Squeeze out all the juices or use the Raspberry pi to its fullest
- From the sandbox
- Tutorial
Hello!
Down with the dull talk that this is my first post and all that. Perhaps I’ll better talk about how to squeeze out all the juices from a little baby called Raspberry PI (hereinafter RPI), priced at $ 35. I am 146.6% sure that there were already posts of this kind, and this post does not claim to be solid five . Rather, it’s just an introductory word about: "How I took up business for a couple of dull evenings." Actually, we get the final Raspberry PI which you can use:
For those who became interested, I ask for a cut (Attention! Traffic).
So, what is needed for all this:
We will also need some programs, PUTTY, WinSCP, XMing. So, we need everything that we plan to work without turning off / restarting the RPI, therefore assemblies like OpenELEC, RaspBMC, XBian can be excluded. We need XBMC to be “inside” our OS as a player, so we will do something like this. We will use Raspbian. You can download from of. site
Further everything is simple. Unzip the downloaded, connect the SD card to the computer, then we need the Win32DiskImager program . Install, run. We indicate the path to the .img file with the OS on board, then in the "Device" field, select our SD card from the list of carriers and click "Write". After that, in the dialog box that appears, select “Yes” and get ready for the first launch of RPI.
For RPI to work, we need a TV with an HDMI output, but in extreme cases, you can get by with the usual one. To do this, we need instead of an HDMI cable, a SCART-RCA cable and ordinary USB speakers with their own power! I think it’s clear what and where to stick. If everything went smoothly, we will see a window with the settings of our OS.
After the reboot, enter the username pi and the password that you made (by default raspberry). I recommend immediately changing the root password:
First of all, download WinSCP . Install, configure.
In the host name field, enter the RPI ip address, I have 192.168.1.100 (you can find out using Advanced IP Scaner, or through a router, I think it’s not worth explaining in detail how to do this). In the user name and password field, specify the data for authorization. It is best to use root, then Save. Then everything is simple, indicate the name, click the checkbox and OK. That’s it, now we are ready to proceed to the next step.
Actually trace. the step is to install X-Ming . We need it more for monitoring, well, and this will make our life easier in the future, since we will put Conky for monitoring and MySqlWorkbench for database administration (but this is rather just a whim) on the RPI. Those who do not need this can safely go to the next step.
Download, install. Installation parameters:
Jackdaw Non US keyboard Support
jackdaw XLaunnch wizard
jackdaw Run Unility
Normal PuTTY Link SSH client
In the properties of the XMing shortcut we prescribe
After that we cut and we can safely connect to the RPI via SSH, the main thing is to remind your SSH client to use X-11 Forwarding.
In PuTTY, go to Connections -> SSH -> X11 ->We enable X11 Forwarding
X display location - localhost: 10.0
Remote X11 authentification protocol - XDM-Authorization-1
Then the session settings themselves (Sessions)
HostName (or IP address) - 192.168.1.100 (your ip RPI) port 22
Connection type - SSH -> Click Save and connect. We launch the terminal and ...
All preparations are completed and I think we have come to the main point. Lyrical digression. Before I decided to do as we do, I installed OpenELEC and RaspBMC for myself. This did not suit me, because I had to restart the RPI to run either Raspbian or XBMC (in the case of OpenELEC), and with RaspBMC I could not even do something close. Although there may be craftsmen who say that I'm a fool, and all that. Move on. The description of this process is not mine, there were craftsmen who invented the wheel for us, I just put it into practice. In order:
We add the user from under whom it is planned to launch XBMC in the following groups ( audio video input dialout plugdev tty ) with the command:
Then, change the settings of the input group with the command:
The file should have:
Launch XBMC with the command:
Wait for the download and profit!
If you need to make XBMC Auto-start, then you need to edit / etc / default / xbmc and change ENABLED to 1:
Plugins that I have:
- repository.superrepo.org.frodo.al - A huge number of all sorts of additions to XBMC
- repository.seppius - Russian repository, with additions of "our" sites similar to LostFilm and Seasonvar and not only. You can find it for every taste
- repository.oneevil - ACEStream add-on service for XBMC and Torrenter add-on in this repository
- repository.nuismons - TSengine api
- plugin.watch.is.latest - Plugin for watch.is website (Invitation website !!)
- plugin.video.torrenter.1.1.5.5 - Plugin for streaming torrent movie playback, let's say.
