Remote user experience: Windows Server 2012R2 RDS and Azure RemoteApp
- Tutorial
Based on a technical webinar, Microsoft solutions for remote users are reviewed, the following topics are considered:
• Building a terminal service based on Windows Server 2012R2.
• Building and using a virtual desktop system.
• Building and using a virtual desktop system based on Azure RemoteApp.
Decoding and recording a webinar under the cut.
Today we’ll talk with you about such a thing as remote user work. Windows Server 2012 has such RDS technology, we’ll talk about it in detail today, and also consider the functionality in Azure RemoteApp.
The plan of our event. We will talk about licensing, about those business tasks that can be solved with the help of the sessions given, we will talk on what basis all this is built, how to manage it all, what RemoteApp is. We will answer the question of how RDS differs from VDI and look live at the technologies that we will talk about.
So, Windows Server 2012 and its server role RDS. Licensing - RDS is included in 2 editions of both the standard and the data center. As we know, Microsoft made it absolutely identical in functionality, they differ in their work with virtualization.
What do we need for RDS?First of all, Server Standart or Datacenter licenses. Do not forget also that the number of processors is taken into account, now for each license there are 2 physical processors. We also need Call licenses for users, as well as RDS licenses, for the ability to connect terminal sessions to a terminal server. In addition, I have not indicated here, I often get questions: some people build the architecture of the terminal server in such a way that one version of the office is installed on the terminal server, and the administrator believes that this is enough to connect all users of the organization. In fact, this is not so, this is a big mistake. Yes, the office is installed in one copy, but you need to buy so many licenses for licenses, so many users or devices are planned to be connected to our server. RDS - a new generation of terminal servers,

Business tasks.The main idea is to prepare a platform that will provide access to either the desktop or applications for all users of our organization. Most often it looks like this. More than once I had to install this server in different organizations - this is most popular in banks and government agencies, because when we, for example, deploy some branch, somewhere in the outback, we establish some kind of branch. Then there is no question of maximum power. It is about ensuring that people timely and efficiently fulfill their task. And for this, as practice shows, it is enough to have such a device as a thin client. Due to this, users connect to RDS, set up a terminal session, log in to the server and work at its capacities, and perform its business tasks. The same goes for government agencies,
What is RDS? It allows us to centrally manage resources, centrally and controlledly provide applications and data for users. In addition, RDS technology implies 2 possible implementations. We will look at an example when we will set, I will show where this role is put.
Type 1 - session-based technology. When a user connects to this server, opens a remote desktop and logs in under his session, under his user.
Type 2 - virtual desktop technology, that is, using VDI / technology
These are 2 parts of one server. In addition, RDS can provide quick access to the workplace. Why? We are not attached to the device. We can connect to the portal, connect to the server and do our job. It is possible to ensure continuous operation of the user - no matter where he is: at his workplace in the office, on a business trip, or even on vacation.
What new products do we have? Updated work with RomoteFX technology, that is, in the RDS server 2012 and 2012R2 updated work with graphics. We have optimized streaming data, in addition, DirectX 11 is supported. To whom this aspect is important, it all works. As we know, these very things were negative reviews on previous versions of the system.
Using RDS, we get a single entry point. The user logged in to our domain, and gets access to all our resources. RDS implements USB redirection, and USB both on the device on which we are conducting the session and to the server.
As we know, Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2 works fine with the SMB 3.0 protocol. This affected the RDS server in the same way, and we can store disks for storing user data on the SMB and RGCDSun protocols. In addition, since this technology is implemented in server 2012 and 2012R2, this service is easily manageable. That is, we have a bookmark in the manager, you and I once considered, thanks to which, the management of the RDS server becomes intuitive, however, like all the tools implemented in winserver 2012.
And of course, this service provides high availability capabilities when the work of our users will not depend on the operation of only one server.
