Removal of the rocket before launch on the East

On the eve of the New Year, Roskosmos is preparing to launch from the Vostochny space center two Canopus-V satellites and associated small vehicles. Three days before the launch, the prepared rocket is taken to the launch pad, and the final pre-launch operations begin. I managed to see and capture this process.
The assembly and test case where the rocket gathers, is huge. On its scale, even the 52-meter Soyuz-2.1a seems quite small.
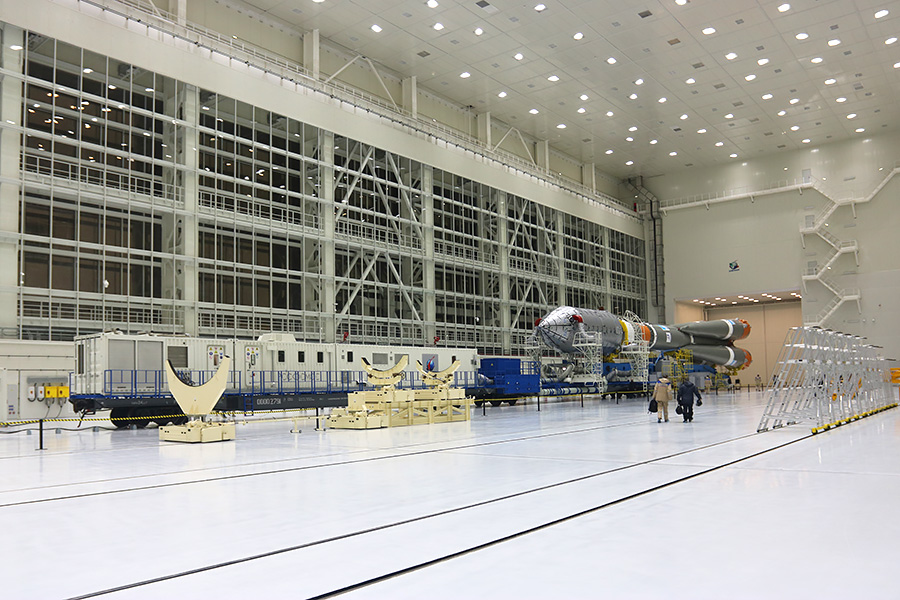

The rocket moves between the MIC and the launch pad by rail on the platform.
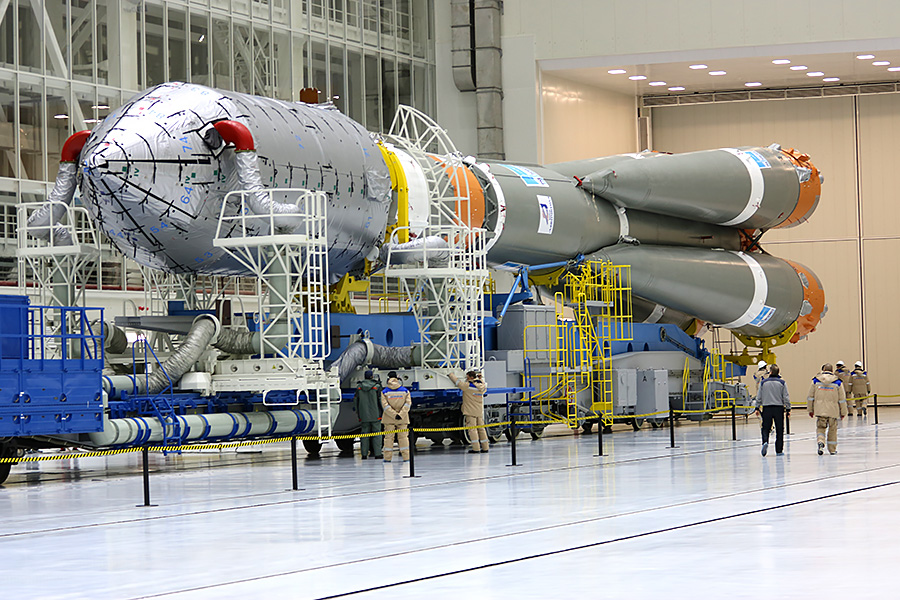

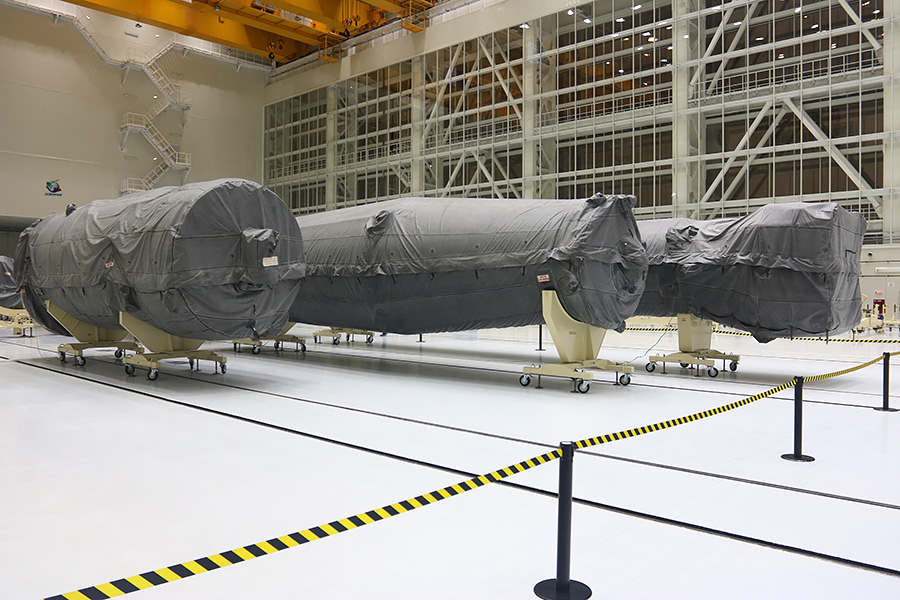
Elements of the rocket come from Samara, too, by train. The next one has already been delivered and is waiting for its time in 2019.

