How fiber networks are built
Hello! My name is Dmitry, I am engaged in the design and construction of fiber-optic communication lines (FOCL) in the DataLine. Today I will tell you how we create optical paths for our clients and how we eliminate accidents.
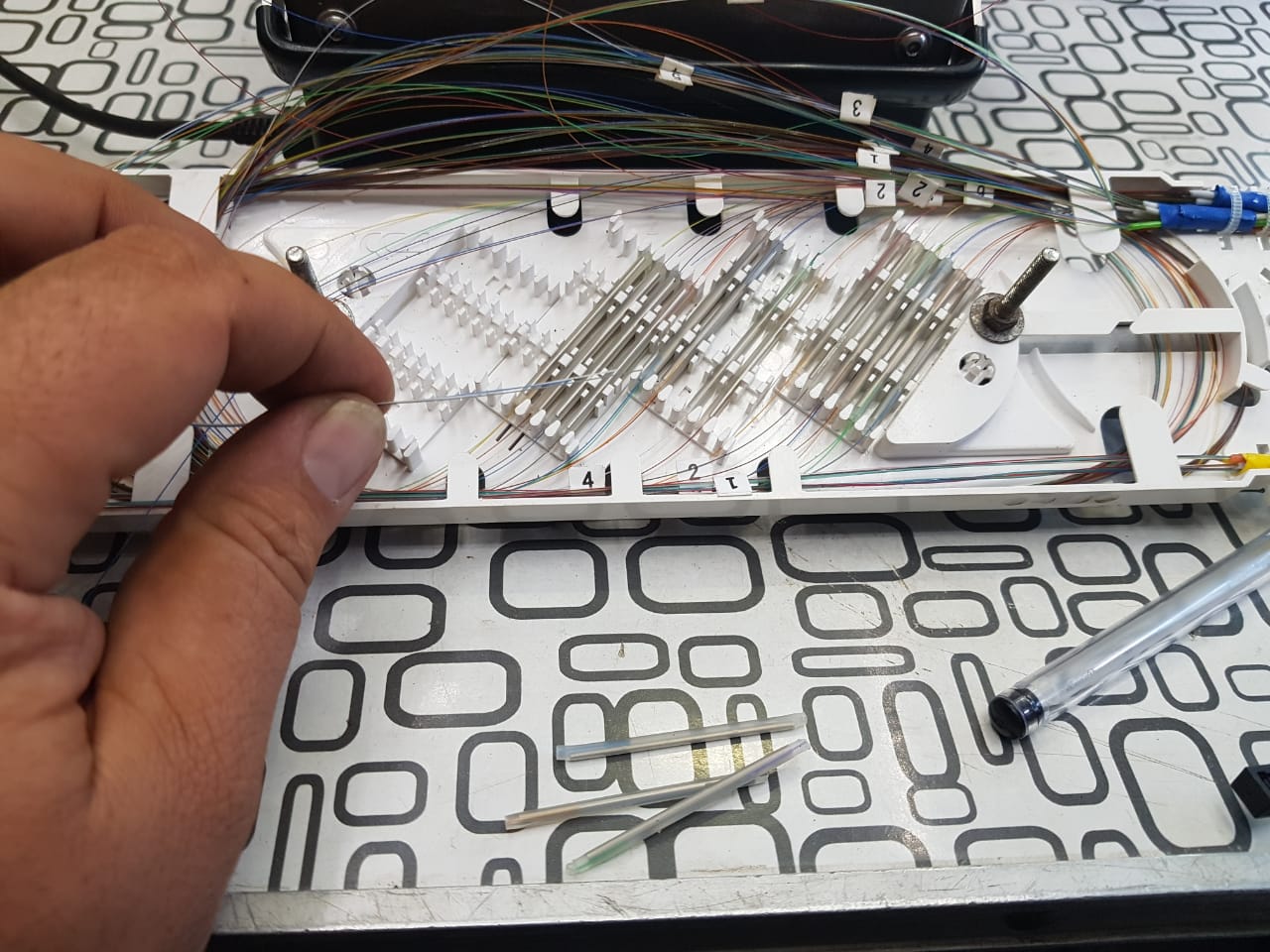
The installer lays the fibers of two cables in an optical coupling.
When I joined the company in 2016, the backbone network, or "trunk", of 144 fibers was already built. It combined our communication nodes (OST data center, NORD data center) with MMTS-9 and MMTS-10 into a single ring. The length of the core network at that time was about 210 km. It was also built about 21 km of the so-called "last miles" - branches from the core network, connecting the remote platform of the client with our nearest communication center. At that time, the company did not have dedicated fiber optic specialists; contractors did everything under the supervision of the network department.
Now we are not building “highways”, as there is still enough available capacity. All my projects are the completion of the tracks from our backbone network to the clients' offices. When I built 70 km of such tracks. The length of the entire network today is 301 km.
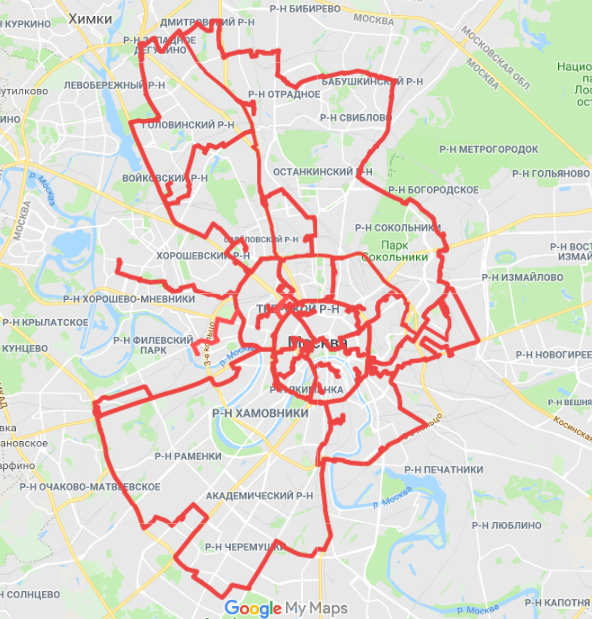
The scheme of the DataLine fiber-optic network transmission for December 2018.
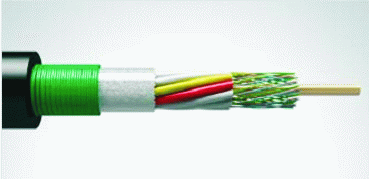
This is an OKKM cable (OK - optical cable, K - sewage, M - multi-module construction) produced by Fujikur. We use it in our projects.
We run optical cables in telephone conduits, sewers, tunnels and bridges. Independently build sewers only in those cases when there is no suitable infrastructure near the route of the future route. Otherwise, it’s like building a separate road from home to work — long and expensive.
In the view of many collectors and telephone sewer about the same thing, but it is not. Not only communication cables are placed in the collectors. There are various engineering communications: heating network, gas pipeline, power cables. Some collectors are so large that a truck can easily pass through them.
Telephone sewage is simply a pipeline buried in the ground with cables. You can look into it only through viewing devices - telephone wells. They are different, but more often they do not turn around. Sometimes it is just a box with a depth of 20 cm. As an exception, I saw several wells across Moscow the size of a three-room apartment.