You also need to install libTorrent in order to stream movies with LostFilm:
Все эти плагины можно спокойно найти в интернете, вдаваться в подробности настройки и установки я не буду.
Что бы заработали скреперы — необходимо в настройках TheMovieDB использовать не TMDB а IMDB. Не понял почему так, но после смены у меня заработали скреперы на поиске некоторых русских фильмов, однако некоторые все еще найти не может.
Он нам нужен для мониторинга за температурой, загрузкой CPU и тд. По порядку:
Затем создаем файл .conkyrc командой:
и вставляем туда:
Запускать командой:
Все настройки можно найти в интернете и настроить «на свой вкус».
The request for this item is not much to beat. This is not an instruction “ how it should be ”, it is an instruction “ how it works for me ”, constructive criticism of the case is welcomed if there are any additions or comments, I will take into account, and adapt myself for work.
Before installation, I recommend in the router settings (for example, my ADSL modem 192.168.1.1 - forward Virtual Rout (Port Forwarding) ports, forward 80 ports to 80 ports 192.168.1.100 (.100 I have Raspberry PI))
So, let's go. GIT:
Apache:
Now php5 with buns:
Rebutim Apache:
We check. We go in the browser on IP_malinki (in my example 192.168.1.100). If the inscription “It works!” Appeared, then I congratulate you, if not, please tryto turn it on and off first. For those who did not forward ports, you can check directly with the RPI. To do this, clings through SSH and start the browser:
Then enterto turn it on and off first.
Next, we check the performance of php5, create the file test.php:
We will make changes to it:
CTRL + X -> Y -> Enter, go to the link
To access phphmyadmin, you need to file /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
enter the following (it is only necessary before the Squeeze version, starting from version 6.0 this will be included in the package installation script
Restart Apache:
Check, go to the browser
I think the installation of the web server is complete. About setting up DNS in bind9 and VIrtual Hosts in Apache will be in another article. I will also say that for myself I installed RhodeCode on the RPI as well and wanted to put some sort of Issue tracker. The choice fell on YouTrack from JetBrain, but the Java machine loads Raspberry heavily, so it did not bother. Since I use phpstorm - here is a small digression about How to make friends phpstorm from our database on RPI :
We cut PHPStorm go to DataBase (button on the left) -> new -> DataBase Source
Database URL - address and port of the remote machine, as well as the database name
User - database username
Password - database user password
SSH tunnel will be opened on localhost and port - the port must be free on the machine with which you need to connect phpstorm to mysql on the remote machine.
We stick the flash drive into the RPI, enter the command:
Result:
We look, remember, TR16GB, type “ntfs”, install ntfs support:
Create a directory where we will mount our flash drive:
Open the file:
We add there:
Where is the UUID, this is the unique id of our flash drive, which we looked at by the team
We proceed to the installation. Just in case, we will update everything that we have done here:
Install the Samba server:
Now open /etc/samba/smb.conf and enter it there:
Where is a workgroup, this is a workgroup, most likely you have WORKGROUP. Access to the server will be without authorization. If you want it to when you connect it was necessary to ask for a password, instead
I "mapped" a network drive for myself, for convenience. You can upload movies directly to your RPI from your computer and watch it already on a huge TV set, for example, in your living room.
First we put rTorrent
Then create a folder on our flash drive, here we will download our films:
And also the folder where we will store download information:
Then we go to the user's home folder, under which rtorrent will work, I have this
Here we create the file ".rtorrent.rc", these are the settings of our rtorrent:
Description of settings can be found here . Set up startup and install screen for rtorrent to work in the background:
Let's edit the script to work correctly:
Configure Apache, enable the modules:
Edit the file
It's time to put the web-face for our rtorrent. I chose ruTorrent, because she is unpretentious and in Russian. First, put Subversion:
Now load ruTorrent:
Set the rights to the folder:
It remains to check the operation of our web-muzzle, go to the browser
Well, that’s all. Now we have a ready-to-work RPI for web developers who can put their favorite TV show on the night from Friday to Saturday and watch this whole thing on a huge TV set on the couch the next morning. Thanks for attention.
PS I want to apologize for the lack of some links to third-party resources, the material of which I was guided by since I did this for a long time, and published only now.