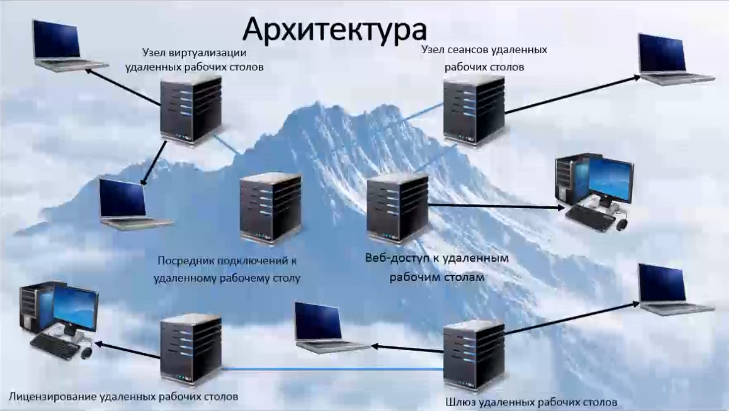
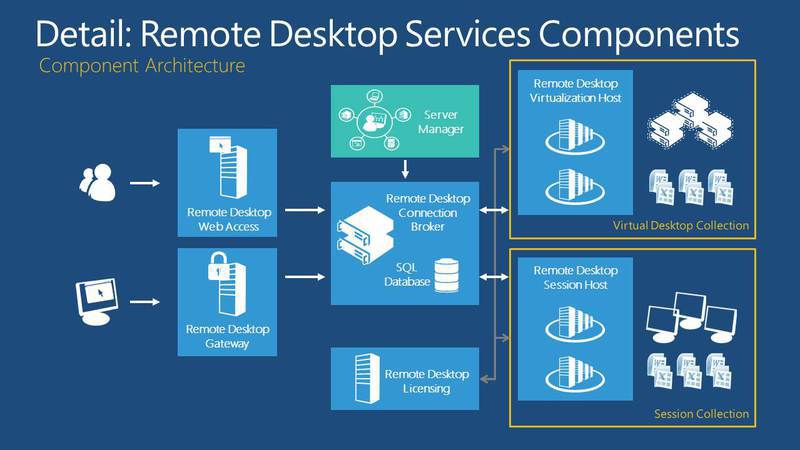
What is RDS based on? It is built on the basis of several roles, which can be configured both on different servers, and choose a simple installation at the time of installation, installing most roles on a single server.
What are the main roles we can highlight here?
Remote Desktop Connection broker. He is engaged in connecting the client device to remote applications RemoteApp as well as desktops based on sessions, or to virtual desktops, depending on which technology we built RDS on.
In addition, we have a role that provides web access to remote desktops. Its mission is to provide resources through a web browser. In addition, we have a remote desktop session host — this role allows you to host remote applications or session-based desktops on the server. We have a remote desktop virtualization node. On this node, this is our Hyper-V server, on which we deploy all the virtual machines that all users will be able to access, using VDI technology.
The latter is a remote desktop gateway, an intermediary between clients from an external network and a collection of sessions on the internal network and applications. The gateway is security, our service is absolutely safe. And due to the fact that RDS in 2012 and 2012R2 becomes more flexible, absolutely all the shortcomings that were earlier worked out. Now this service is easily implemented for huge, large-scale projects, for large corporations. Previously, some questions arose.

So, when we connect as a user to our RDS server, we often had several questions. First of all: how to manage it all? I will show you the control, it is very simple and intuitive for any user here. There are no difficulties here, but it would be possible to single out such parameters that will allow administrators primarily to save resources and ensure the quality work of their users.
We can limit, set the end time of a disconnected session. This parameter specifies the time after which the server ends the disconnected session. If the user has disconnected for some reason, this is most often applicable in places where communication is unstable. If during the specified time the user is connected back, he gets into his own session, that is, all the resources with which he works, they are active, he will connect and will continue to work. If the time is up, the server deletes all temporary user files and cancels the entire session.
