Grammar of English. Than vs. Then - how to understand which word to use
- Transfer
One of the finest points in the grammar of the English language is to learn in which situations to use a particular word. It doesn’t sound very difficult, but there are a lot of situations like “who vs whom” that I wrote about earlier in English. One of the most common such questions is the difference in the use of “than and then”.
I found an interesting post with rules to help deal with this issue. I present to you an adapted translation of this useful material.
When to use "than"
The word “than” usually plays the role of a union that combines two separate sentences into one or links the words in a phrase. Most often, “than” is used for comparisons, and sometimes a word can take the meaning “except” or “when”.
Examples:
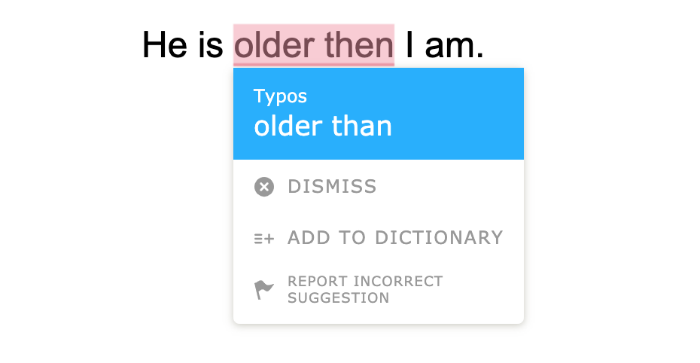
He is older than I am.
I'd rather die than accept this job offer.
In some cases, “than” acts as a preposition connecting a noun or pronoun with a verb / adjective. This technique is used to express temporal relationships and, again, for comparisons.
In addition, you can use “than” with past tense verbs (especially past perfect), as well as in phrases where events immediately follow one after another.
Example:
Hardly had I prepared for a meeting than the fire alarm rang.
Also, the word “than” is part of a large number of English idioms:
- “More dead than alive”
- "Better late than never" ("better late than never")
- “Actions speak louder than words”
- “Bite off more than you can chew” (“bite off more than you can swallow”)
- Etc.
When to use "then"
In turn, the word “then” often acts as an adverb, which refers to the adjective, verb and other adverbs. Then can have many meanings, but there are two of the most common. The first is a description of a specific time in the past or future, and the second is a description of a sequence of events.
Examples:
First, do your homework, then play soccer.
This afternoon I'll go to a business meeting, then hang up with an old friend in a bar.
In addition, the word "then" is found in many idioms and stable expressions:
- then and there ("then and there")
- every now and then ("from time to time")
- If you're born to be hanged, then you'll never be drowned (“He who is destined to be hanged will not drown”)
- see you then
- etc.
Conclusion
“Then and“ Than ”are very similar in pronunciation, writing, and even use. Therefore, it is so difficult to decide in which case which one should be applied. But there is still a difference, and in order to avoid mistakes, you will have to deal with these subtle points. Or you can install a tool for checking grammar and spelling - as a rule, such software can correctly use then / than.