Down with the dull talk that this is my first post and all that. Perhaps I’ll better talk about how to squeeze out all the juices from a little baby called Raspberry PI (hereinafter RPI), priced at $ 35. I am 146.6% sure that there were already posts of this kind, and this post does not claim to be solid five . Rather, it’s just an introductory word about: "How I took up business for a couple of dull evenings." Actually, we get the final Raspberry PI which you can use:
- as a home web server (if you are some kind of PHP developer, and you are not alien to fun);
- as a multimedia set-top box with the popular XBMC Media Center (
or a super-duper-cool-shnyazhkato the TV for a modest $ 1800); - and like a night torrent rocking chair, with a web-based interface (for the lazy);
For those who became interested, I ask for a cut (Attention! Traffic).
Training
So, what is needed for all this:
- Raspberry PI model B
- 8GB SD card, speed should be high. (Grades 6 and 10 are suitable)
- USB Flash card, in order not to clog the already small SD card memory with movies that you want to watch
- HDMI or SCART-RCA cable
- Power supply, any mini USB charger with a 5V output and a current of up to 2A, with a MicroUSB output or MicroUSB adapter for connecting to a computer is suitable
- Some free time
- Straight arms (in any case, I definitely needed them)
Photo of my model



We will also need some programs, PUTTY, WinSCP, XMing. So, we need everything that we plan to work without turning off / restarting the RPI, therefore assemblies like OpenELEC, RaspBMC, XBian can be excluded. We need XBMC to be “inside” our OS as a player, so we will do something like this. We will use Raspbian. You can download from of. site
Further everything is simple. Unzip the downloaded, connect the SD card to the computer, then we need the Win32DiskImager program . Install, run. We indicate the path to the .img file with the OS on board, then in the "Device" field, select our SD card from the list of carriers and click "Write". After that, in the dialog box that appears, select “Yes” and get ready for the first launch of RPI.
For RPI to work, we need a TV with an HDMI output, but in extreme cases, you can get by with the usual one. To do this, we need instead of an HDMI cable, a SCART-RCA cable and ordinary USB speakers with their own power! I think it’s clear what and where to stick. If everything went smoothly, we will see a window with the settings of our OS.
Menu items with detailed descriptions and photos
- Expand filesystem - Expand the main partition to the entire SD card.
- Change User Password - Set the password for the user "pi" (the default password is "raspberry"). Password must be entered twice!
- Enable Boot to Desktop - Download / not load the graphical interface at startup. Turn off, because we don’t need it, but you can turn it on as a team
- Internationalization Options - The choice of location and language, there are 3 points:
- Add to Rastrack - Register the device in a common database. Skipping.
- Overclock - Overclocking the processor. The default frequency is 700 MHz, can be increased to 1000 MHz. Raspberry Pi can now officially overclock to 1 GHz and not lose the guarantee ( click! ). We set 1000 MHz, this will give us performance when working with XBMC.
- Advanced Options - Advanced settings. There is a trace. points:
Now press TAB, select FINISH.

- Expand filesystem - Expand the main partition to the entire SD card.
- Change User Password - Set the password for the user "pi" (the default password is "raspberry"). Password must be entered twice!
- Enable Boot to Desktop - Download / not load the graphical interface at startup. Turn off, because we don’t need it, but you can turn it on as a team
startx. After the selection, there are 2 more points: the first line is to load, the second line is not to load (there is a third line, but in this article we are not interested). - Internationalization Options - The choice of location and language, there are 3 points:
- Change Locale - Select a language, select "ru_RU.UTF-8 UTF-8".
- Change Timezone - Select a time zone, choose your own.
- Change Keyboard Layout - Keyboard settings. Leave it as it is.
- Add to Rastrack - Register the device in a common database. Skipping.
- Overclock - Overclocking the processor. The default frequency is 700 MHz, can be increased to 1000 MHz. Raspberry Pi can now officially overclock to 1 GHz and not lose the guarantee ( click! ). We set 1000 MHz, this will give us performance when working with XBMC.
- Advanced Options - Advanced settings. There is a trace. points:
- Overscan - If you have a wide black bar along the edge of the image, you must turn off this mode.
- Hostname - The network name of the RPI. Leave by default.
- Memoy Split - Allocation of video memory for the GPU. We put 128.
- SSH - SSH Access. Turn on, because Further we will configure everything on SSH. I got some errors.
Initial ssh key generation still running. Please wait and try again.
It is treated with simple actions after a reboot:sudo rm /var/log/regen_ssh_keys.logsudo rm /etc/ssh/ssh_host*sudo ssh-keygen -A - Update - Update the OS. This requires internet access.
- About raspi-config - Skip, not interesting.
