Mathematical logic of terrorist attacks
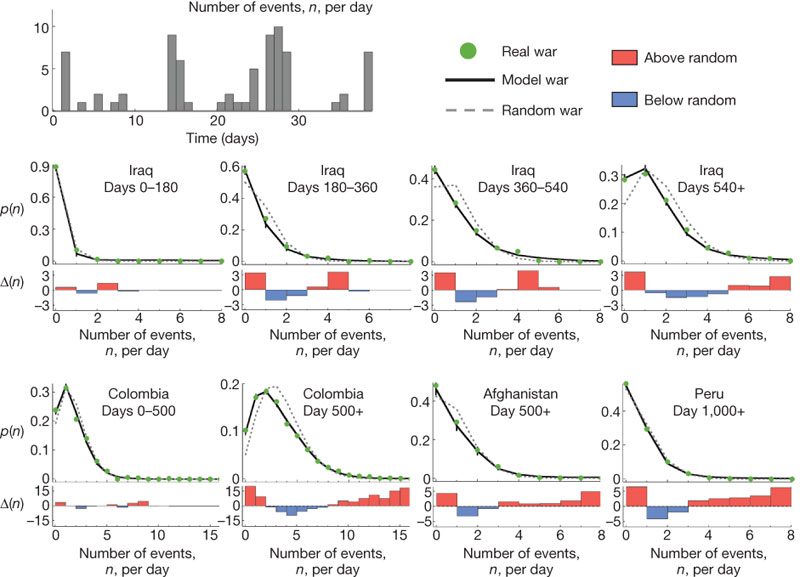
American scientists have discovered a mathematical pattern in world terrorism, namely the dependence of the number of victims in each terrorist attack on the total frequency of terrorist attacks, Nature writes . The value of α in the power dependence p (x) ≈ x -α was calculated from the statistics of nine partisan wars (in our time, the partisan attack is usually called a terrorist act). Alpha reflects the degree of aggressiveness and is surprisingly stable in many wars (about 2.5).

That is, in a guerrilla warfare, an attack with ten victims is 316 times more likely than an attack with a hundred victims (316 = 10 2.5 ).
This universal law allows you to combine in a single formula all the partisan wars that have been fought in the history of mankind. Although the war scale can be located to the left or right of the average value, but together they make up a single overall picture. As one of the authors of the study noted, this is a general formula for collective violence in human society. That is, 2.5 is a certain constant inherent in our genes. via slashdot

That is, in a guerrilla warfare, an attack with ten victims is 316 times more likely than an attack with a hundred victims (316 = 10 2.5 ).
This universal law allows you to combine in a single formula all the partisan wars that have been fought in the history of mankind. Although the war scale can be located to the left or right of the average value, but together they make up a single overall picture. As one of the authors of the study noted, this is a general formula for collective violence in human society. That is, 2.5 is a certain constant inherent in our genes. via slashdot