Vostochny has absorbed all the previous experience of other cosmodromes, from which they launch the Soyuz: Baikonur, Plesetsk, Kuru. The assembly and test building is constructed so that without leaving the premises it was possible to import wagons and platforms with rocket elements and satellites through one gate, and the product ready for launch from the other gates to be taken out.
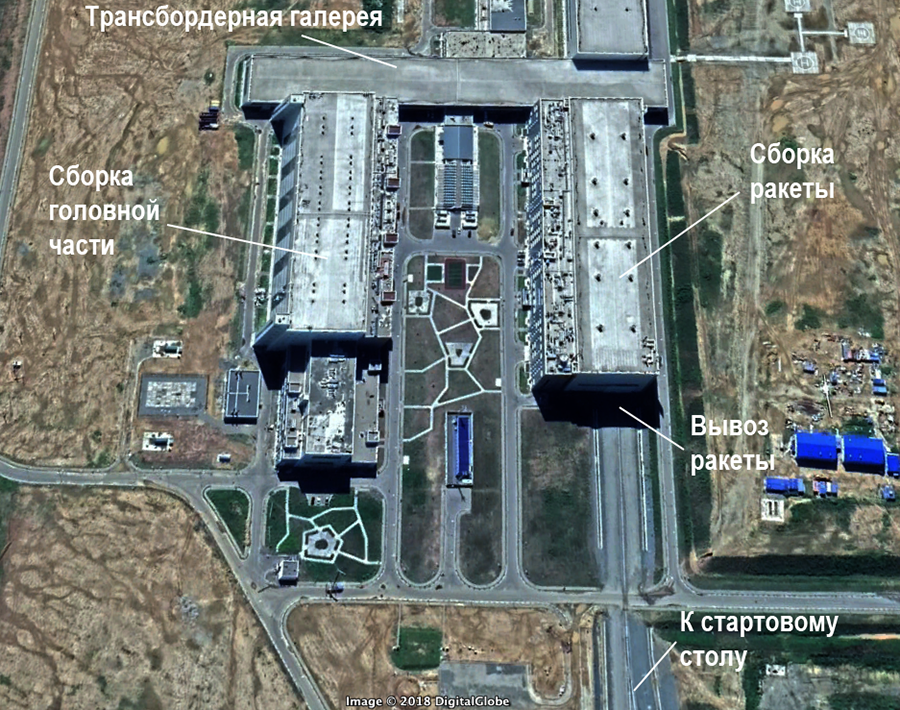
In terms of the Assembly and test body consists of two parts: for the preparation of spacecraft - the head part - and for the preparation of the rocket. About the sites where the satellites are preparing to launch, I have already told . Today I’ll tell you a little about the tool that allows you to do without rail transportation between the buildings.
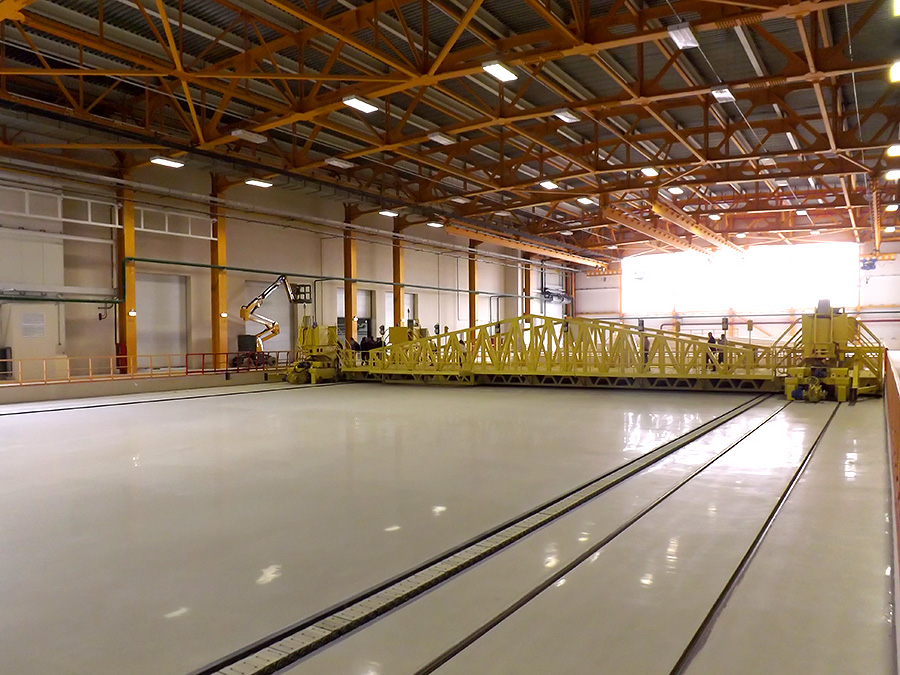

