ADSL Internet
Probably the one who has Internet access via ADSL looked into the modem settings and came across the vpi / vci settings. The first time I came across them, a reasonable question arises: “what is it and why?” In this article I decided to tell you a little more about how the ADSL technology is accessed, about PPPoE and, of course, about vpi / vci parameters.
Access via ADSL technology is carried out using a DSL modem on the subscriber side and DSLAM on the provider side. Probably the DSL technology ( Digital Subscriber Line ) will say more correctly , but more often you can hear ADSL ( Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line ), this is the most common form of xDSL. And in this article I want to talk a little about ADSL.
Asymmetry (from the name) consists in different bandwidth of the channels, the subscriber download speed is higher than the return.
Probably each provider, when connecting the subscriber, gives the subscriber an instruction with a diagram of how to turn everything on in order to work. And the first half of the picture (up to and including splitter A) from below should seem familiar to all ADSL Internet owners.
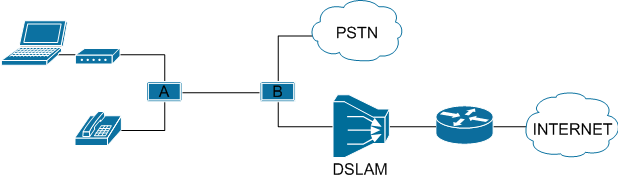
But the second part, this is already provider =)
One of the main advantages of DSL technology for subscribers is the ability to use the phone and the Internet at the same time.
To ensure this, DSL uses a higher frequency range on the line (AB span) than the telephone. Splitters are used to separate these frequencies, both on the subscriber side and on the provider side.
Further, according to the scheme, the subscriber behind the splitter has a modem turned on, and the provider behind the splitter has a DSLAM.
DSLAM ( DSL Access Multiplexer ) collects many subscriber lines and routes them higher to the provider's backbone. It can be compared with a large switch; it also works on the second level of the OSI model.
ATM ( Asynchronous Transfer Mode ) is a cell switching protocol that transfers data in fixed-size cells and provides the link layer of the OSI model.
ATM works very well on low-speed channels up to 2 Mbps and can support multiple logical connections on one physical channel. ATM standards provide for the transfer of heterogeneous traffic (digital, voice and multimedia data) over the same systems and communication lines.
These advantages caused the use of ATM between the subscriber’s modem and DSLAM.
ATM is a connection-oriented protocol and always establishes a virtual circuit ( virtual circuit ) before starting data transfer.
A pair of values is used to identify this channel.VPI / VCI .
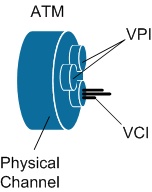
On the DSL modem of the subscriber and on the subscriber port on the DSLAM, these values must match. A subscriber can go several virtual channels (several pairs of vpi / vci ).
On the DSLAM, VLANs are assigned for certain virtual channels of subscriber ports and the traffic goes tagged to a router, where PPPoE subscription sessions are terminated.
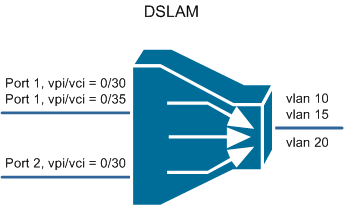
Also on DSLAM, various filters can be applied to certain types of traffic, packet marking is carried out for the organization of QoS .
After the subscriber traffic has gone tagged with DSLAM , it passes through the chain of provider switches and gets to the aggregation router.
The aggregation router performs the following functions:
To whom it is curious, I give an example of setting up an aggregation router =)
Setting up a router for PPPoE termination :
We start the PPPoE session and see what we get:
You can see how many sessions have been created now, using the command.
PPPoE-ROU # sh pppoe summ
PTA: Locally terminated sessions
FWDED: Forwarded sessions
TRANS: All other sessions (in transient state)
TOTAL PTA FWDED TRANS
TOTAL 2 2 0 0
GigabitEthernet0 / 1 2 2 0 0
When a subscriber connects via PPPoE, for him created on the basis of Virtual-Template its interface - Virtual-Access, abbreviated as Vi.
PPPoE-ROU # sh caller
To end the PPPoE session of the 11101 @ pppoe subscriber from the router, you must enter "clear int vi2".
