How to "make friends" Mitel SIP-DECT and Asterisk
- Tutorial
This article will focus on the installation of the Mitel SIP-DECT system, using the free IP-PBX Asterisk (v 11.2.1) as an office telephone exchange, however, everything described below can equally apply to any IP-PBX that supports standard Sip. We will not go into all the subtleties of this solution, but give a practical minimum how to configure the SIP-DECT system in the existing sip-infrastructure.
The advantages of Mitel's SIP-DECT technology are that the DECT mobile communications subsystem is deployed on the basis of the existing SIP installation of any manufacturer - be it Mitel MX-One, Cisco Call Manger, IP-PBX Asterisk and any other SIP-PBX that use for connecting subscribers, as a protocol, open SIP.
In the infographic below, we see what the SIP-DECT solution consists of.
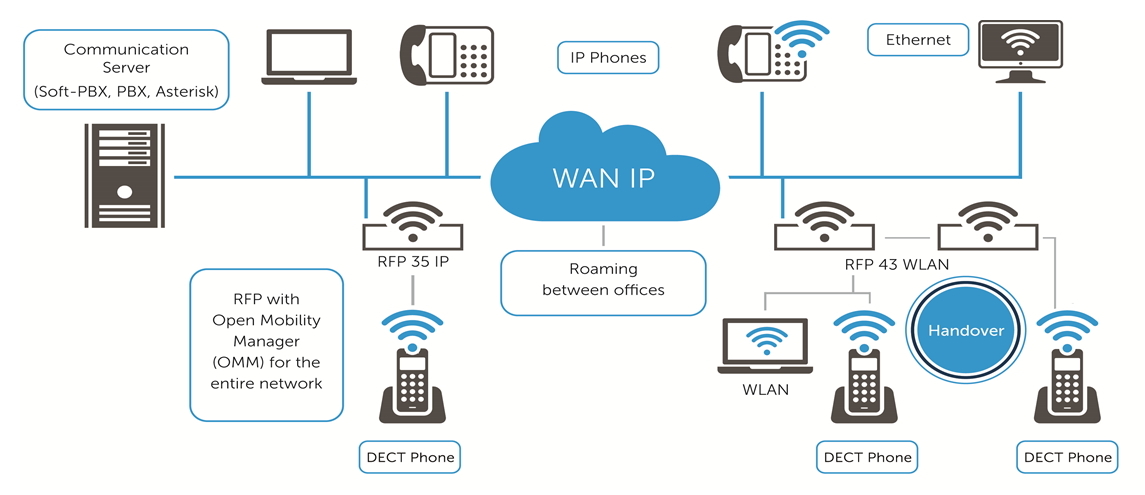
First of all, these are, of course, the SIP-DECT bases themselves, the so-called RFP (Radio Fixed Part), which can be installed both indoors and outdoors. In addition, the RFP 43IP model supports WLAN (802.11 a / b / g / n). All bases from the line have 8 talk channels and several service channels for servicing subscribers who switched to this database with a handover.
From the point of view of mobility, any DECT-terminals of the GAP standard can be used in this configuration, and from the point of view of SIP-ATS, subscribers will be represented as ordinary SIP-subscribers. Thus, if simplified, the SIP-DECT technology converts the voice stream in the DECT standard into IP packets of the SIP standard.
We have at our disposal one SIP-DECT RFP 35IP base station, several Dect Mitel 612d terminals and, as mentioned above, IP-PBX Asterisk.
The communication organization scheme is as follows.

