What is the crop factor
Now there are many SLR cameras. The most popular of them are amateur and semi-professional cameras with a "crop matrix". But what is a crop? What does crop factor mean?
In this article I will try to open the veil of mystery.
Historically, the film frame has a size of 24 × 36 mm. In digital photography, such a matrix is called a “full-size” or FF (Full Frame). But in the production of plates of this size, various problems arise, a lot of defects, for example, which leads to the high cost of such a matrix.
Marketers came up with the following move: cut the blank for the matrices into smaller sizes. This leads to a significant reduction in the price of the final matrix: a blank of the same size can be cut into a larger number of photomatrixes, and the influence of marriage is less significant.
For different firms, matrices decreased in different ways. Canon began to make the matrix smaller by 1.6 times, and Nikon by 1.5 times, Sony, also reduced the crop matrix by 1.5 times.
Since the crop matrix is smaller, only part of the light passing through the lens is incident on it. This caused the appearance of the term crop factor.
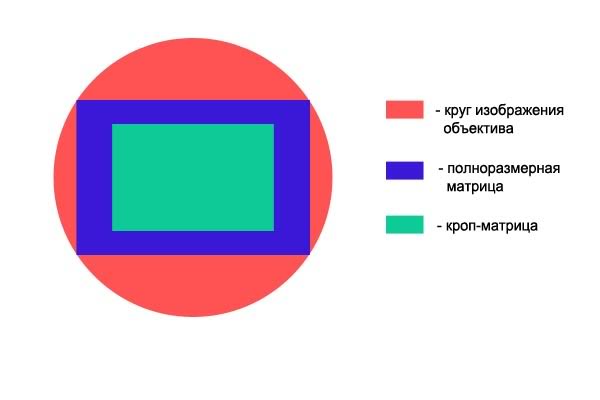
When shooting, you get the feeling that the camera with the crop sensor zooms closer than full-frame. In fact, the camera itself cuts out a rectangle 1.6 times smaller from a full-sized frame and saves it.
Having photographed the device on the FF and cutting out a rectangle 1.6 times smaller on the computer from the photo in the center, you will get exactly the same frame as you would get on the crop matrix.
It is also mistakenly believed that the crop matrix increases because in order to get the same amount of space in the frame, the lens needs a lens with a focal length 1.6 times larger than on the crop. For example, about the same space will fit into a 50mm lens on a crop that would fit into a lens with a focal length of 80mm on the FF. But this is due to the “cutting out” of a smaller region of the image circle than that of a full-frame matrix, and not an increase in the picture, since the focal length is a physical characteristic of the lens (lens), and the matrix size does not affect it.
It is this imaginary increase in focal length when shooting on the crop and is the "effective focal length." And to get it you need to multiply the value of the focal length of the lens by the crop factor, which is equal to the ratio of the crop matrix and full size.
DOF - Depth of Dramatic Space - This is what the photograph sharply depicted.
Again, the depth of field is matrix independent. It directly depends on the distance to the subject, and vice versa on the openness of the aperture and focal length of the lens. That is, the closer the subject is photographed, the larger the focal length, the more the aperture is open, the smaller the area of sharpness in your image.
And the size of the matrix depends only on how much this area gets into your frame.

