Agile Mobile Development Methodology
- Tutorial
Agile development is especially useful for mobile app development. The agile methodology provides our clients with a continuous feedback loop. Sourcebits mobile app design and development clients see milestones every 2-3 weeks. They aren't left to wait until the very end of the project. Agile development for mobile apps means clients provide feedback every step of the way to ensure the success of the project. - Joe Chen, CTO, Sourcebits
It is no secret that development for mobile platforms has important distinctive characteristics that apply to most phases of the life cycle, such as:
- the need for a short time of product delivery to a dynamic market, and further constant updates;
- a large number of users from around the world;
- difficulty in identifying application requirements, including due to difficulties in identifying stakeholders;
- a high probability of changes in the needs and expectations of users, and, accordingly, the need to make changes during development;
- high pace of technological evolution - new devices, OS releases, PL, mobile communications & IoT, etc.
In order to meet these characteristics, reduce risk, and streamline the process of mobile development, the Agile methodology is widely used with its adaptive (permissible frequent changes), iterative-incremental (feedback from the customer at each iteration, and multiple releases), cooperative (tight collaboration between developers, customers and end users) and a simple (easy to understand, change and improve) development approach.
Agile
Agile is a series of approaches to the development of software products through the continuous and quick delivery of valuable work functionality by a self-organized team of professionals in collaboration with the customer.
Agile is a combined version of iterative and spiral models of the life cycle: step-by-step development and availability of ready-made fragments of working software taken from an iterative model + the leading role of the human factor and analysis of possible risks taken from a spiral model.
The advantages of Agile, and the reasons why companies use it, have been well illustrated in a number of well-known studies: State of Agile , CHAOS Report , Agile Quantitative Assessment .
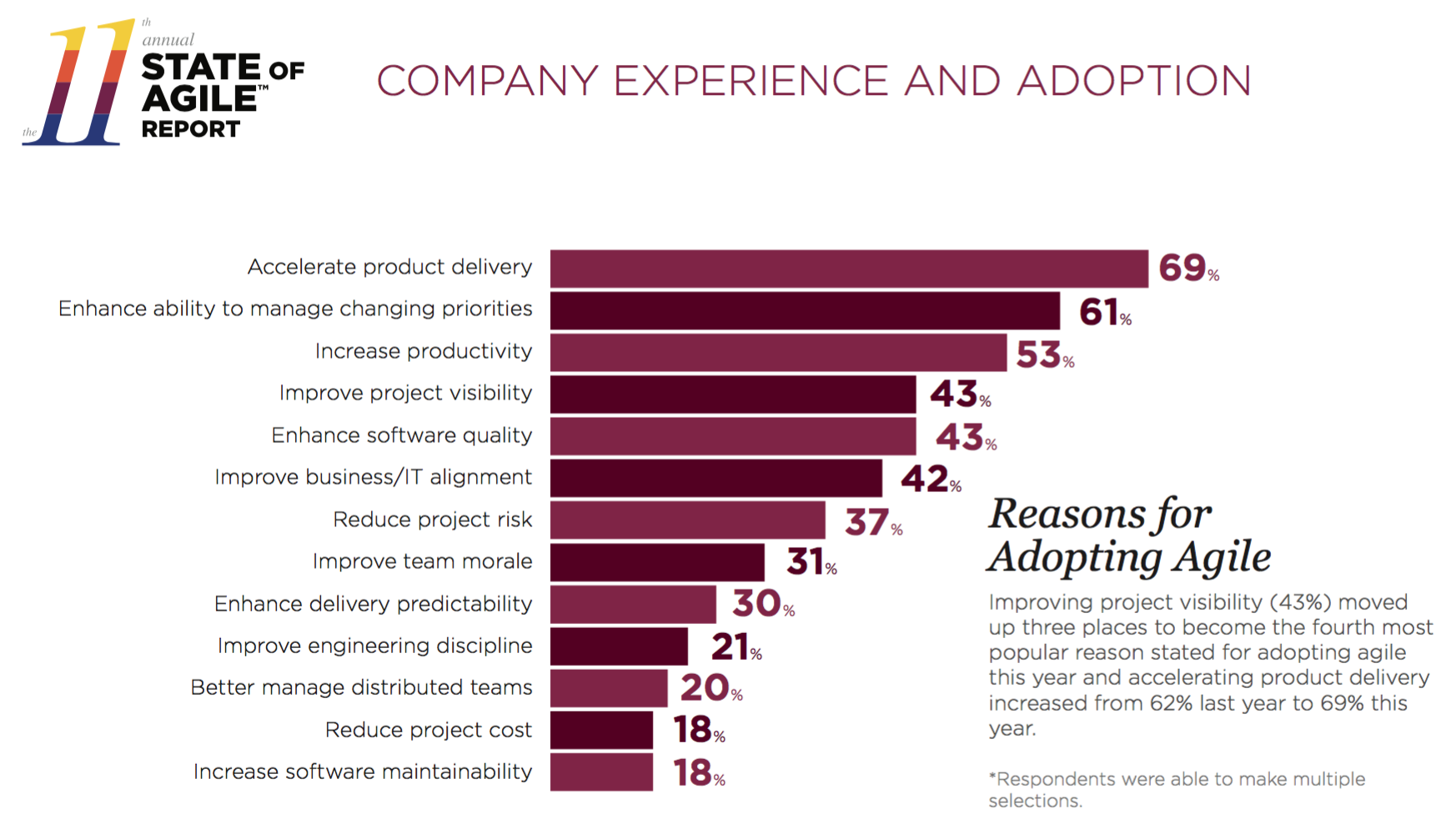
State of Agile : Why Agile is Used
Agile’s core ideas were presented in a document called the Agile Manifesto. It also contains twelve specific principles of Agile. The full text of both documents (and their translations) are available at http://agilemanifesto.org .