In addition, we can limit the activity, the duration of the session. Why is this needed? Now the tendency is widespread when companies struggle with the fact that users work too long, “work must be at work”, etc. If this principle is respected, then it can be very easily established by the rules: we set the maximum user time on the RDS server. Most often, this time put a little more.
Limit an idle session. If for some time the user has not performed any actions, then it is disconnected. A useful thing: very often they encounter sessions hanging, the user forgot about them, and the server load is on, and other users lack power.
When setting all these settings, you must remember thatusers really do not like when their session is interrupted . Therefore, it is advisable to conduct an analysis, audit, collect all the wishes, and on the basis of this set all these parameters.
RDS server allows now to provide a separate disk for the user. That is, in the settings of the RDS server, in the parameters you can specify the place where the virtual disk for each user will be stored.
Virtual disk- this is a new "feature", which is designed to eliminate the outdated service of remote profiles, roaming profiles. Here, for each user, it is possible to create a limited VHDD-drive, it will be placed along the path that you specify. This disk will connect to the user using its settings. Using a redirected profile, folder redirection, we can implement for each user his own settings, his profile.
Personally, I recommend implementing a file server when deploying an IT infrastructure system in all my projects. This allows you to create a Home folder for all users, and we can connect this folder as a disk when users log in using group policies. This is another option for providing a drive for users.
We considered the first possibility when a user logs in with a separate session connecting to his remote desktop, and uses the server as his working machine. What he has on his desktop, he uses only as a device to connect.
The second implementation of the RDS server. Remote applications. This is the portal on which the user logs in and sees those applications that are accessible to him, with which he can work.
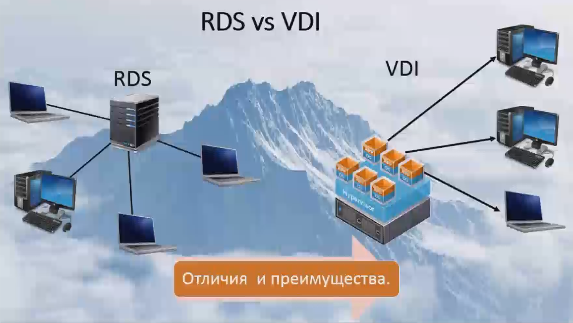
Very often I have heard the question: how is RDS different from VDI?
The question was correct until we had Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2, where VDI is included in RDS. If we are talking about the difference in connections at the session and virtual desktop levels, then in the first case we connect devices directly to the server, log in as a remote user to the remote desktop, we simply work on the server with its own profile. What are the dangers? In the event that a user obtains administrator rights, no one is safe from this; there is the possibility of server infection, or harm to the entire organization, to all users.
When using VDI, each user works on his own virtual machine. Therefore, any harm will only be done to a specific virtual machine, using VDI technology, we can quickly raise a “fallen” virtual machine. However, we do not harm our organization, and all users continue to work. RDS is a critical server, so you need to be very careful about planning for its use. There are many companies where this is implemented, companies that can give you advice on its implementation.

We will move from local services to what we now have in the clouds.
Let's consider how the RDS technology is implemented now in cloud infrastructures. Of course, we'll talk about Microsoft Azure - it's a Microsoft cloud. One of its functions is to provide access to remote applications. Azure is a business designer. You put a deposit on the portal, on your personal account, and when using this or that technology, whether you need it or not, you decide, and money is withdrawn from your account for using the services. As you remember, there is a calculator there - it will show the cost of all the resources used, and you can estimate the budget before you start using it.
In addition, it is possible to use the trial version. You can already use the services, see how they work, even before they are purchased. You can look at all the features for free.
We will now see Microsoft Azure RemoteApp. Provides universal access to all applications, secure access, and, most interestingly, it will be access from anywhere in the world.
This technology allows us to use it as templates that already exist - these are the most frequent applications that we use through the terminal session: office applications + some things that we have on the server, maybe a calculator, a graphical editor, etc.
What does it look like?
The RDS server that we will work with is located in the virtual infrastructure. This is the question of whether it is possible to implement an RDS server in a virtual infrastructure? - yes you can. Connect to the RDS server. The server manager has a very simple management.