You can get more complete information (the address that was issued from the pool and statistics) about the PPPoE session using the command:
PPPoE-ROU # sh caller full
User: 11102 @ pppoe, line Vi2, service PPPoE
Connected for 1d04h, Idle for 1d03h
Timeouts: Limit Remaining Timer Type
- - -
PPP: LCP Open, PAP (<-), IPCP
IP: Local 10.0.0.1, remote 172.16.0.2
Counts: 14720708 packets input, 1911626778 bytes, 0 no buffer
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun
10736210 packets output, 3331626512 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
The number of subscribers will increase and we must not forget to check the address pool so that everyone has enough =)
PPPoE-ROU # sh ip local pool
Pool Begin End Free In use Blocked
PPPoE 172.16.0.1 172.16.0.254 50 77 0
Another very useful command:
PPPoE- ROU # sh pppoe sess
2 sessions in LOCALLY_TERMINATED (PTA) State
2 sessions total
Here we ran a short walk along the way from the subscriber modem to the aggregation router. I really wanted to talk about how access is provided at all stages in order to form the whole picture. And now I hope that when you connect to the Internet through an ADSL modem, you won’t blame him for being slow - after all, he does a lot of work for you =)
Access via ADSL technology is carried out using a DSL modem on the subscriber side and DSLAM on the provider side. Probably the DSL technology ( Digital Subscriber Line ) will say more correctly , but more often you can hear ADSL ( Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line ), this is the most common form of xDSL. And in this article I want to talk a little about ADSL.
Asymmetry (from the name) consists in different bandwidth of the channels, the subscriber download speed is higher than the return.
Probably each provider, when connecting the subscriber, gives the subscriber an instruction with a diagram of how to turn everything on in order to work. And the first half of the picture (up to and including splitter A) from below should seem familiar to all ADSL Internet owners.

But the second part, this is already provider =)
One of the main advantages of DSL technology for subscribers is the ability to use the phone and the Internet at the same time.
To ensure this, DSL uses a higher frequency range on the line (AB span) than the telephone. Splitters are used to separate these frequencies, both on the subscriber side and on the provider side.
Further, according to the scheme, the subscriber behind the splitter has a modem turned on, and the provider behind the splitter has a DSLAM.
DSLAM ( DSL Access Multiplexer ) collects many subscriber lines and routes them higher to the provider's backbone. It can be compared with a large switch; it also works on the second level of the OSI model.
A bit about ATM.
ATM ( Asynchronous Transfer Mode ) is a cell switching protocol that transfers data in fixed-size cells and provides the link layer of the OSI model.
ATM works very well on low-speed channels up to 2 Mbps and can support multiple logical connections on one physical channel. ATM standards provide for the transfer of heterogeneous traffic (digital, voice and multimedia data) over the same systems and communication lines.
These advantages caused the use of ATM between the subscriber’s modem and DSLAM.
ATM is a connection-oriented protocol and always establishes a virtual circuit ( virtual circuit ) before starting data transfer.
A pair of values is used to identify this channel.VPI / VCI .
- VPI Virtual path identifier - virtual path identifier.
- VCI Virtual call identifier - virtual channel identifier.

On the DSL modem of the subscriber and on the subscriber port on the DSLAM, these values must match. A subscriber can go several virtual channels (several pairs of vpi / vci ).
What happens to DSLAM traffic?
On the DSLAM, VLANs are assigned for certain virtual channels of subscriber ports and the traffic goes tagged to a router, where PPPoE subscription sessions are terminated.

Also on DSLAM, various filters can be applied to certain types of traffic, packet marking is carried out for the organization of QoS .
Aggregation.
After the subscriber traffic has gone tagged with DSLAM , it passes through the chain of provider switches and gets to the aggregation router.