This is the so-called. “Transborder”, it can be called a “horizontal elevator” or a transverse platform that can move along rails laid in the gallery connecting the hull, and carry cargo from one railway line to another.
On the website of the Russian developer Ascon , which creates the Compass software for engineering design, we managed to find the schemeswhich can explain a little how this system works:
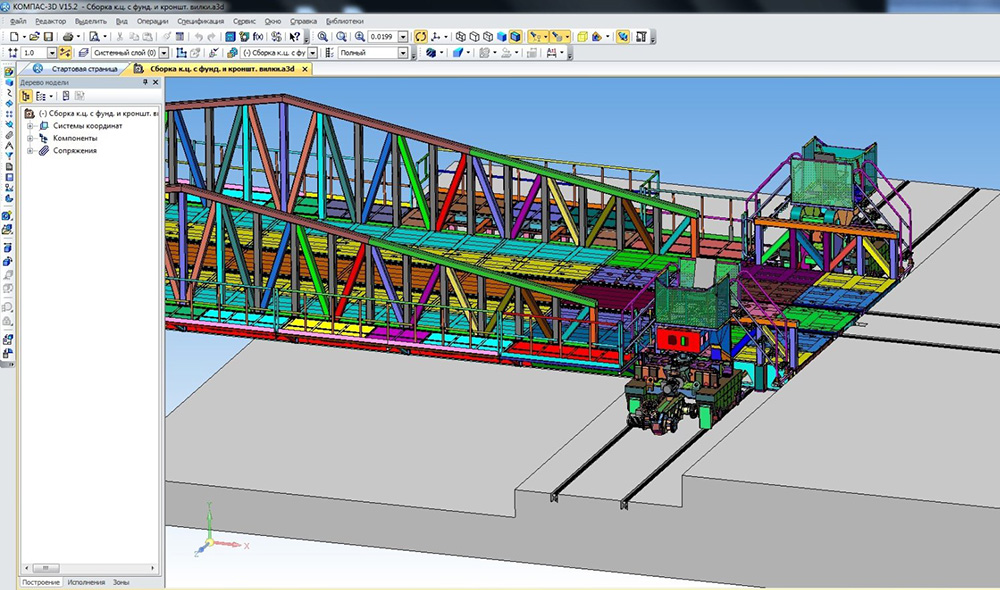
I didn’t find the work of a transborder on this day - the rocket is already in full assembly.
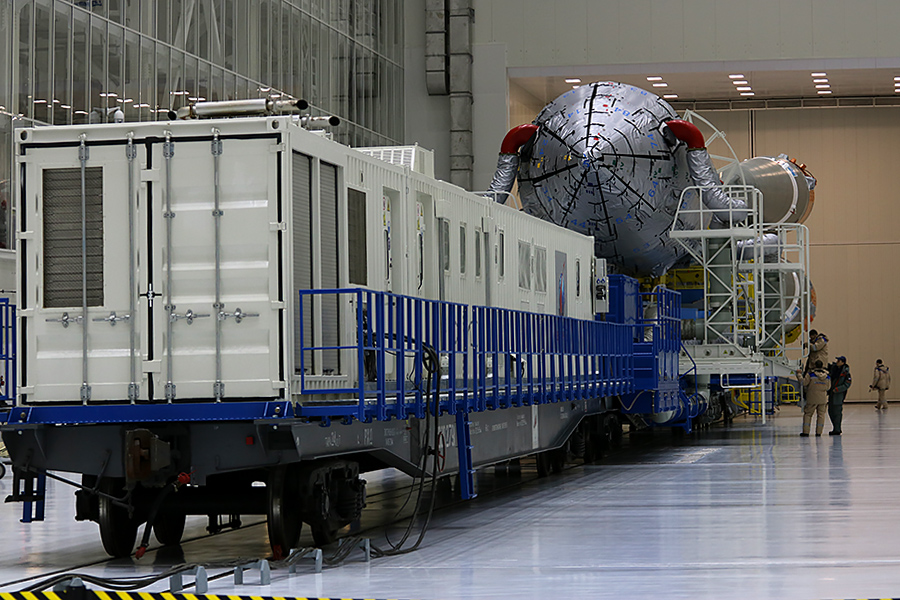
By the time of export, the head part is already docked to the rocket, and is covered with a layer of thermal insulation that saves satellites from 30-degree Amur frosts. The air ducts of the temperature control system are connected to it - this is an autonomous "air conditioner" that maintains the temperature comfortable for the satellites under the fairing during the movement from the MIC to the launch site for a distance of 5 km.
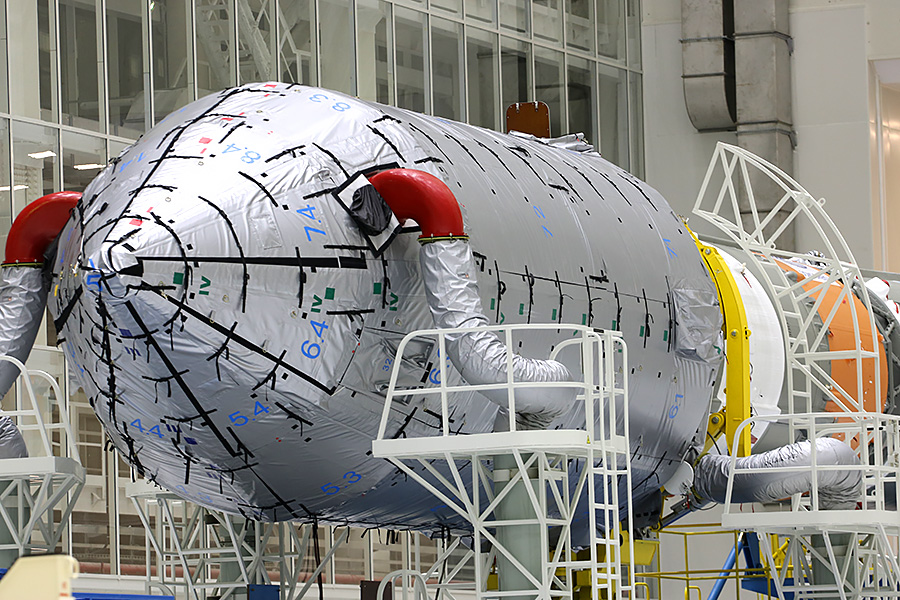
The “air conditioner” itself is moving nearby, on a nearby railway platform.

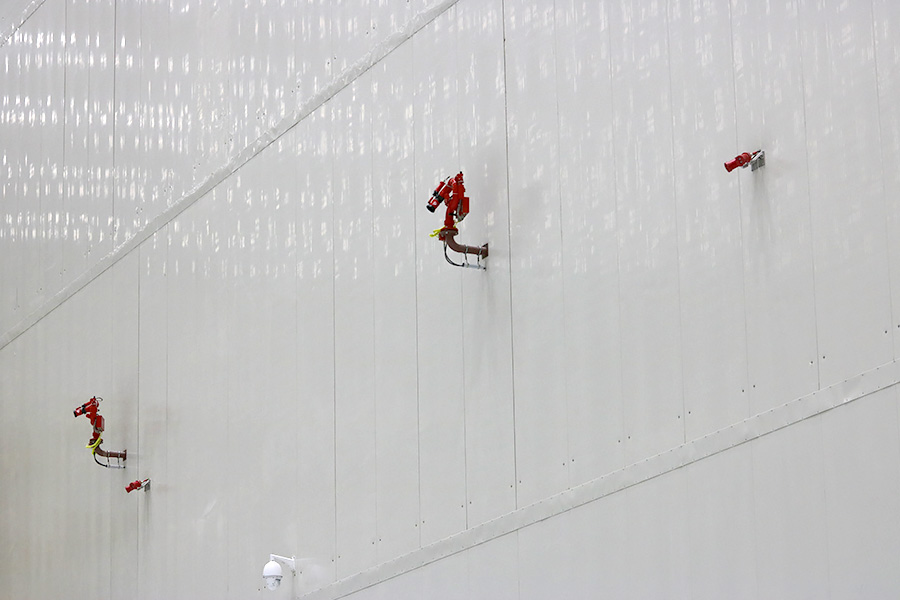
All work in the MIC is carried out under the supervision of video cameras, fire detectors and fire-extinguishing turrets.