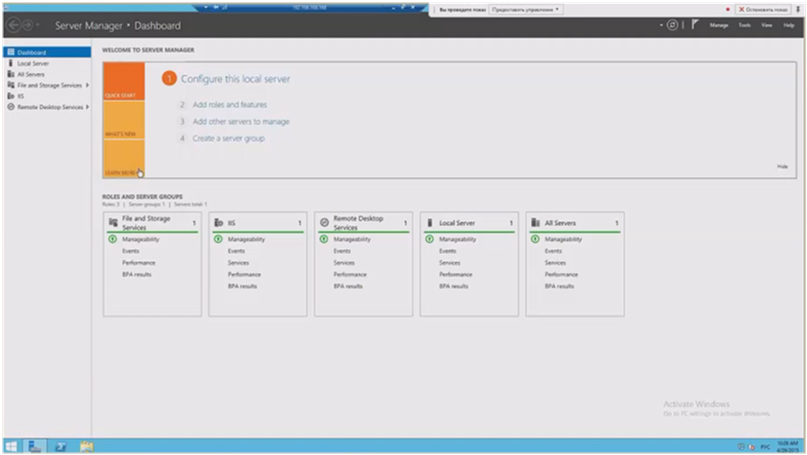
I have this server implemented on the basis of sessions. Everything is very simple here, I can see the settings for all my roles: how they are implemented, on the basis of what they are implemented, which server is responsible for each role, etc. I can add a new server with 1-2 clicks if I need it. I have collections based on sessions. I have openly published several applications.
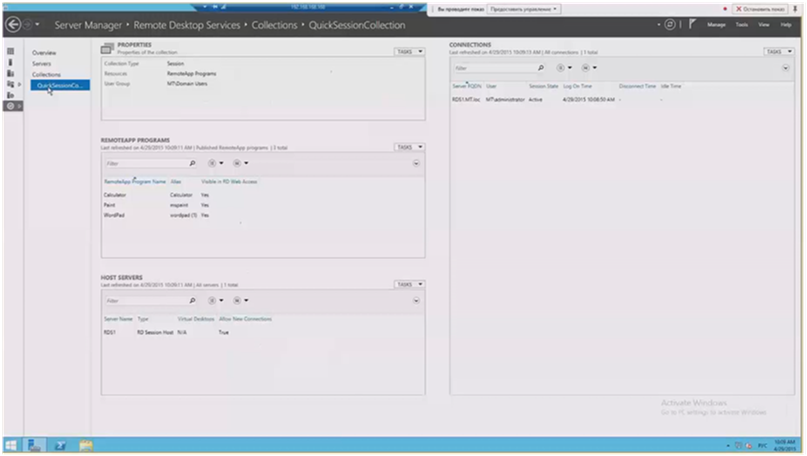
I can provide access to the collection of applications to certain user groups. Here there are those management parameters that we talked about, here they are easily configured: the path to the disk, delays in disconnecting sessions, conditions for disconnecting sessions, etc. I can publish the applications that I need by selecting their checkmarks.
Now a demonstration (with 24 minutes in recording )
Let's see the session option.If I connect to this session with the help of different users, then I can configure these users with their rights, how they will see the server itself, the server settings for them, the applications with which they will work. I can configure security as I need it. All options: default applications, desktop, we can all do this. We also see a second user who, for example, does not even have rights to see the start menu, if, for example, he has such a restriction in rights. By this, I wanted to show that the administrator has the ability to flexibly configure terminal sessions for different users. To make it simple and as safe as possible so that the user uses only what he needs to work.