First of all, you need to configure the SIP-DECT system. Regardless of what type of base stations you use, the manufacturer always recommends that you first download the latest, current release of OMM software from the vendor’s website .
OMM (Open Mobility Manager) is a SIP-DECT management system (software). This software can be installed both on the base station itself (by default), and on a separate server running Linux or a virtual machine.
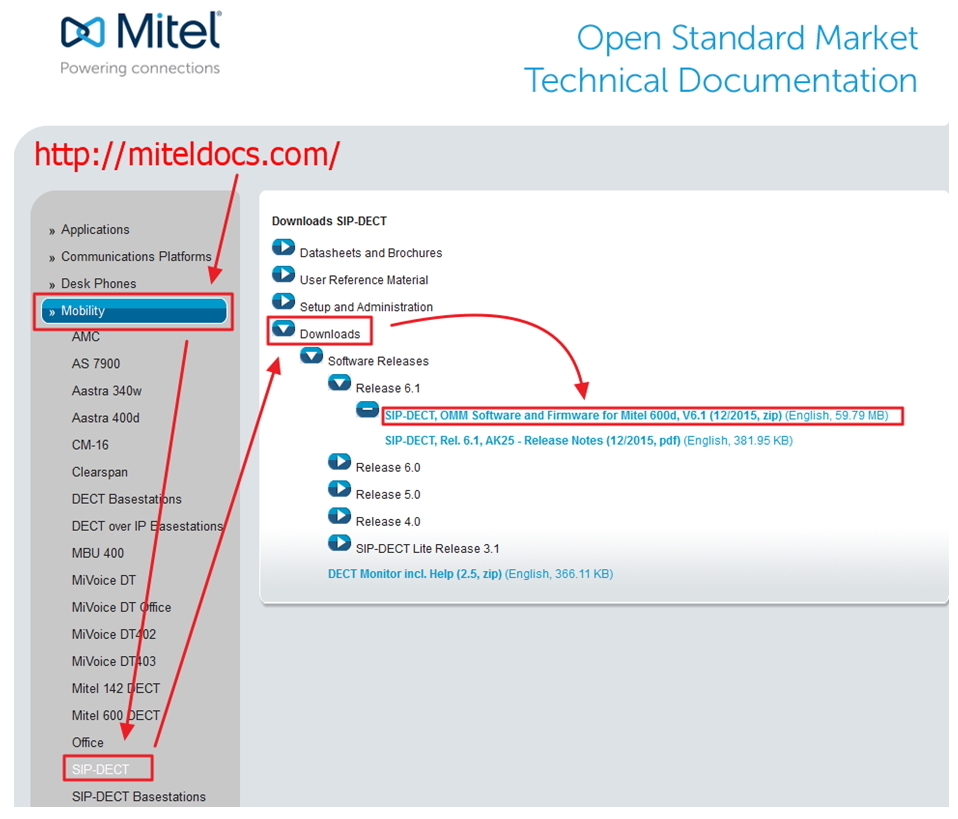
Here are the main documents to download:
After the zip archive is unpacked, you will have several files at your disposal, the most important of them:

So, run the OM_Configuration.jar file, then click Scan.
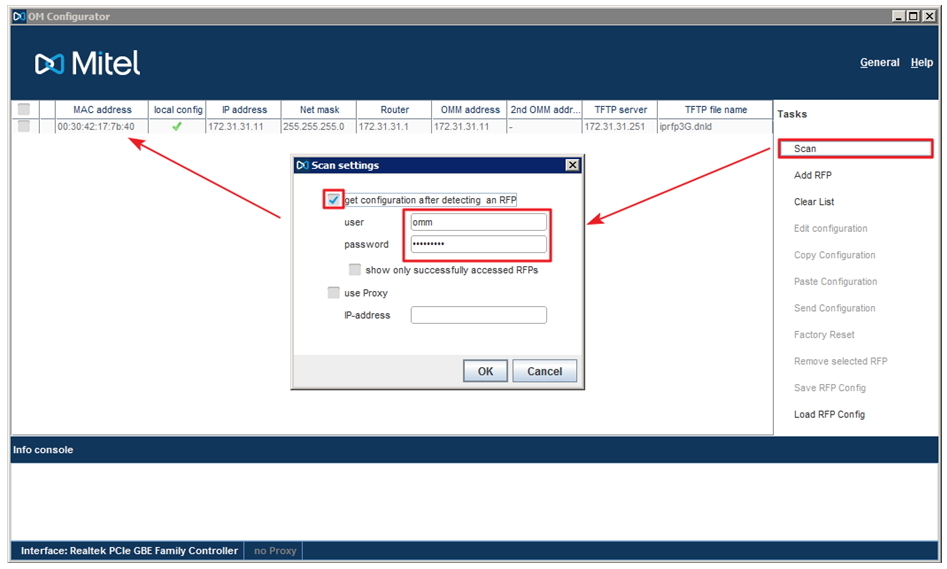
The system offers us to get the current configuration of the system, after its discovery, for which it is necessary to enter a username / password. By default, on new RFP - login / password - omm / omm.
Important! In order for OM_Configuration to be able to detect your RFP database, it must be included in the same subnet (located in the same broadcast domain) from the PC running the configurator.
Further, if the database is loaded, OM_Configuration is correctly detected and detected, then the MAC address of this RFP should be displayed on the screen. If this does not happen, then either the base station has not yet booted, or it is faulty or is on a different subnet.
In this case, we see the MAC address of the desired base station and network parameters.
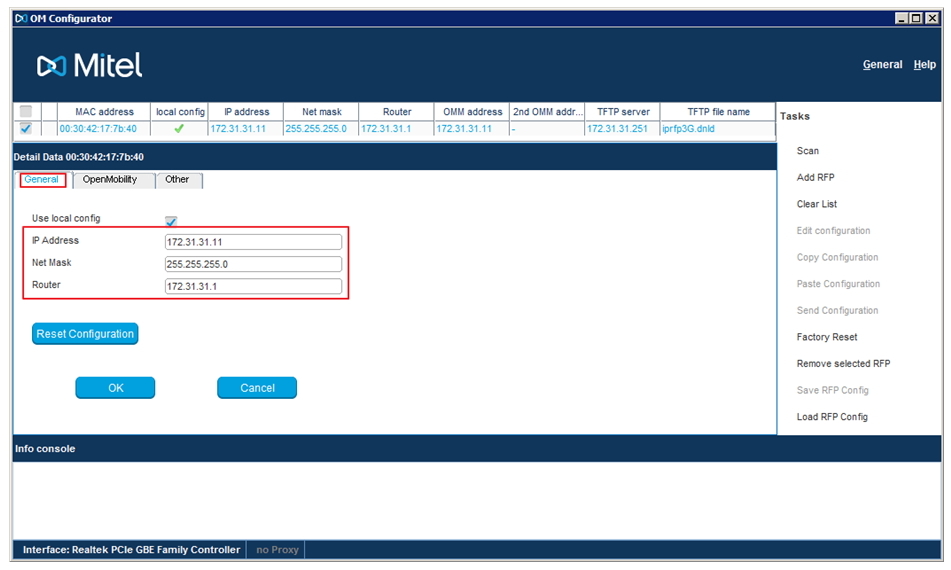
We click on the desired database (if there are more than one in the search list) to select it. Next, configure the network settings for RFP, specifying IP addresses for: the base itself, network mask, gateway, OMM, TFTP, etc.
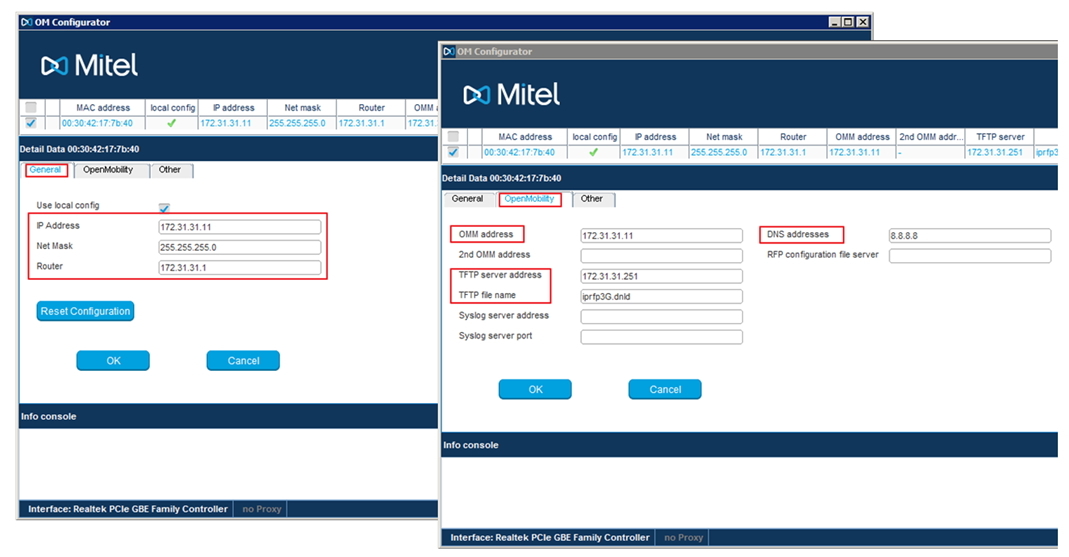
It is worth noting that if this database is configured as the main one, then the IP address and OMM IP address must match. If the base will be “slave” in the cluster, then the address of the control base should be indicated in the OMM IP address field. Do not forget to specify DNS addresses, as Park code will be received through the Mitel web portal, directly from the interface of the database itself.
Another important feature - you must have raised the TFTP server (TFTP server address), which will contain the firmware files for updating the RFP database software.
TFTP file name: iprfp3G.dnld (for RFP 35/36/37/43), iprfp2G.tftp (for RFP 32/34/42). After all the parameters are specified, click - Send config. Next, the database is rebooted and new software is downloaded.

