Energy Efficient Data Center
It is a well-known fact that the lion's share of the costs associated with the functioning of data centers is the ventilation system of server rooms. First, kilowatts are indirectly used to heat equipment, then these kilowatts are also used to remove heat generated by the equipment. Often the most effective way of cooling a hot server equipment is through atmospheric ventilation, without prior cooling. Using the widest possible cool air from outside, data center owners receive significant energy savings, because the main energy consumption of ventilation systems is not for air delivery, but rather for its cooling. The ventilation method, in which the air masses coming from outside do not undergo additional processing, is called free ventilation.
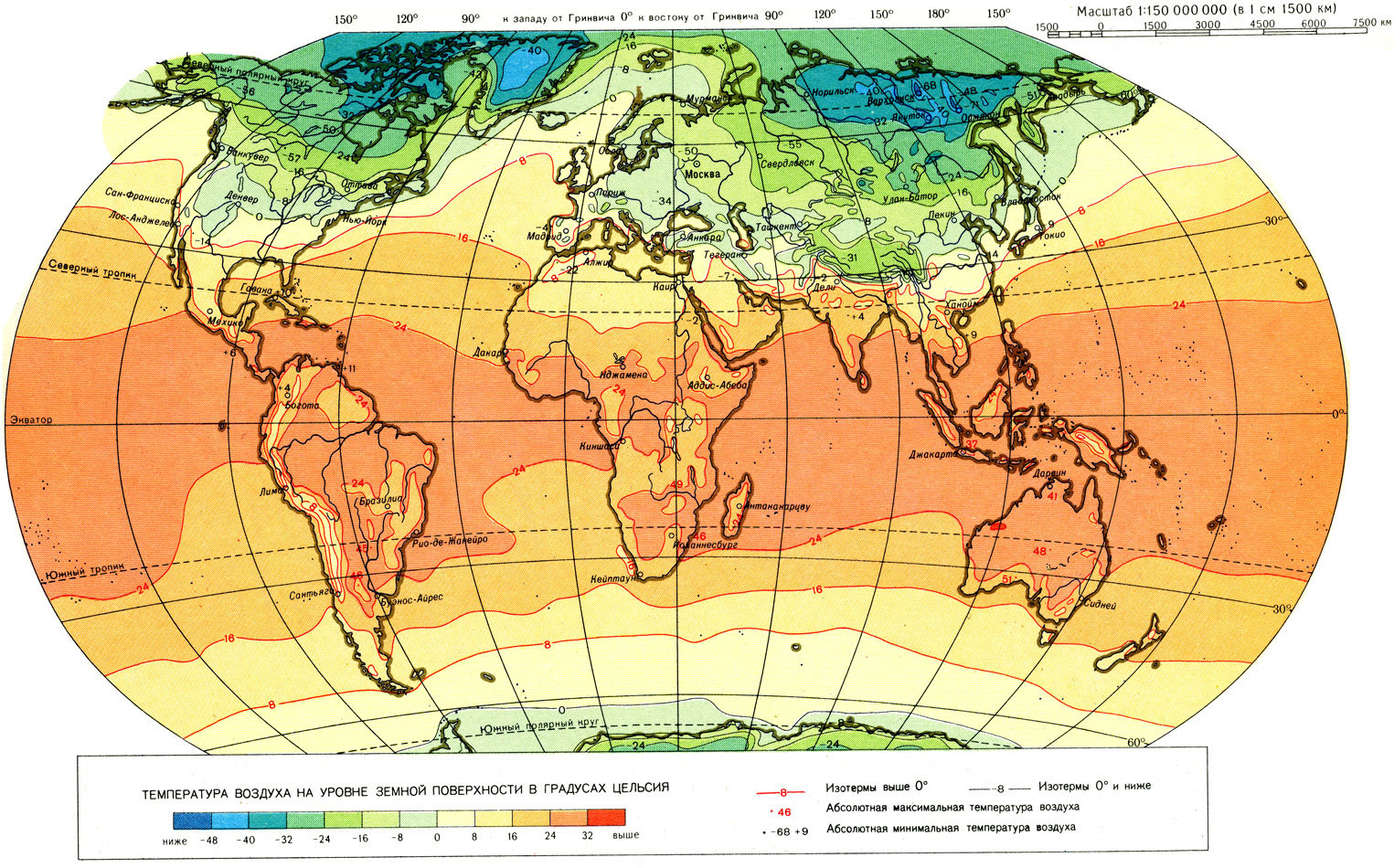
Obviously, the climate of each particular area imposes its limitations on the possibility of using the air selected from the atmosphere as a free cooling medium. First of all, it must be taken into account that it can not be used everywhere and secondly not always, moreover, the air masses throughout the planet are not very homogeneous, which is especially critical, in addition to the air temperature, of its humidity.
