NetApp StorageGrid Object Storage
In this article, I digress from the traditional FAS topic for me and raise the topic of object storage on NetApp StorageGrid WebScale systems. In short, object storage is the third type of storage along with NAS and SAN. Imagine that each file consists of data and meta-information (owner, rights, modification time, etc.), so object storage allows you to separate these parts and store them in the form of "key / value". This approach to information storage opens up the possibility of decentralized, distributed storage of huge data with transparent data migration, replication and transparent switching of end users between nodes of an object cluster. In a broad sense, object storage can be implemented both at the device level (hard disk), using specialized SCSI commands (Object-based Storage Device Commands), and at the level of the access protocol to the storage system, which consists of several disks (which, in turn, do not have to be object). In both cases, Ethernet is used for connection and IP protocol for data transfer. An example of the implementation of object storage at the device level is the hard drives of the Seagate Kinetic Open Storage platform line. An example of cloud storage is Microsoft Azure BLOB, Amazon S3. In this article, I will focus on object storage systems that can be deployed on your site and, if necessary, connected to the cloud. S3, SWIFT, CDMI object protocols have gained wide popularity, all of them are add-ons over HTTP. which consists of several disks (which, in turn, do not have to be object at all). In both cases, Ethernet is used for connection and IP protocol for data transfer. An example of the implementation of object storage at the device level is the hard drives of the Seagate Kinetic Open Storage platform line. An example of cloud storage is Microsoft Azure BLOB, Amazon S3. In this article, I will focus on object storage systems that can be deployed on your site and, if necessary, connected to the cloud. S3, SWIFT, CDMI object protocols have gained wide popularity, all of them are add-ons over HTTP. which consists of several disks (which, in turn, do not have to be object at all). In both cases, Ethernet is used for connection and IP protocol for data transfer. An example of the implementation of object storage at the device level is the hard drives of the Seagate Kinetic Open Storage platform line. An example of cloud storage is Microsoft Azure BLOB, Amazon S3. In this article, I will focus on object storage systems that can be deployed on your site and, if necessary, connected to the cloud. S3, SWIFT, CDMI object protocols have gained wide popularity, all of them are add-ons over HTTP. An example of the implementation of object storage at the device level is the hard drives of the Seagate Kinetic Open Storage platform line. An example of cloud storage is Microsoft Azure BLOB, Amazon S3. In this article, I will focus on object storage systems that can be deployed on your site and, if necessary, connected to the cloud. S3, SWIFT, CDMI object protocols have gained wide popularity, all of them are add-ons over HTTP. An example of the implementation of object storage at the device level is the hard drives of the Seagate Kinetic Open Storage platform line. An example of cloud storage is Microsoft Azure BLOB, Amazon S3. In this article, I will focus on object storage systems that can be deployed on your site and, if necessary, connected to the cloud. S3, SWIFT, CDMI object protocols have gained wide popularity, all of them are add-ons over HTTP.

Initially, StorageGRID was developed for healthcare, as storing millions of large and small objects required a specialized solution. Large manufacturers of healthcare equipment such as Siemens, AGFA and other major PACS systems support the ability to send objects directly to StorageGRID. This approach allowed the implementation of a previously impossible scenario for file storages, for example, when a doctor needs to obtain patient data for the last 10 years, although the patient moved from Minnesota to Los Angeles. StorageGRID is still extremely popular in the healthcare industry, but could also find application in cloud solutions for storing a variety of data.
The NetApp StorageGrid family consists of two representatives:
Both of these options can coexist in one cluster.

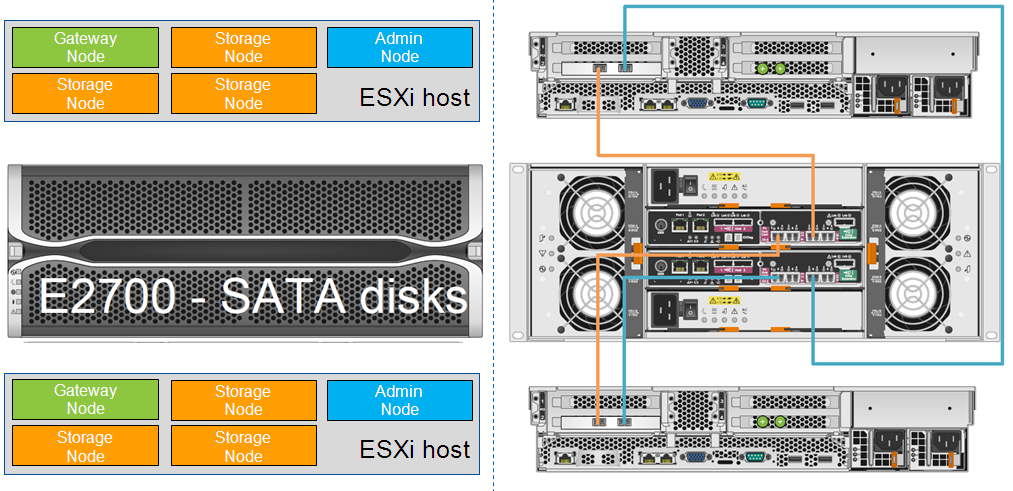
The first option consists of a dual-controller system, where one controller is a Storage node, and the second is a Compute node. Those. there are two controllers in the chassis, but this is not a High-Avalability system in itself - a minimum of 2 such SG5660 systems (i.e. 4 controllers) are recommended for fault tolerance. In addition to SG5600, a hardware solution also requires a minimum of 2 servers to host the Gateway and Admin nodes.