Inspection well telephone sewage.
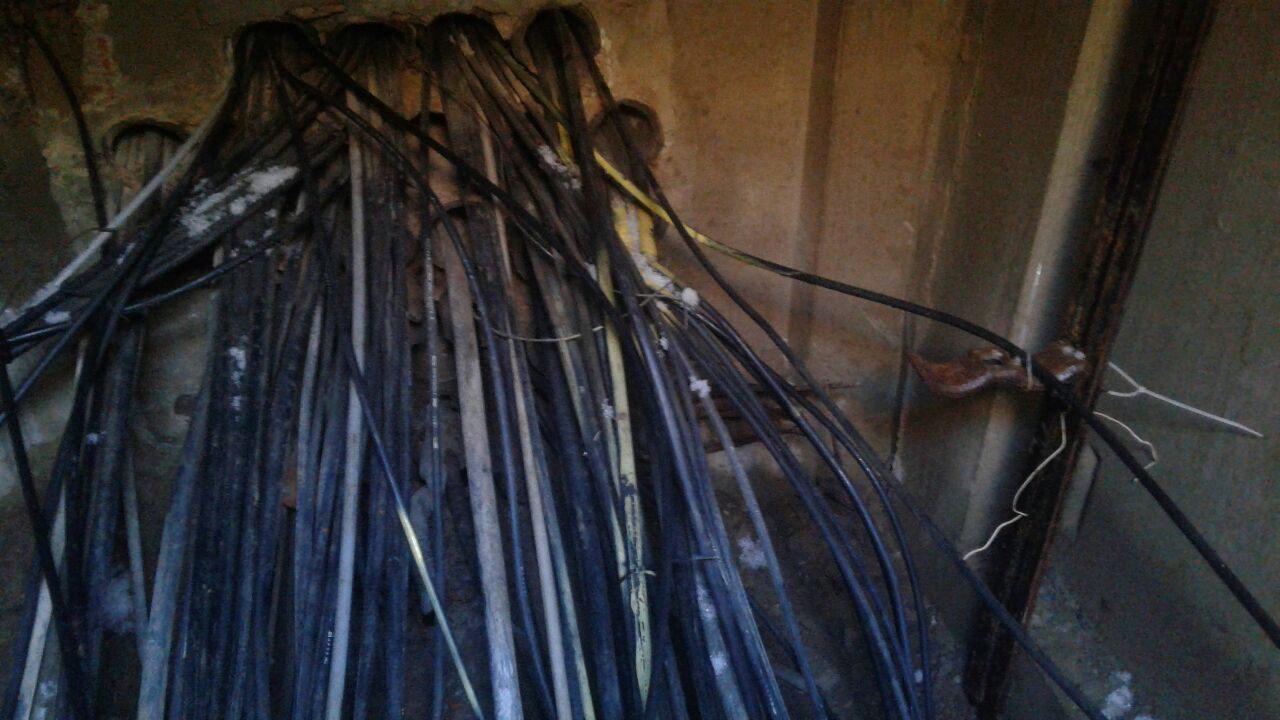

Here is a view of the viewing well. The cables just go to the channels in the wall.
Typically, for our customers, we build two fiber-optic routes that run independent routes to our data center. This is necessary for reserve, in case of damage or complete break of the main cable. Here, many will immediately recall instructive stories about the excavator and they will be right. Fresh: during the work on the program “My street”, one of our clients was “lucky” with an excavator 4 times in 3 months. It is good that he had a backup route that did not intersect with the main route, and his service did not stand idle while we were restoring the affected route.
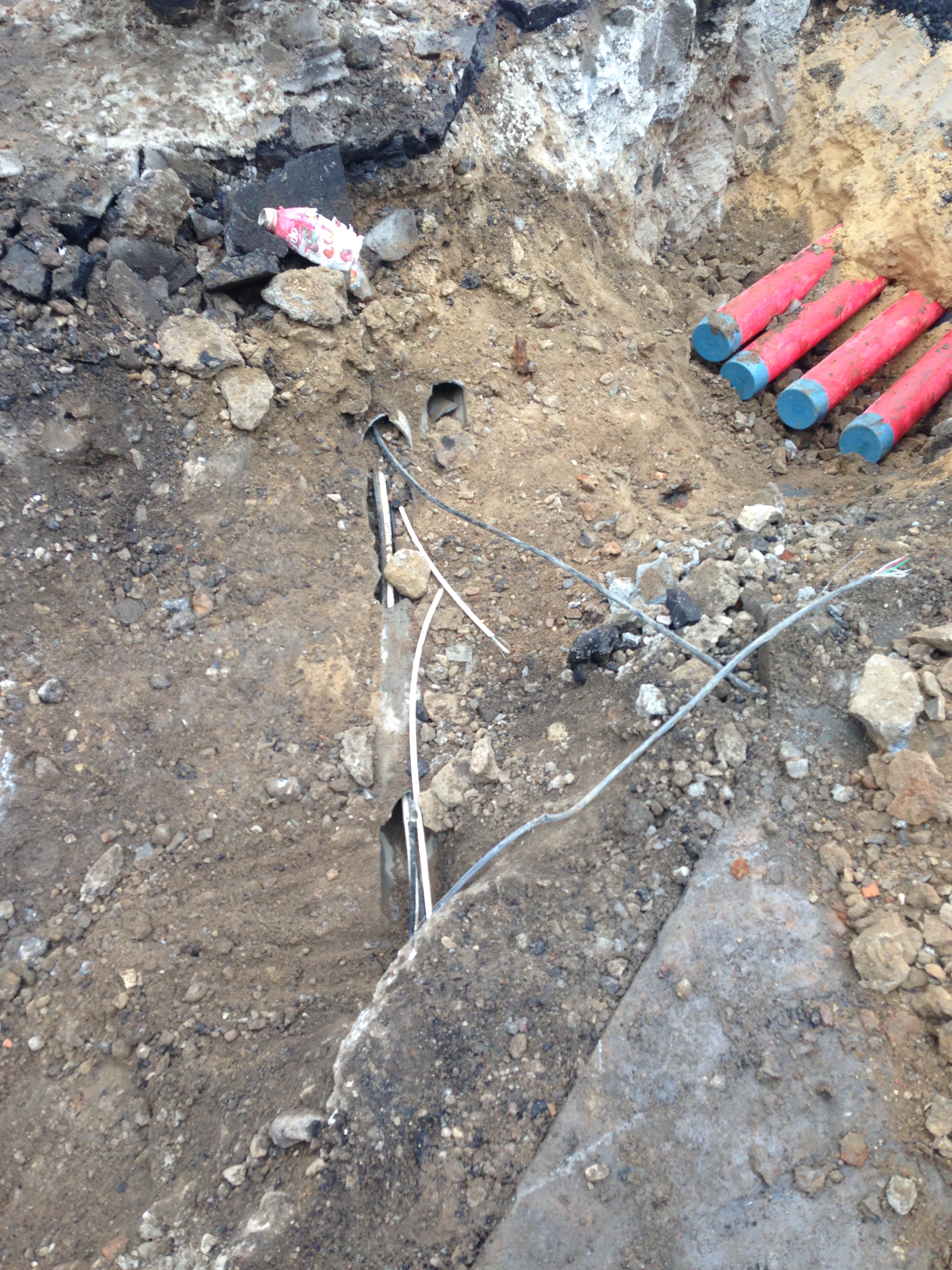

