vCloud Director

Hello, Habr!
We upgraded the VMware vCloud Director platform from version 8.10 to 8.20.
What's new and what are the features of version 8.20? The answer to this question is probably of interest to those who have previously used the IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service) clouds and are familiar with the vCloud Director product. We will talk about this in the second half of our article, but first we would like to give a brief overview of vCloud Director modules and components for less experienced readers in virtualization issues.
What should we build a data center?
VMware vCloud Director is a platform that allows you to create software-defined, virtual data centers by converting physical data centers into flexible pools of computing resources that end users are encouraged to use for various distribution and consumption models. vCloud Director has a control panel that helps cloud service providers delegate some of their daily IT operations to their customers.
All physical resources of the data center, such as computing power, drives and networks, are combined into large pools of virtual resources. In the future, parts of these resources are provided in the form of “prefabricated” v data centers, which are allocated to tenants.
VCloud Director uses VMware vCenter and VMware vSphere to transform physical computing and storage resources into virtual pools, and NSX / vCNS to create virtual networks with different topologies. How does VMware vCloud Director accumulate resources for use, and how can individual tenants consume them? vSphere provides VCloud Director with all the resources to use to create a shared pool called Provider vDC (virtual data centers). Provider vDC creates an abstraction layer from which resources can be obtained for consumption by end users as separate computing units, the so-called Org vDC. vCloud Director maintains a database of all resources from vSphere, periodically synchronizing with vSphere Inventory.

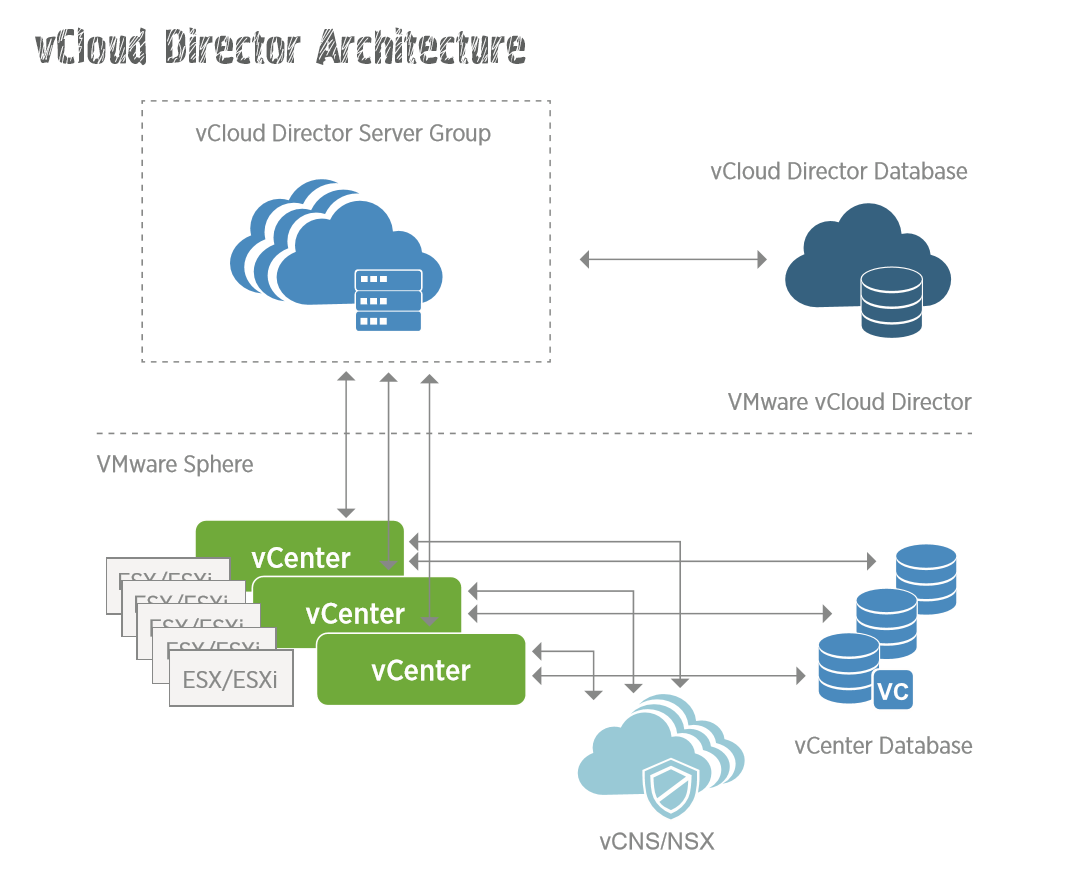
Org vDC is a computing unit that can be consumed by cloud users. This is the container for all virtual machines that are used in the cloud by a group of users. An enterprise using a provider’s cloud can have multiple Org vDataCenters, each designed to match a specific service profile, such as gold, silver, and bronze, or a business group, such as HR, finance, or marketing.