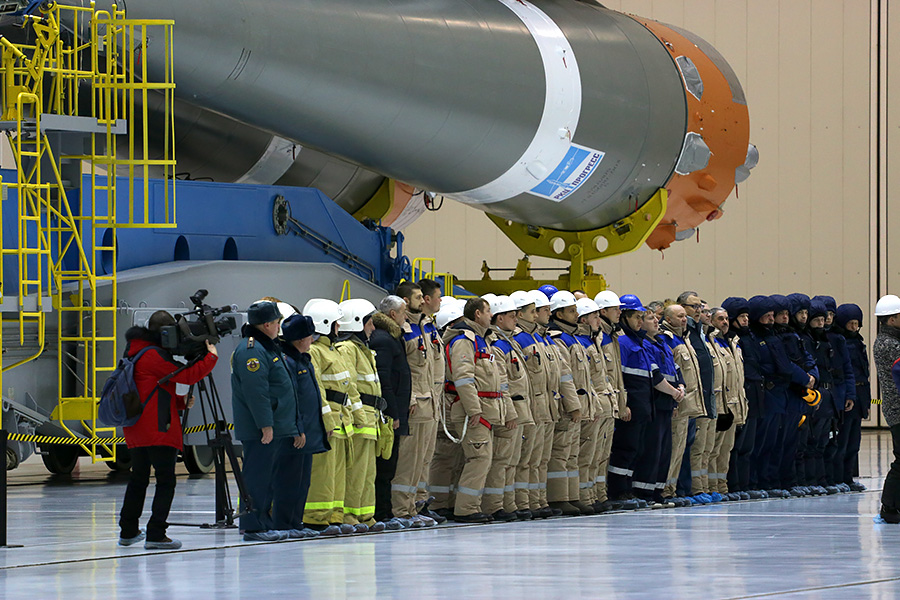
Before departure - the construction of the entire maintenance crew: railroad workers, employees of the Center for the operation of ground-based space infrastructure, firefighters, rocket manufacturers from RCC Progress, even security helmets and body armor (but without machine guns, unlike Baikonur).

Finally, the gate opened and a diesel locomotive drove in from the street to deliver the rocket to the launch pad.
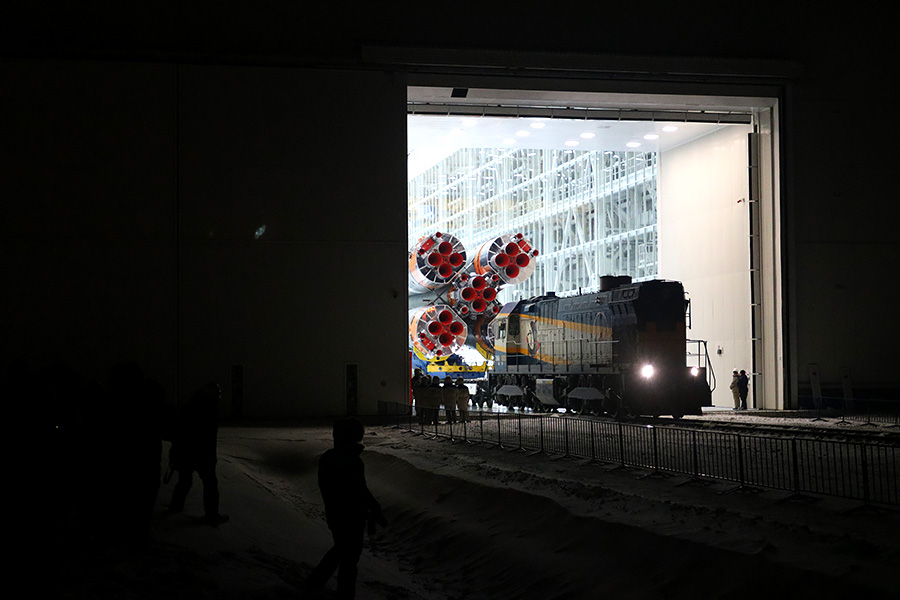

Work begins to produce early in the morning, before sunrise.
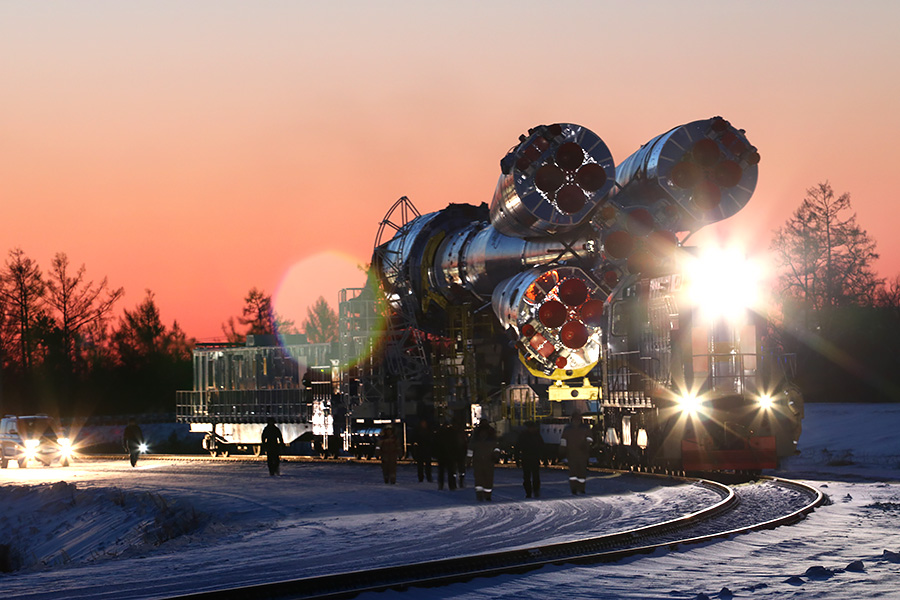