Let's see the implementation of RemoteApp.I enter a line for web access, we can take it either by name or by IP address. We get to the portal, it looks standard for everyone. It published those applications that the user can run on his local workstation. After we open the list of applications installed on the server, we can select the ones that we want to publish for the user. Thus, we can publish different application groups for different users, for different user groups: for different departments, for example. And do not bother installing any local applications. Once deployed - and all users get access. This practice is very widely used especially in international companies, when offices located in different countries use VPNs and gain access to the main office, the main data center,
Now let's look at Azure . We go to the portal azure.microsoft.com. Benefits of using RemoteApp through Azure. We do not spend resources on publishing, on supporting the work of our applications: everything is implemented in the cloud. Access from everywhere, the main thing is that there is Internet access. When you enter the portal you see all the services that are. Today we need the RemoteAPP service. In the lower left corner there is a “create” button and here it is easy and simple to create a collection, just enter the name of our collection and select the type of template that we have. By default, we have 2 types of templates: office and applications that we have on the server. But in addition, we have the opportunity to upload our templates here to deploy our own applications - for this you need to connect azure to your network.
On management.I have deployed 2 collections: office and windows. Their access to users can be configured through the corresponding tab, where I need to specify just the username. In the same way as in the local RDS server, we have the ability to publish applications, or you can remove the publication that is. Everything works the same as in the local RDS server.
With regard to work with this service. To use it you need to install an agent. It will allow us to connect to the Azure RemoteApp service and use the programs that we already have. On the portal, opposite each of my collections, my templates, there will be a link to the portal where I will be asked to download the agent to use Azure RemoteApp in my local infrastructure.
Azure RemoteAppIs an application for local access to applications for users. I can install this application at once to all users who need applications.
The functionality that most companies need to complete their work has already been implemented in Azure - we can already use this business tool.
We have implemented a terminal server in the cloud. To deploy a new branch, you should try this tool. Since we have in this case:
- there is no need to allocate your computing power,
- there is no need to allocate administrators for support and configuration.
We just create collections of applications, and add users to them, to whom these applications will be available.
Based on customer experience- they are pleased with this decision, I have not heard any negative reviews. I urge you to take advantage of these new features. Or at least try them if you use your terminal servers.
Having seen the work of Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2, we saw how much everything became simpler, intuitively clear and accessible. Now there is no difficulty in implementing this solution - it can be done in one day for one organization.
I think that Azure RemoteApp is quite interesting. In the future, if there is interest, we will upload our templates and show a hybrid implementation when we can use one or the other resources, showing how much this application is in demand.
Thank you, I look forward to seeing you at our next webinars. You can also voice your wishes, topics that we have not taken into account and you would like to dwell on them in more detail.
Recording a webinar.
We invite you on May 29 to the next free webinar in this series, with the theme: “Office 365. Overview. The work of SharepointOnline users. Yammer . " From 09.30 to 11.00 (in Kiev). To register, please send an application to training@muk.com.ua.
Distribution of Microsoft solutions Microsoft
training courses
MUK-Service - all types of IT repair: warranty, non-warranty repair, sale of spare parts, contract service
• Building a terminal service based on Windows Server 2012R2.
• Building and using a virtual desktop system.
• Building and using a virtual desktop system based on Azure RemoteApp.

Decoding and recording a webinar under the cut.
Today we’ll talk with you about such a thing as remote user work. Windows Server 2012 has such RDS technology, we’ll talk about it in detail today, and also consider the functionality in Azure RemoteApp.
The plan of our event. We will talk about licensing, about those business tasks that can be solved with the help of the sessions given, we will talk on what basis all this is built, how to manage it all, what RemoteApp is. We will answer the question of how RDS differs from VDI and look live at the technologies that we will talk about.
So, Windows Server 2012 and its server role RDS. Licensing - RDS is included in 2 editions of both the standard and the data center. As we know, Microsoft made it absolutely identical in functionality, they differ in their work with virtualization.
