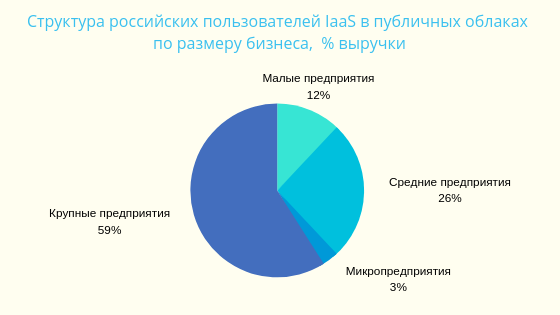
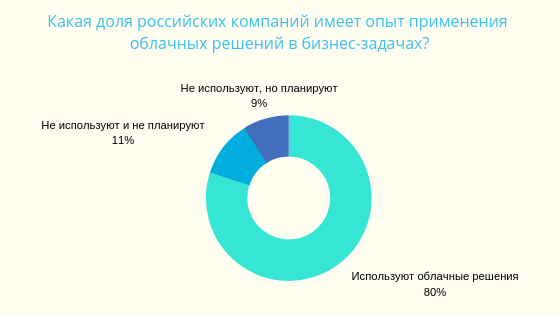
▍ Cloud statistics for Russia

Source: iKS-Consulting, 2016.

Source: iKS-Consulting, 2018.
Comparison of dedicated server, virtual server, shared hosting and cloud hosting

Summarizing, we note: choosing a hosting provider, focus not only on the promised information from his site and reviews - ask him questions! Until fire safety in the data center is ensured. Remember the scalability of projects - what your site is now can be very different from what it will be in 2 years. Having decided on the type of hosting, follow our recommendations from the sections "selection criteria" that are in each block.