Org vDCs are combined into one or more networks. Org vDC networks provide network services to virtual machines residing in Org vDC. In addition, the virtual machine can create an additional network segment (vApp network). The vApp network has its own gateway associated with the Org vDC network.
There are three types of networks to which you can connect a virtual machine or a vApp network:
- Isolated network: A completely isolated and non-routable network suitable for virtual machines that require high security and do not need access to external networks / Internet.
- Org vDC Routed Network: Virtual machines connected to routed networks can send and receive external network traffic using NAT, a firewall, and VPN tunnels.
- External network.
A service provider can assign a tenant administrator role to a user from this organization. A tenant administrator can add and remove users, allocate resources, and create network services for the organization. Each organization has a unique URL created on top of the vCD base URL. Authorized users can log in through their organization’s unique URL. Tenant administrators can also mount service directories for cloud users. These directories may include virtual machines or multi-machine virtual appliance templates, ISO images, or files. Users can use these templates to accelerate the deployment of virtual machines.
vCloud Director is designed to optimize resource consumption, provide prefabricated services while maintaining isolation between the resources of each client in the cloud. Listed below are some of the features of vCloud Director that make this possible.
Elastic Resource Pool
From an abstract layer, Provider vDC vCloud Director can retrieve resources for clients when necessary, and return resources to the pool when they are no longer needed.
How it's done? (Distribution Models)
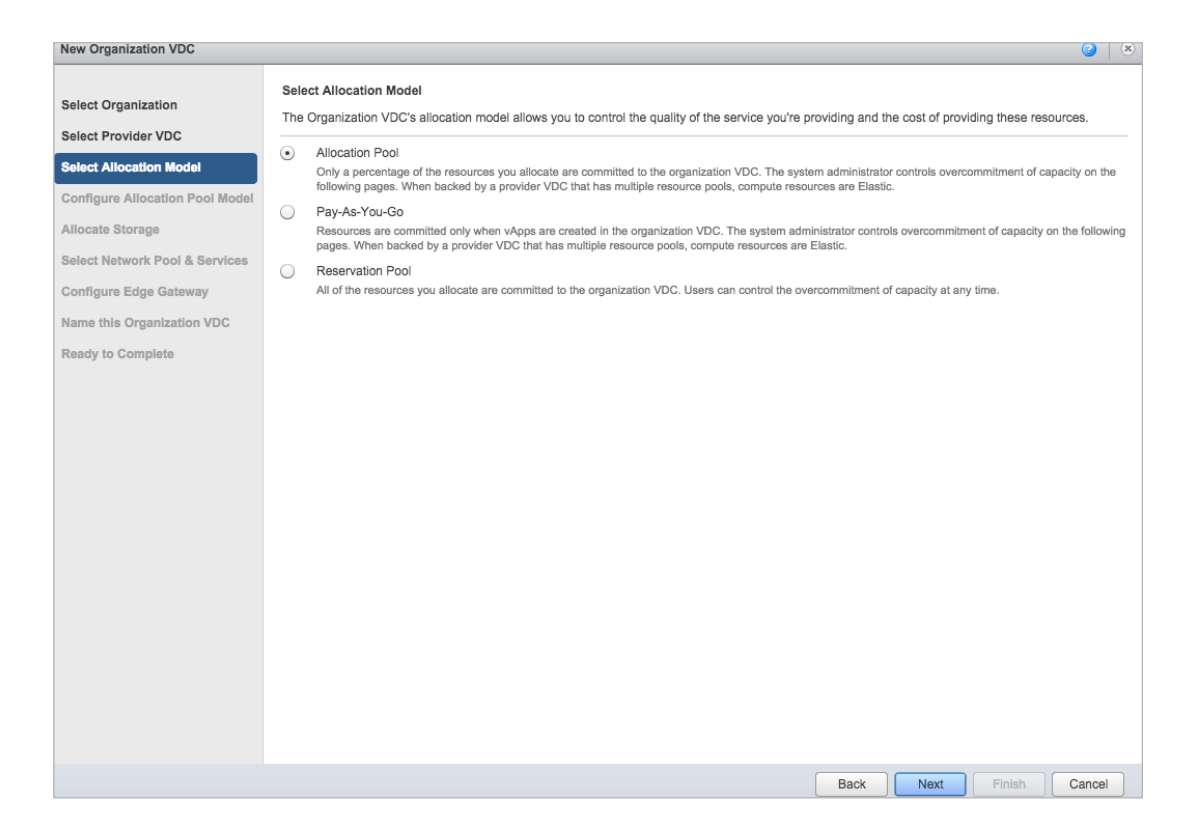
vCloud Director has three types of models with which it allocates resources for Org vDC. Org vDC is essentially mapped to a resource pool in vSphere.