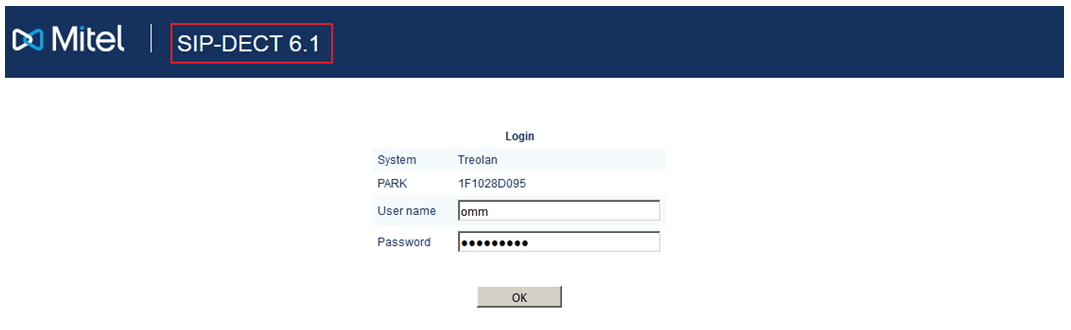
Now you can connect to the database via the web interface using the IP address that we indicated above and make sure which version of the software is installed.
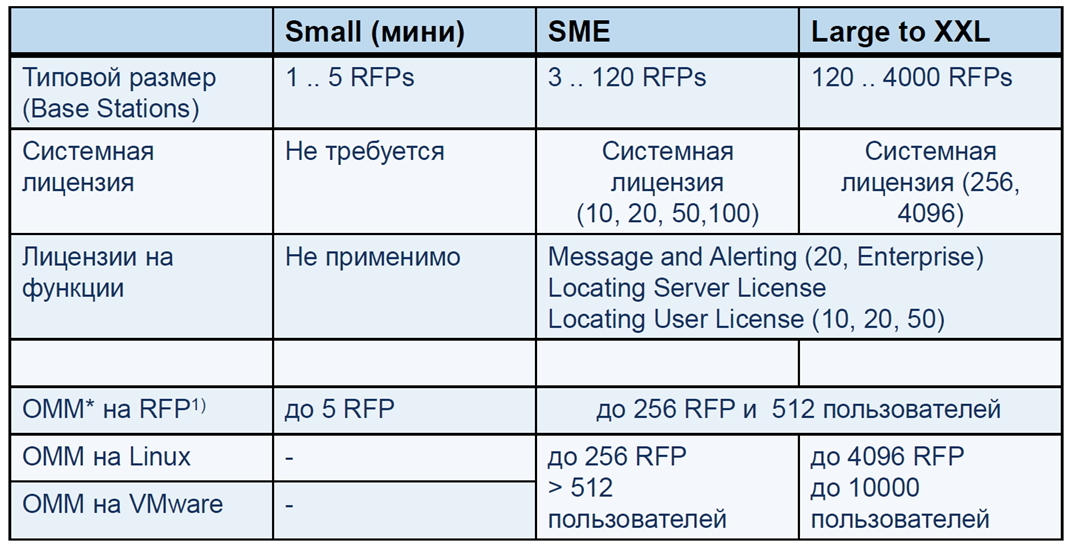
So, you need to license the system: get the park code and download the license file (with more than 5 databases).
The SIP-DECT licensing system is shown below.
Go to the system settings section (System → System settings).
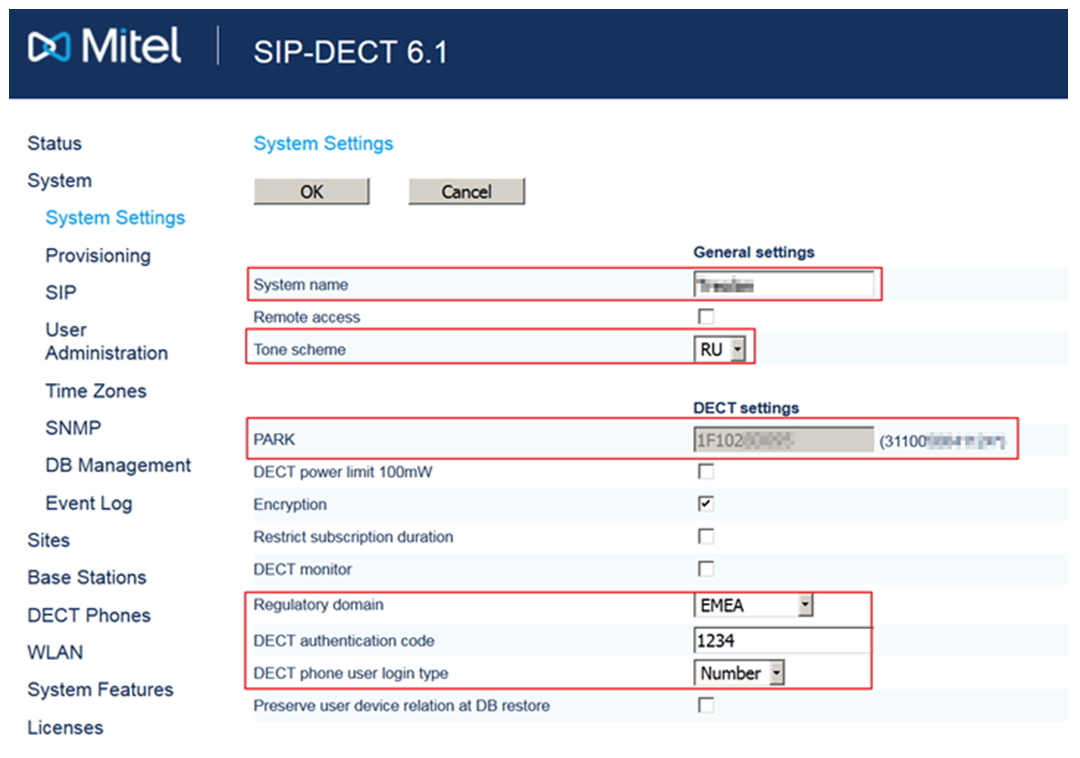
We indicate the necessary system parameters:
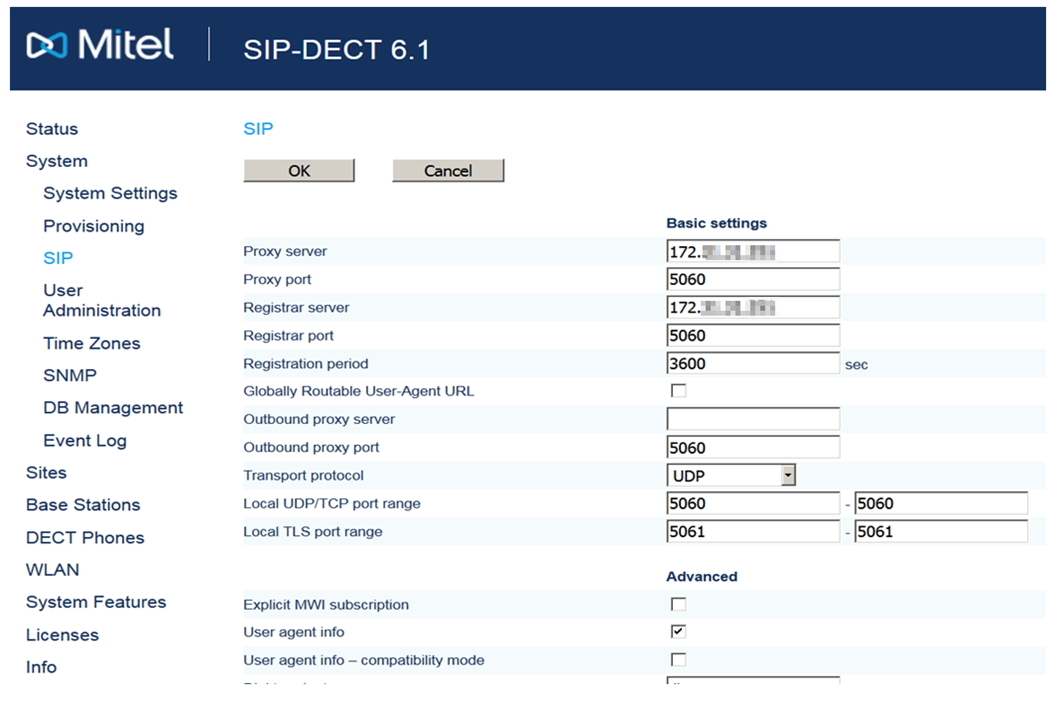