Small bucket movement is a big problem for the provider. Cable breaks in telephone conduit.
Most customers understand the importance of the reserve and immediately ask us to work out two separated routes to their site. Or they order a route from us that will be backed up in addition to the main one from another provider.
For example, a client wants to bring fiber from our NORD data center to his office.
Based on sketches of linear cable structures, I determine the approximate route of the future route. I calculate the distance of completion from the client’s office to our network and choose a place to accommodate couplings. Along the way, I collect information about the object in which the client's office is located: whether there are linear cable facilities on the way of the future route, who owns them. This information will be needed when agreeing on a working draft.
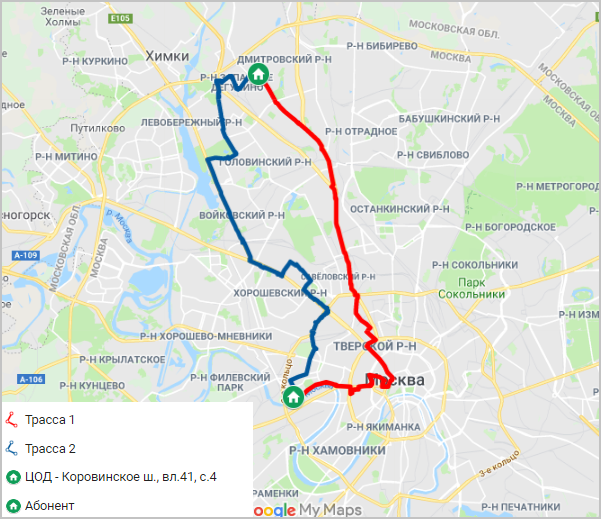
The route of the optical routes from the NORD data center to the client's office.
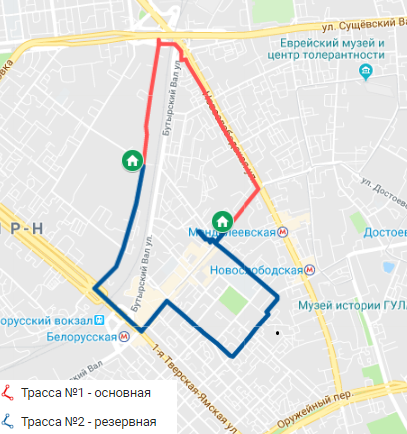
In this project we connected two client offices.
With these initial data, I am counting on a budget for organizing a new communication line. It will include our one-time costs for obtaining technical conditions from the owners of linear cable structures (Moskollektor, MGTS) and agreeing on a working draft with them, design and survey work on the linear part, construction and installation work on cable laying, the cost of materials used, and also our monthly rental fees for line-cable facilities. According to the market, design and turnkey construction of a 1 km fiber optic route with a capacity of up to 32 fibers will now cost an average of 200 thousand rubles.
The standard construction period is 45 calendar days, but sometimes it works faster. This is an official term with the registration of all necessary documentation, and there is a lot of it. We are preparing a large package of documents for MGTS, Moskollektora, draw up a technical task for contractors. Based on our requirements, they make a working draft of the linear part - the section of the road that goes through the city to the building of the client. Contractors know how everything works under the ground in Moscow, and have all the necessary certificates, a license from the FSB, and admissions to work related to the hotel room.
We independently do the working draft of laying of a cable on the building and we coordinate it with the owner. In this document, we describe how the entry into the building, the laying of the cable through the building to the destination (server or office) and the installation of the optical cross will be organized.

An example of the layout of the optical cable inside the building.
As soon as all projects are agreed, the long-awaited construction begins. In the existing fiber optic network embed a new cable that will be laid to the building of the client. Below are some working photos.
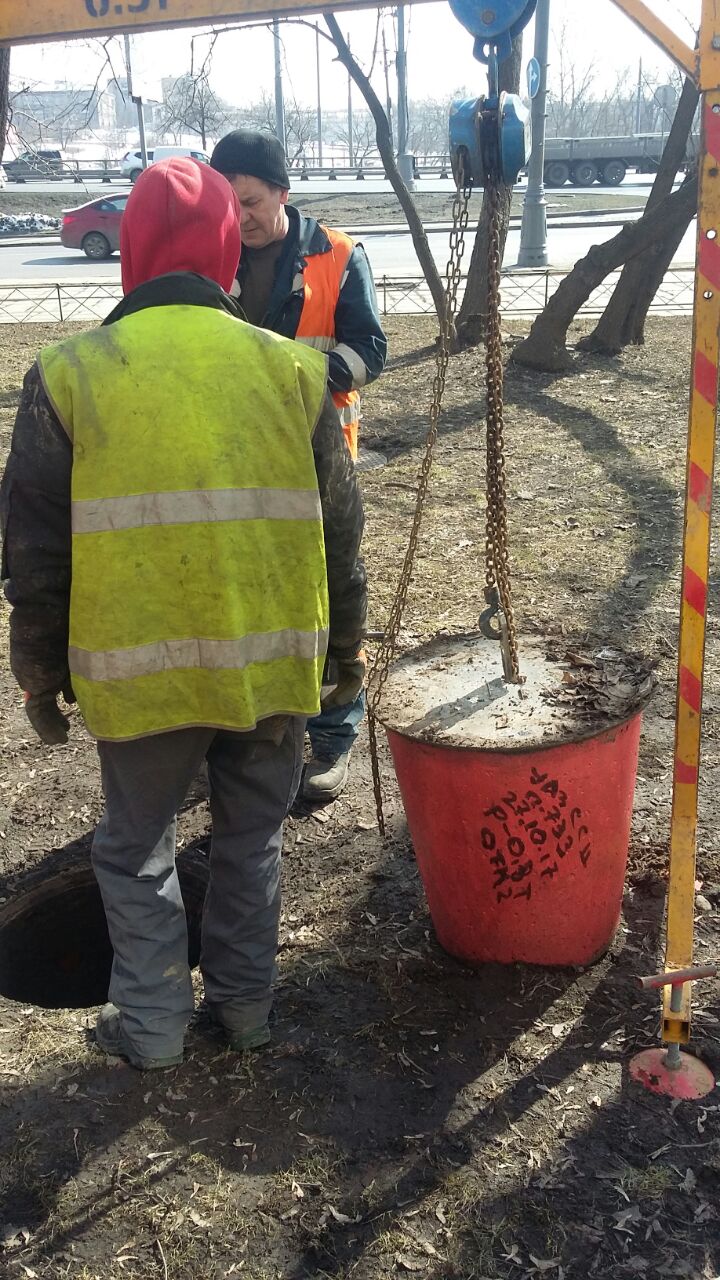

Sometimes telephone wells are equipped with anti-vandal devices (plugs). We have to spend time opening them with a special lift.