What do we need for RDS?First of all, Server Standart or Datacenter licenses. Do not forget also that the number of processors is taken into account, now for each license there are 2 physical processors. We also need Call licenses for users, as well as RDS licenses, for the ability to connect terminal sessions to a terminal server. In addition, I have not indicated here, I often get questions: some people build the architecture of the terminal server in such a way that one version of the office is installed on the terminal server, and the administrator believes that this is enough to connect all users of the organization. In fact, this is not so, this is a big mistake. Yes, the office is installed in one copy, but you need to buy so many licenses for licenses, so many users or devices are planned to be connected to our server. RDS - a new generation of terminal servers,

Business tasks.The main idea is to prepare a platform that will provide access to either the desktop or applications for all users of our organization. Most often it looks like this. More than once I had to install this server in different organizations - this is most popular in banks and government agencies, because when we, for example, deploy some branch, somewhere in the outback, we establish some kind of branch. Then there is no question of maximum power. It is about ensuring that people timely and efficiently fulfill their task. And for this, as practice shows, it is enough to have such a device as a thin client. Due to this, users connect to RDS, set up a terminal session, log in to the server and work at its capacities, and perform its business tasks. The same goes for government agencies,
What is RDS? It allows us to centrally manage resources, centrally and controlledly provide applications and data for users. In addition, RDS technology implies 2 possible implementations. We will look at an example when we will set, I will show where this role is put.
Type 1 - session-based technology. When a user connects to this server, opens a remote desktop and logs in under his session, under his user.
Type 2 - virtual desktop technology, that is, using VDI / technology
These are 2 parts of one server. In addition, RDS can provide quick access to the workplace. Why? We are not attached to the device. We can connect to the portal, connect to the server and do our job. It is possible to ensure continuous operation of the user - no matter where he is: at his workplace in the office, on a business trip, or even on vacation.
What new products do we have? Updated work with RomoteFX technology, that is, in the RDS server 2012 and 2012R2 updated work with graphics. We have optimized streaming data, in addition, DirectX 11 is supported. To whom this aspect is important, it all works. As we know, these very things were negative reviews on previous versions of the system.
Using RDS, we get a single entry point. The user logged in to our domain, and gets access to all our resources. RDS implements USB redirection, and USB both on the device on which we are conducting the session and to the server.
As we know, Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2 works fine with the SMB 3.0 protocol. This affected the RDS server in the same way, and we can store disks for storing user data on the SMB and RGCDSun protocols. In addition, since this technology is implemented in server 2012 and 2012R2, this service is easily manageable. That is, we have a bookmark in the manager, you and I once considered, thanks to which, the management of the RDS server becomes intuitive, however, like all the tools implemented in winserver 2012.
And of course, this service provides high availability capabilities when the work of our users will not depend on the operation of only one server.

What is RDS based on? It is built on the basis of several roles, which can be configured both on different servers, and choose a simple installation at the time of installation, installing most roles on a single server.
What are the main roles we can highlight here?
Remote Desktop Connection broker. He is engaged in connecting the client device to remote applications RemoteApp as well as desktops based on sessions, or to virtual desktops, depending on which technology we built RDS on.
In addition, we have a role that provides web access to remote desktops. Its mission is to provide resources through a web browser. In addition, we have a remote desktop session host — this role allows you to host remote applications or session-based desktops on the server. We have a remote desktop virtualization node. On this node, this is our Hyper-V server, on which we deploy all the virtual machines that all users will be able to access, using VDI technology.
The latter is a remote desktop gateway, an intermediary between clients from an external network and a collection of sessions on the internal network and applications. The gateway is security, our service is absolutely safe. And due to the fact that RDS in 2012 and 2012R2 becomes more flexible, absolutely all the shortcomings that were earlier worked out. Now this service is easily implemented for huge, large-scale projects, for large corporations. Previously, some questions arose.

So, when we connect as a user to our RDS server, we often had several questions. First of all: how to manage it all? I will show you the control, it is very simple and intuitive for any user here. There are no difficulties here, but it would be possible to single out such parameters that will allow administrators primarily to save resources and ensure the quality work of their users.