We proceed to configure SIP (System → SIP). Here you need to specify the SIP server on which SIP-DECT subscribers will be registered. You can specify localhost - 127.0.0.1 (i.e., the database itself acts as a SIP server), which is enough to check the basic functionality of the system.
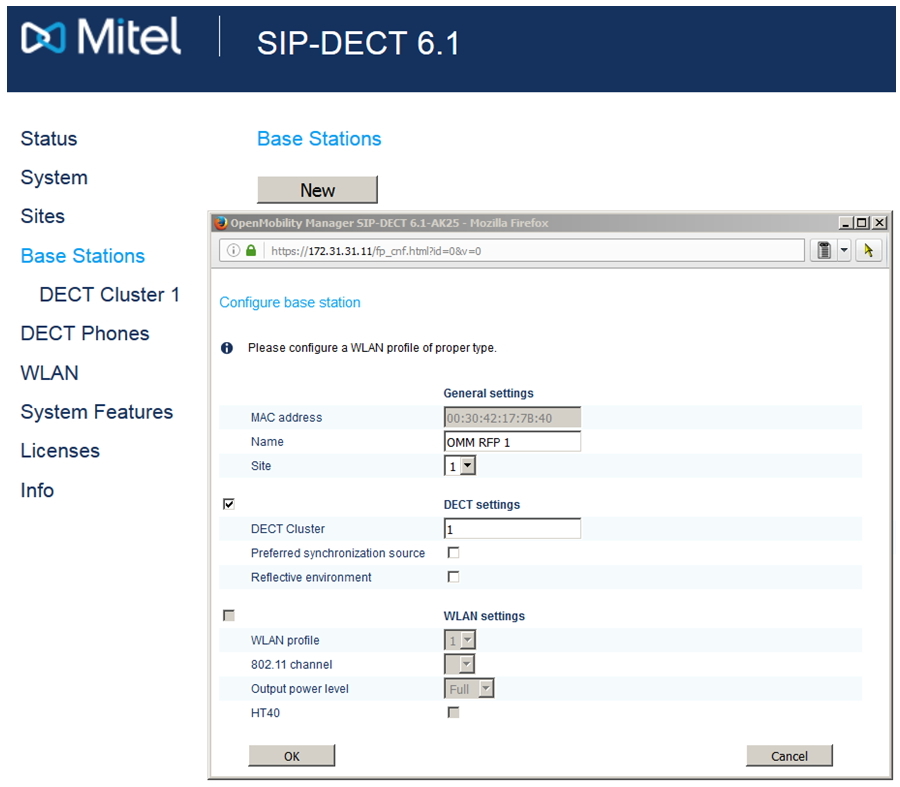
Let's move on to setting up the dect cluster (Base stations → New). Click New and add a new base.
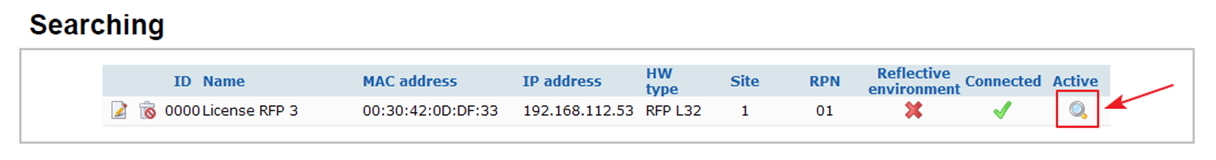
In case everything is done correctly, then you should see the following: Connected and Active will be active.