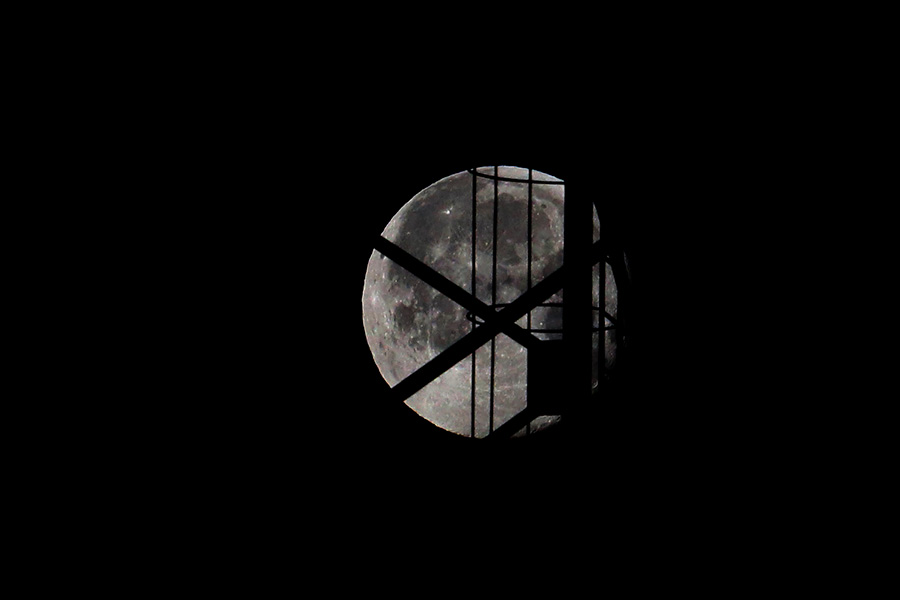
On the one hand illuminated the full moon.
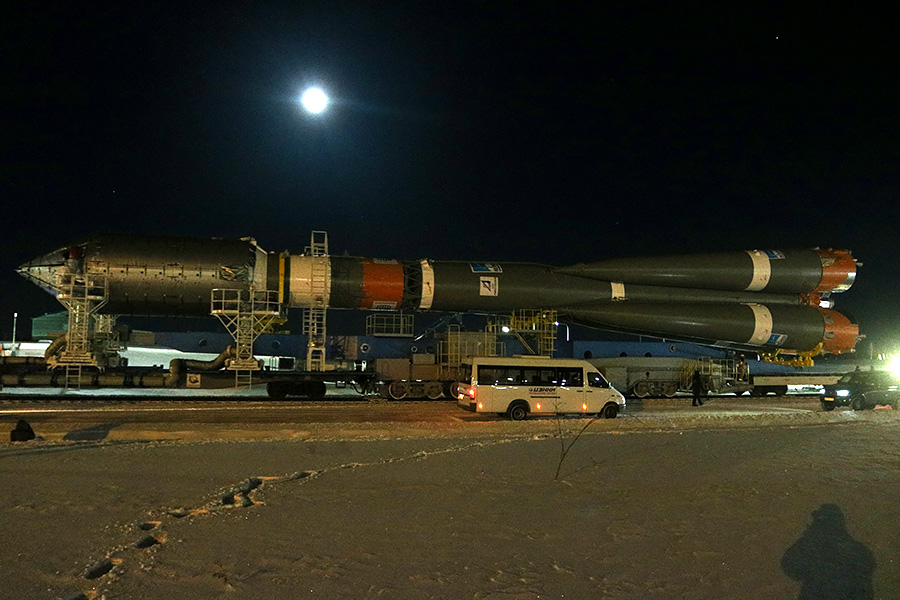