The second option (software) can be delivered as an ESXi appliance or as a Docker image based on Debian Linux. In this version, you can use one regular E-Series, with two controllers and High-Availability, with standard OS SANtricity and on top of all this at least two servers with Storage, Gateway and Admin nodes. In the software version, more server capacities are needed due to the need to contain the Storage node (the most resource-demanding one) on the server.
The growth of unstructured data is steadily gaining momentum, examples of such data generators are the growing IoT market, photo and video cameras with unprecedented resolution and frame quality that appeared on the market, medical equipment and other devices. To close all these tasks, StorageGrid was developed from scratch:
Web data repositories
Data archives
Media repositories
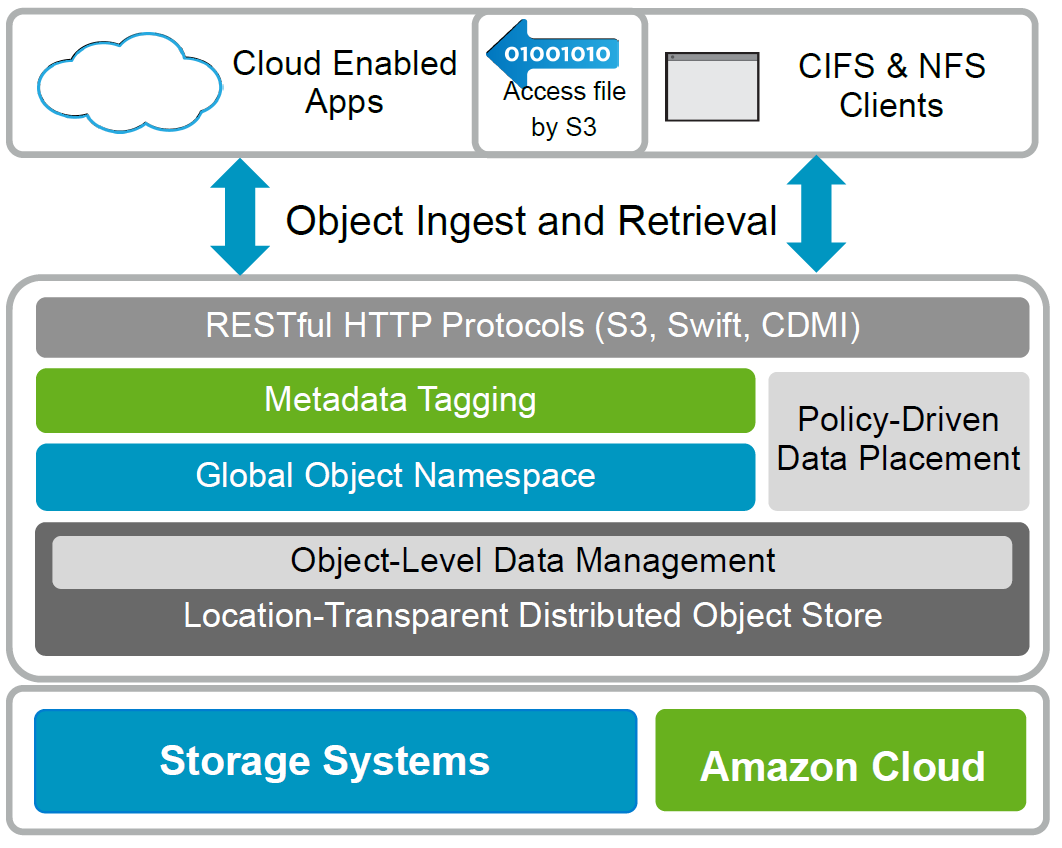
Allows you to manage geo-distributed unstructured data. With a single control panel, management policies for all sites where the StorageGrid cluster nodes are located, thus pulling data to where it is needed. Tape libraries and RESTful HTTP-like protocols are supported, such as CDMI, S3 and Swift, with which the system can be integrated with cloud providers. Data can seamlessly move between all tiers: local storage, the cloud, and tape libraries.