- ALLOCATION POOL -% of the resource is guaranteed, and the maximum possible limit is set in the resource pool.
- PAY-AS-YOU-GO - there are no guaranteed resources and maximum limits set in the reservation pool. Resource limits are set at the virtual machine level.
- RESERVATION POOL - guaranteed resources and maximum limits are equal, all resources are allocated. No resource parameters are set at the virtual machine level, however, the user can change the restrictions and reserve resources on the virtual machine.
A client who needs a fixed set of resources can work with Org vDC with guaranteed resources, or choose PAY-AS-YOU-GO when there is no data on how much resources they will consume in the cloud. Due to the flexibility of the pool, the vDC provider can avoid the redundancy of physical data centers and reduce capital costs by adding physical hosts only as needed without interruption.
Multi-tenancy
Multi-Tenancy is one of the essential features of the IaaS cloud. VCloud Director has special modules and designs built around this basic feature. An organization in vCloud Director is a multi-tenancy unit that represents a single logical security frontier. The organization includes users, virtual data centers, and networks. vCloud Director allows service providers to create isolated containers that can be mapped to individual cloud tenants. This is done by “cutting” resources from the Provider vDC to one or more separate Org vDC for organizations.
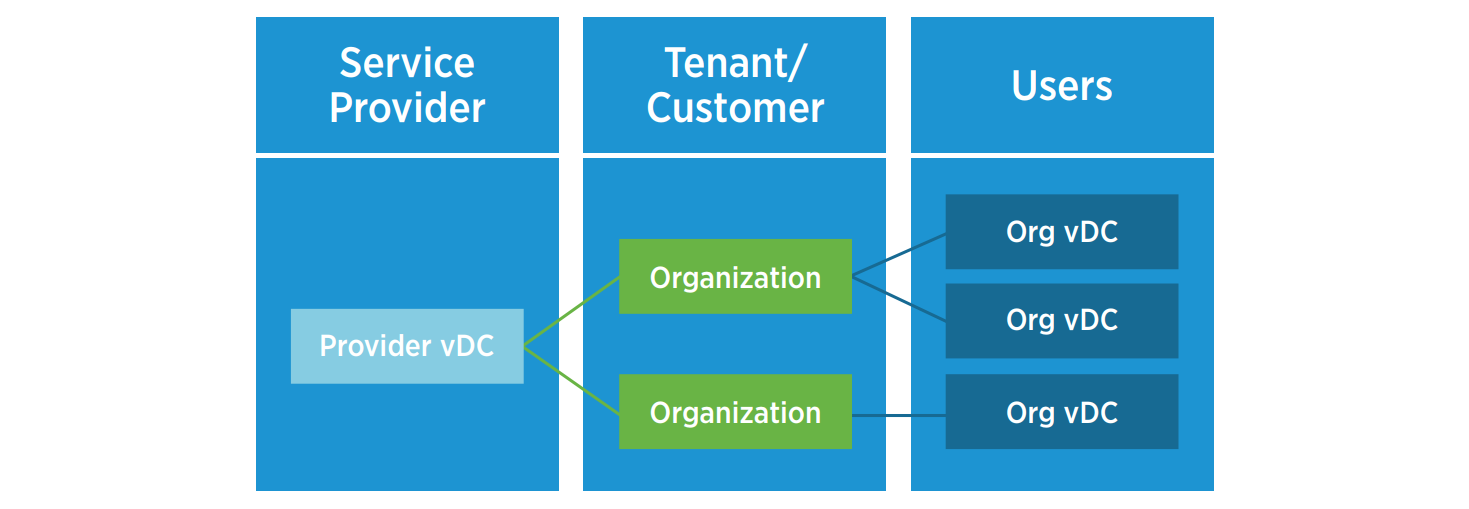
Instead of supporting individual client environments, vCloud Director provides standard methods of obtaining and providing services that help maintain a unified environment for tenants, reducing transaction costs. Standard and predefined ways of applying services to tenants help reduce the time needed to support or create conditions for tenants.