We can limit, set the end time of a disconnected session. This parameter specifies the time after which the server ends the disconnected session. If the user has disconnected for some reason, this is most often applicable in places where communication is unstable. If during the specified time the user is connected back, he gets into his own session, that is, all the resources with which he works, they are active, he will connect and will continue to work. If the time is up, the server deletes all temporary user files and cancels the entire session.
In addition, we can limit the activity, the duration of the session. Why is this needed? Now the tendency is widespread when companies struggle with the fact that users work too long, “work must be at work”, etc. If this principle is respected, then it can be very easily established by the rules: we set the maximum user time on the RDS server. Most often, this time put a little more.
Limit an idle session. If for some time the user has not performed any actions, then it is disconnected. A useful thing: very often they encounter sessions hanging, the user forgot about them, and the server load is on, and other users lack power.
When setting all these settings, you must remember thatusers really do not like when their session is interrupted . Therefore, it is advisable to conduct an analysis, audit, collect all the wishes, and on the basis of this set all these parameters.
RDS server allows now to provide a separate disk for the user. That is, in the settings of the RDS server, in the parameters you can specify the place where the virtual disk for each user will be stored.
Virtual disk- this is a new "feature", which is designed to eliminate the outdated service of remote profiles, roaming profiles. Here, for each user, it is possible to create a limited VHDD-drive, it will be placed along the path that you specify. This disk will connect to the user using its settings. Using a redirected profile, folder redirection, we can implement for each user his own settings, his profile.
Personally, I recommend implementing a file server when deploying an IT infrastructure system in all my projects. This allows you to create a Home folder for all users, and we can connect this folder as a disk when users log in using group policies. This is another option for providing a drive for users.
We considered the first possibility when a user logs in with a separate session connecting to his remote desktop, and uses the server as his working machine. What he has on his desktop, he uses only as a device to connect.

The second implementation of the RDS server. Remote applications. This is the portal on which the user logs in and sees those applications that are accessible to him, with which he can work.

Very often I have heard the question: how is RDS different from VDI?
The question was correct until we had Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2, where VDI is included in RDS. If we are talking about the difference in connections at the session and virtual desktop levels, then in the first case we connect devices directly to the server, log in as a remote user to the remote desktop, we simply work on the server with its own profile. What are the dangers? In the event that a user obtains administrator rights, no one is safe from this; there is the possibility of server infection, or harm to the entire organization, to all users.
When using VDI, each user works on his own virtual machine. Therefore, any harm will only be done to a specific virtual machine, using VDI technology, we can quickly raise a “fallen” virtual machine. However, we do not harm our organization, and all users continue to work. RDS is a critical server, so you need to be very careful about planning for its use. There are many companies where this is implemented, companies that can give you advice on its implementation.

We will move from local services to what we now have in the clouds.
Let's consider how the RDS technology is implemented now in cloud infrastructures. Of course, we'll talk about Microsoft Azure - it's a Microsoft cloud. One of its functions is to provide access to remote applications. Azure is a business designer. You put a deposit on the portal, on your personal account, and when using this or that technology, whether you need it or not, you decide, and money is withdrawn from your account for using the services. As you remember, there is a calculator there - it will show the cost of all the resources used, and you can estimate the budget before you start using it.
In addition, it is possible to use the trial version. You can already use the services, see how they work, even before they are purchased. You can look at all the features for free.

We will now see Microsoft Azure RemoteApp. Provides universal access to all applications, secure access, and, most interestingly, it will be access from anywhere in the world.
This technology allows us to use it as templates that already exist - these are the most frequent applications that we use through the terminal session: office applications + some things that we have on the server, maybe a calculator, a graphical editor, etc.
What does it look like?
The RDS server that we will work with is located in the virtual infrastructure. This is the question of whether it is possible to implement an RDS server in a virtual infrastructure? - yes you can. Connect to the RDS server. The server manager has a very simple management.

I have this server implemented on the basis of sessions. Everything is very simple here, I can see the settings for all my roles: how they are implemented, on the basis of what they are implemented, which server is responsible for each role, etc. I can add a new server with 1-2 clicks if I need it. I have collections based on sessions. I have openly published several applications.