Installers are pulling a new cable.
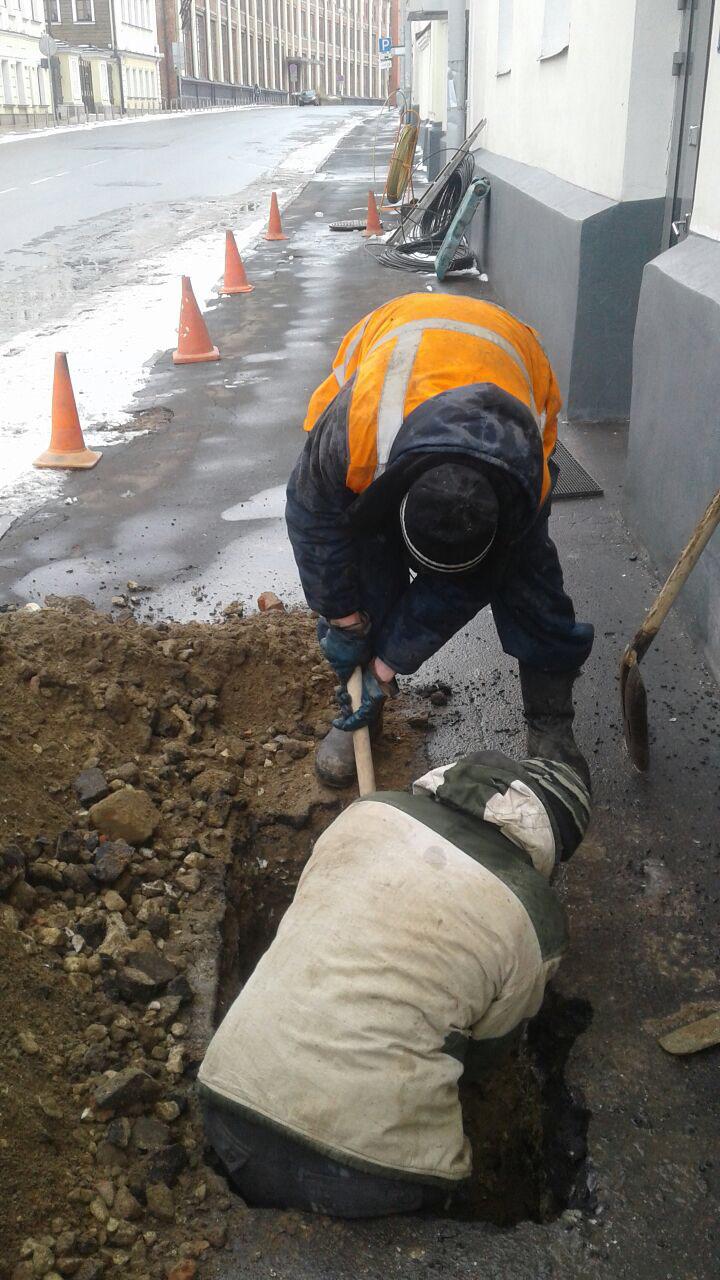

At the very approach to the client’s building, an impassable area appeared: a fracture was detected in the channel, and the cable could not be pushed out of the viewing well. It was necessary to remove the pavement and open the ground.

On the table is an optical coupling. There is a preparation of installation of a new cable to the trunk.
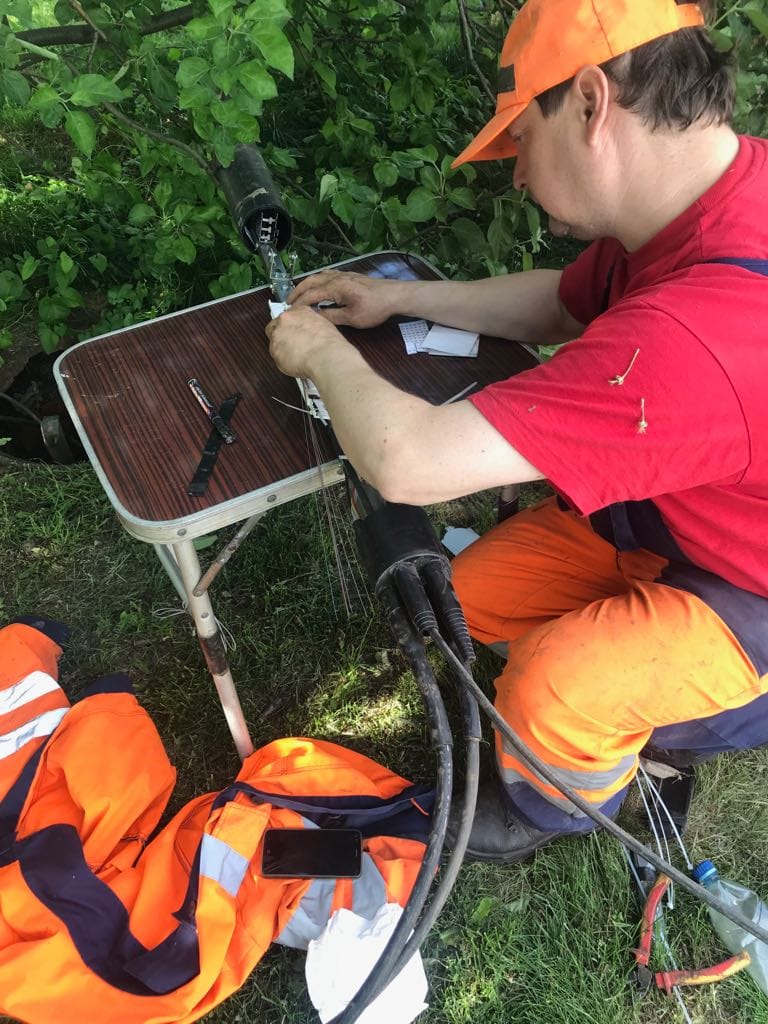

Insert new cable into the trunk.
For installers-solders, we prepare the execution schemes. According to them, experts recognize the necessary fibers in the trunk cables and weld them with the fibers of the new cable. Then the welded fibers are laid in the optical coupling.
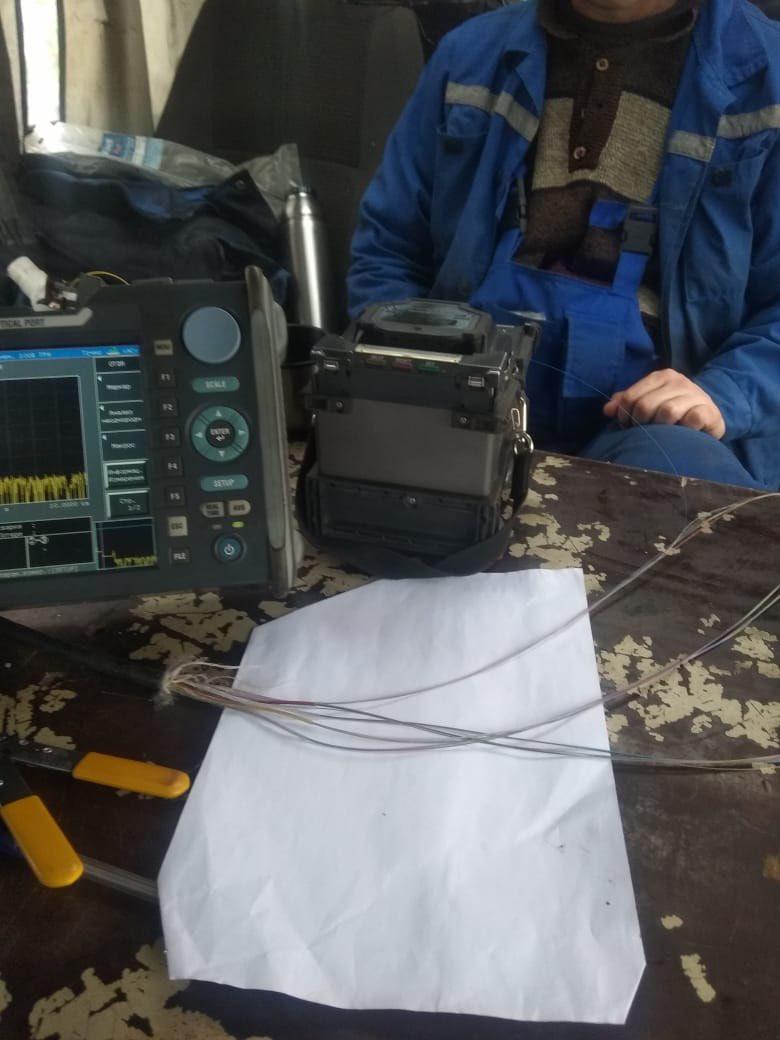