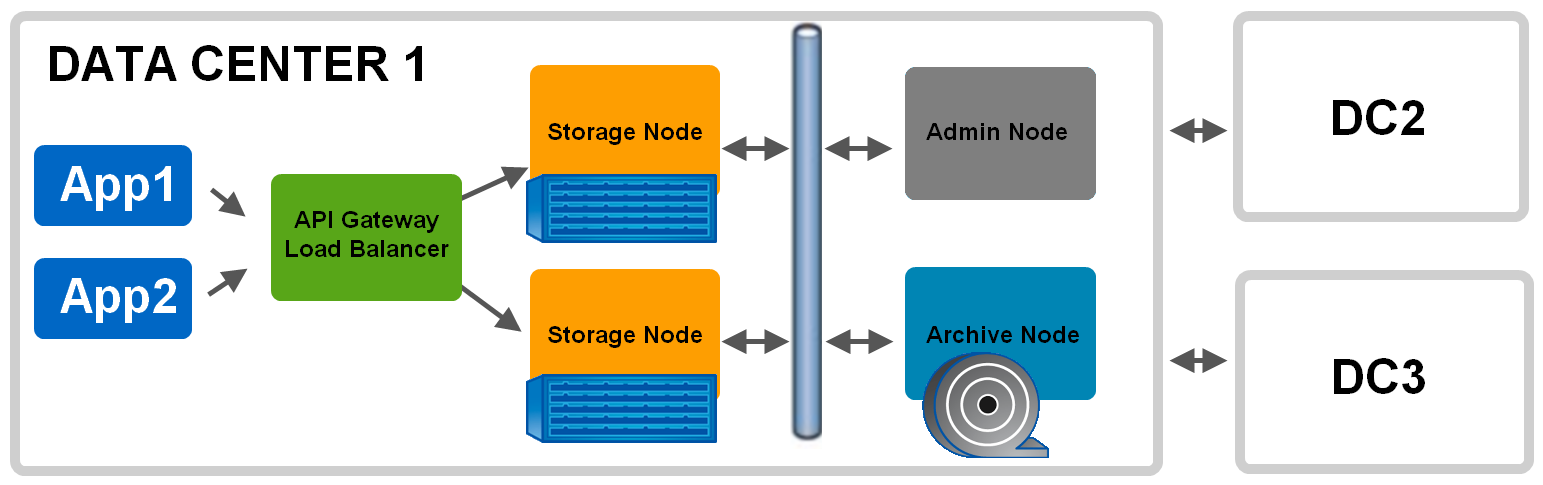
The advantages of the StorageGrid platform include:
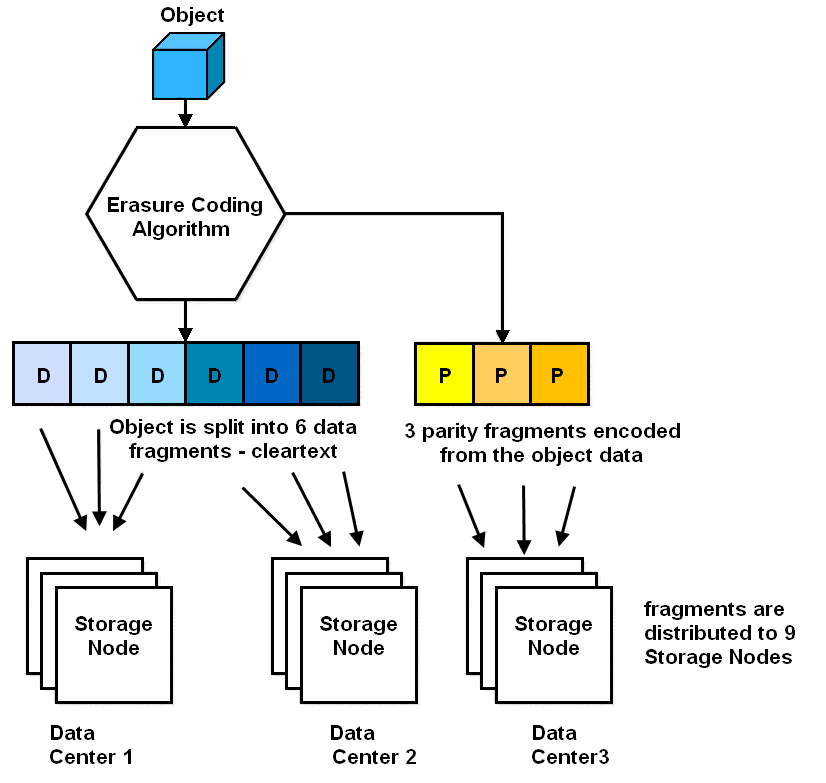
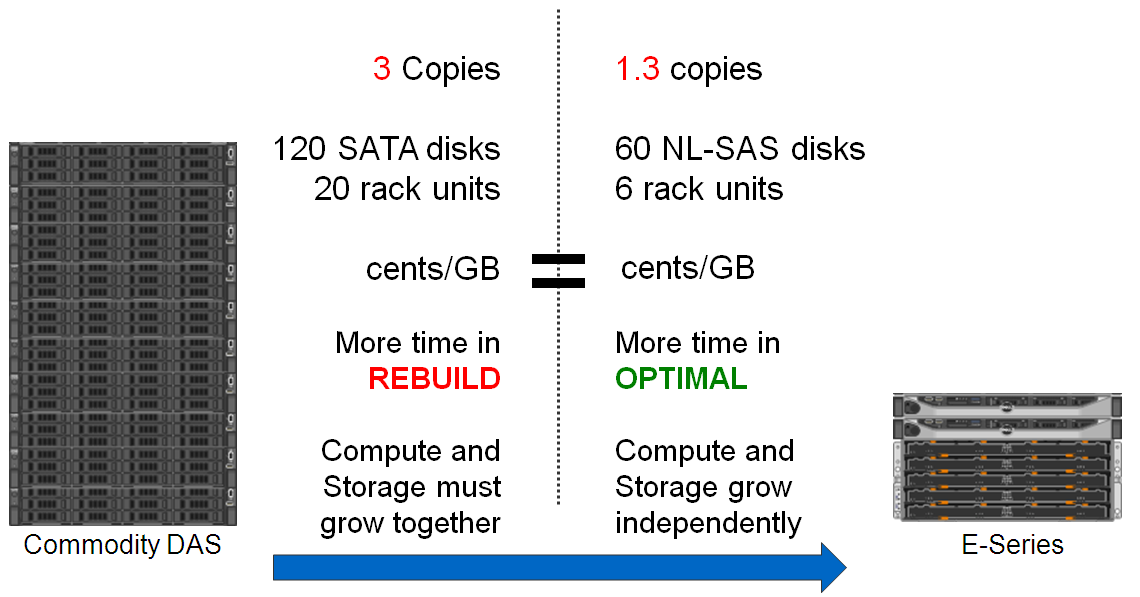
Almost all object storage systems can store several copies of one object (replication), duplicating data on different nodes and sites, thus ensuring fault tolerance. And Erasure Coding (EC) is a mechanism similar to RAID, but running at the object level, which is divided into several parts, and not at the level of entire hard drives. EC allows significantly less storage space, providing a fault tolerance mechanism.

Geo Distributed Erasure Coding is an EC where the parts of an object that make up such a “RAID group” can be on systems located in different parts of the world, store two or three copies of data, and allow you to achieve incredible availability indicators, but this gives rise to the corresponding amount traffic and space occupied. Here the geo-distributed function Erasure Coding comes to the rescue, which allows not to worsen fault tolerance and availability, significantly reducing the amount of occupied space. The following EC schemes are available:
Erasure Coding on the one hand saves disk space, on the other hand adds overhead when calculating the checksum and restoring the object. In the case of Geo-EC, when reading an object, the response speed also increases since reading is performed from two sites. Those. EC must be used wisely, and later in the ILM paragraph I will tell you how.
StorageGrid allows you to distribute data based on the policies of their durability and fault tolerance. Hierarchical Erasure Coding allows the local EC and Geo-EC to be automatically executed based on these policies. Hierarchical EC is well suited for installations with at least 3 sites to protect against the failure of an entire site.
