AR - Augmented Reality (article plus video)

Truly the general public came across her when Google wanted to hang smart glasses on our nose. After that came the era of funny masks that made of us cats, bunnies and Leonardo DiCaprio. Then the Pokémon captured both realities and forced them to wind kilometers. Recently, Apple has shown ARKit , and Google - Arcore , and then we will cover just about a new wave of games and applications with the use of augmented reality, the possibility of a much broader and more useful to society than fishing sloupoki.
This is a popular article. It does not contain a detailed description of the technical side, but there is a history of the development of EIAA, references to the mentioned developments and many interesting illustrations.
A lot of pictures!
What is EyAr
Augmented reality is an environment that in real time complements the physical world, as we see it, with digital data using any devices - tablets, smartphones or others, and the software part. For example, Google Glass or Iron Man helmet. Aiming systems in modern combat aircraft are also an augmented reality.
Augmented reality (augmented reality, AR) should be distinguished from virtual (virtual reality, VR) and mixed reality (MR).
In augmented reality, virtual objects are projected onto the real environment.
Virtual reality is a world created by technical means, transmitted to a person through (so far) sense organs.
Mixed or hybrid reality combines both approaches.
That is, virtual reality creates its own world, where a person can plunge, and augmented adds virtual elements to the real world. It turns out that ViAr interacts only with users, and EyAr interacts with the outside world.
EIAA History
Like many other interesting studies, the history of manipulation of reality begins in science fiction. The author of The Wizard of Oz, Lyman Frank Baum, in the novel Master Key, described a device that could mark people in real time with letters indicating their character and level of intelligence. The primitive tools of complementing reality were known long before: these were masks that Roman archers wore to aim better, and telescopes with distance markings, and so on.
But the story of augmented reality, as we know it now, originates from developments concerning ViAr. The father of virtual reality is considered Morton Heilig. He received this title for research and inventions made in the 1950s and 60s. On August 28, 1962, he patented the Sensorama simulator . Heilig himself also called it the immersion theater.
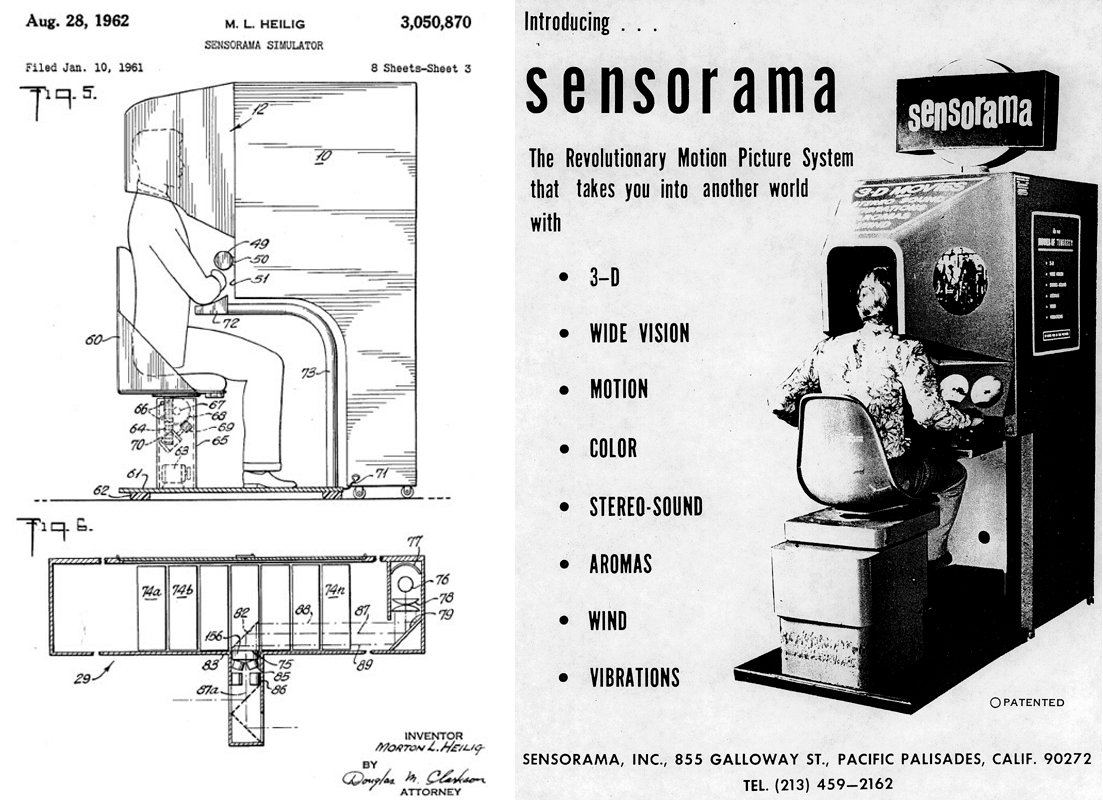
The patent describes a virtual technology in which visual images are complemented by air movements and vibrations. The rationale for its existence was given this:
“Today, the demand for methods of teaching and training people is constantly growing in such a way as to eliminate the risks and danger of real situations”
It was a device of an earlier version of virtual reality, and not augmented, but it gave impetus to the development of both directions. Heilig even invented a special 3D camera to make films for the Sensory.