The photo is a cable cut. If you look closely, you can see the fiber that enters the welding machine.
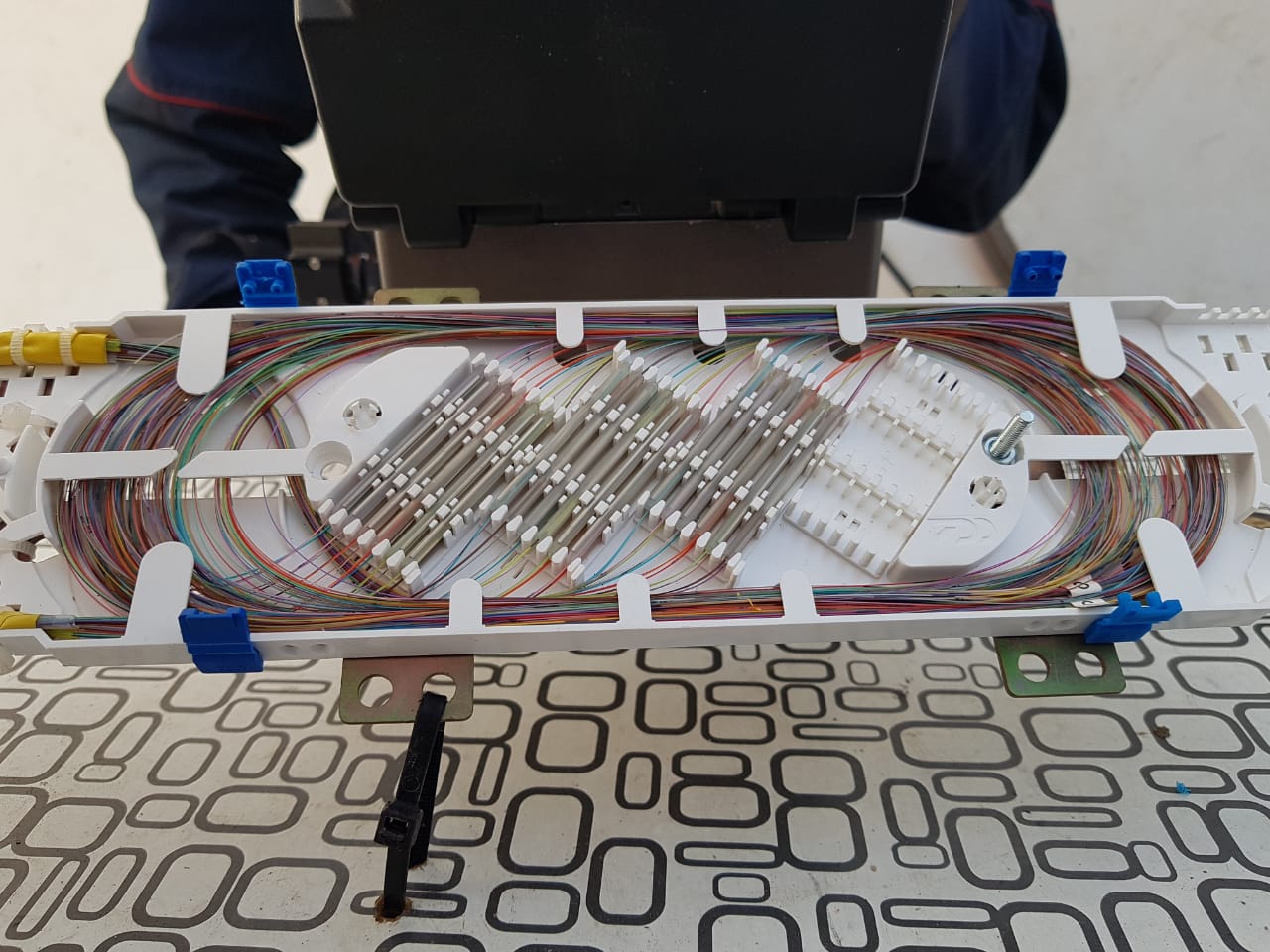
Optical coupling with connected fibers of two cables.

So the optical cable comes into the building.
When the cable is laid to the building, an optical cross is mounted on its end, which is mounted in a rack or on a wall.
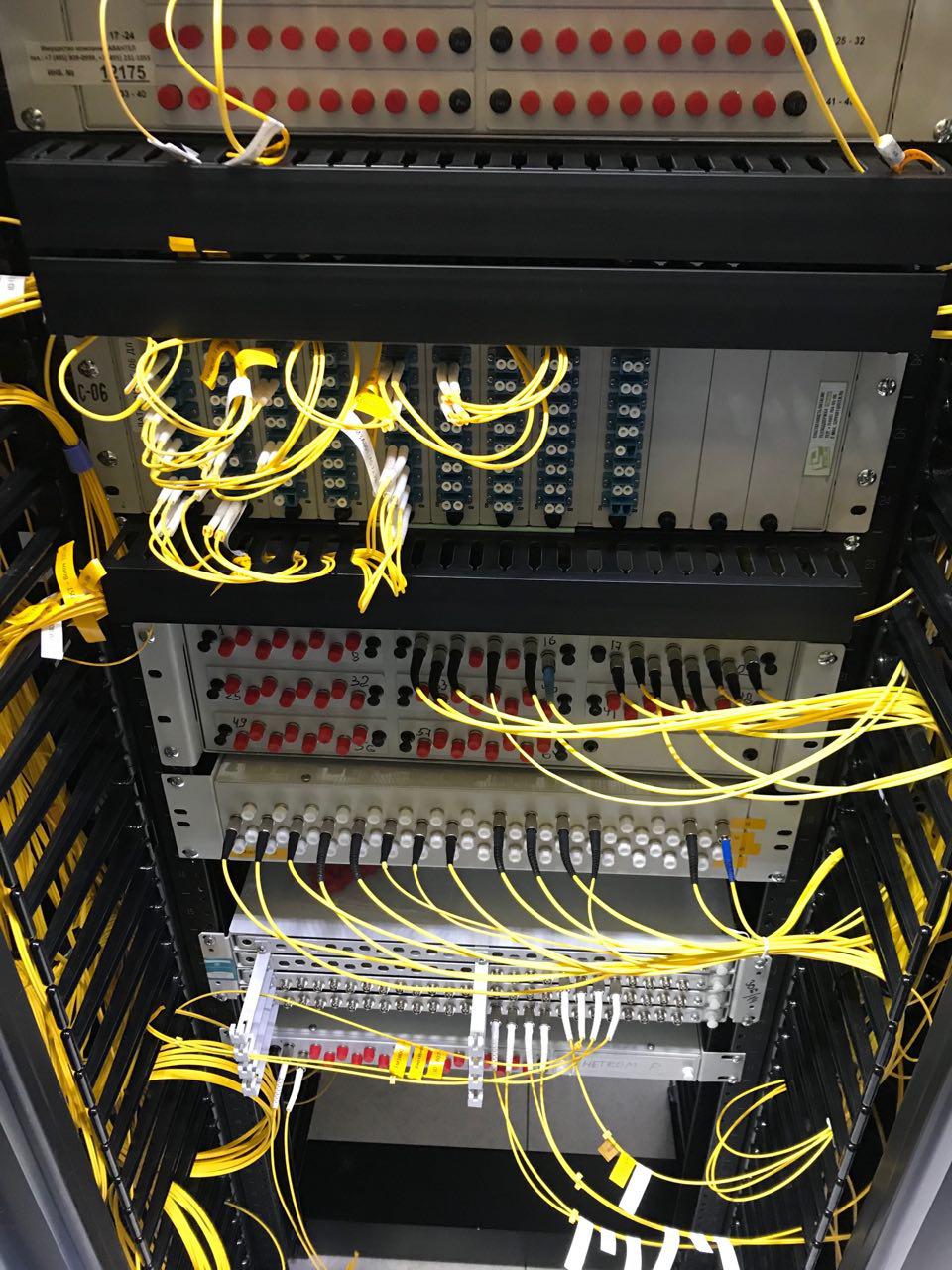

