A new object is seen in the solar system
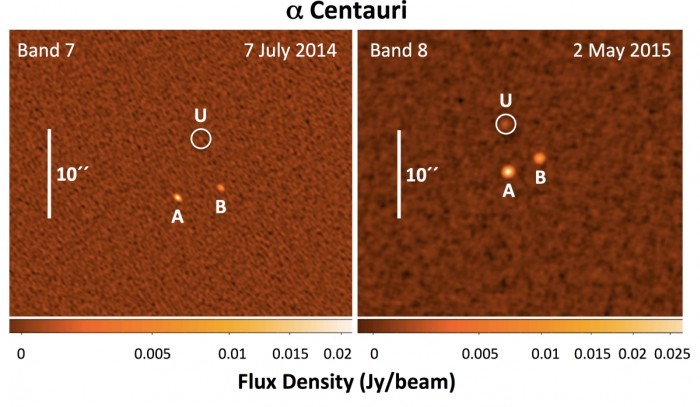
Using data from the Atakama Large Millimeter / Submillimeter Grid (ALMA) radio interferometer, astrophysicists discovered a previously unknown distant object in the direction of Alpha Centauri. The scientific article was published on December 8, 2015.
The distance and, accordingly, the size of the object is unknown. From two observations it is impossible to determine its orbit. Theoretically, it may well turn out to be a super-earth close to us . But the more likely version is that it is the farthest trans-Neptune object. Even so, the discovery is very significant.
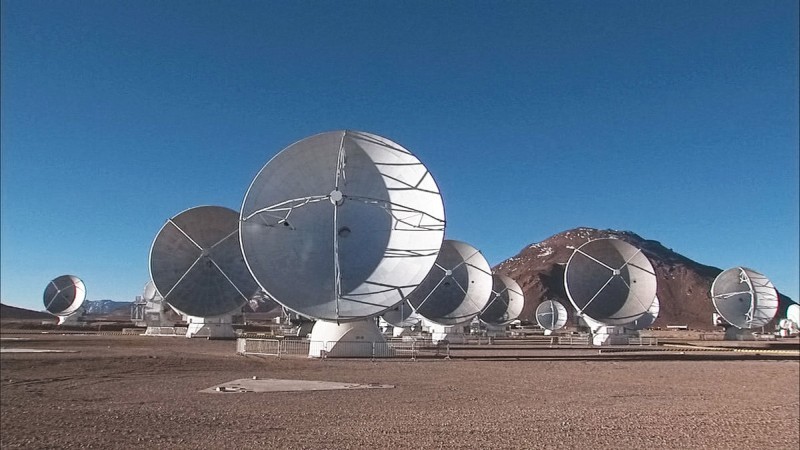
ALMA consists of 66 radio telescopes with plates with a diameter of 12 and 7 m, which observe the millimeter and submillimeter ranges. To “zoom in on the picture” the antennas are moved over a distance of 150 m to 16 km. No radio telescope in the world can be compared even more closely with the sensitivity and resolution given by ALMA.
In the millimeter and submillimeter ranges, cold gas and dust are usually emitted, but objects at the edge of the solar system also emit in this range. At the same time, they are not detected by infrared telescopes, so only ALMA can see such an object.
So, in July 2014, for the first time in the direction of Alpha Centauri A and B, a dim object was noticed. The second time it was registered in May 2015, this time more clearly. It can be assumed that this is another object in the Alpha Centauri system four light years from us. Judging by the brightness, it could be a red dwarf. But in this case, infrared telescopes would have been recording it for a long time.
Since the object does not belong to the Alpha Centauri system, it should be much smaller and closer to us. According to independent astrophysicists, this is most likely an unusual trans-Neptune object (TNO) at a distance of about 100 astronomical units from the Sun, that is, farther than Sedna (86 AU). Thus, this is the farthest known object of the solar system, which is probably smaller than Pluto.
The authors of the scientific work consider another hypothesis probable: the object is located at a distance of 300 AU and is 1.5 times the size of the Earth. The first super-earth in the solar system!
Such an option is not ruled out, since observations of TNO have recently led to speculation that one or two super-earths may be hiding at the outer borders of the solar system.
The negative argument against this version is that Alpha Centauri and, accordingly, the discovered TNO, have too much orbital inclination: 79 degrees. But even Sedna has an inclination of only 12 degrees. It is very unlikely that a super-earth will exist in such an inclined orbit to the plane of the solar system.
A cold brown dwarf at a distance of 20,000 AU would also be visible through infrared telescopes.
Answers to questions will be given by further observations of the object. In any case, there is something there.
Atakama Large Millimeter / Submillimeter Grill
ALMA is an international project, the largest and most expensive astronomical project on Earth: construction cost ≈ $ 1.4 billion.
ALMA antennas combined as a single interferometer.

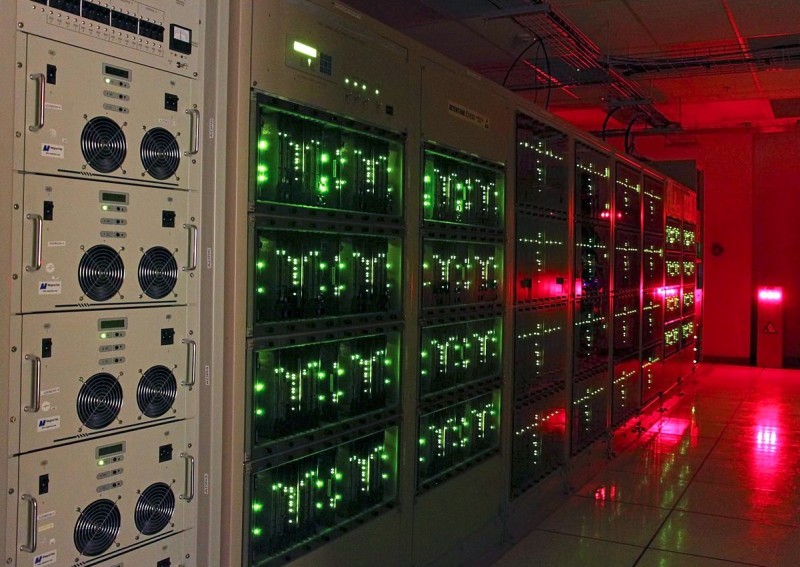
ALMA correlator. Atacama Compact Array (ACA) Correlator
supercomputer consists of 35 Fujitsu Primergy servers on x86- compatible processors and specialized calculator. It includes an array of 4096 FPGA blocks interconnected by 1024 fiber-optic connections. The system is capable of real-time processing of 512 billion radio signal samples (approximately 200 GB / s) every second, which corresponds to a performance of 120 trillion. operations per second.

The radio interferometer in the Chilean Atacama Desert was launched at full power quite recently, in March 2013 - and now such a discovery.
