Cheating live in the accident "Ariane 5"
The fourth launch of Ariane 5 was partially successful - the satellites were in orbits with more than planned inclinations. They can get from there to geostationary orbit on their engines. Due to the fact that the devices are electrojet engines, a little fuel will be needed for orbit correction, and the estimated active life of 15 years may not decrease. It is good that the satellites are not lost, but the accident causes outrage at the actions of Arianespace - the MCC from the first minutes should have been clear that something was wrong with the missile, but the commentator continued to report as if everything was in order. What happened?

AFP Photo / Getty Images
On the live broadcast, the launch looked normal until about 9:29, when the cross of the step position marker on the trajectory disappeared, and the telemetry field at the bottom of the screen that appeared after the titles of the CEO Yahsat was empty. It could not mean anything terrible - problems could arise from the broadcast of the launch, and not the rocket. Moreover, the screen displayed the animation of normal flight, and the announcer led a typical story. The broadcast even saidthat "apparently" ground stations received confirmation of the successful separation of the first satellite! And on the 38th minute, the broadcast was simply stopped. And only about an hour later it was announced that an “anomaly” had occurred during the launch, and the connection with the launch vehicle was lost “a few seconds after the third stage was switched on” (10 minutes of flight). An hour later, an official confirmation appeared that the satellites were in orbit. The next day, the parameters of the orbits of satellites were published in open access, and it turned out that they were in orbit with an approximately normal pericenter and apocenter, but with an error of 20 ° inclination.
The error will cost the satellites approximately 150 additional meters per second of the characteristic speed to enter the geostationary orbit. This is approximately three years of compensation of disturbances at the geostationary, but the satellites most likely have a supply of fuel in case of the extension of the fifteen-year estimated lifetime.
A careful analysis of what was shown in the broadcast, almost immediately allows you to form an accident hypothesis. If the displayed trajectory is correct in the first minutes of the flight, when telemetry was still there, then it turns out that the rocket flew with an error of about 20 ° relative to the correct course.
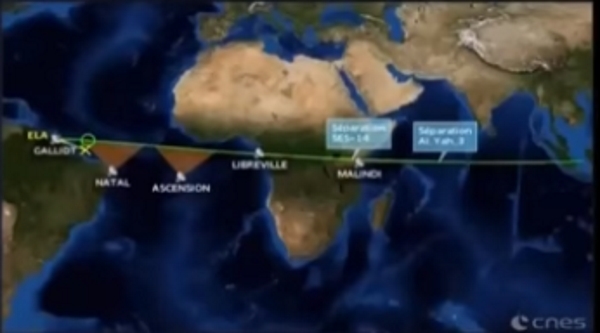
An enlarged frame from the broadcast, the yellow line and the dagger of the current position are located south of the green line and the circle of the calculated
hypothesis was quickly confirmed by space enthusiasts, among them was Sease Bass, about whom I wrote quite recently. They found a video of the launch of the rocket, taken from the beach near the town of Kourou, located southeast of the cosmodrome of the same name.
The height of the moon at that moment was 83 °, that is, the rocket passed almost overhead taking off, which is unacceptable during normal flight. The permitted azimuths for the Kourou space center are limited to 93 ° so that in the event of an accident you do not fall to the city, and on the night of Friday the rocket passed just a couple of kilometers from it!

Minimum and maximum azimuths of the flight, as assessed by Suzanne Auer.
Green sector - permitted directions
The erroneous azimuth hypothesis also perfectly explains the loss of communication - the launch vehicle just turned out to be beyond the horizon for ground tracking points. Only after about two hours, when the satellites gained sufficient height, they were able to communicate with them.
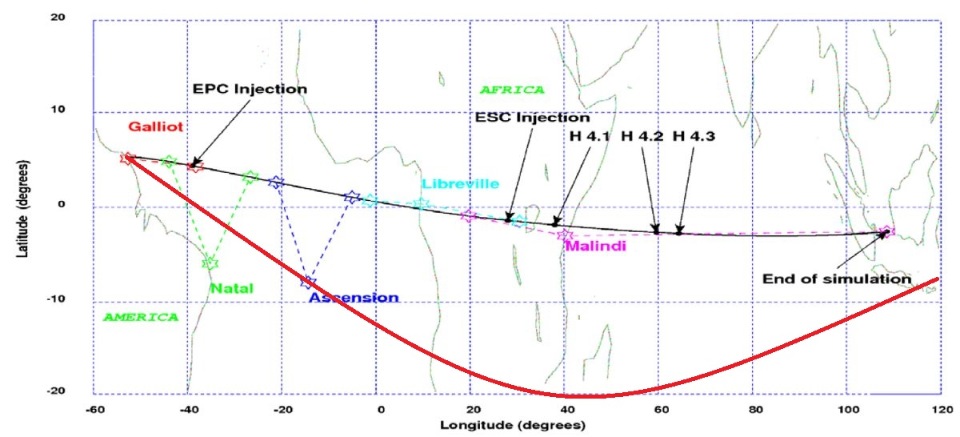
Approximate flight track diagramCheburashka user of the Cosmonautics News magazine forum
The reason for such a strange behavior of the rocket will be established by a commission convened by Arianespace. The Internet is already jokingthat when programming a flight task, someone confused the equator with the ecliptic - the error roughly corresponds to the angle between these planes. But in terms of reputation and public relations, this is already a catastrophe - the behavior of the announcer telling about a successful launch in the absence of telemetry, especially since the MCC should have noticed the problem even earlier, it is difficult to call it anything other than deception. Separately, it is worth noting the lack of reaction of operators, managers of emergency termination of the flight. An incorrect missile course should be exactly in the list of parameters for its detonation, but we still do not know what explains the continuation of the flight. Probably, this is an indirect argument in favor of the hypothesis of an incorrect flight task - the control system could signal a healthy state and flight according to the program, but the fact that the course was in dangerous proximity to the city, could not be displayed on the monitors of people making decisions. The alternative that the operators simply ignored the wrong azimuth is much worse. Ariane 5 is renowned for its reliability, and the previous accident was 15 years and 63 starts back, but in the space industry you cannot relax.