Optical cross in Meet-Me-Room OST data center.
Further, in parallel with the contractor, we are testing a new route: we are measuring the cable with the method of pulse reflectometry. The readings are taken from the optical cross with a reflectometer. The values below indicate that everything works. They are recorded in the SLA with the client:
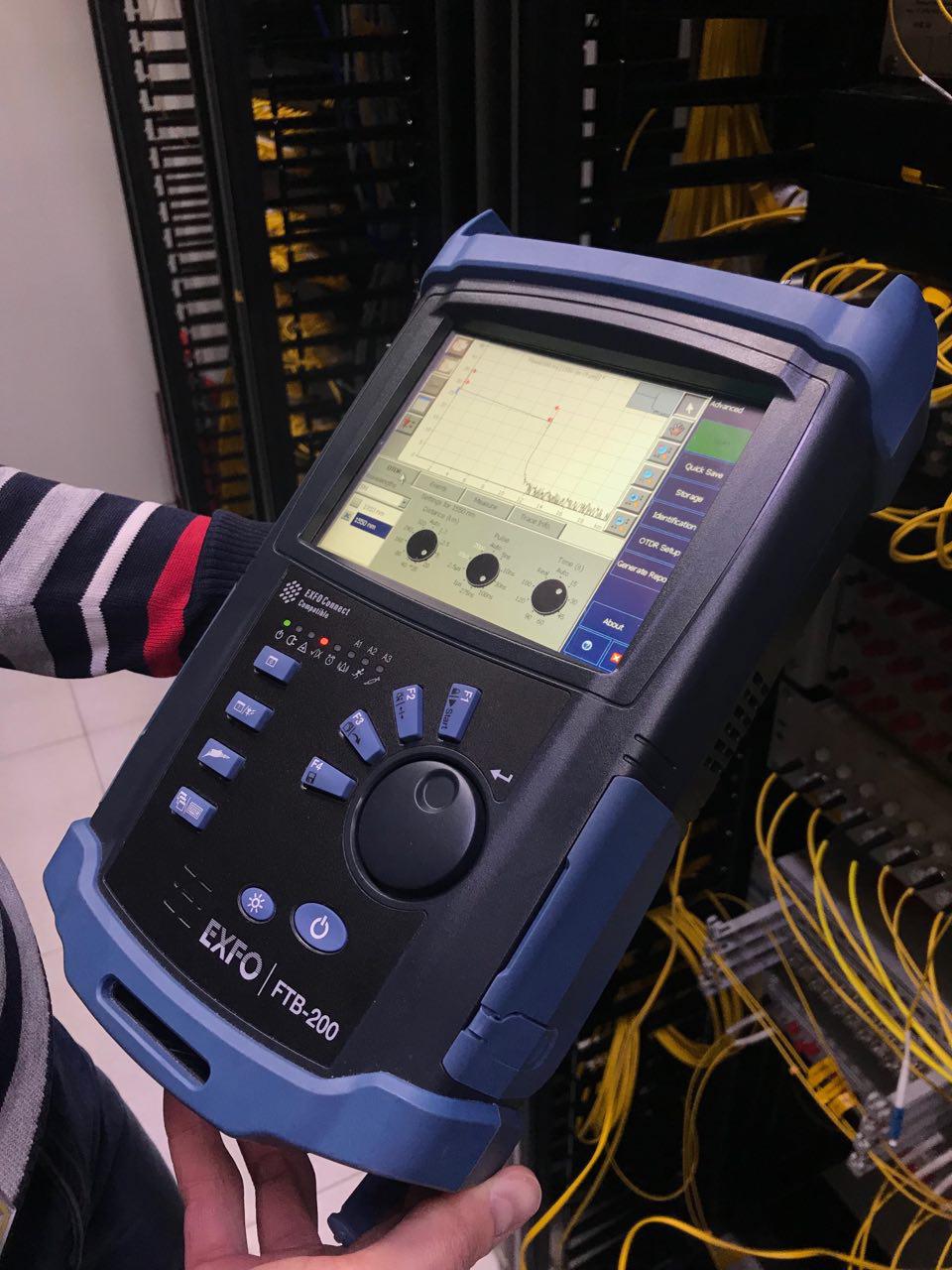