Agile for mobile development
As noted, Agile allows you to adapt processes to the unsustainable needs of the mobile field. Agile provides the flexibility to understand the market, structure the product and release it in a short time.
Over the past few years, a number of frameworks have been developed suitable for use in the mobile field: Mobile-D, MASAM, Hybrid, Scrum, SLeSS.
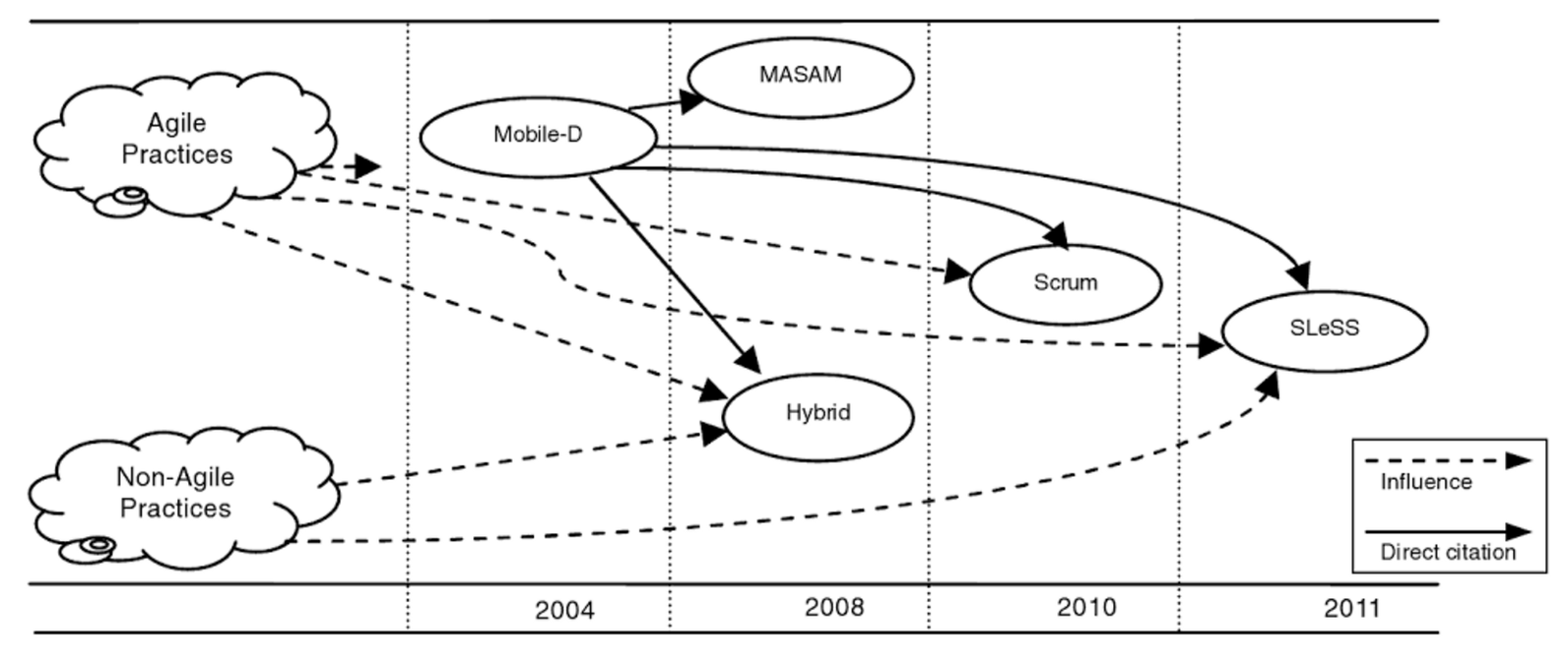
The evolution of agile development methodology for mobile software ( Image source )
Scrum and SLeSS are the most modern, while the basis of SLeSS is the same Scrum. The very first attempt to adapt Agile for mobile development - Mobile-D - is also of interest, especially for the reason that it includes elements of XP engineering practices.
Scrum and XP will be discussed in more detail later.
Scrum
Scrum is one of the agile methods in which the product is created as a series of iterations of a fixed duration. The technique focuses on the quality control of the development process, on task management in a team development environment.