The ASHRAE Research Group (an abbreviation for the American Community of Heating and Cooling Ventilation Systems Engineers) has been working for many years to study the permissible range of air masses that can be used to cool equipment in data centers. The special subcommittee of this organization, which is directly involved in the study of data centers, provided a report in which the researchers reached an unambiguous conclusion. An increase in temperature in the server room by only a few degrees, in comparison with the most often recommended range of 18-24 degrees, can significantly expand the geography and time periods of cooling the data center equipment with atmospheric air, without additional mechanical manipulations with it. The main condition, which must have been met during the research,
But to what measure can this temperature be raised? After all, in the pursuit of profit, you can compromise expensive equipment - say skeptics of the revision of the rules. In this context, a study of engineers at Google has become very interesting. Having an enormous network infrastructure, for the company the issue of temperature increase became crucial for the effective conduct of its activities. In the first place, the researchers identified in the network link the “weak link” that is most at risk of failure. In this contest, with a serious margin, the "hard drives" took the palm. They are most exposed to high temperatures, in addition to this, they themselves are also powerful generators of excess heat. After the subject was determined, all kinds of tests with entire batches of discs were used.

Согласно представленной статистике низкие рабочие температуры(от 15оС до 30оС) могут стать не менее опасными для дисков нежели температурный режим 45оС и выше.
В этом контексте можно вспомнить то обстоятельство, что дата-центры это не только сетевое «железо», но также и живые люди, без которых это все оборудование не более чем высоко технологический металлолом. Согласно действующим, к примеру у нас санитарным нормам(ГОСТ30494—2011), максимально допустимая температура в публичных, не жилых помещениях, может достигать 31оС. К слову, этот допуск тоже существенно выше рекомендуемого температурного диапазона в серверных залах.
During its existence, the ASHRAE research team has already revised the recommended operating temperature range in server rooms three times and each time the review was in the direction of its increase. Chronology of these decisions 2004, 2008, 2011, apparently now the time has come, without violating the time step, again wait for another such decision. In addition to the temperature range, a rather important factor is the humidity of the air circulating in the data center. The relationship between moisture and air temperature is inextricable. Although now there are new data centers where these characteristics are placed under tight control, for many previously built data centers this is a significant reserve for modernization.
According to the prepared specification from ASHRAE, there are three modes of operation of the equipment with different physical properties of air masses:
Recommended: environmental conditions that ensure high performance and uninterrupted operation of the equipment.
Acceptable: the operating mode of the equipment is carried out at parameters not exceeding those recommended by the supplier.
Temporary: the equipment may work for some time under conditions significantly exceeding the parameters recommended by the supplier, however, during prolonged operation, environmental conditions can lead to equipment failure.
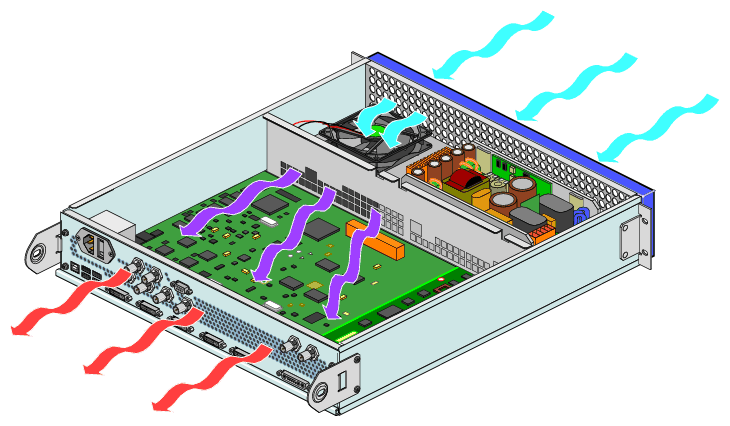
As follows from the last report of the mentioned group, the most efficient use of equipment consists precisely in a clearly planned alternation of all three operating modes.