But in 1968, Harvard computer specialist and professor Ivan Sutherland with his student Bob Sproullom developed a device called the Sword of Damocles . And this was the first system of precisely augmented reality based on the head display.
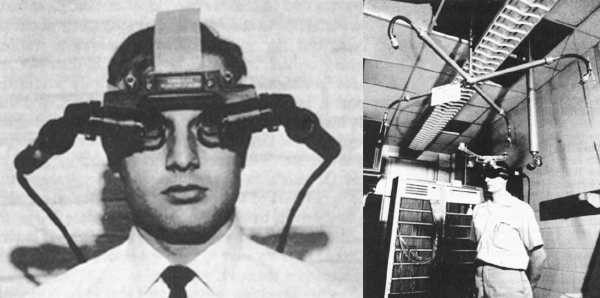
The glasses were so heavy that they had to be fixed to the ceiling. The design loomed threateningly over the subject, hence the name. In glasses with a stereoscopic display a simple picture was transmitted from a computer. The perspective of observing objects varied depending on the movements of the user's head, so a mechanism was needed to track the direction of gaze. For that time, it was a fantastic breakthrough.
The next step was the creation of Myron Kruger laboratory with artificial reality Videoplace in 1974 year.
Its main goal was to save users from having to wear special helmets, goggles and other devices to interact with artificial reality. VideoPlayers used projectors, video cameras and other equipment. People, being in different rooms, could interact with each other. Their movements were recorded on video, analyzed and translated into silhouettes of artificial reality. Users saw how their silhouettes interact with objects on the screen and this created the impression that they were part of artificial reality. Although it would be more correct to call it a project of an interactive environment.
Four years later, in 1978, Steve Mann invented the first device for EyAr, which was not bolted to the ceiling. In EyeTapA camera and a display supplementing the environment in real time were used. This invention became the basis for future projects, but was not widely used.
The first massive use of augmented reality was made possible thanks to Den Rayton, who in 1982 used radar and cameras in space to show the movement of air masses, cyclones and winds in weather forecasts. There EyAr is still used in this way.
In the 90s, the search for new ways of using continued, and the scientist Tom Caudell first proposed the term “augmented reality”. A task was set before him and his colleague: to reduce the cost of expensive diagrams that were used to mark the factory areas for assembling Boeing airplanes. And the solution was the replacement of plywood signs with symbols for special helmets that displayed information for engineers. This made it possible not to rewrite the designations every time manually, but simply to change them in a computer program.

Further development occurred rapidly. The jump made in the production of microprocessors, and, as a result, in the entire technological sector, has greatly accelerated the work.
In 1993, at Columbia State University, Steve Fayner introduced the KARMA system (Knowledge-based Augmented Reality for Maintenance Assistance, translated roughly as “Interactive Service Assistant”), which allowed us to see an interactive instruction manual for the printer through a virtual reality helmet.

But in the 95th June, Recimoto collected Navicam, a prototype of augmented reality mobile device, which smartphone users now know. Navikam was a portable display with a camera attached to the back side, whose video stream was processed by a computer and, upon detecting a color mark, would display information about the object.
In 96th year, Jun Recimoto and Yuzhdi Ayattsuka developed the Matrix Method (or CyberCode ). It describes real and virtual objects using flat labels like QR codes. It allowed to enter virtual things in the real world, simply transferring tags. For example, put a piece of code on the floor, look at the room with a camera - and here you have a dinosaur in the room.
In the 98th year, the NFL for the first time used the augmented reality developed by Sport Vision in the live broadcast of sports games. During the matches, technical lines and account information were added to the picture from the camera, which clearly shows the playing field. On the "magic yellow line" is an old story .