However, the following picture is often observed when there is no synchronization “over the air” between the bases. In this case, it is necessary to bring the bases closer to each other so that they “see” each other, or, when this is not possible, to spread the bases into different clusters. With this separation, the handover function disappears.
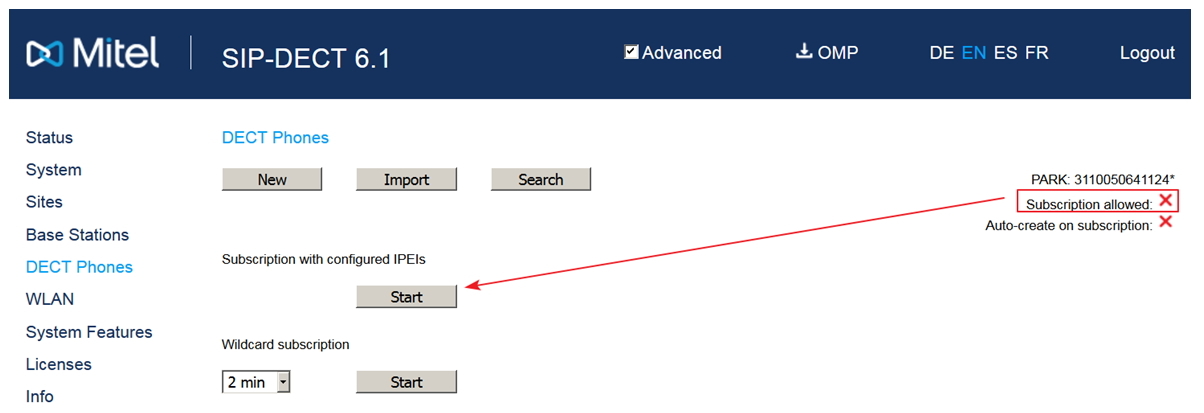
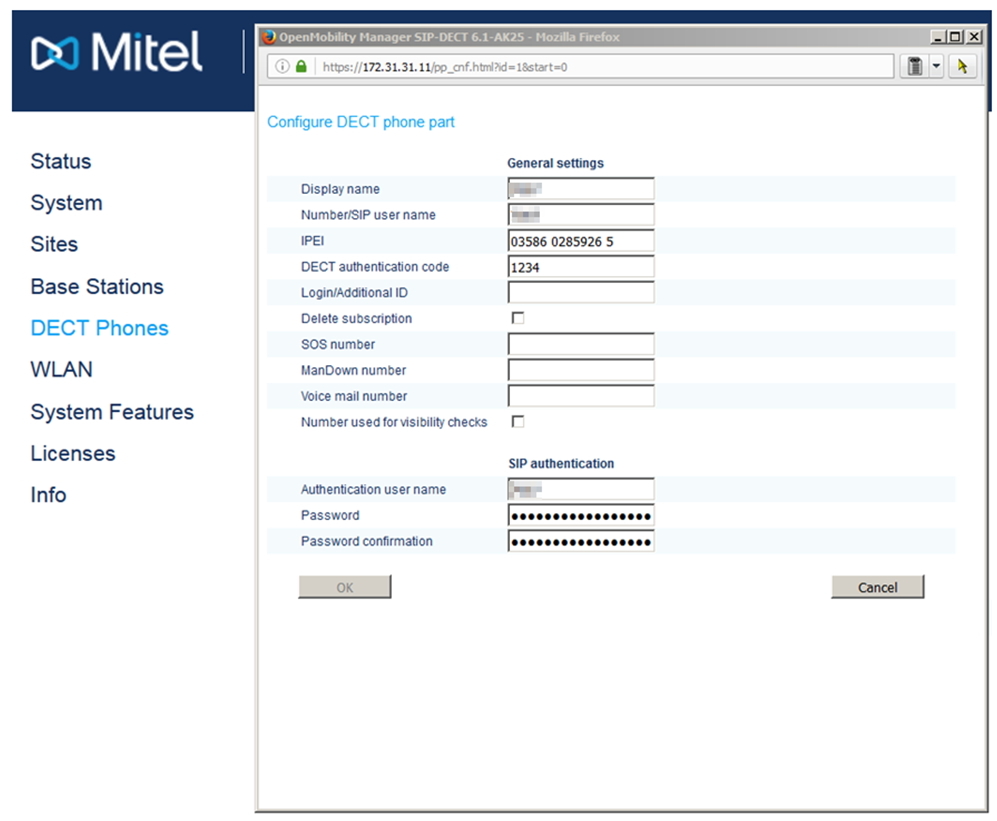
Now configure the DECT terminals in the section (System → DECT phones). Important! By default, the ability to register terminals in the system is disabled, it must be activated by clicking - Start in Subscription with configured IPEIs.
Now you can make new subscribers (mobile terminals) by clicking New. If the database itself is used as the SIP server, then the SIP authentication section can be left blank. When filling in, the entered data must correspond to the subscribers wired to IP-PBX (user name and password).