Operational efficiency is at the heart of the value proposition of VMware vCloud Director, allowing providers, for example, to improve their VM-to-admin ratio up to 3 times, as in the Zettagrid example(from one administrator on 200 virtual machines to one administrator on 600 VMs), or save $ 1.35 million and $ 250,000 in annual maintenance costs by implementing vCloud Director instead of a special solution, as happened in phoenixNAP .
Customer self service
vCloud Director offers a model that helps cloud service providers delegate some of their daily IT operations to their customers. This gives customers greater flexibility and control over the cloud. The control panel allows you to create and manage virtual machines, migrate them from another cloud, flexibly manage access rights to the pool of virtual resources, create internal routed and isolated networks, configure flexible Firewall rules, create VPN connections, configure load balancing between virtual machines and much more.
Real-time monitoring and analysis of cloud infrastructure
VMware vRealize Operations Manager and VMware vRealize Log Insight offer a single window for monitoring infrastructure status. Through it, it is possible to control the use of infrastructure, receive performance reports and run analytics. VRealize Operations connects to vSphere environments through vCenter Server and provides hierarchical information about all the components in the data center: from vCenter servers and ESXi hosts to virtual machines, storage and networks.
VRealize Log Insight collects application and system logs through Syslog and provides analytics capabilities through a visual panel. Logs help to understand the behavior and status of systems, catch problems that are missed by operational warnings.
vCloud Director has an extensive set of RESTFull APIs available through REST Clients via HTTP. To learn more, we recommend that you study the vCloud Director API Programming Guide and the vCloud Director SDK for Java / .NET / PHP Developers guide.
We hope that readers who were previously not familiar with the platform for managing the virtual infrastructure vCloud Director, got an idea of its purpose and functions. Now we would like to talk about what gives the cloud provider and its customers an update to version 8.20.
What's New in vCloud Director 8.20
Version 8.20 is a continuation of VMware’s work to transfer control of virtual infrastructure to end-users of the cloud provider. The previously released vCloud Director 8.10 release provided customers with the ability to use useful and expected functionality. For example, the vCloud Director 8.10 web console made it possible to use the granular Storage Policy management feature for individual VMs for each VM. Previously, changing storage policies was only possible through the vCloud API.
In turn, vCloud Director 8.20 now integrates more closely with VMware NSX network virtualization, which means that end users can create any network topology on their own in a few seconds - from simple to multi-level using the new HTML5 interface.
Like virtual machines in computing environments, virtual networks are initialized programmatically and operate independently of the underlying hardware. VMware NSX reproduces the network model at the software level. NSX Networking is a library of logical network elements and services such as logical switches, routers, firewalls, load balancers, VPNs, and security.
NSX Advanced Networking
- Dynamic Routing - Added Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) algorithms to automatically create dynamic routing tables between VMware NSX Edge gateways.
- Distributed firewall. The ability to manage granular security policies, including firewall rules for traffic passing inside Org vDC.
- Tenant layer 2 (L2) VPN access to support hybrid clouds. Allows tenants to create a tunnel between the networks in Org VDC and the local network at their facility, creating a seamless, seamless network.
- Tenant SSL VPN - remote access through a browser, in addition to IPSec and L2-VPN.
- Load balancing - dynamic distribution of incoming traffic to maintain SLA.