Now press TAB, select FINISH.
After the reboot, enter the username pi and the password that you made (by default raspberry). I recommend immediately changing the root password:
sudo passwd root
Configuring SSH access to the RPI file system (from Windows)
First of all, download WinSCP . Install, configure.
In the host name field, enter the RPI ip address, I have 192.168.1.100 (you can find out using Advanced IP Scaner, or through a router, I think it’s not worth explaining in detail how to do this). In the user name and password field, specify the data for authorization. It is best to use root, then Save. Then everything is simple, indicate the name, click the checkbox and OK. That’s it, now we are ready to proceed to the next step.
Xming: X-Server for Windows
Actually trace. the step is to install X-Ming . We need it more for monitoring, well, and this will make our life easier in the future, since we will put Conky for monitoring and MySqlWorkbench for database administration (but this is rather just a whim) on the RPI. Those who do not need this can safely go to the next step.
Download, install. Installation parameters:
Jackdaw Non US keyboard Support
jackdaw XLaunnch wizard
jackdaw Run Unility
Normal PuTTY Link SSH client
In the properties of the XMing shortcut we prescribe
путь_до_программы\Xming.exe :10 -clipboard -multiwindowAfter that we cut and we can safely connect to the RPI via SSH, the main thing is to remind your SSH client to use X-11 Forwarding.
In PuTTY, go to Connections -> SSH -> X11 ->We enable X11 Forwarding
X display location - localhost: 10.0
Remote X11 authentification protocol - XDM-Authorization-1
Then the session settings themselves (Sessions)
HostName (or IP address) - 192.168.1.100 (your ip RPI) port 22
Connection type - SSH -> Click Save and connect. We launch the terminal and ...
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ lxterminal&
[1] 2997
pi@raspberrypi ~ $
Voila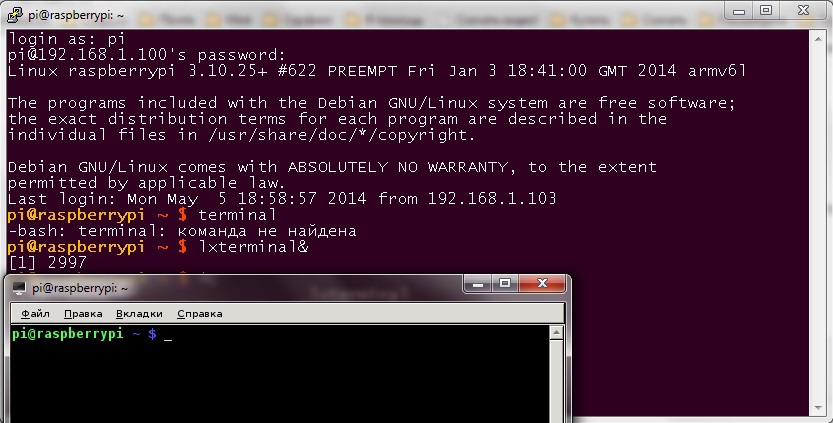

Install XBMC on Raspberry Pi under Raspbian
All preparations are completed and I think we have come to the main point. Lyrical digression. Before I decided to do as we do, I installed OpenELEC and RaspBMC for myself. This did not suit me, because I had to restart the RPI to run either Raspbian or XBMC (in the case of OpenELEC), and with RaspBMC I could not even do something close. Although there may be craftsmen who say that I'm a fool, and all that. Move on. The description of this process is not mine, there were craftsmen who invented the wheel for us, I just put it into practice. In order:
cd /etc/apt/sources.list.d/deb http://archive.mene.za.net/raspbian wheezy contrib
CTRL + X -> Y -> Enter
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-key 5243CDED
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install xbmc
We add the user from under whom it is planned to launch XBMC in the following groups ( audio video input dialout plugdev tty ) with the command:
sudo usermod -a -G имя_группы пользователь
Then, change the settings of the input group with the command:
sudo nano /etc/udev/rules.d/99-input.rules
The file should have:
SUBSYSTEM=="input", GROUP="input", MODE="0660"
KERNEL=="tty[0-9]*", GROUP="tty", MODE="0660"
Launch XBMC with the command:
xbmc-standalone
Wait for the download and profit!
Cry!
This is an already configured XBMC with plugins already installed, I will list below.

This is an already configured XBMC with plugins already installed, I will list below.