In the 99th, NASA used the augmented reality system in the dashboard of the X-38 spacecraft, which learned how to display objects on the ground regardless of weather conditions and actual visibility.
And in the same year, Hirokazu Kato created an open library for writing applications with EIAA-functionality ARToolKit (still on GitHub ). It used a system for recognizing the position and orientation of the camera in real time. This allowed us to dock the picture of the real and virtual cameras, which made it possible to smoothly overlay a layer of computer graphics on the markers of the real world.
We can say that with the release of the first version of this library, the modern stage of active development of augmented reality began.
How augmented reality works
If you recline the very ancient implementations, then EyAr is the pattern recognition and tracking of markers.
With pattern recognition everything is more or less clear. If the application needs to recognize the table, then it is enough to upload a table photo library to the server, designate the general structure, color, arbitrary parameters and assign this action to a specific action when it is detected in the image.
The second part is tracking the markers. Markers can act as a specially printed image, and any objects.
The application recognizes the magazine cover in a simple form with right angles and a specific pattern, and will track its position in space, noting the offset relative to the background. In this case, the cover itself is the marker.
With special markers, everything is even easier. Suppose we want to try on the car new wheels. To do this, it is enough for us to stick QR-tags on the disks and the system will automatically understand that it is in these places that the image of the new wheels should be inserted into the picture. Another example: we put a label on the floor and the application understands that this plane is the floor, and place arbitrary objects on it.
But you can’t stick markers everywhere, but making a unique marker for each situation and unifying the whole system is too difficult.
This is where SLAM comes to the rescue - the Simultaneous Localization and Map Building method, which is used to build a map in an unknown space with simultaneous control of the current location and the distance traveled.
It sounds hard. In a simplified form, Slam is a way to recognize the environment and the location of the camera, by decomposing the image into geometric objects and lines. After that, the system assigns a point (or many, many points) to each individual form, fixing their location in spatial coordinates on successive frames of the video stream. Thus, the conventional building is laid out on the plane of the walls, windows, faces and other prominent elements. A conditional room - on the plane (floor, ceiling, walls) and objects inside. Due to the fact that the algorithm allows you to memorize the position of points in space, returning to the same room from another you will see points in the same places where they were before.
This method received a particularly strong push after the smartphone manufacturers began to build additional cameras to calculate the depth of field into their devices.
You should not think that Slam is an advanced version of conventional pattern recognition and marker tracking. Rather, it is a tool that is much better suited to orienting augmented reality systems in space. It lets the application know where the user is located. But it is much worse for identifying, for example, the bear in the picture.
For maximum efficiency, both approaches are combined for a specific task. Which leads us to the current situation.
Present: from glasses to phones
At the very beginning of the development of EyAr, it was clear that its success would depend on how comfortable it would be for our eyes.
Back in 1984, the concept of augmented reality and computer vision was visualized in the film “Terminator” by James Cameron . But Cameron was well ahead of his time, because it was not possible to embed EyAr directly into the eye in those years even in bold fantasies. Ideal seen form factors of contact lenses or glasses. The first and now only at the concept stage, but as the cost and appearance of more subtle production processes became cheaper, the shape of the glasses became closer. Over the years, the second version of the implementation has finally stuck to it: with the help of becoming ubiquitous smartphones.
The most high-profile event of the augmented reality of recent years were the glasses released in 2013Google Glass , with which there is a little confusion. Despite the fact that it was they who first came to mind when it comes to augmented reality, these glasses almost had nothing to do with it. The virtual environment practically did not interact with the real one. Is that navigation can be attributed to EyAr-content, but it was implemented in the style of maps for the phone, and not some arrows hanging above the road.

But glasses were able to take photos and shoot video on command, with automatic sending to the cloud. This experiment, which has not become a mass one, nevertheless did its job: it launched a wave, letting other companies understand that it is possible to take seriously the development of augmented reality devices for the masses.
Microsoft immediately took up the baton, after a couple of years, covertly announced (and in 2016, presented the) Hololens mixed reality glasses . True, only for developers and journalists. The product is complex, it is still being developed. But there are many enthusiastic reviews on the Internet, where people share their experiences of interacting with the virtual environment.
Hololens do not require connection to another PC or phone. The glasses have four cameras, with the help of which they analyze the room and combine virtual objects with the real world.
Glasses allow you to almost fully work with Windows 10, and the name “Windows” acquires a new meaning: the windows of the system are easily hung on the walls in the manner of windows itself. Points remember the room, so when the user returns to the same room, all application windows and other elements of mixed reality are waiting for him in their places.