In this light, it became a very interesting study by the University of Missouri, on the effect of low humidity on the occurrence of electrostatic discharges in server equipment. It is this circumstance that at the moment acts as the main limiting parameter with an extreme decrease in moisture in the circulating air. The study, as expected, showed a direct relationship between the increase in static charge in the “chains” with a decrease in atmospheric humidity, and the opposite result with an increase in humidity. The study proved that the lower threshold for air humidity in the server room can be a value in the range of 8-25%. It is at this moisture level that static electricity does not affect the operation of the equipment.
The relationship between temperature and humidity is quite simple: the colder the air, the more dry it is. In turn, excessively dry air, as already mentioned, can cause the accumulation of static charge in electrical circuits and, as a result, can lead to the failure of sensitive components. The latter circumstance brings understanding that the problem of excessively dry air may be encountered not only by data centers built in desert regions, with a hot, dry climate, but also operating in quite “comfortable” temperate latitudes. In the winter season, those operating the IT infrastructure of the service, not taking into account all the risks of air taken from the atmosphere, may receive emergency situations that threaten the failure of network equipment.
At the same time, engineers in their published work consider the problem particularly broadly, for example, knowing such a negative feature of dry air as the generation of a static charge, they immediately propose a set of measures to combat it. The main ally in this matter are materials that are not so prone to the accumulation of statics, as well as effective methods for its dispersion.
A successfully functioning example, where a full-scale air humidity control system is fully implemented, is the recently built Facebook data centers in Oregon and North Carolina. By controlling the humidity in the server rooms, network engineers were able to reach an average PUE of less than 1.1.

“Observing at the moment a slight decline in the pace of progress in the hardware of the IT infrastructure, we are witnessing a more intensive growth in the breadth. Over the past 20 years, the world has transformed so quickly that sometimes simple decisions that can make IT infrastructure components work much more efficiently are overlooked, ”the report says, and also summarizes“ Instead of building strongholds across the planet opposing the world around us, we must use each specific location as efficiently as possible, and we must also effectively use the inexhaustible supply of energy contained in the atmosphere. Naturally, on a small scale it’s not possible to use this kind of cooling system, but when it comes to giant data centers,


Obviously, the climate of each particular area imposes its limitations on the possibility of using the air selected from the atmosphere as a free cooling medium. First of all, it must be taken into account that it can not be used everywhere and secondly not always, moreover, the air masses throughout the planet are not very homogeneous, which is especially critical, in addition to the air temperature, of its humidity.
The ASHRAE Research Group (an abbreviation for the American Community of Heating and Cooling Ventilation Systems Engineers) has been working for many years to study the permissible range of air masses that can be used to cool equipment in data centers. The special subcommittee of this organization, which is directly involved in the study of data centers, provided a report in which the researchers reached an unambiguous conclusion. An increase in temperature in the server room by only a few degrees, in comparison with the most often recommended range of 18-24 degrees, can significantly expand the geography and time periods of cooling the data center equipment with atmospheric air, without additional mechanical manipulations with it. The main condition, which must have been met during the research,
But to what measure can this temperature be raised? After all, in the pursuit of profit, you can compromise expensive equipment - say skeptics of the revision of the rules. In this context, a study of engineers at Google has become very interesting. Having an enormous network infrastructure, for the company the issue of temperature increase became crucial for the effective conduct of its activities. In the first place, the researchers identified in the network link the “weak link” that is most at risk of failure. In this contest, with a serious margin, the "hard drives" took the palm. They are most exposed to high temperatures, in addition to this, they themselves are also powerful generators of excess heat. After the subject was determined, all kinds of tests with entire batches of discs were used.