Configuring NSX Advanced Features

Right-click on the NSX Edge gateway and select “Convert to Advanced Gateway”. This action will upgrade NSX Edge to a higher version of the software if version 5.5 or earlier was used and enable a new HTML5 user interface to configure advanced NSX features.
Dynamic Routing vCloud Director 8.20 adds support for configuring dynamic routing between different NSX Edge gateways. Previously, there was only support for static routes between different vApp networks connected to the same or different organization vDC network.
Dynamic routing reduces the need to manually configure routes when a virtual machine (VM) in an Org vDC network needs to “talk” to another virtual machine in a different organization vDC network. This reduces the overall time that organization administrators spend maintaining network routing tables.
vCloud Director 8.20 provides the tenant with the ability to configure distributed firewall rules in Org vDC. Firewall rules determine how traffic flows between virtual machines on an Org vDC network. In previous versions of vCloud Director, you could configure a firewall to control the flow of traffic between your organization’s external and routed vDC networks, also known as north-south traffic. But there was essentially no possibility to define rules for traffic between virtual machines within one or several networks inside Org vDC (east-west traffic).
Now you can create rules using individual IP or MAC addresses, or a predefined set of IP / MAC addresses. You can apply the rules to individual ports or choose from a predefined list of services (for example, SNMP, ICMP, HTTP, etc.). or groups (e.g. Microsoft Exchange, Oracle, etc.).
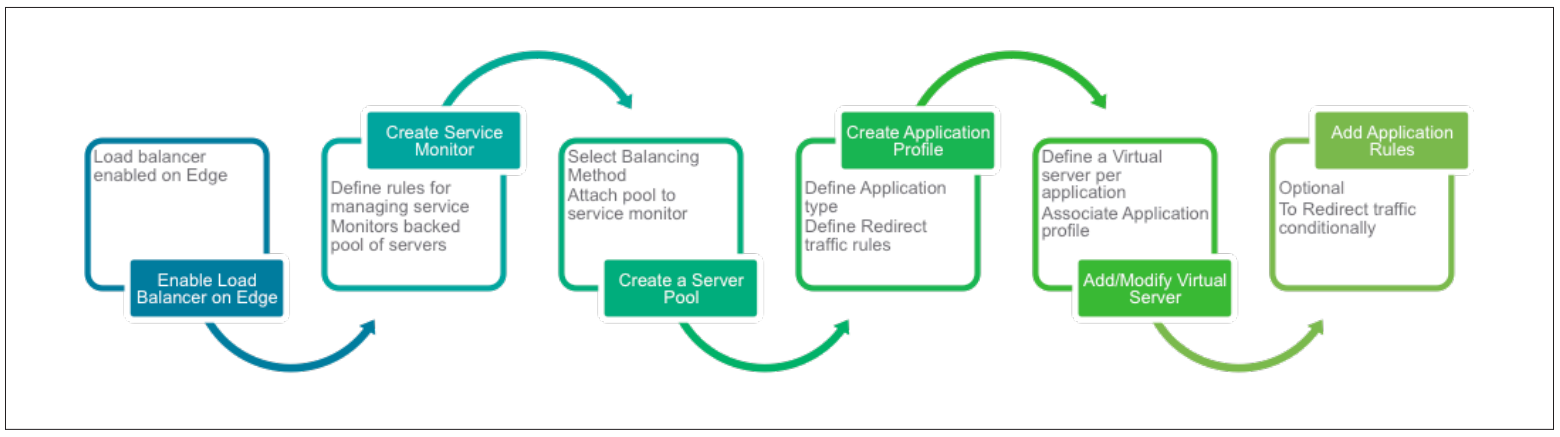
NSX Edge load balancer now allows you to evenly distribute incoming traffic to the vDC server pool with the IP addresses of virtual machines that will distribute the load of incoming traffic.

The general process for setting load balancing on the NSX Edge gateway.