The aggregation router performs the following functions:
- aggregation of traffic coming from the DSLAM 'and
- establishing PPPoE sessions
- applying QoS policies
- routing traffic from subscribers further to the Internet
To whom it is curious, I give an example of setting up an aggregation router =)
Setting up a router for PPPoE termination :
| aaa new-model ! ! | Turn on aaa (Authentication, Authorization, Accounting) |
| aaa authentication ppp default local ! ! ! ! ! | We indicate that authentication will be carried out through local accounts, this is done in order not to load the config. Typically, aaa uses a RADIUS server. |
| username 11101 @ pppoe password 0 pass01 username 11102 @ pppoe password 0 pass02 ! ! | And these are the same local entries "login - password". |
| bba-group pppoe PPPoE_TEST virtual-template 1 pppoe limit per-mac 10 ! ! ! ! | We create a profile for PPPoE, specify which interface will be the "template" for the virtual interfaces that are created when the PPPoE session is established. And we limit the number of PPPoE sessions established from one MAC address. |
| interface Loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ! | |
| interface GigabitEthernet0 / 1.10 description User 11101 @ pppoe encapsulation dot1Q 10 pppoe enable group PPPoE_TEST ! interface GigabitEthernet0 / 1.20 description User 11102 @ pppoe encapsulation dot1Q 20 pppoe enable group PPPoE_TEST ! | We create a subinterface with encapsulation of IEEE 802.1Q, i.e. on it we will accept vlan 10 in the first case and 20 in the second. And we allow PPPoE connection on this interface. |
| interface Virtual-Template1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 peer default ip address pool PPPoE ppp authentication pap ! ! ! | We create a "template" for all future interfaces of Virtual-Access (Vi) address, which will be created when connecting subscribers. We specify from which pool we issue addresses by the PPPoE subscriber and the authorization type will be PAP. |
| ip local pool PPPoE 172.16.0.1 172.16.0.254 | And this is the address pool itself. |
We start the PPPoE session and see what we get:
You can see how many sessions have been created now, using the command.
PPPoE-ROU # sh pppoe summ
PTA: Locally terminated sessions
FWDED: Forwarded sessions
TRANS: All other sessions (in transient state)
TOTAL PTA FWDED TRANS
TOTAL 2 2 0 0
GigabitEthernet0 / 1 2 2 0 0
When a subscriber connects via PPPoE, for him created on the basis of Virtual-Template its interface - Virtual-Access, abbreviated as Vi.
PPPoE-ROU # sh caller
| Line | User | Service | Active time | Idle time |
| Vi2 | 11101 @ pppoe | PPPoE | 1d04h | 1d03h |
| Vi5 | 11102 @ pppoe | PPPoE | 00:23:39 | 00:02:00 |
To end the PPPoE session of the 11101 @ pppoe subscriber from the router, you must enter "clear int vi2".
You can get more complete information (the address that was issued from the pool and statistics) about the PPPoE session using the command:
PPPoE-ROU # sh caller full
User: 11102 @ pppoe, line Vi2, service PPPoE
Connected for 1d04h, Idle for 1d03h
Timeouts: Limit Remaining Timer Type
- - -
PPP: LCP Open, PAP (<-), IPCP
IP: Local 10.0.0.1, remote 172.16.0.2
Counts: 14720708 packets input, 1911626778 bytes, 0 no buffer
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun
10736210 packets output, 3331626512 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
The number of subscribers will increase and we must not forget to check the address pool so that everyone has enough =)
PPPoE-ROU # sh ip local pool
Pool Begin End Free In use Blocked
PPPoE 172.16.0.1 172.16.0.254 50 77 0
Another very useful command:
PPPoE- ROU # sh pppoe sess
2 sessions in LOCALLY_TERMINATED (PTA) State
2 sessions total
| Uniq | ID | PPPoE | Remmac | Port | Source | VA state | SID | Locmac | Va-st |
| 888 | 9193 | 0017.9aa0.75fd | Gi0 / 1.10 | Vt1 | Vi2 | Pta | 0023.5e2b.691a | VLAN: 10 | UP |
| 985 | 39929 | 001e.52f7.d544 | Gi0 / 1.20 | Vt1 | Vi5 | Pta | 0023.5e2b.691a | VLAN: 20 | UP |
Here we ran a short walk along the way from the subscriber modem to the aggregation router. I really wanted to talk about how access is provided at all stages in order to form the whole picture. And now I hope that when you connect to the Internet through an ADSL modem, you won’t blame him for being slow - after all, he does a lot of work for you =)