AFP Photo / Getty Images
On the live broadcast, the launch looked normal until about 9:29, when the cross of the step position marker on the trajectory disappeared, and the telemetry field at the bottom of the screen that appeared after the titles of the CEO Yahsat was empty. It could not mean anything terrible - problems could arise from the broadcast of the launch, and not the rocket. Moreover, the screen displayed the animation of normal flight, and the announcer led a typical story. The broadcast even saidthat "apparently" ground stations received confirmation of the successful separation of the first satellite! And on the 38th minute, the broadcast was simply stopped. And only about an hour later it was announced that an “anomaly” had occurred during the launch, and the connection with the launch vehicle was lost “a few seconds after the third stage was switched on” (10 minutes of flight). An hour later, an official confirmation appeared that the satellites were in orbit. The next day, the parameters of the orbits of satellites were published in open access, and it turned out that they were in orbit with an approximately normal pericenter and apocenter, but with an error of 20 ° inclination.
43174 / 2018-012A: 232 x 43163 km, 20.6 °
43175 / 2018-012B: 232 x 43198 km, 20.6 °
43176 / 2018-012C: 169 x 42790 km, 21.0 °
43177 / 2018-012D: 235 x 43153 km, 20.6 °
The error will cost the satellites approximately 150 additional meters per second of the characteristic speed to enter the geostationary orbit. This is approximately three years of compensation of disturbances at the geostationary, but the satellites most likely have a supply of fuel in case of the extension of the fifteen-year estimated lifetime.
Analysis
A careful analysis of what was shown in the broadcast, almost immediately allows you to form an accident hypothesis. If the displayed trajectory is correct in the first minutes of the flight, when telemetry was still there, then it turns out that the rocket flew with an error of about 20 ° relative to the correct course.

An enlarged frame from the broadcast, the yellow line and the dagger of the current position are located south of the green line and the circle of the calculated
hypothesis was quickly confirmed by space enthusiasts, among them was Sease Bass, about whom I wrote quite recently. They found a video of the launch of the rocket, taken from the beach near the town of Kourou, located southeast of the cosmodrome of the same name.
The height of the moon at that moment was 83 °, that is, the rocket passed almost overhead taking off, which is unacceptable during normal flight. The permitted azimuths for the Kourou space center are limited to 93 ° so that in the event of an accident you do not fall to the city, and on the night of Friday the rocket passed just a couple of kilometers from it!

Minimum and maximum azimuths of the flight, as assessed by Suzanne Auer.
Green sector - permitted directions
The erroneous azimuth hypothesis also perfectly explains the loss of communication - the launch vehicle just turned out to be beyond the horizon for ground tracking points. Only after about two hours, when the satellites gained sufficient height, they were able to communicate with them.

Approximate flight track diagramCheburashka user of the Cosmonautics News magazine forum
The reason for such a strange behavior of the rocket will be established by a commission convened by Arianespace. The Internet is already jokingthat when programming a flight task, someone confused the equator with the ecliptic - the error roughly corresponds to the angle between these planes. But in terms of reputation and public relations, this is already a catastrophe - the behavior of the announcer telling about a successful launch in the absence of telemetry, especially since the MCC should have noticed the problem even earlier, it is difficult to call it anything other than deception. Separately, it is worth noting the lack of reaction of operators, managers of emergency termination of the flight. An incorrect missile course should be exactly in the list of parameters for its detonation, but we still do not know what explains the continuation of the flight. Probably, this is an indirect argument in favor of the hypothesis of an incorrect flight task - the control system could signal a healthy state and flight according to the program, but the fact that the course was in dangerous proximity to the city, could not be displayed on the monitors of people making decisions. The alternative that the operators simply ignored the wrong azimuth is much worse. Ariane 5 is renowned for its reliability, and the previous accident was 15 years and 63 starts back, but in the space industry you cannot relax.
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Sign in , please.
The cause of the accident, in your opinion:
- 30% They mixed up the equator with the ecliptic in the preparation of the flight mission 227
- 43.5% Another, not anecdotal, error in the preparation of the flight task 329
- 16.9% Control System Error 128
- 9.5% Other reason 72