Согласно представленной статистике низкие рабочие температуры(от 15оС до 30оС) могут стать не менее опасными для дисков нежели температурный режим 45оС и выше.
В этом контексте можно вспомнить то обстоятельство, что дата-центры это не только сетевое «железо», но также и живые люди, без которых это все оборудование не более чем высоко технологический металлолом. Согласно действующим, к примеру у нас санитарным нормам(ГОСТ30494—2011), максимально допустимая температура в публичных, не жилых помещениях, может достигать 31оС. К слову, этот допуск тоже существенно выше рекомендуемого температурного диапазона в серверных залах.
During its existence, the ASHRAE research team has already revised the recommended operating temperature range in server rooms three times and each time the review was in the direction of its increase. Chronology of these decisions 2004, 2008, 2011, apparently now the time has come, without violating the time step, again wait for another such decision. In addition to the temperature range, a rather important factor is the humidity of the air circulating in the data center. The relationship between moisture and air temperature is inextricable. Although now there are new data centers where these characteristics are placed under tight control, for many previously built data centers this is a significant reserve for modernization.
According to the prepared specification from ASHRAE, there are three modes of operation of the equipment with different physical properties of air masses:
Recommended: environmental conditions that ensure high performance and uninterrupted operation of the equipment.
Acceptable: the operating mode of the equipment is carried out at parameters not exceeding those recommended by the supplier.
Temporary: the equipment may work for some time under conditions significantly exceeding the parameters recommended by the supplier, however, during prolonged operation, environmental conditions can lead to equipment failure.

As follows from the last report of the mentioned group, the most efficient use of equipment consists precisely in a clearly planned alternation of all three operating modes.
The effect of low humidity on electrical circuits
In this light, it became a very interesting study by the University of Missouri, on the effect of low humidity on the occurrence of electrostatic discharges in server equipment. It is this circumstance that at the moment acts as the main limiting parameter with an extreme decrease in moisture in the circulating air. The study, as expected, showed a direct relationship between the increase in static charge in the “chains” with a decrease in atmospheric humidity, and the opposite result with an increase in humidity. The study proved that the lower threshold for air humidity in the server room can be a value in the range of 8-25%. It is at this moisture level that static electricity does not affect the operation of the equipment.
Thermodynamics
The relationship between temperature and humidity is quite simple: the colder the air, the more dry it is. In turn, excessively dry air, as already mentioned, can cause the accumulation of static charge in electrical circuits and, as a result, can lead to the failure of sensitive components. The latter circumstance brings understanding that the problem of excessively dry air may be encountered not only by data centers built in desert regions, with a hot, dry climate, but also operating in quite “comfortable” temperate latitudes. In the winter season, those operating the IT infrastructure of the service, not taking into account all the risks of air taken from the atmosphere, may receive emergency situations that threaten the failure of network equipment.
At the same time, engineers in their published work consider the problem particularly broadly, for example, knowing such a negative feature of dry air as the generation of a static charge, they immediately propose a set of measures to combat it. The main ally in this matter are materials that are not so prone to the accumulation of statics, as well as effective methods for its dispersion.
A successfully functioning example, where a full-scale air humidity control system is fully implemented, is the recently built Facebook data centers in Oregon and North Carolina. By controlling the humidity in the server rooms, network engineers were able to reach an average PUE of less than 1.1.

“Observing at the moment a slight decline in the pace of progress in the hardware of the IT infrastructure, we are witnessing a more intensive growth in the breadth. Over the past 20 years, the world has transformed so quickly that sometimes simple decisions that can make IT infrastructure components work much more efficiently are overlooked, ”the report says, and also summarizes“ Instead of building strongholds across the planet opposing the world around us, we must use each specific location as efficiently as possible, and we must also effectively use the inexhaustible supply of energy contained in the atmosphere. Naturally, on a small scale it’s not possible to use this kind of cooling system, but when it comes to giant data centers,