If you need to make XBMC Auto-start, then you need to edit / etc / default / xbmc and change ENABLED to 1:
ENABLED=1
Plugins that I have:
- repository.superrepo.org.frodo.al - A huge number of all sorts of additions to XBMC
- repository.seppius - Russian repository, with additions of "our" sites similar to LostFilm and Seasonvar and not only. You can find it for every taste
- repository.oneevil - ACEStream add-on service for XBMC and Torrenter add-on in this repository
- repository.nuismons - TSengine api
- plugin.watch.is.latest - Plugin for watch.is website (Invitation website !!)
- plugin.video.torrenter.1.1.5.5 - Plugin for streaming torrent movie playback, let's say.
You also need to install libTorrent in order to stream movies with LostFilm:
sudo apt-get install python-libtorrent
Все эти плагины можно спокойно найти в интернете, вдаваться в подробности настройки и установки я не буду.
Что бы заработали скреперы — необходимо в настройках TheMovieDB использовать не TMDB а IMDB. Не понял почему так, но после смены у меня заработали скреперы на поиске некоторых русских фильмов, однако некоторые все еще найти не может.
Клик!




Установка Conky
Он нам нужен для мониторинга за температурой, загрузкой CPU и тд. По порядку:
sudo apt-get install conky
Затем создаем файл .conkyrc командой:
sudo nano .conkyrc
и вставляем туда:
alignment top_left
background no
border_width 1
cpu_avg_samples 2
default_color white
default_outline_color white
default_shade_color white
double_buffer yes
draw_borders no
draw_graph_borders yes
draw_outline no
draw_shades no
use_xft yes
xftfont DejaVu Sans Mono:size=12
gap_x 5
gap_y 60
minimum_size 5 5
net_avg_samples 2
no_buffers yes
out_to_console no
out_to_stderr no
extra_newline no
own_window yes
own_window_class Conky
own_window_type desktop
stippled_borders 0
update_interval 1.0
uppercase no
use_spacer none
show_graph_scale no
show_graph_range no
TEXT
${color grey}Uptime:$color $uptime
${color grey}Frequency (in MHz):$color $freq
${color grey}Frequency (in GHz):$color $freq_g
${color grey}RAM Usage:$color $mem/$memmax - $memperc% ${membar 4}
${color grey}Swap Usage:$color $swap/$swapmax - $swapperc% ${swapbar 4}
${color grey}CPU Usage:$color $cpu% ${cpubar 4}
${color red}Temp: $color ${alignr 4}${color red}${acpitemp}°С$color
${color grey}Processes:$color $processes ${color grey}Running:$color $running_processes
$hr
${color grey}File systems:
/ $color${fs_used /}/${fs_size /} ${fs_bar 6 /}
${color grey}Networking:
Up:$color ${upspeed eth0} ${color grey} - Down:$color ${downspeed eth0}
$hr
${color grey}Name PID CPU% MEM%
${color lightgrey} ${top name 1} ${top pid 1} ${top cpu 1} ${top mem 1}
${color lightgrey} ${top name 2} ${top pid 2} ${top cpu 2} ${top mem 2}
${color lightgrey} ${top name 3} ${top pid 3} ${top cpu 3} ${top mem 3}
${color lightgrey} ${top name 4} ${top pid 4} ${top cpu 4} ${top mem 4}
Запускать командой:
conky
Все настройки можно найти в интернете и настроить «на свой вкус».
Клик!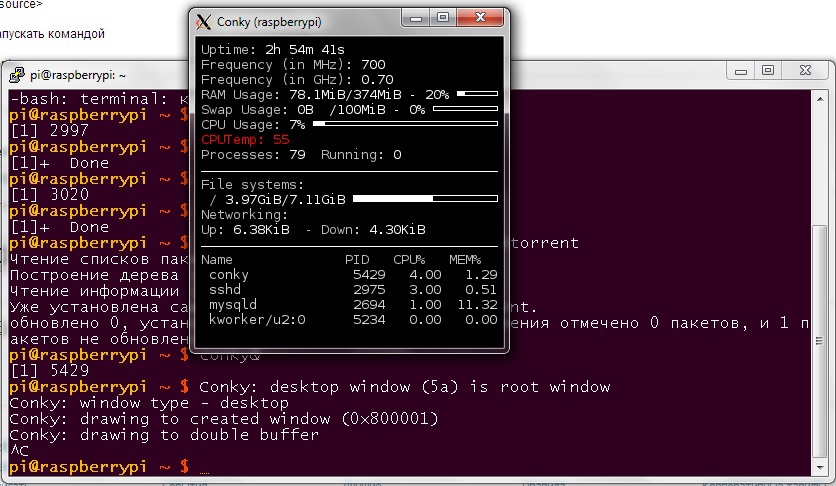

Установка и настройка WebServer-а Apache2.2, php5, mysql, phpmyadmin, mysql-workbench
The request for this item is not much to beat. This is not an instruction “ how it should be ”, it is an instruction “ how it works for me ”, constructive criticism of the case is welcomed if there are any additions or comments, I will take into account, and adapt myself for work.