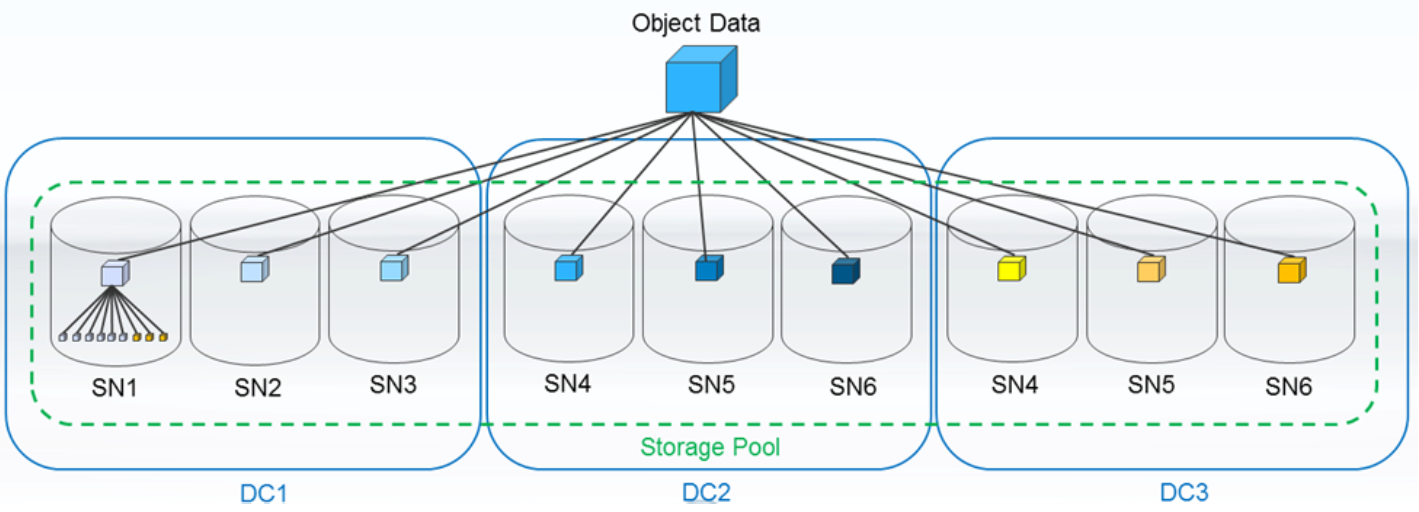
Dynamic Disk Pools (used by StorageGrid WebScale as a local EC) is NetApp E-Series hardware functionality, a kind of RAID, like regular RAID groups, it is created on one local system. DDP allows you not to lose performance in the event of a local failure of one or several disks (otherwise the objects will be pulled from other nodes or sites), plus energy and network (WAN / LAN) traffic are saved: data access and recovery will be performed locally. This functionality perfectly complements the Geo-EC.
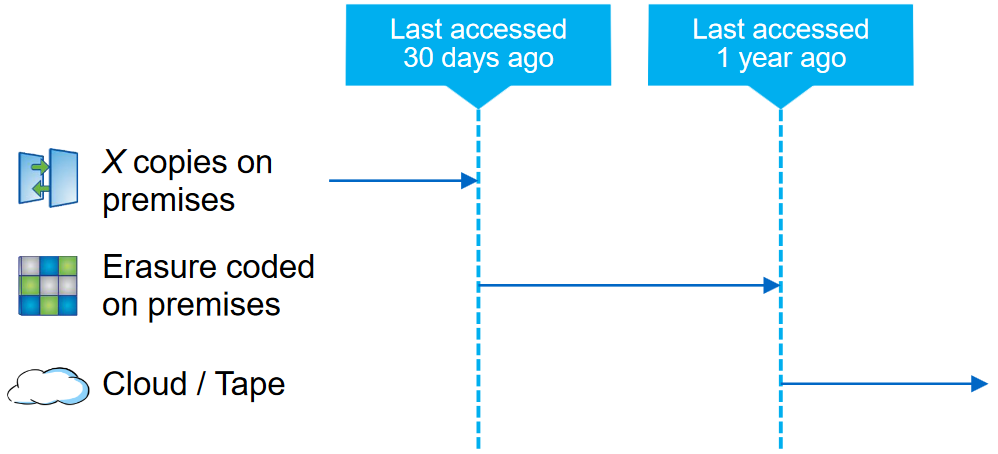
ILM on StorageGRID systems allows for flexible and much more efficient use of disk space thanks to data lifecycle policies. So, for example, you can configure the policy so that if the object was recorded or there was at least one call to it within 30 days, store X copies of it on several different sites. If it has not been accessed for more than 30 days, then delete copies and run it through the EC, in which case the increased reading time of the object will no longer be such a problem. And if the object has not been accessed for 1 year, then send it to the cloud or to tape. It is important to note that the above example works granularly at the level of each individual object and not at the level of a large data set, such as a LUN or file ball (in a SAN or NAS, respectively). If the price of resources changes,
It can be divided into two parts: data integrity and availability.
Data integrity is ensured through: the use of digital hashes when data is written, read, migrated, and periodically checked. Damaged objects are transparently recreated from copies. The geo-distributed mechanism of Erasure Coding allows you to economically use the space for storing copies of data.
Data availability is ensured by the Fault-tolerent architecture, support for business continuity, software updates and platform equipment. Load distribution, both during normal operation and during failure. NetApp AutoSupport can automatically notify support for proactive troubleshooting. Erasure coding at the node level improves the availability of each node, recovery time, performance impact and network activity (available only on the E-Series platform with Dynamic Disk Pools).