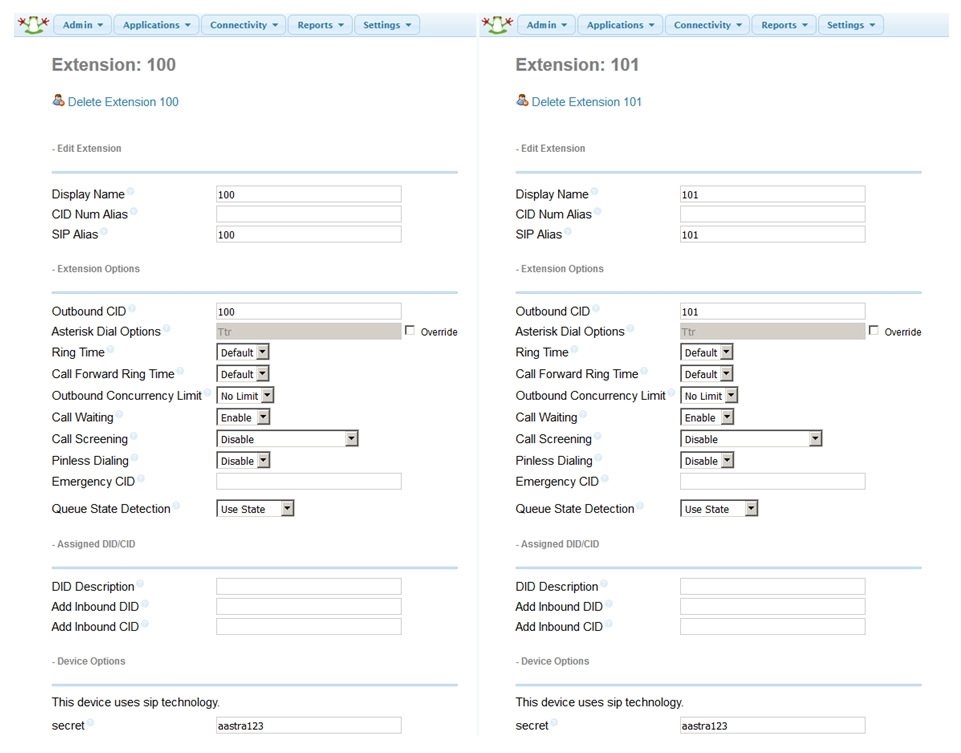
And finally, for clarity, a screen of settings from Asterisk.
The advantages of Mitel's SIP-DECT technology are that the DECT mobile communications subsystem is deployed on the basis of the existing SIP installation of any manufacturer - be it Mitel MX-One, Cisco Call Manger, IP-PBX Asterisk and any other SIP-PBX that use for connecting subscribers, as a protocol, open SIP.
In the infographic below, we see what the SIP-DECT solution consists of.