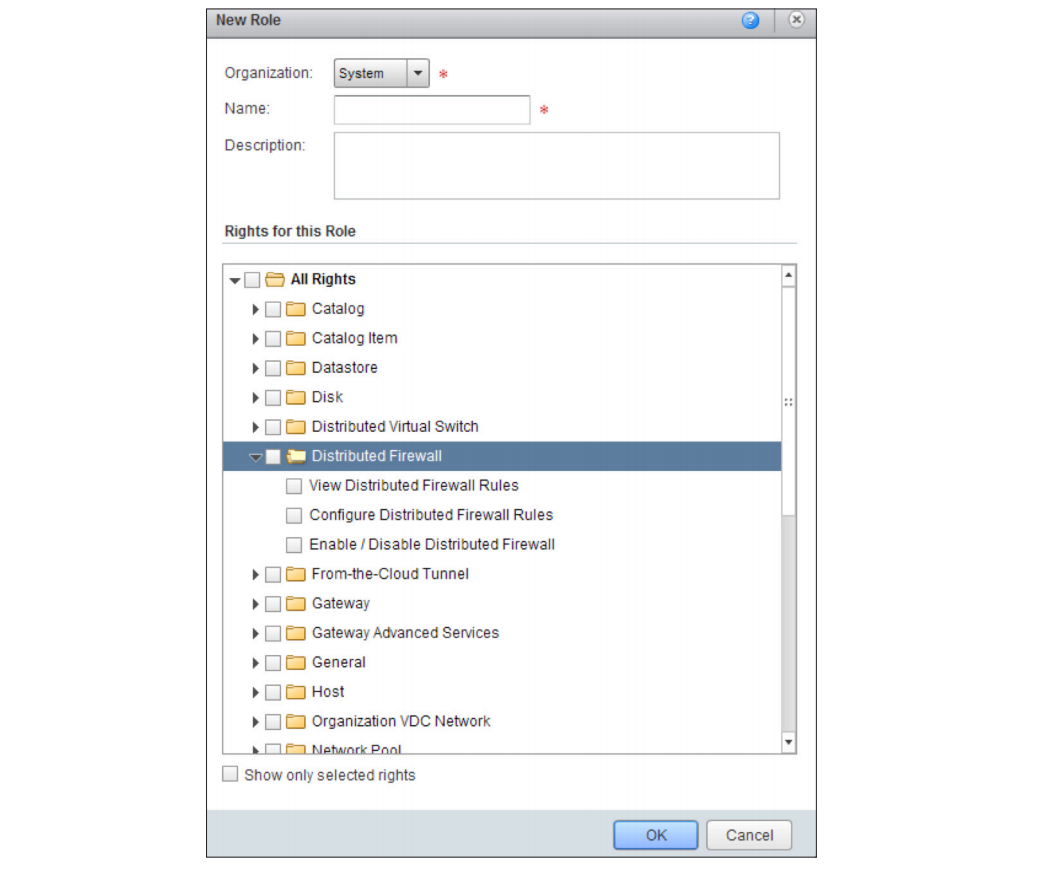
Role-based user access control for service provider and tenants
VCloud Director 8.20 allows you to create custom roles for tenants. You can define roles based on functional tasks and subtasks in vCloud Director.
VM to ESXi Host Affinity Rules
The rules for linking virtual machines to a group of ESXi hosts ensure that virtual machines defined in a set of rules are hosted on a specific set of hosts.
When used by the VMware vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) provider, an algorithm is used to select the appropriate ESXi host for the virtual machine to distribute the load evenly. However, there are scenarios in which you need to host a virtual machine in Org vDC on a specific host that is not recommended by DRS. For example, delay-sensitive applications or applications with licensing requirements that must be hosted on the same host. For such cases, VM-Host Affinity Rules apply.
Among the new features it is worth noting
- automatic discovery and import of virtual machines;
- Multi-Cell Upgrade update utility now supports updating all cells in a server group with a single operation;
- utility for migrating vCDNI networks to VXLAN;
- Support for Windows Server 2016 and Virtual Hardware 13.
You can familiarize yourself with the full range of new features of the vCloud Director control panel using the free test access to the Cloud4Y cloud for legal entities. As they say, it is better to see once than hear a hundred times.
To summarize
With this release, the vCloud Director UI has begun moving from the current Flex-based technology to an HTML5-based interface. All NSX network services have been ported to the new interface, while the rest of the user interface elements are still based on Flex.
VMware vCloud Director 8.20 is packed with new features that will help increase the security and convenience of managing virtual resources, consolidating the trend for a hybrid cloud infrastructure and delegating management capabilities from provider to client.