Before installation, I recommend in the router settings (for example, my ADSL modem 192.168.1.1 - forward Virtual Rout (Port Forwarding) ports, forward 80 ports to 80 ports 192.168.1.100 (.100 I have Raspberry PI))
So, let's go. GIT:
sudo apt-get install git
Apache:
sudo apt-get install apache2 apache2-doc libapache2-mod-scgi
Now php5 with buns:
sudo apt-get install php5 libapache2-mod-php5 libapache2-mod-auth-mysql php5 php5-common php5-curl php5-mysql php-image-graph imagemagick
Rebutim Apache:
sudo service apache2 restart
We check. We go in the browser on IP_malinki (in my example 192.168.1.100). If the inscription “It works!” Appeared, then I congratulate you, if not, please try
midori&
Then enter
localhost/or localhost/apache2-default. If the inscription “It works!” Appeared, then I congratulate you, if not, please try /var/www/- daddy with your sites and scripts. /etc/php5/ и /etc/apache2/- here are the php5 and apache configs. Next, we check the performance of php5, create the file test.php:
sudo nano /var/www/phpinfo.php
We will make changes to it:
CTRL + X -> Y -> Enter, go to the link
IP_адрес_малины/test.php(if through RPI then localhost/test.php). If there is information about PHP5, then everything is fine. Next, put PHPMyAdmin:sudo apt-get install phpmyadmin
To access phphmyadmin, you need to file /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
enter the following (it is only necessary before the Squeeze version, starting from version 6.0 this will be included in the package installation script
/etc/apache2/conf.d/phpmyadmin.conf-> ../../phpmyadmin/apache.confautomatically):Include /etc/phpmyadmin/apache.conf
Restart Apache:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
Check, go to the browser
192.168.1.100/phpmyadmin (c RPI localhost/phpmyadmin). I think the installation of the web server is complete. About setting up DNS in bind9 and VIrtual Hosts in Apache will be in another article. I will also say that for myself I installed RhodeCode on the RPI as well and wanted to put some sort of Issue tracker. The choice fell on YouTrack from JetBrain, but the Java machine loads Raspberry heavily, so it did not bother. Since I use phpstorm - here is a small digression about How to make friends phpstorm from our database on RPI :
We cut PHPStorm go to DataBase (button on the left) -> new -> DataBase Source
Cry!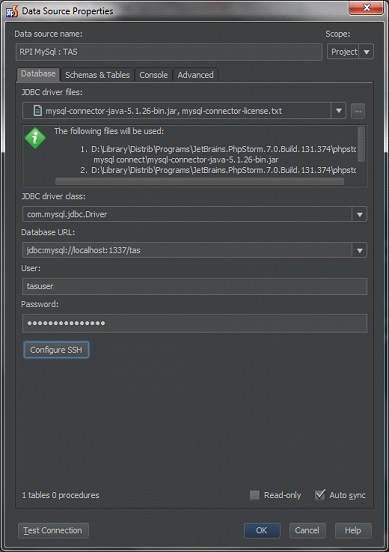

Database URL - address and port of the remote machine, as well as the database name
User - database username
Password - database user password
Cry!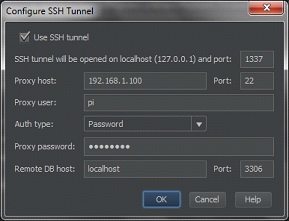

SSH tunnel will be opened on localhost and port - the port must be free on the machine with which you need to connect phpstorm to mysql on the remote machine.