And on the other - bright Venus.
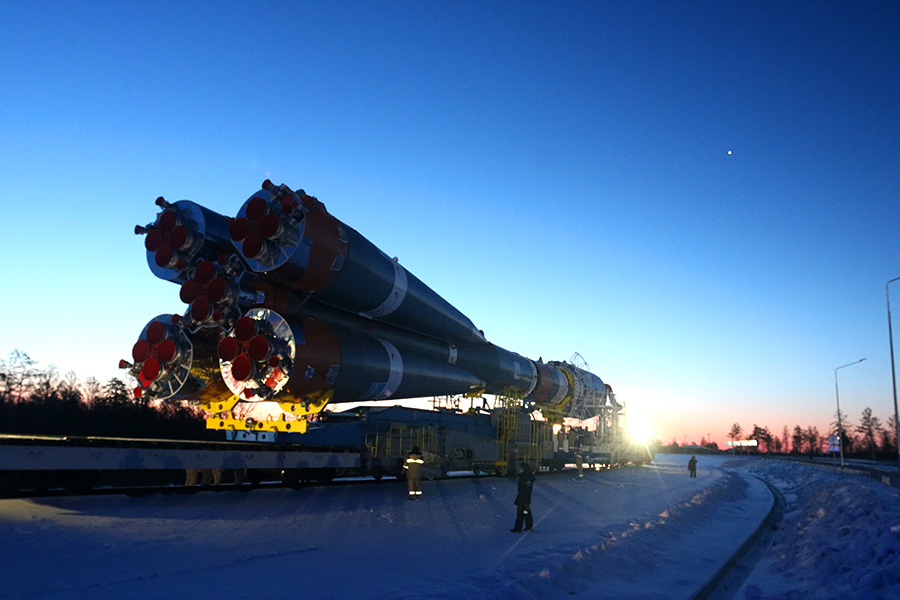

Movement occurs at a speed of 5 km / h - the train is moving, accompanied by a foot escort.
Shortly before the launch site, a takeover occurs - first, the locomotive would pull, and from here it would push.
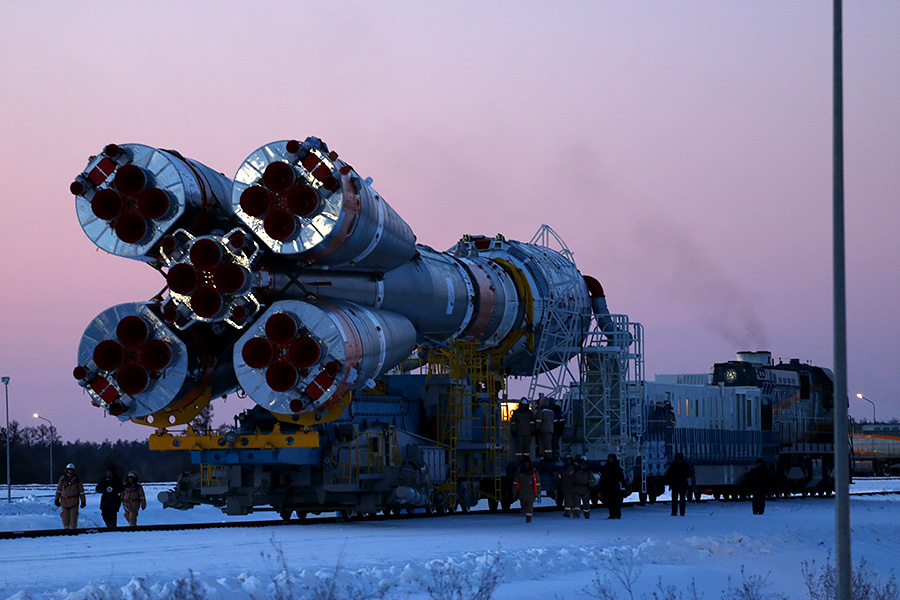

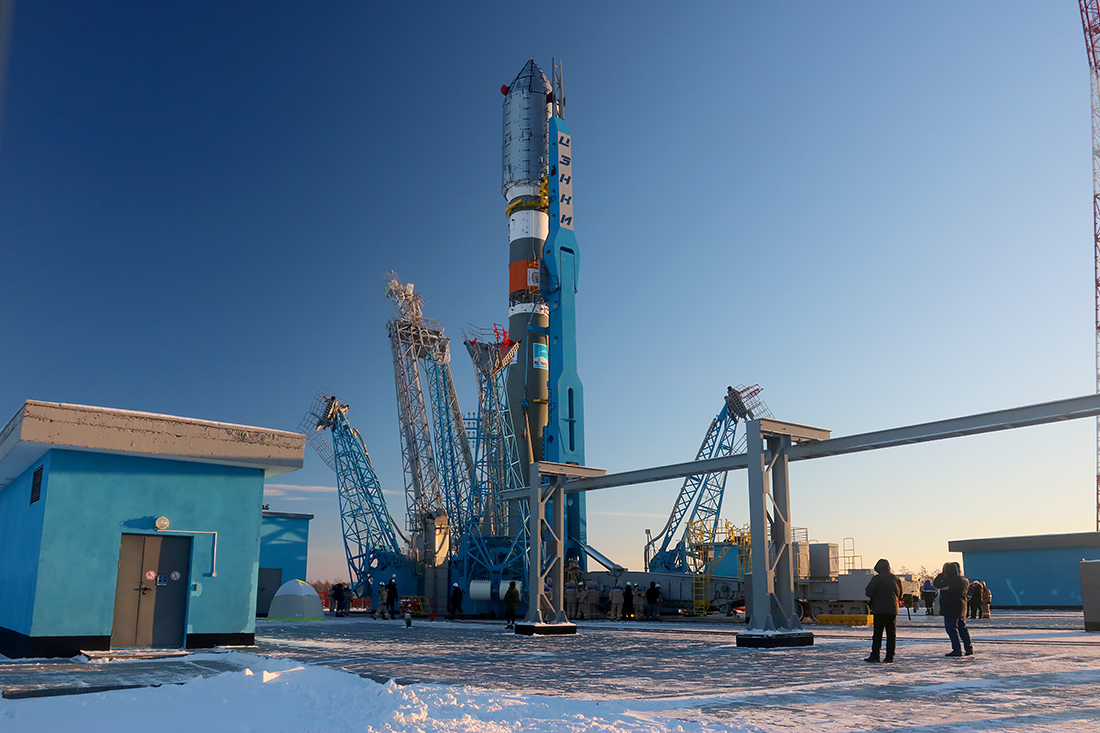
The rocket service tower on the launch pad is already shining in the searchlight beams.
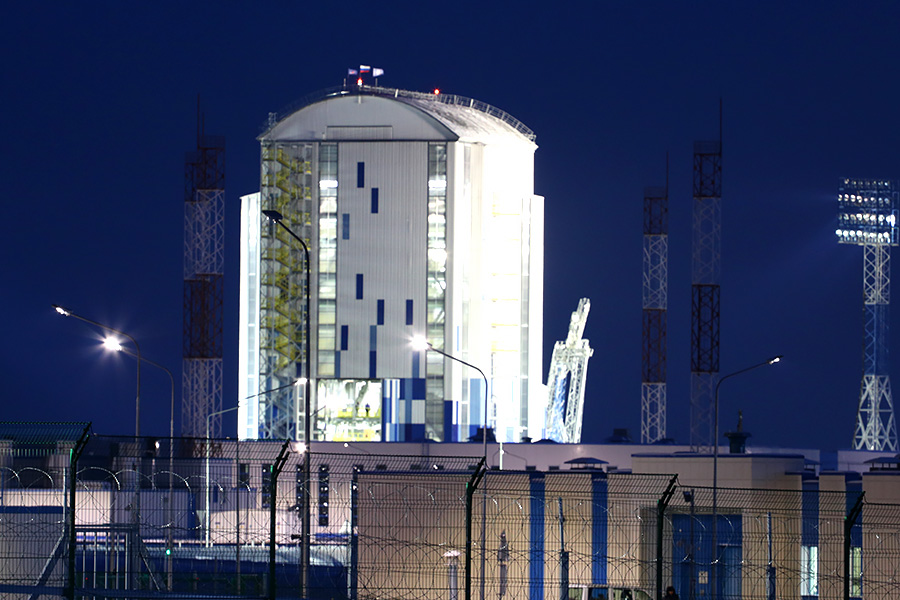