Now there are about a dozen of the most promising developers and products for augmented reality in the form factor of points: Vuzix , Sony , ODG , Solos .
But one manufacturer came closest to what can be not only technologically advanced, but also convenient. This is the company Magic Leap .
The first concept video
Launched in 2010 in an atmosphere of absolute secrecy, after a couple of years, it collected investments of more than half a billion dollars from such giants as Google and Qualkom. No one outside the narrow circle of investors knew what this company had attracted such attention and what its product was.
But the information still leaked. And later it was officially announced: the company is working on an advanced version of augmented reality glasses, which are a bit stronger than Google Glass and Hololens. And, unlike other manufacturers, Magic Lip pays equal attention to both hardware and software and interfaces. Despite the fact that the company is more interested in the entertainment industry than in the application, today it is a leader in the convenience of user interfaces.
But for now, EyAr is mostly found in phones. This convenience, ready-made technical base, the prevalence of devices and ease of writing software.
Sharpened under the photo for social networks applications offer about the same functions: masks and placing characters in space. That is - fun. But more and more companies understand the importance of this niche and present more utilitarian applications:
AirMeasure is a virtual roulette that can determine distances and sizes in a 3D environment;
Google Translate is able to translate the text that the camera sees in real time;
Sun Seeker helps to see the trajectory of the sun on the ground any day of the year;
Google Sky Map helps you find out which stars are visible in the sky.
It is in the mobile segment that the most interesting mass-media start-up startups are now concentrated:
YouAR
6D
Selerio
Ubiquity6 and others.
And one of the most investing companies in technology is Facebook, which runs new ideas on its massive user base.
Entertainment
The main mobile area where Augmented Reality found itself is, of course, entertainment.
You must have played first-person shooters. But have you ever thought that the display of the number of cartridges, health and first-aid kits is also an augmented reality, only for your character?
In the early 2000s, the AiAr port of the legendary Quake game came out. He was called: ARQuake .
In our time, you can become the hero of a shooter yourself. For example, in the game Father.IO . Such projects appear more often.
In 2014, the game came out Night Terrors , one of the first popular horror films in augmented reality. Try it at night in some basement - do not forget.
In 2016, Nyantic studio released the heiress of its game Ingress and the most important AyAr game, probably for many years to come: Pokemon Go . Augmented reality, geo-tracking and the popular universe - everything went so well that Pokemon Gow downloaded over a hundred million people. The game quickly became a phenomenon and began to gather scandals around it, including in Russia. Pokémon Gow is also unique in that it made millions of people walk in the fresh air.
Board games have received a new form thanks to technology.
Companies such as Lego and Disney are actively developing games using EIAA, and practically all major toy manufacturers have expressed their intention to join them. Research teams have already started collecting data on how young children interact with augmented reality games and applications, and how this affects their perception of the real world. Perhaps in the future, the most interesting ideas on the development of technology will be heard from those for whom this technology was just a part of childhood.
It is entertainment that today develops augmented reality research base. And thanks to the enormous amounts of data voluntarily transferred by people to software companies, technology, coupled with machine learning, is taking steps towards more serious areas.
From entertainment to real life
Background information, announcements and virtual pointers will be included in our virtual space. A virtual guide will take us through the ruins of the castle, and even show the scene, how this castle was destroyed, and how it was before. Well, social functions, like the filter by status “in active search”, will help to find the second half right in the crowd.
Well, advertising. This is the realm that is asleep and sees the earliest possible introduction of augmented reality into everyday life. And the freshness and novelty of the format will provide a wow effect. EyRp even appeared in print editions. For example, in the 2009 Esquire issue, you had to scan the cover, and then Robert Downey Jr. came to life on it .
Even before EyAr and prints crossedBMW, which launched in several German magazines an advertisement for the MINI model, which on the screen became three-dimensional and allowed itself to be viewed from all sides.
A cover, by the way, there is not only magazines and books. In order to start talking to you with a bottle label , today you don’t even need to drink.
The commercial possibilities of augmented reality are so vast that it is difficult to delineate the boundaries. Even graffiti does not remain aloof from AyAr technology.
EyAA can be used for quick fitting in stores: the idea to go to a furniture store and immediately assemble a room with furniture and household appliances on a test stand, taking advantage of compatibility tips, suggests itself.
More interesting and useful idea embodied the marketing department of Ikea back in 2014. Trying out furniture from the catalog directly to the interior of your room turned out to be extremely tempting.