Functionality of NAS with CIFS / NFS protocols can be implemented using NAS bridge. This will allow not to modify the existing infrastructure and provide end users with standard file access. StorageGrid, in turn, thanks to life cycle policies, will be able to transparently move this data across storage levels based on meta-information (for example, the last time a file was modified or created). File bridge licenses are included with StorageGrid; you do not need to purchase them. Integration with Active Directory and LDAP is supported. NAS bridge, as it were, "from above" provides access via CIFS / NFS and this is the most common NAS.
Bottom on the back end, the same NAS bridge is connected using the object protocol and converts files to objects, then they are already stored and processed as ordinary objects.
Support for end-to-end encryption of each object and Secure Multi-Tenancy. Support for authentication and security mechanisms for S3 and CDMI. Integration with LDAP / AD is supported to authenticate users within a single Tenant.
This is a very important moment when the customer does not have an army of programmers and administrators, it is important that the complex is reliable. StorageGrid technologies are already more than 14 years old (in 2001 the first installation), and it managed to grow with a large number of integrations with other well-known products for backup, archiving, file synchronization, collaboration, etc.
The product is licensed terabyte, regardless of the number and type of nodes. StorageGRID hardware and software implementations can coexist in the same cluster. All possible functionality is included in the basic delivery:
StorageGRID is a product for applications that support RESTful HTTP, which is suitable for large and small objects, high bandwidth, transactional and automatic, transparent movement of data across storage levels. Geo-clustering allows you to achieve incredibly high fault tolerance and data availability, hiding the failure of entire sites. EC technology can significantly save space by using a RAID-like architecture. StorageGRID has support for multiple storage tiers and one of the most advanced data lifecycle management mechanisms. ILM will automatically move data when the price changes at one or another storage level, which will allow more rational use of resources and flexible response to changes in the cost of data storage (for example, in the Cloud or in Tape libraries). StorageGRID is a well-established, mature product with a broad list of third-party software integration, which simplifies support and integration into existing infrastructure. Object encryption and LDAP / AD authentication support provide protection against data theft. StorageGRID can act as a complete replacement for Amazon S3, allowing you to lease storage to several companies and acting as a private cloud for those who can not host data in a public cloud. And it can be an addition to AWS S3, using it as a level of data storage and has a mechanism for calculating the cost of their storage for tenants of StorageGRID storage. Object encryption and LDAP / AD authentication support provide protection against data theft. StorageGRID can act as a complete replacement for Amazon S3, allowing you to lease storage to several companies and acting as a private cloud for those who can not host data in a public cloud. And it can be an addition to AWS S3, using it as a level of data storage and has a mechanism for calculating the cost of their storage for tenants of StorageGRID storage. Object encryption and LDAP / AD authentication support provide protection against data theft. StorageGRID can act as a complete replacement for Amazon S3, allowing you to lease storage to several companies and acting as a private cloud for those who can not host data in a public cloud. And it can be an addition to AWS S3, using it as a level of data storage and has a mechanism for calculating the cost of their storage for tenants of StorageGRID storage.
This may contain links to Habra articles that will be published later .
Please send messages about errors in the text to the LAN .
Comments, additions and questions on the opposite article, please comment .

History
Initially, StorageGRID was developed for healthcare, as storing millions of large and small objects required a specialized solution. Large manufacturers of healthcare equipment such as Siemens, AGFA and other major PACS systems support the ability to send objects directly to StorageGRID. This approach allowed the implementation of a previously impossible scenario for file storages, for example, when a doctor needs to obtain patient data for the last 10 years, although the patient moved from Minnesota to Los Angeles. StorageGRID is still extremely popular in the healthcare industry, but could also find application in cloud solutions for storing a variety of data.
The NetApp StorageGrid family consists of two representatives:
- Pure software, NetApp StorageGrid WebScale
- NetApp StorageGrid appliance based on E-Series - SG5660.
Both of these options can coexist in one cluster.
The first option consists of a dual-controller system, where one controller is a Storage node, and the second is a Compute node. Those. there are two controllers in the chassis, but this is not a High-Avalability system in itself - a minimum of 2 such SG5660 systems (i.e. 4 controllers) are recommended for fault tolerance. In addition to SG5600, a hardware solution also requires a minimum of 2 servers to host the Gateway and Admin nodes.
The second option (software) can be delivered as an ESXi appliance or as a Docker image based on Debian Linux. In this version, you can use one regular E-Series, with two controllers and High-Availability, with standard OS SANtricity and on top of all this at least two servers with Storage, Gateway and Admin nodes. In the software version, more server capacities are needed due to the need to contain the Storage node (the most resource-demanding one) on the server.