OTDR
If all the readings are normal, the route is taken into service and transferred to operation. The client only needs to connect to the correct port.
We notify our customers about all planned work. Even if this is just a tie-in of a new cable, the client will receive a letter with the contacts of the shift shift, account managers and a situational plan with marked areas where the work will take place. With such work goes all the regular, but there are also funny cases. Somehow after a few minutes from the start of work in the coupling, located not far from Red Square, a car with an EKH number approached the installers. From there came people in suits and with weapons. Having checked the availability of work permits for installers, they politely asked me to work carefully in this place. So they stood until the work was completed. Apparently, there was one of those “Kremlin” cables in the well and the alarm went off.
When an accident occurs, it is not always immediately clear where the damage is. Together with the engineers, we conduct control measurements using a reflectometer at the optical cross-over in our data centers in order to determine the intended place of the accident. While the emergency crew is going, I have time to orient them where to go, and I myself leave for the place of the cliff.
At the same time, we compile a list of clients whose services were disrupted during an accident, and colleagues from related departments notify clients. Our department switches customers to backup channels - customer and our own (to free fibers) - if the customer does not have a reserve. If necessary, draw new crossings and start switching.
The last major accident occurred due to a fire in the Novo-Dorogomilovsky collector. All providers were allowed to work only after 5 days, because at first they restored all city communications and special purpose communications. Everyone who did not have a reserve, had to wait (once again to the question of the reserve :)). But such cases are more likely an exception, and usually we restore the operability of the services promptly, for large-scale accidents - this is 8 hours maximum.
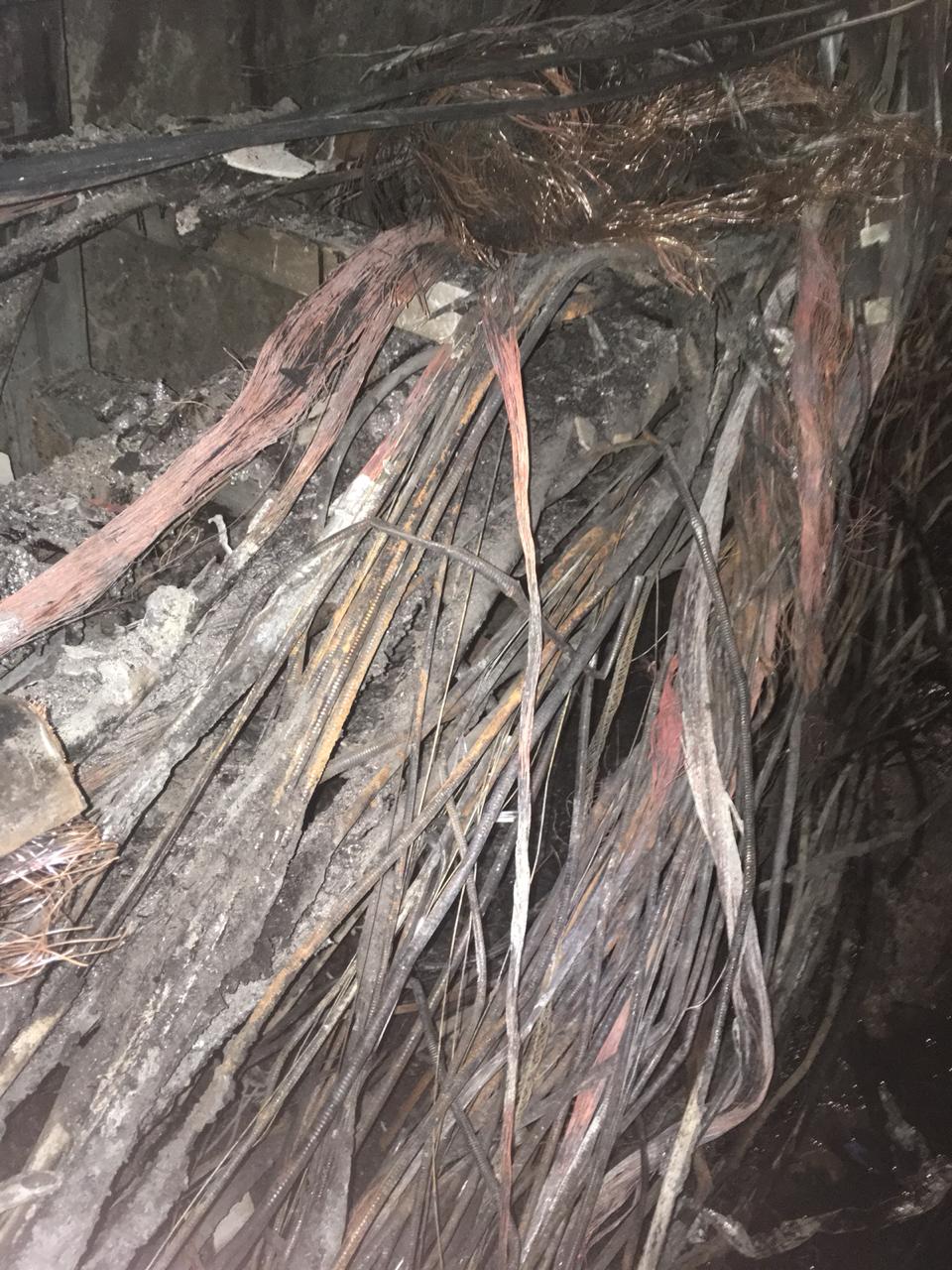

This is what burned cables look like. The consequences of a fire in the Novo-Dorogomilovsky collector.
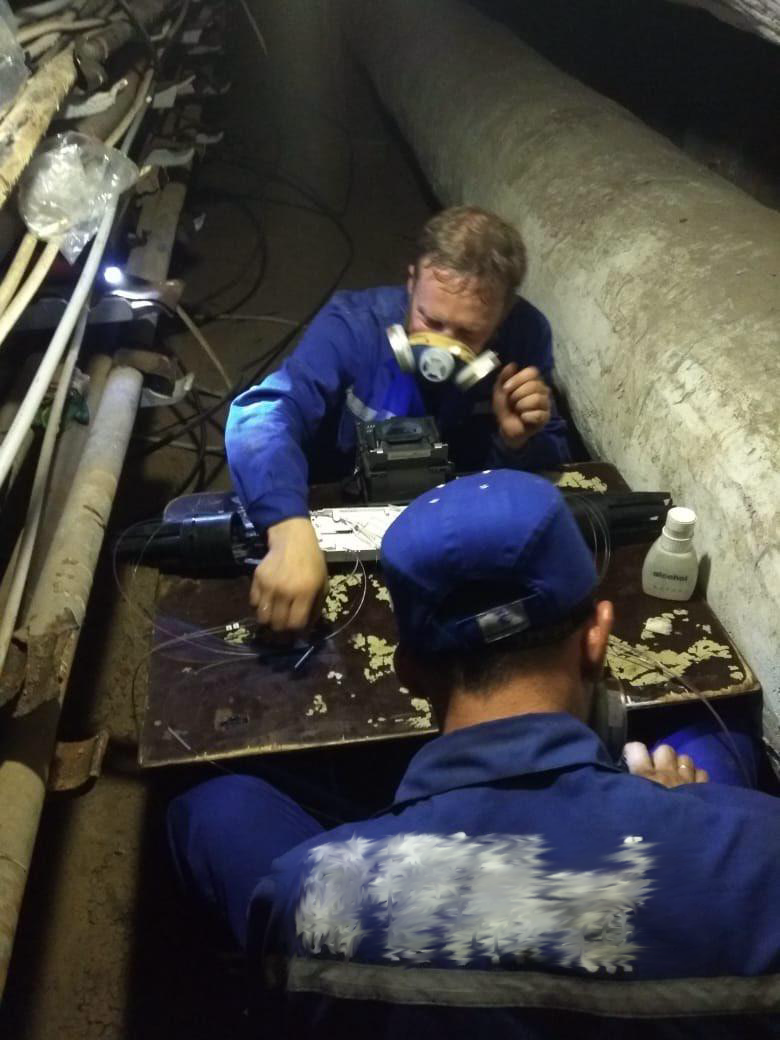

Recovery work in the same collector. Installers make cable insert for damaged cable. The smell of burning after the fire is still very strong, so they work in respirators.