As you can see, from the same distance, at the same focal length, with the same aperture, I got the same field of sharpness on the crop matrix as on the full-frame. The only difference is how much unsharp ruler breaks into the frame.
But again, due to the fact that a much smaller region of the image circle fits into the crop matrix (see Fig. 1), in order to photograph the facial portrait of a person, you will have to move further than with a full-frame camera. And the farther the object, the larger the field of sharpness, the greater the depth of field, so the feeling is created that the crop matrix erodes the background worse.
In this regard, there is also the term "effective aperture" in relation to crop cameras. The essence of this term is that if you shoot with the camera’s FF, then you will have the following parameters: focal length 85mm, aperture 2.8, distance to the object 1m.
On a crop camera, you already have to take a 50mm lens to fit the same amount of space into the frame from 1 meter, and since the focal length is 1.6 times less, so that the depth of field remains the same, you will have to open the aperture 1.6 times more, t. e. up to 1.8.
Crop largely justify their translation from English - crop. Due to the smaller matrix, the camera captures only less space per image, and the optical size is not affected by the size of the sensor in any way. Its size affects only the human sensation, because will have to go further and lose in the degree of blur.
In this article I will try to open the veil of mystery.
Historically, the film frame has a size of 24 × 36 mm. In digital photography, such a matrix is called a “full-size” or FF (Full Frame). But in the production of plates of this size, various problems arise, a lot of defects, for example, which leads to the high cost of such a matrix.
Marketers came up with the following move: cut the blank for the matrices into smaller sizes. This leads to a significant reduction in the price of the final matrix: a blank of the same size can be cut into a larger number of photomatrixes, and the influence of marriage is less significant.
For different firms, matrices decreased in different ways. Canon began to make the matrix smaller by 1.6 times, and Nikon by 1.5 times, Sony, also reduced the crop matrix by 1.5 times.
Shooting Impact
Since the crop matrix is smaller, only part of the light passing through the lens is incident on it. This caused the appearance of the term crop factor.

When shooting, you get the feeling that the camera with the crop sensor zooms closer than full-frame. In fact, the camera itself cuts out a rectangle 1.6 times smaller from a full-sized frame and saves it.
Having photographed the device on the FF and cutting out a rectangle 1.6 times smaller on the computer from the photo in the center, you will get exactly the same frame as you would get on the crop matrix.
It is also mistakenly believed that the crop matrix increases because in order to get the same amount of space in the frame, the lens needs a lens with a focal length 1.6 times larger than on the crop. For example, about the same space will fit into a 50mm lens on a crop that would fit into a lens with a focal length of 80mm on the FF. But this is due to the “cutting out” of a smaller region of the image circle than that of a full-frame matrix, and not an increase in the picture, since the focal length is a physical characteristic of the lens (lens), and the matrix size does not affect it.
It is this imaginary increase in focal length when shooting on the crop and is the "effective focal length." And to get it you need to multiply the value of the focal length of the lens by the crop factor, which is equal to the ratio of the crop matrix and full size.
IMF impact
DOF - Depth of Dramatic Space - This is what the photograph sharply depicted.
Again, the depth of field is matrix independent. It directly depends on the distance to the subject, and vice versa on the openness of the aperture and focal length of the lens. That is, the closer the subject is photographed, the larger the focal length, the more the aperture is open, the smaller the area of sharpness in your image.
And the size of the matrix depends only on how much this area gets into your frame.

As you can see, from the same distance, at the same focal length, with the same aperture, I got the same field of sharpness on the crop matrix as on the full-frame. The only difference is how much unsharp ruler breaks into the frame.
But again, due to the fact that a much smaller region of the image circle fits into the crop matrix (see Fig. 1), in order to photograph the facial portrait of a person, you will have to move further than with a full-frame camera. And the farther the object, the larger the field of sharpness, the greater the depth of field, so the feeling is created that the crop matrix erodes the background worse.
In this regard, there is also the term "effective aperture" in relation to crop cameras. The essence of this term is that if you shoot with the camera’s FF, then you will have the following parameters: focal length 85mm, aperture 2.8, distance to the object 1m.
On a crop camera, you already have to take a 50mm lens to fit the same amount of space into the frame from 1 meter, and since the focal length is 1.6 times less, so that the depth of field remains the same, you will have to open the aperture 1.6 times more, t. e. up to 1.8.
Summary
Crop largely justify their translation from English - crop. Due to the smaller matrix, the camera captures only less space per image, and the optical size is not affected by the size of the sensor in any way. Its size affects only the human sensation, because will have to go further and lose in the degree of blur.