The growth of unstructured data is steadily gaining momentum, examples of such data generators are the growing IoT market, photo and video cameras with unprecedented resolution and frame quality that appeared on the market, medical equipment and other devices. To close all these tasks, StorageGrid was developed from scratch:
Web data repositories
- For small objects with extremely high transactional loads
- To store billions of objects
Data archives
- Large objects, low transaction load
- Long-term storage, not demanding response speed
Media repositories
- Globally distributed, large objects
- StorageGRID is great for healthcare
- StorageGRID also works very well for Video on Demand (VoD) tasks.
- Stream data access, high bandwidth
Key Features of StorageGrid
Allows you to manage geo-distributed unstructured data. With a single control panel, management policies for all sites where the StorageGrid cluster nodes are located, thus pulling data to where it is needed. Tape libraries and RESTful HTTP-like protocols are supported, such as CDMI, S3 and Swift, with which the system can be integrated with cloud providers. Data can seamlessly move between all tiers: local storage, the cloud, and tape libraries.
Storage Grid Web GUI

The advantages of the StorageGrid platform include:
- Support for all the most popular object protocols
- Scalability up to 100 billion objects (375 million per node), 70PiB information (soft limit)
- Distribution: up to 16 sites
- Ability to use tape libraries as a level for storing data archives
- When policies change, the data life cycle will be automatically tuned to match the changes.
- One of the most advanced data lifecycle policy ( ILM ) settings : Automatically distribute data across local levels (SSD, SATA, SAS, Tape, Geo-EC), public clouds (such as AWS S3) and between customer sites. Data distribution can be carried out on the basis of information about the cost of data, the need for their level of security, performance, availability, cost of the network and the durability of the stored data.

Erasure coding
Almost all object storage systems can store several copies of one object (replication), duplicating data on different nodes and sites, thus ensuring fault tolerance. And Erasure Coding (EC) is a mechanism similar to RAID, but running at the object level, which is divided into several parts, and not at the level of entire hard drives. EC allows significantly less storage space, providing a fault tolerance mechanism.

Geo-ec
Geo Distributed Erasure Coding is an EC where the parts of an object that make up such a “RAID group” can be on systems located in different parts of the world, store two or three copies of data, and allow you to achieve incredible availability indicators, but this gives rise to the corresponding amount traffic and space occupied. Here the geo-distributed function Erasure Coding comes to the rescue, which allows not to worsen fault tolerance and availability, significantly reducing the amount of occupied space. The following EC schemes are available:
- 2 + 1 for three sites
- 4 + 2 for three sites
- 6 + 3 for three sites
- 9 + 3 for four sites
- 8 + 2 for five sites.

Erasure Coding on the one hand saves disk space, on the other hand adds overhead when calculating the checksum and restoring the object. In the case of Geo-EC, when reading an object, the response speed also increases since reading is performed from two sites. Those. EC must be used wisely, and later in the ILM paragraph I will tell you how.
Hierarchical EC
StorageGrid allows you to distribute data based on the policies of their durability and fault tolerance. Hierarchical Erasure Coding allows the local EC and Geo-EC to be automatically executed based on these policies. Hierarchical EC is well suited for installations with at least 3 sites to protect against the failure of an entire site.
DDP - Local EC
Dynamic Disk Pools (used by StorageGrid WebScale as a local EC) is NetApp E-Series hardware functionality, a kind of RAID, like regular RAID groups, it is created on one local system. DDP allows you not to lose performance in the event of a local failure of one or several disks (otherwise the objects will be pulled from other nodes or sites), plus energy and network (WAN / LAN) traffic are saved: data access and recovery will be performed locally. This functionality perfectly complements the Geo-EC.
Information Lifecycle Management
ILM on StorageGRID systems allows for flexible and much more efficient use of disk space thanks to data lifecycle policies. So, for example, you can configure the policy so that if the object was recorded or there was at least one call to it within 30 days, store X copies of it on several different sites. If it has not been accessed for more than 30 days, then delete copies and run it through the EC, in which case the increased reading time of the object will no longer be such a problem. And if the object has not been accessed for 1 year, then send it to the cloud or to tape. It is important to note that the above example works granularly at the level of each individual object and not at the level of a large data set, such as a LUN or file ball (in a SAN or NAS, respectively). If the price of resources changes,

Durability
It can be divided into two parts: data integrity and availability.
Data integrity is ensured through: the use of digital hashes when data is written, read, migrated, and periodically checked. Damaged objects are transparently recreated from copies. The geo-distributed mechanism of Erasure Coding allows you to economically use the space for storing copies of data.