In general, Scrum involves working on a project in short iterations (usually 2-4 weeks), each of which is a reduced version of the project , and includes all the tasks necessary to produce an increase in functionality.
A scrum meeting is held every day, where the team synchronizes its work and discusses problems.
Every time a new feature, module or update is completed, testing is carried out. Thanks to testing during development, possible bugs are fixed on time, which ultimately leads to a much more stable product.
At the end of the iteration, the customer receives a new version of the product, and, if required, the project or any part of it is reviewed. It also takes into account feedback from end users. In addition, in the process of retrospective team gets the opportunity to optimize their work processes. Then the implementation loop starts again. As a result, a solution is created that most closely meets the requirements of the customer and is in demand by the market.
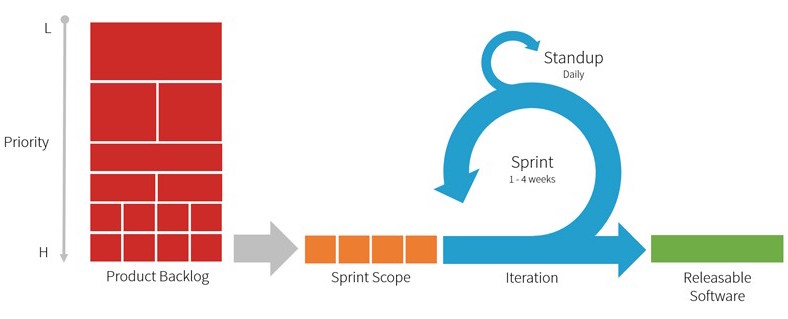
Scrum Process ( Image Source )
Scrum main tools:
- Product Backlog
- User Stories
- Sprint planning (iteration in Scrum);
- Sprint backlog
- Task board (in the form of physical or digital, for example, inside JIRA )
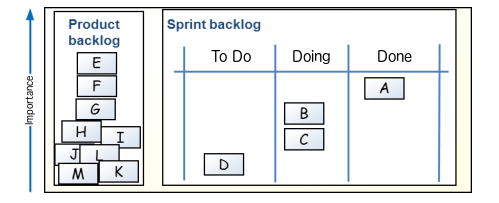
Task board example
- Chart combustion tasks (Burndown Chart);
- Quick meetings (stand-ups / rallies);
- Sprint review (demo and retrospective).
XP
XP Agile (Extreme Programming) focuses on the engineering side of product development. This is a systematic approach to programming. While Scrum pays more attention to management and release, XP is focused on the production process. XP includes practices that significantly improve the quality of the final product:
- Continuous Integration (CI)
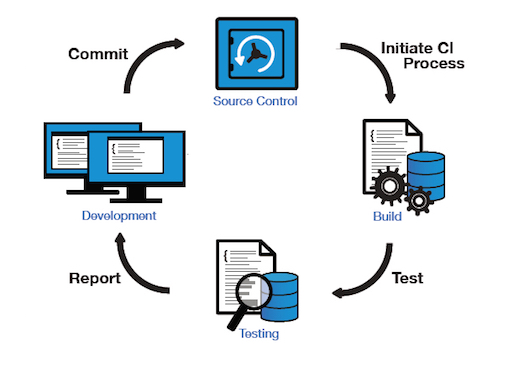
Continuous Integration Cycle ( Image Source )
- Automated Testing
- Refactoring
- Code review;
- Pair programming;
- Coding Standards, and others.
Adaptation of techniques
Quite often, in mobile development, classical techniques must be adapted to the specifics of the project, team and customer. Some options for such adaptation:
- modification of the time frame of agile practices . For example, reducing the sprint time to 1 week - as a rule, the application customer wants to receive new releases, and the team receives feedback as often as possible. Another example: a retrospective may be once a month or each iteration, depending on the needs of the project;
- modification of the implementation of agile practices . For example, conducting asynchronous stand-ups through Slack / Stride / etc. If the team works remotely, this is especially true. Another example: due to the often “vague” requirements of the customer, and the corresponding difficulties of the team when planning work, Dual-Track Scrum looks interesting ;
- modification of a set of agile practices . Obviously, it is not always necessary to include all the tools of the chosen technique in the work at once, especially in a startup. Therefore, at first only the most necessary and “working” ones can be selected.
What about waterfall?
It should be noted that one cannot say definitely about the inapplicability of the traditional waterfall methodology with its successive phases in mobile development. It all depends on the specifics of a particular project. There are examples of projects (for example, performing super-critical work; in a completely new field that requires preliminary research; with a large size, complexity and length of development period; government contracts), the essence of which contradicts the principles of Agile, and then the waterfall is an appropriate choice. However, there are very few such projects in commercial development.
Total
A mobile project is often subject to internal or external uncertainties, such as vague requirements or frequent changes in user needs, so it is prudent to plan its life cycle using some kind of agile technique, or, as is often the case in practice, a combination of both. Good results showed the use of adapted versions of Scrum and XP.
The English version is available here .