I can provide access to the collection of applications to certain user groups. Here there are those management parameters that we talked about, here they are easily configured: the path to the disk, delays in disconnecting sessions, conditions for disconnecting sessions, etc. I can publish the applications that I need by selecting their checkmarks.
Now a demonstration (with 24 minutes in recording )
Let's see the session option.If I connect to this session with the help of different users, then I can configure these users with their rights, how they will see the server itself, the server settings for them, the applications with which they will work. I can configure security as I need it. All options: default applications, desktop, we can all do this. We also see a second user who, for example, does not even have rights to see the start menu, if, for example, he has such a restriction in rights. By this, I wanted to show that the administrator has the ability to flexibly configure terminal sessions for different users. To make it simple and as safe as possible so that the user uses only what he needs to work.
Let's see the implementation of RemoteApp.I enter a line for web access, we can take it either by name or by IP address. We get to the portal, it looks standard for everyone. It published those applications that the user can run on his local workstation. After we open the list of applications installed on the server, we can select the ones that we want to publish for the user. Thus, we can publish different application groups for different users, for different user groups: for different departments, for example. And do not bother installing any local applications. Once deployed - and all users get access. This practice is very widely used especially in international companies, when offices located in different countries use VPNs and gain access to the main office, the main data center,
Now let's look at Azure . We go to the portal azure.microsoft.com. Benefits of using RemoteApp through Azure. We do not spend resources on publishing, on supporting the work of our applications: everything is implemented in the cloud. Access from everywhere, the main thing is that there is Internet access. When you enter the portal you see all the services that are. Today we need the RemoteAPP service. In the lower left corner there is a “create” button and here it is easy and simple to create a collection, just enter the name of our collection and select the type of template that we have. By default, we have 2 types of templates: office and applications that we have on the server. But in addition, we have the opportunity to upload our templates here to deploy our own applications - for this you need to connect azure to your network.
On management.I have deployed 2 collections: office and windows. Their access to users can be configured through the corresponding tab, where I need to specify just the username. In the same way as in the local RDS server, we have the ability to publish applications, or you can remove the publication that is. Everything works the same as in the local RDS server.
With regard to work with this service. To use it you need to install an agent. It will allow us to connect to the Azure RemoteApp service and use the programs that we already have. On the portal, opposite each of my collections, my templates, there will be a link to the portal where I will be asked to download the agent to use Azure RemoteApp in my local infrastructure.
Azure RemoteAppIs an application for local access to applications for users. I can install this application at once to all users who need applications.
The functionality that most companies need to complete their work has already been implemented in Azure - we can already use this business tool.
We have implemented a terminal server in the cloud. To deploy a new branch, you should try this tool. Since we have in this case:
- there is no need to allocate your computing power,
- there is no need to allocate administrators for support and configuration.
We just create collections of applications, and add users to them, to whom these applications will be available.
Based on customer experience- they are pleased with this decision, I have not heard any negative reviews. I urge you to take advantage of these new features. Or at least try them if you use your terminal servers.
Having seen the work of Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2, we saw how much everything became simpler, intuitively clear and accessible. Now there is no difficulty in implementing this solution - it can be done in one day for one organization.
I think that Azure RemoteApp is quite interesting. In the future, if there is interest, we will upload our templates and show a hybrid implementation when we can use one or the other resources, showing how much this application is in demand.
Thank you, I look forward to seeing you at our next webinars. You can also voice your wishes, topics that we have not taken into account and you would like to dwell on them in more detail.
Recording a webinar.
We invite you on May 29 to the next free webinar in this series, with the theme: “Office 365. Overview. The work of SharepointOnline users. Yammer . " From 09.30 to 11.00 (in Kiev). To register, please send an application to training@muk.com.ua.
Distribution of Microsoft solutions Microsoft
training courses
MUK-Service - all types of IT repair: warranty, non-warranty repair, sale of spare parts, contract service