First of all, these are, of course, the SIP-DECT bases themselves, the so-called RFP (Radio Fixed Part), which can be installed both indoors and outdoors. In addition, the RFP 43IP model supports WLAN (802.11 a / b / g / n). All bases from the line have 8 talk channels and several service channels for servicing subscribers who switched to this database with a handover.
From the point of view of mobility, any DECT-terminals of the GAP standard can be used in this configuration, and from the point of view of SIP-ATS, subscribers will be represented as ordinary SIP-subscribers. Thus, if simplified, the SIP-DECT technology converts the voice stream in the DECT standard into IP packets of the SIP standard.
SIP-DECT Setup
We have at our disposal one SIP-DECT RFP 35IP base station, several Dect Mitel 612d terminals and, as mentioned above, IP-PBX Asterisk.
The communication organization scheme is as follows.

First of all, you need to configure the SIP-DECT system. Regardless of what type of base stations you use, the manufacturer always recommends that you first download the latest, current release of OMM software from the vendor’s website .
OMM (Open Mobility Manager) is a SIP-DECT management system (software). This software can be installed both on the base station itself (by default), and on a separate server running Linux or a virtual machine.

Here are the main documents to download:
- Release of the current version of SIP-DECT software - OMM Software and Firmware for Mitel 600d, V6.1 (12/2015, zip) (English, 59.79 MB)
- Instructions for setting up and configuring - SIP-DECT, Rel. 6.1, AK25 - Release Notes (12/2015, pdf) (English, 381.95 KB)
After the zip archive is unpacked, you will have several files at your disposal, the most important of them:

- OM_Configuration.jar - Java application for initial tuning of base stations
- OMP.jar - Java-based application for configuring SIP-DECT systems (similar to the web-based interface, but has more functionality)
- aafon6xxd.dnld - software file for download to Mitel 600d dect terminals
- iprfp3G.dnld - software file for downloading to RFP base stations (35/36/37/43)
- iprfp2G.tftp - software file for downloading to previous generation RFP base stations (32/34/42).
So, run the OM_Configuration.jar file, then click Scan.

The system offers us to get the current configuration of the system, after its discovery, for which it is necessary to enter a username / password. By default, on new RFP - login / password - omm / omm.
Important! In order for OM_Configuration to be able to detect your RFP database, it must be included in the same subnet (located in the same broadcast domain) from the PC running the configurator.
Further, if the database is loaded, OM_Configuration is correctly detected and detected, then the MAC address of this RFP should be displayed on the screen. If this does not happen, then either the base station has not yet booted, or it is faulty or is on a different subnet.
In this case, we see the MAC address of the desired base station and network parameters.

We click on the desired database (if there are more than one in the search list) to select it. Next, configure the network settings for RFP, specifying IP addresses for: the base itself, network mask, gateway, OMM, TFTP, etc.

It is worth noting that if this database is configured as the main one, then the IP address and OMM IP address must match. If the base will be “slave” in the cluster, then the address of the control base should be indicated in the OMM IP address field. Do not forget to specify DNS addresses, as Park code will be received through the Mitel web portal, directly from the interface of the database itself.
Another important feature - you must have raised the TFTP server (TFTP server address), which will contain the firmware files for updating the RFP database software.
TFTP file name: iprfp3G.dnld (for RFP 35/36/37/43), iprfp2G.tftp (for RFP 32/34/42). After all the parameters are specified, click - Send config. Next, the database is rebooted and new software is downloaded.

Web interface
Now you can connect to the database via the web interface using the IP address that we indicated above and make sure which version of the software is installed.

So, you need to license the system: get the park code and download the license file (with more than 5 databases).
The SIP-DECT licensing system is shown below.

Go to the system settings section (System → System settings).

We indicate the necessary system parameters:
- System name
- Tone scheme - RU
- PARK code
- Regulatory domain - EMEA
- DECT authentication code - 1234 (for terminal authorization)
- Portable part user login type - Number
- Regulatory domain (WLAN) - RU (for systems with Wi-Fi)
- Time zone
We proceed to configure SIP (System → SIP). Here you need to specify the SIP server on which SIP-DECT subscribers will be registered. You can specify localhost - 127.0.0.1 (i.e., the database itself acts as a SIP server), which is enough to check the basic functionality of the system.

Let's move on to setting up the dect cluster (Base stations → New). Click New and add a new base.

In case everything is done correctly, then you should see the following: Connected and Active will be active.

However, the following picture is often observed when there is no synchronization “over the air” between the bases. In this case, it is necessary to bring the bases closer to each other so that they “see” each other, or, when this is not possible, to spread the bases into different clusters. With this separation, the handover function disappears.

Now configure the DECT terminals in the section (System → DECT phones). Important! By default, the ability to register terminals in the system is disabled, it must be activated by clicking - Start in Subscription with configured IPEIs.

Now you can make new subscribers (mobile terminals) by clicking New. If the database itself is used as the SIP server, then the SIP authentication section can be left blank. When filling in, the entered data must correspond to the subscribers wired to IP-PBX (user name and password).


And finally, for clarity, a screen of settings from Asterisk.