It's funny that in two years the motto “Lift your head” was removed from there, which was launched by the previous press service of “Roscosmos”.
The trusses and service masts raise steel “palms” to the dark blue sky, missing the Union waist. Before launching, they will keep the rocket over the failure of the gas outlet, and will disperse under the weight of the counterweights when the rocket engines start working.
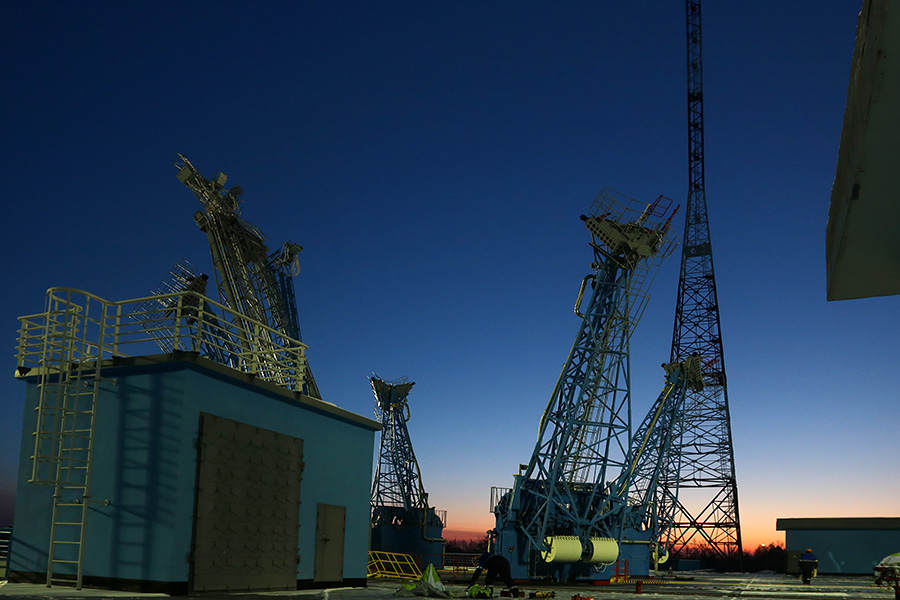

The rocket passes through the service tower.

This tower is also the result of previous experience gained at the equatorial cosmodrome in French Guiana. There is a completely different climate, but here and there, the weather is not always gracious to complex equipment and the people who serve it. Inside the tower is not heated, but protects from the wind and allows people to more calmly prepare a rocket for launch.
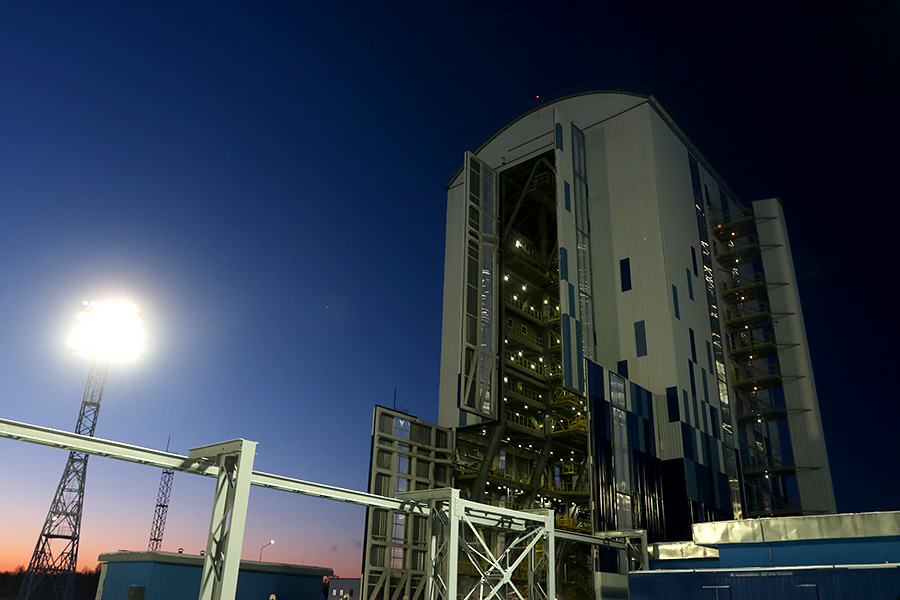

The launch pad dies down, waiting for the rocket and the sun to rise.
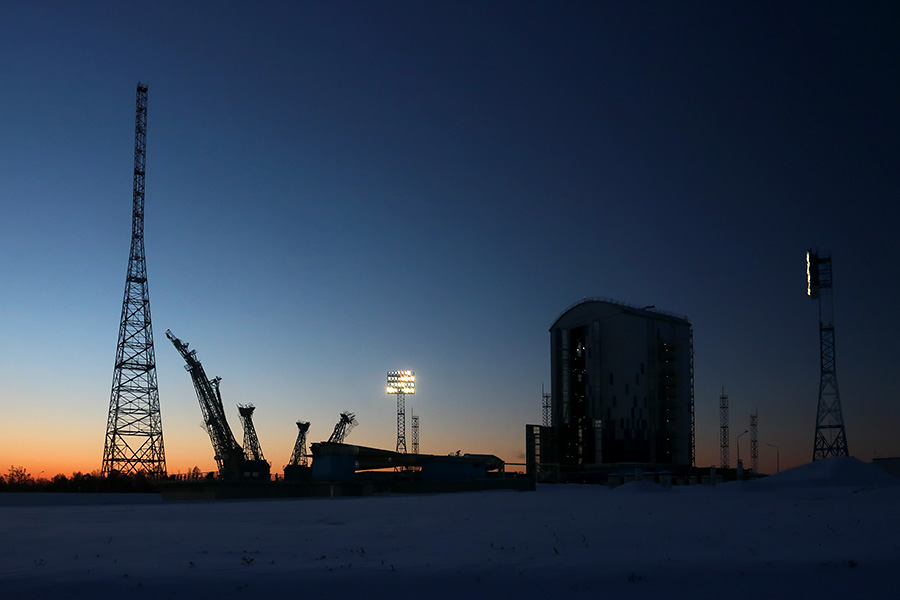

