3 popular tools for organizing continuous deployment (Continuous Deployment)
- Transfer
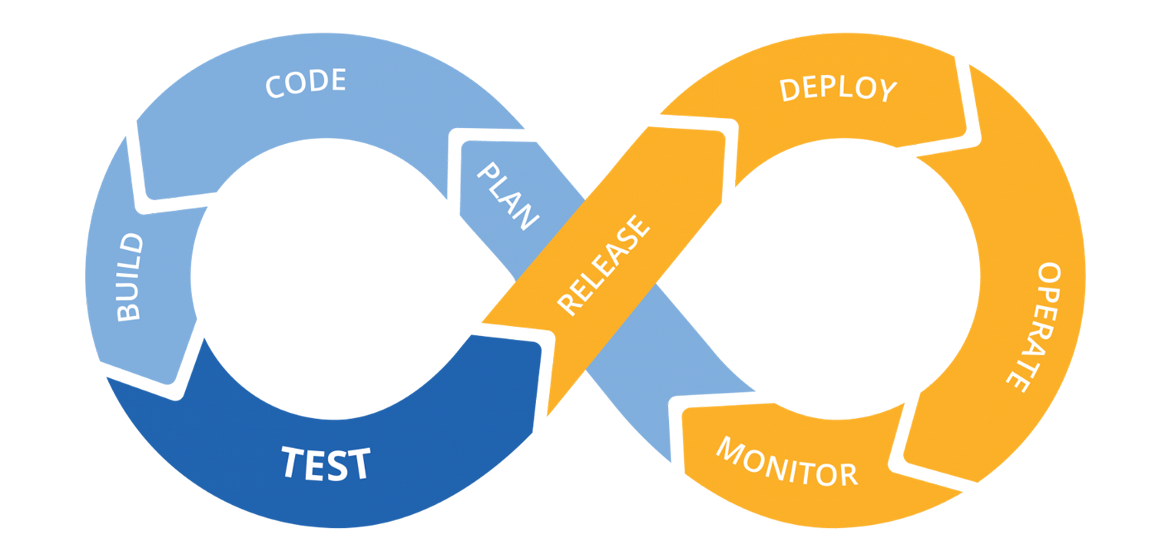
Continuous Deployment is a special approach in software development that is used to quickly, safely and efficiently implement various functions in software.
The main idea is to create a reliable automated process that allows a developer to quickly provide a finished product to a user. At the same time, constant changes are made to production - this is called the continuous delivery pipeline (CD Pipeline).
Skillbox recommends: Practical course “Mobile Developer PRO” .
We remind you: for all readers of “Habr” - a discount of 10,000 rubles when registering for any Skillbox course using the “Habr” promo code.

To control the flow, you can use a wide range of tools, among which there are both paid and completely free. This article describes the three most popular solutions among developers that may be useful to every programmer.
Jenkins
A fully standalone open source automation server. It is worth working with him to automate all kinds of tasks related to the assembly, testing, delivery or deployment of software.
Minimum PC requirements:
- 256 MB RAM, 1 GB file space.
Optimal:
- 1 GB of RAM, 50 GB of hard disk space.
For work, you will also need additional software - Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 8. The
architecture (distributed computing) is as follows:

Jenkins Server - an installation that is responsible for GUI hosting, as well as the organization and execution of the entire assembly.
Jenkins Node / Slave / Build Server - devices that can be configured to perform assembly work on behalf of Master (the main node).
Installation for Linux
First you need to add the Jenkins repository to the system:
cd / tmp && wget -q -O - pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add - echo 'deb pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary /' | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/je
Update package repository:
sudo apt update
Install Jenkins:
sudo apt install jenkins
After that, Jenkins will be available on the system by default port 8080.
To check the functionality, open the localhost : 8080 address in the browser . Then the system will prompt you to enter the initial password of the user with root rights. This password is located in the file / var / lib / jenkins / secrets / initialAdminPassword.
Now everything is ready to work, you can start creating CI / CD streams. The graphical interface of the working environment is as follows:


Jenkins Strengths:
- scalability provided by the Master / Slave architecture;
- the presence of REST XML / JSON API;
- the ability to connect a large number of extensions thanks to plugins;
- An active and constantly evolving community.
Minuses:
- missing analytical unit;
- not too convenient interface.
Teamcity
Commercial development from JetBrains. The server is good for simple setup and excellent interface. There are a large number of functions in the default configuration; the number of available plugins is constantly increasing.
This product requires the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 8.
Server requirements for hardware are not critical:
- RAM - 3.2 GB;
- processor - dual core, 3.2 GHz;
- communication channel with a bandwidth of 1 Gb / s.
The server allows you to achieve high performance in work:
- 60 projects with 300 assembly configurations;
- allocation of 2 MB to the assembly log;
- 50 build agents;
- the ability to work 50 users in the web version and 30 users in the IDE;
- 100 external SLE connections, usually Perforce and Subversion. The average change time is 120 seconds;
- more than 150 modifications per day;
- work with the database on one server;
- JVM server process settings: -Xmx1100m -XX: MaxPermSize = 120m.
Agent requirements are determined by running assemblies. The main task of the server is to monitor all connected agents and distribute assemblies from the queue to these agents based on compatibility requirements, with the results reported. Agents have various platforms and operating systems, plus a pre-configured environment.
All information about the results of the assembly is stored in the database. First of all, this is history and other similar data, VCS changes, agents, build queues, accounts and user permissions. Only assembly logs and artifacts are not included in the database.

Installation for Linux
To manually install TeamCity with the Tomcat servlet container, use the TeamCity archive: TeamCity .tar.gz. You can download it from here .
tar -xfz TeamCity.tar.gz
/ bin / runAll. sh [start | stop]
At the first start, you need to select the type of database in which the assembly data will be stored.

The default configuration runs on localhost : 8111 / with one registered build agent running on the same PC.
TeamCity Strengths:
- simple setup;
- convenient interface;
- a large number of built-in functions;
- support;
- There is a RESTful API;
- good documentation;
- good security.
Minuses:
- limited integration;
- it is a paid tool;
- a small community (which, however, is growing).
Gocd
An open source project that requires Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 8 to install and operate.
System requirements:
- RAM - 1 GB minimum, better more;
- processor - dual-core, with a core frequency of 2 GHz;
- Hard disk - at least 1 GB of free space.
Agent:
- RAM - at least 128 MB, better more;
- processor - at least 2 GHz.
The server provides agents and provides a convenient interface for the user:

Stages / Jobs / Tasks:

Installation for Linux
echo “deb download.gocd.org /” | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gocd.list
curl download.gocd.org/GOCD-GPG-KEY.asc | sudo apt-key add -
add-apt-repository ppa: openjdk-r / ppa
apt-get update
apt-get install -y openjdk-8-jre
apt-get install go-server
apt-get install go-agent
/ etc / init.d / go-server [start | stop | status | restart]
/etc/init.d/go-agent [start | stop | status | restart]
By default, GoCd runs on localhost : 8153.
GoCd Strengths:
- open source
- simple installation and configuration;
- good documentation;
- great user interface:

- Possibility of step-by-step display of the GoCD deployment path in one view:

- excellent display of the conveyor structure:

- GoCD optimizes CD workflow in the most popular cloud environments, including Docker, AWS;
- the tool makes it possible to correct faults in the pipeline, for which there is a tracking of each change from a commit to deployment in realtime mode.
Minuses:
- at least one agent is needed;
- there is no console to display all completed tasks;
- To execute each command, you need to create one task for the pipeline configuration;
- to install the plugin, you need to move the .jar file to <go-server-location> / plugins / external and restart the server;
- relatively small community.
As a conclusion
These are just three tools, in fact there are many more. It’s difficult to choose, so you need to pay attention to additional aspects.
The open source code of the tool makes it possible to understand what it is, plus it’s faster to add new functions. But if something does not work, then you have to rely only on yourself and on the help of the community. Paid tools provide support that can sometimes be critical.
If safety is most important, you should work with a local tool. If not, then choosing a SaaS solution is a good option.
And the last: in order to ensure a truly effective process of continuous deployment, it is necessary to formulate criteria, the specificity of which will make it possible to narrow the range of choice of available tools.
Skillbox recommends:
- Two-year practical course “I am a Web Developer PRO” .
- Online course "C # -developer" .
- Practical annual course "PHP-developer from 0 to PRO" .