Mount our USB flash drive
We stick the flash drive into the RPI, enter the command:
sudo blkid
Result:
/dev/mmcblk0p1: SEC_TYPE="msdos" LABEL="boot" UUID="993B-8922" TYPE="vfat"
/dev/mmcblk0p2: UUID="fc254b57-8fff-4f96-9609-ea202d871acf" TYPE="ext4"
/dev/sda: LABEL="TR16GB" UUID="D29807B898079A5D" TYPE="ntfs"
We look, remember, TR16GB, type “ntfs”, install ntfs support:
sudo apt-get install ntfs-3g
Create a directory where we will mount our flash drive:
sudo mkdir /mount/flash
Open the file:
sudo nano /etc/fstab
We add there:
"UUID="D29807B898079A5D" /mount/flash ntfs-3g rw,force,exec,users 0 0"
Where is the UUID, this is the unique id of our flash drive, which we looked at by the team
sudo blkidat the very beginning. Reboot RPI:sudo reboot
Install Samba
We proceed to the installation. Just in case, we will update everything that we have done here:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
Install the Samba server:
sudo apt-get install samba samba-common-bin
Now open /etc/samba/smb.conf and enter it there:
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
security = share
guest ok = yes
browseable = yes
[flash]
path = /mount/flash
writeable = yes
readonly = no
browseable = yes
guest ok = yes
Where is a workgroup, this is a workgroup, most likely you have WORKGROUP. Access to the server will be without authorization. If you want it to when you connect it was necessary to ask for a password, instead
security = share, and guest ok = yeswrite security = user. You also need to create a new user, enter the command sudo smbpasswd -a [имя], where [name] is the username. Save the config, reboot:sudo /etc/init.d/samba restart
I "mapped" a network drive for myself, for convenience. You can upload movies directly to your RPI from your computer and watch it already on a huge TV set, for example, in your living room.
Cry!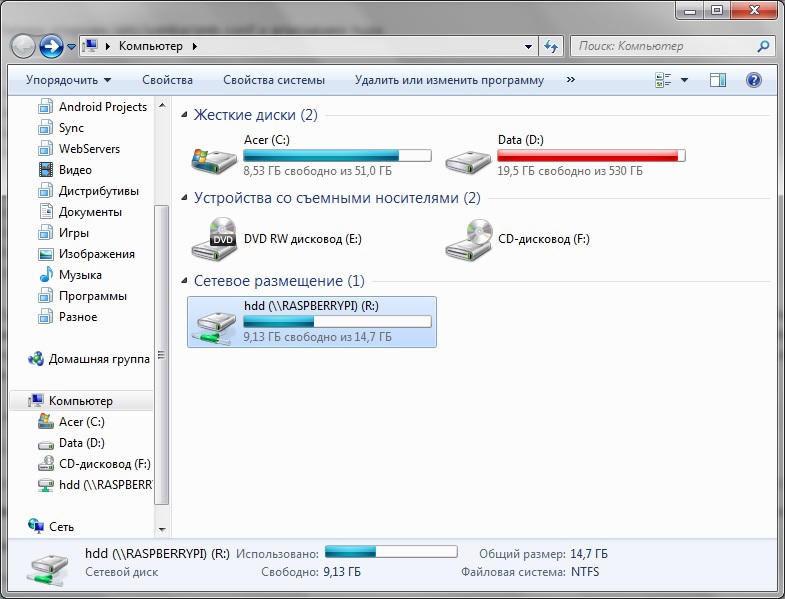

Install rTorrent, Screen, RuTorrent
First we put rTorrent
sudo aptitude install rtorrent
Then create a folder on our flash drive, here we will download our films:
mkdir /mount/flash/Torrent/
And also the folder where we will store download information:
mkdir /mount/flash/Torrent/.rt/
Then we go to the user's home folder, under which rtorrent will work, I have this