The sun is shown first.
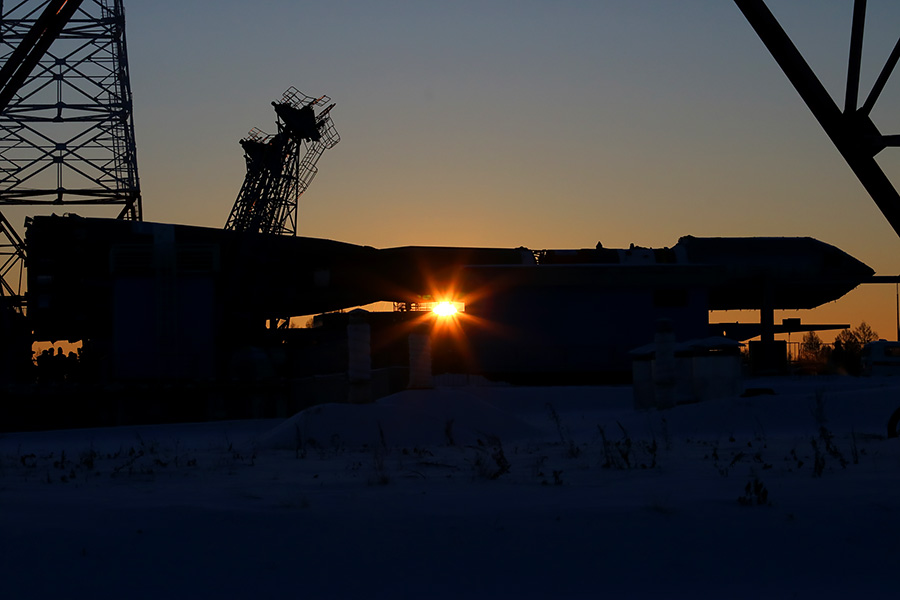

The moon is slowly slipping behind technical structures and hiding in the tops of taiga trees.

About an hour after the delivery of the rocket, its verticalization begins.
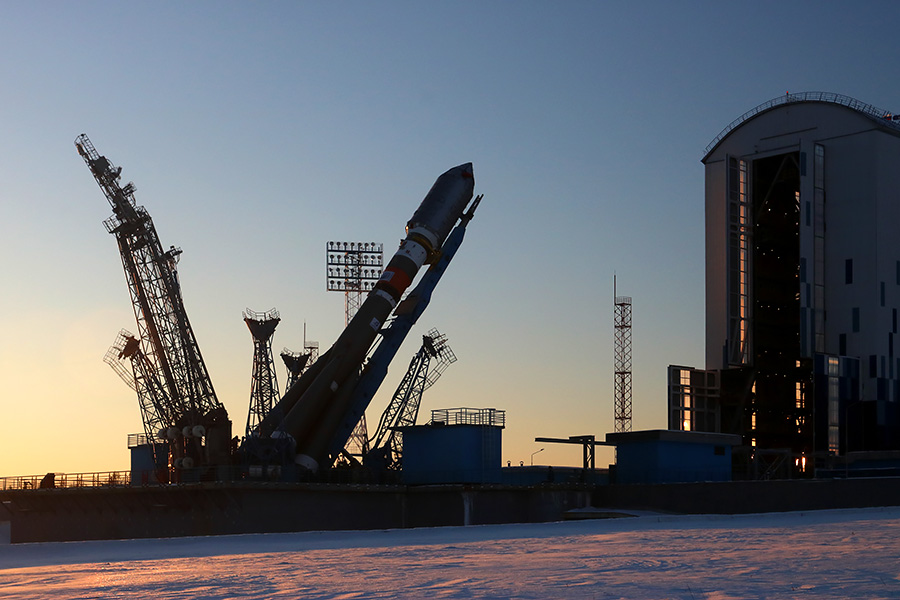

Lifting is carried out by a mast on a transport platform. After successful verticalization, the launch pad will close the service tower and within three days there will be a launch preparation.
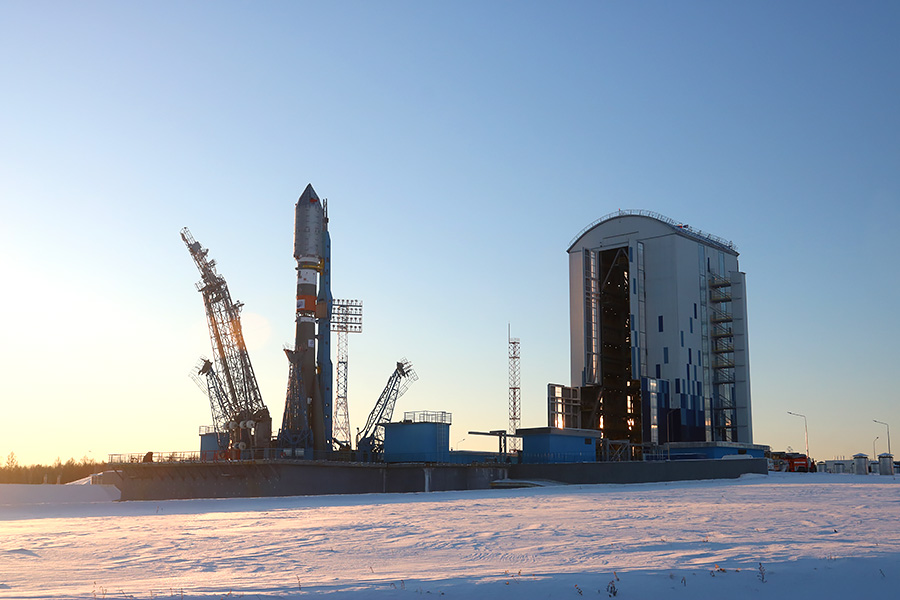

To see the technical magic of the cosmos and tell you about it, I was allowed by the invitation of the company GKLaunch , which was created in order to provide the Union with commercial demand on the world market.