Data availability is ensured by the Fault-tolerent architecture, support for business continuity, software updates and platform equipment. Load distribution, both during normal operation and during failure. NetApp AutoSupport can automatically notify support for proactive troubleshooting. Erasure coding at the node level improves the availability of each node, recovery time, performance impact and network activity (available only on the E-Series platform with Dynamic Disk Pools).
NAS
Functionality of NAS with CIFS / NFS protocols can be implemented using NAS bridge. This will allow not to modify the existing infrastructure and provide end users with standard file access. StorageGrid, in turn, thanks to life cycle policies, will be able to transparently move this data across storage levels based on meta-information (for example, the last time a file was modified or created). File bridge licenses are included with StorageGrid; you do not need to purchase them. Integration with Active Directory and LDAP is supported. NAS bridge, as it were, "from above" provides access via CIFS / NFS and this is the most common NAS.
Bottom on the back end, the same NAS bridge is connected using the object protocol and converts files to objects, then they are already stored and processed as ordinary objects.
Security
Support for end-to-end encryption of each object and Secure Multi-Tenancy. Support for authentication and security mechanisms for S3 and CDMI. Integration with LDAP / AD is supported to authenticate users within a single Tenant.
Production-ready
This is a very important moment when the customer does not have an army of programmers and administrators, it is important that the complex is reliable. StorageGrid technologies are already more than 14 years old (in 2001 the first installation), and it managed to grow with a large number of integrations with other well-known products for backup, archiving, file synchronization, collaboration, etc.
- NTP Hierarchical storage management service: Software Object Storage & Cloud Connector (File Vacuum)
- Ctera File sync and share, collaboration
- Stealth Microsoft SQL / Exchange / SharePoint integration
- PoINT Hierarchical storage management service
- Commvault Backup and archive
- Citrix Sharefile File sync and share, collaboration
- Egnyte File sync and share, collaboration
- SoftNAS General purpose NFS and CIFS gateway
- NetApp AltaVault (SteelStore) . The link will be available after the publication of the next article.
- Symantec Enterprise Vault with NetApp StorageGRID Adapter
- Amazon s3
- Amazon cloudfront
- Open stack stack with white box
- Inktank Ceph with Calamari
- Swift API
- OpenStack Glance Integration: Leverage StorageGRID Webscale as Glance image repository via S3 and Swift
- NetApp OpenStack Cinder driver
- Openstack kilo
- Openstack heat orchestration
- Other.
StorageGrid Licensing Policy
The product is licensed terabyte, regardless of the number and type of nodes. StorageGRID hardware and software implementations can coexist in the same cluster. All possible functionality is included in the basic delivery:
- In the case of hardware implementation, the product is licensed by the number of raw (RAW) terabytes
- If you purchase a software license (without using hardware StorageGRID), the product is licensed by the amount of usable space, and the coefficient of x1.25 is used.
conclusions
StorageGRID is a product for applications that support RESTful HTTP, which is suitable for large and small objects, high bandwidth, transactional and automatic, transparent movement of data across storage levels. Geo-clustering allows you to achieve incredibly high fault tolerance and data availability, hiding the failure of entire sites. EC technology can significantly save space by using a RAID-like architecture. StorageGRID has support for multiple storage tiers and one of the most advanced data lifecycle management mechanisms. ILM will automatically move data when the price changes at one or another storage level, which will allow more rational use of resources and flexible response to changes in the cost of data storage (for example, in the Cloud or in Tape libraries). StorageGRID is a well-established, mature product with a broad list of third-party software integration, which simplifies support and integration into existing infrastructure. Object encryption and LDAP / AD authentication support provide protection against data theft. StorageGRID can act as a complete replacement for Amazon S3, allowing you to lease storage to several companies and acting as a private cloud for those who can not host data in a public cloud. And it can be an addition to AWS S3, using it as a level of data storage and has a mechanism for calculating the cost of their storage for tenants of StorageGRID storage. Object encryption and LDAP / AD authentication support provide protection against data theft. StorageGRID can act as a complete replacement for Amazon S3, allowing you to lease storage to several companies and acting as a private cloud for those who can not host data in a public cloud. And it can be an addition to AWS S3, using it as a level of data storage and has a mechanism for calculating the cost of their storage for tenants of StorageGRID storage. Object encryption and LDAP / AD authentication support provide protection against data theft. StorageGRID can act as a complete replacement for Amazon S3, allowing you to lease storage to several companies and acting as a private cloud for those who can not host data in a public cloud. And it can be an addition to AWS S3, using it as a level of data storage and has a mechanism for calculating the cost of their storage for tenants of StorageGRID storage.
This may contain links to Habra articles that will be published later .
Please send messages about errors in the text to the LAN .
Comments, additions and questions on the opposite article, please comment .