The installer lays the fibers of two cables in an optical coupling.
When I joined the company in 2016, the backbone network, or "trunk", of 144 fibers was already built. It combined our communication nodes (OST data center, NORD data center) with MMTS-9 and MMTS-10 into a single ring. The length of the core network at that time was about 210 km. It was also built about 21 km of the so-called "last miles" - branches from the core network, connecting the remote platform of the client with our nearest communication center. At that time, the company did not have dedicated fiber optic specialists; contractors did everything under the supervision of the network department.
Now we are not building “highways”, as there is still enough available capacity. All my projects are the completion of the tracks from our backbone network to the clients' offices. When I built 70 km of such tracks. The length of the entire network today is 301 km.

The scheme of the DataLine fiber-optic network transmission for December 2018.

This is an OKKM cable (OK - optical cable, K - sewage, M - multi-module construction) produced by Fujikur. We use it in our projects.
We run optical cables in telephone conduits, sewers, tunnels and bridges. Independently build sewers only in those cases when there is no suitable infrastructure near the route of the future route. Otherwise, it’s like building a separate road from home to work — long and expensive.
In the view of many collectors and telephone sewer about the same thing, but it is not. Not only communication cables are placed in the collectors. There are various engineering communications: heating network, gas pipeline, power cables. Some collectors are so large that a truck can easily pass through them.
Telephone sewage is simply a pipeline buried in the ground with cables. You can look into it only through viewing devices - telephone wells. They are different, but more often they do not turn around. Sometimes it is just a box with a depth of 20 cm. As an exception, I saw several wells across Moscow the size of a three-room apartment.

Inspection well telephone sewage.

Here is a view of the viewing well. The cables just go to the channels in the wall.
Typically, for our customers, we build two fiber-optic routes that run independent routes to our data center. This is necessary for reserve, in case of damage or complete break of the main cable. Here, many will immediately recall instructive stories about the excavator and they will be right. Fresh: during the work on the program “My street”, one of our clients was “lucky” with an excavator 4 times in 3 months. It is good that he had a backup route that did not intersect with the main route, and his service did not stand idle while we were restoring the affected route.

Small bucket movement is a big problem for the provider. Cable breaks in telephone conduit.
Most customers understand the importance of the reserve and immediately ask us to work out two separated routes to their site. Or they order a route from us that will be backed up in addition to the main one from another provider.
About the process
For example, a client wants to bring fiber from our NORD data center to his office.
Based on sketches of linear cable structures, I determine the approximate route of the future route. I calculate the distance of completion from the client’s office to our network and choose a place to accommodate couplings. Along the way, I collect information about the object in which the client's office is located: whether there are linear cable facilities on the way of the future route, who owns them. This information will be needed when agreeing on a working draft.

The route of the optical routes from the NORD data center to the client's office.

In this project we connected two client offices.
With these initial data, I am counting on a budget for organizing a new communication line. It will include our one-time costs for obtaining technical conditions from the owners of linear cable structures (Moskollektor, MGTS) and agreeing on a working draft with them, design and survey work on the linear part, construction and installation work on cable laying, the cost of materials used, and also our monthly rental fees for line-cable facilities. According to the market, design and turnkey construction of a 1 km fiber optic route with a capacity of up to 32 fibers will now cost an average of 200 thousand rubles.
The standard construction period is 45 calendar days, but sometimes it works faster. This is an official term with the registration of all necessary documentation, and there is a lot of it. We are preparing a large package of documents for MGTS, Moskollektora, draw up a technical task for contractors. Based on our requirements, they make a working draft of the linear part - the section of the road that goes through the city to the building of the client. Contractors know how everything works under the ground in Moscow, and have all the necessary certificates, a license from the FSB, and admissions to work related to the hotel room.
We independently do the working draft of laying of a cable on the building and we coordinate it with the owner. In this document, we describe how the entry into the building, the laying of the cable through the building to the destination (server or office) and the installation of the optical cross will be organized.

An example of the layout of the optical cable inside the building.
As soon as all projects are agreed, the long-awaited construction begins. In the existing fiber optic network embed a new cable that will be laid to the building of the client. Below are some working photos.

Sometimes telephone wells are equipped with anti-vandal devices (plugs). We have to spend time opening them with a special lift.

Installers are pulling a new cable.

At the very approach to the client’s building, an impassable area appeared: a fracture was detected in the channel, and the cable could not be pushed out of the viewing well. It was necessary to remove the pavement and open the ground.

On the table is an optical coupling. There is a preparation of installation of a new cable to the trunk.

Insert new cable into the trunk.
For installers-solders, we prepare the execution schemes. According to them, experts recognize the necessary fibers in the trunk cables and weld them with the fibers of the new cable. Then the welded fibers are laid in the optical coupling.

The photo is a cable cut. If you look closely, you can see the fiber that enters the welding machine.

Optical coupling with connected fibers of two cables.

So the optical cable comes into the building.
When the cable is laid to the building, an optical cross is mounted on its end, which is mounted in a rack or on a wall.

Optical cross in Meet-Me-Room OST data center.
Further, in parallel with the contractor, we are testing a new route: we are measuring the cable with the method of pulse reflectometry. The readings are taken from the optical cross with a reflectometer. The values below indicate that everything works. They are recorded in the SLA with the client:
| ≤ 0.2 dB maximum loss on one-piece connections (welding) with bidirectional averaged measurement. ≤ 0.5 dB optical signal attenuation at wavelengths of 1310 and 1550 nm at the points of detachable connection (transit) of optical fibers. ≤ 40 dB reflectance per event. ≥ 29 dB Optical Return Loss (ORL) value at the measurement site. |

OTDR
If all the readings are normal, the route is taken into service and transferred to operation. The client only needs to connect to the correct port.
Polite people, fires in the sewers: how the work goes and the accidents on roads are eliminated
We notify our customers about all planned work. Even if this is just a tie-in of a new cable, the client will receive a letter with the contacts of the shift shift, account managers and a situational plan with marked areas where the work will take place. With such work goes all the regular, but there are also funny cases. Somehow after a few minutes from the start of work in the coupling, located not far from Red Square, a car with an EKH number approached the installers. From there came people in suits and with weapons. Having checked the availability of work permits for installers, they politely asked me to work carefully in this place. So they stood until the work was completed. Apparently, there was one of those “Kremlin” cables in the well and the alarm went off.
When an accident occurs, it is not always immediately clear where the damage is. Together with the engineers, we conduct control measurements using a reflectometer at the optical cross-over in our data centers in order to determine the intended place of the accident. While the emergency crew is going, I have time to orient them where to go, and I myself leave for the place of the cliff.
At the same time, we compile a list of clients whose services were disrupted during an accident, and colleagues from related departments notify clients. Our department switches customers to backup channels - customer and our own (to free fibers) - if the customer does not have a reserve. If necessary, draw new crossings and start switching.
The last major accident occurred due to a fire in the Novo-Dorogomilovsky collector. All providers were allowed to work only after 5 days, because at first they restored all city communications and special purpose communications. Everyone who did not have a reserve, had to wait (once again to the question of the reserve :)). But such cases are more likely an exception, and usually we restore the operability of the services promptly, for large-scale accidents - this is 8 hours maximum.

This is what burned cables look like. The consequences of a fire in the Novo-Dorogomilovsky collector.

Recovery work in the same collector. Installers make cable insert for damaged cable. The smell of burning after the fire is still very strong, so they work in respirators.