/home/pi:cd /home/pi
Here we create the file ".rtorrent.rc", these are the settings of our rtorrent:
min_peers = 1
max_peers = 30
download_rate = 0
upload_rate = 0
directory = /mount/flash/Torrent/
session = /mount/flash/Torrent/.rt/
port_range = 40890-40890
port_random = no
check_hash = yes
session_save = yes
encryption = allow_incoming,enable_retry,prefer_plaintext
use_udp_trackers = yes
dht = auto
dht_port = 6881
encoding_list = UTF-8
scgi_port = 127.0.0.1:5000
Description of settings can be found here . Set up startup and install screen for rtorrent to work in the background:
sudo aptitude install screen
sudo wget http://libtorrent.rakshasa.no/attachment/wiki/RTorrentCommonTasks/rtorrentInit.sh?format=raw -O /etc/init.d/rtorrent
Let's edit the script to work correctly:
sudo nano /etc/init.d/rtorrent
user="user"write
in the line user="pi". Save. Now we’ll add this whole thing to autoload and run:sudo chmod 755 /etc/init.d/rtorrent && sudo update-rc.d rtorrent defaults && sudo /etc/init.d/rtorrent start
Configure Apache, enable the modules:
sudo a2enmod scgi
Edit the file
/etc/apache2/apache2.conf - at the very end of the file you need to add the line - " SCGIMount /RPC2 127.0.0.1:5000". Restart Apache:sudo service apache2 restart
It's time to put the web-face for our rtorrent. I chose ruTorrent, because she is unpretentious and in Russian. First, put Subversion:
sudo apt-get install subversion
Now load ruTorrent:
cd /var/www/
sudo svn checkout http://rutorrent.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/rutorrent
Set the rights to the folder:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data ./rutorrent/
It remains to check the operation of our web-muzzle, go to the browser
ip_адрес_RPI/rutorrent(if with an RPI then localhost/rutorrent):Voila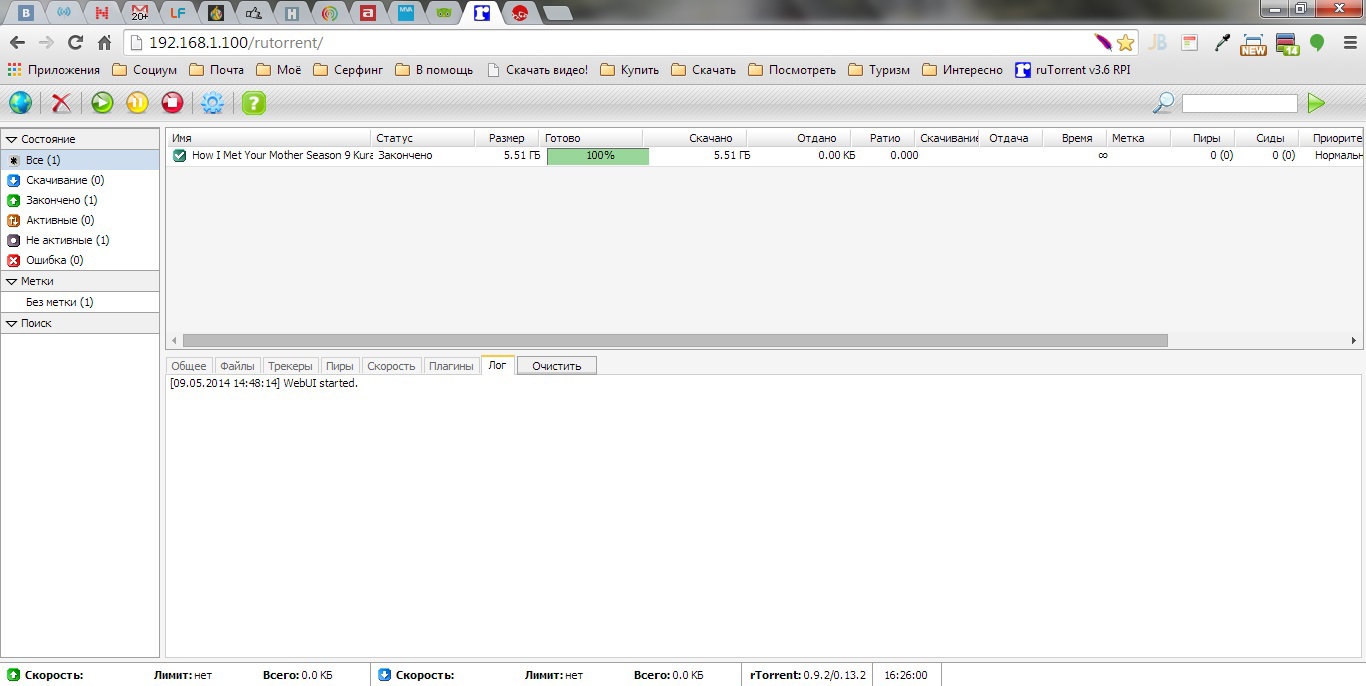

Well, that’s all. Now we have a ready-to-work RPI for web developers who can put their favorite TV show on the night from Friday to Saturday and watch this whole thing on a huge TV set on the couch the next morning. Thanks for attention.
PS I want to apologize for the lack of some links to third-party resources, the material of which I was guided by since I did this for a long time, and published only now.