Inspiring EIAA's educational opportunities.
Education
Technology can occupy that niche that is given to holograms in science fiction. Only holograms will not be soon, and devices like Hololens are technically almost ready. The prospect of seeing in universities, and after schools, virtual interactive illustrations that can be viewed from all sides, with which you can interact and immediately see the result of your experiences, seems wonderful far from bright fantasies about the future. Training in any engineering specialties may become much more visible and easy to understand.
Another important area is medicine.
The medicine
Here, straight eyes run away from the possibilities. In addition to the most visual training of students of medical schools, the visualization of data directly on the patient, instead of screens arranged around it, is immediately presented. Ultrasound will be as clear as possible. Well, the expectant mother will be happy to receive on the phone a three-dimensional baby, which she will gladly twist and examine, looking for the similarity of that with her father and herself.
But ultrasound is one thing, which does not require surgery, and another is life-threatening surgery, where visibility can help the doctor to respond faster and work more accurately.
HoloAnatomy for Hololens, which is about medicine and education, demonstrates visual anatomy in the augmented space . And at the same time - and one of the iconic demos for maykrosoftovskogo helmet.
Less dramatic, but no less useful - helpers for the blind and deaf who report first to objects and events around and show the subtitles to the second.
For example, Aira startupat the same time, it offers a neural network assistant, recognizing and pronouncing everything that the camera of points sees, and a live employee of a startup, which will help to orient in the same camera in a particularly difficult situation. The system is tied to a smartphone application. A subscriber receives points with a camera and the ability to broadcast an image of them to the support staff on duty. But there is no need to constantly call up with them: Aira’s voice assistant recognizes texts and images, overlapping many everyday urban tasks. It is logical that, as computer vision develops, a superstructure with living employees will become less relevant, but today this is a good compromise from human and computer resources.
Well: who has more budgets than advertisers and igrodelov? In the military.
Military technology
And if the guidance system in combat fighters, drones and tanks for the army - this is now a common thing, because It was from early augmented reality systems for pilots that other military projects in this area grew. For example, advanced augmented reality systems for infantry, which will be introduced in a couple of years.
The official fantasy of the US Army.
In the American Army today, the HUD 1.0 system is used: a highly advanced night vision device that also performs the functions of a thermal imager and projects a target indicator on a helmet showing the bullet at the current barrel position.
Lightweight semi-analogs of such systems have been available on the market for more than five years. The ballistic calculator from the TrackingPoint company actually replaces the sniper, well, or anyone who wants to, partner spotter.
Next in line is HUD 3.0, which is due out next year. He will be able to impose on the real image completely digital layers of the terrain, building models, floor plans, the positions of enemies and even the enemies themselves. And this is an application to reduce the cost of military exercises. War games cost the state budgets enormous sums every year, and with the help of augmented reality systems, soldiers can train with a conditional opponent without leaving the base.
The Russian army is developing similar systems for sappers.
Of course, I would like technology to develop not thanks to military projects and interests, but if you recall history, many inventions have found widespread peaceful application, despite their war roots and past. For example, microwave, Teflon and the Internet.
Future
Summing up, augmented reality is not only games and selfies with virtual masks. This is a huge number of opportunities for commercial use, new horizons in education, industry, medicine, construction, commerce and even tourism. And then it should only be more interesting.
EiAr’s commercial growth is astounding. She, unlike virtual reality, does not necessarily rely on specialized hardware and bulky devices. The technology works perfectly on the most mass wearable device - a smartphone.
Augmented reality is already changing our present: virtual masks, the hunt for Pokémon in cities and swamps, children shooting at each other not from wood, but through the phone screen. Now it is a reality.
The next step is a massive exit of AiAr from the zone of entertainment and social networks to the information support sector. Automakers (so far only Hyundai, BMW and Audi, but the list is growing) are starting to issue attachments to user instructions that help owners visually examine their cars. More and more manufacturers of technology are beginning to produce applications for repair shops that help craftsmen orient themselves in the internal structure of complex devices. Amazon thinks about making it easier for buyers: they liked the sneakers on a passerby — pointed the phone at that and immediately ordered the same ones.
Today we live in the midst of stormy research in the industry. Even technological giants do not have a clear picture of the further development of augmented reality. This is a time of continuous birth of ideas, finding unexpected ways of applying and realizing the full power of this once fantastic technology - augmented reality.
Roller
I prepared this article on EyAr for Habr, but initially we made a video. It contains off-screen text with technical, historical and simply beautiful illustrations.
