Win32 / Olmarik or TDL3 study in detail
Recently, again they began to talk a lot about the TDSS rootkit, and more specifically about its latest modification TDL3. According to ESET classification, this rootkit belongs to the Win32 / Olmarik family of malware. According to our statistics, he is most active in the United States. Other antivirus companies also confirm this fact.
It is worth noting that for a fairly short period of time, several independent studies on this topic have already appeared: one , two , three . Today the Center for Viral Research and Analytics of the Russian representative office of ESET released its analytical report “Rootkit Win32 / Olmarik: Work and Distribution Technologies”, which was prepared on the basis of long-term monitoring and analysis of various modifications of this rootkit. We provide excerpts from this document below.
In our study, there is a description of not only implementation and functioning technologies, but also methods of distribution monetization. Our report contains a number of technological issues that were not considered in other analytical works.
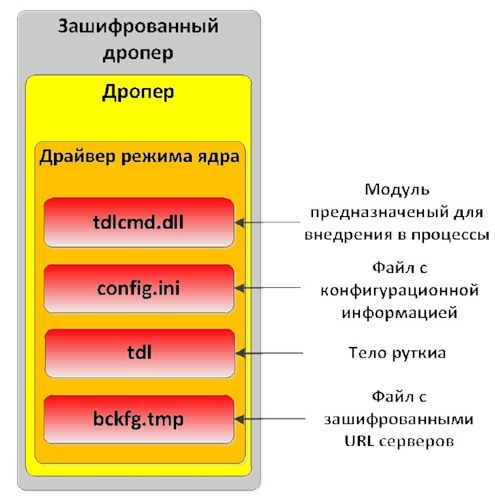
WIN32 / OLMARIK is distributed through a special program - dropper, whose task is to install the rootkit hiddenly. The dropper’s body is encrypted and obfuscated in order to make it difficult for antivirus software to detect it. During decryption, the dropper uses some tricks to counteract debugging, emulation, and determining execution in a virtual machine environment.
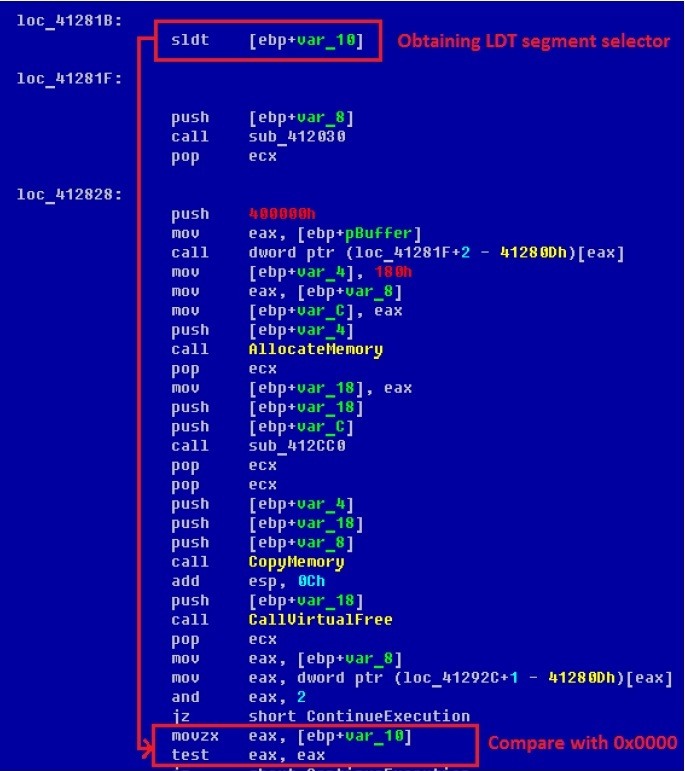
The dropper checks to see if it is running in the virtual machine environment by reading the contents of the LDTR register containing the segment selector that contains the local segment descriptor table. This table is used to calculate a linear address from a pair of segment_selector: offset. Microsoft Windows operating systems do not use local segment descriptor tables and initialize the LDTR register to zero. At the same time, most modern virtual machines (VMware, Virtual PC, etc.) use them and, therefore, initialize the LDTR register with a value other than zero. This fact is used by malware to detect execution in a virtual environment. The contents of the LDTR register can be obtained using the sldt (store local descriptor table) instruction, which is not privileged and can be performed in the 3rd ring of protection. The figure below shows a code snippet performing a similar check.
Some varieties of rootkits of this family are specially designed for distribution in certain countries. So, for example, a sample that has become widespread in the UK, before installation, checks the locale with values from the following list:
• Azerbaijan;
• Belarus;
• Kazakhstan;
• Kyrgyzstan;
• Russia;
• Uzbekistan;
• Ukraine;
• Czech Republic;
• Poland.
If a match is found, then the dropper shuts down without installing a rootkit.
Read more in our analytical report “Rootkit Win32 / Olmarik: technologies of work and distribution”
It is worth noting that for a fairly short period of time, several independent studies on this topic have already appeared: one , two , three . Today the Center for Viral Research and Analytics of the Russian representative office of ESET released its analytical report “Rootkit Win32 / Olmarik: Work and Distribution Technologies”, which was prepared on the basis of long-term monitoring and analysis of various modifications of this rootkit. We provide excerpts from this document below.
In our study, there is a description of not only implementation and functioning technologies, but also methods of distribution monetization. Our report contains a number of technological issues that were not considered in other analytical works.
WIN32 / OLMARIK is distributed through a special program - dropper, whose task is to install the rootkit hiddenly. The dropper’s body is encrypted and obfuscated in order to make it difficult for antivirus software to detect it. During decryption, the dropper uses some tricks to counteract debugging, emulation, and determining execution in a virtual machine environment.

The dropper checks to see if it is running in the virtual machine environment by reading the contents of the LDTR register containing the segment selector that contains the local segment descriptor table. This table is used to calculate a linear address from a pair of segment_selector: offset. Microsoft Windows operating systems do not use local segment descriptor tables and initialize the LDTR register to zero. At the same time, most modern virtual machines (VMware, Virtual PC, etc.) use them and, therefore, initialize the LDTR register with a value other than zero. This fact is used by malware to detect execution in a virtual environment. The contents of the LDTR register can be obtained using the sldt (store local descriptor table) instruction, which is not privileged and can be performed in the 3rd ring of protection. The figure below shows a code snippet performing a similar check.

Some varieties of rootkits of this family are specially designed for distribution in certain countries. So, for example, a sample that has become widespread in the UK, before installation, checks the locale with values from the following list:
• Azerbaijan;
• Belarus;
• Kazakhstan;
• Kyrgyzstan;
• Russia;
• Uzbekistan;
• Ukraine;
• Czech Republic;
• Poland.
If a match is found, then the dropper shuts down without installing a rootkit.
Read more in our analytical report “Rootkit Win32 / Olmarik: technologies of work and distribution”
