Tesla Autopilot: Implementation Strategy

In January 2016, Elon Musk predicted that Tesla cars would be able to drive independently from the US east coast to the west “in about 2 years,” but this did not happen. Recently, the Tesla autopilot page was finally updated, and according to its author, it can become so good that in the foreseeable future it will no longer require human control.
Tesla clings to old conventional wisdom
In 2014, Tesla began supplying the first generation of autopilot equipment. The Society of Automotive Engineers published a five-level taxonomy of autonomous driving systems , which included the gradual transformation of driver assistance systems, known as “level 2” in SAE, into fully autonomous systems that could work without human control, “levels 4 and 5”. But in the last five years there have been major changes in the company's philosophy. Most automakers now view human control and full autonomous driving as completely separate, independent sectors of the automotive market.

None of the companies have advanced as far as autopilot like Google, whose autopilot project has been singled out as Waymo. Around 2012, Google engineers developed a highway driving system and allowed some ordinary users to test it. Drivers were warned that the system was not yet completely autonomous, and they were instructed to constantly monitor the road. But the self-management team found that users too quickly began to trust the system . Car cameras have shown that controller users are napping or talking on their cell phones with their heads down. And this posed a great risk to their safety.

“It's hard to win because beta testers have lost contextual awareness,” said Waymo CEO John Krafchik in 2017.
Thus, Google abandoned plans for a project to help a driver on the highway and decided to take up another type of unmanned traffic - a taxi service, which will initially be distributed in the metropolitan area of Phoenix (Washington DC). There are wide, well-marked streets, and snow and ice are extremely rare there. The provision of autopilot services in Phoenix should be much simpler than developing a car with autopilot with its use in different cities.
There are other benefits to this approach. Cars with automatic control receive information from the database of high-resolution maps. Collecting cartographic data in one district of a city is much easier to do than trying to map a whole world. Such cars do not use lidar orientation sensors, worth tens of thousands of dollars, which significantly reduces the cost of the car. The proposed economical project is more viable for taxi services without a driver, since the autopilot system replaces an expensive live taxi driver.
Over the past three years, most other self-driving technology companies have followed Waymo's lead. So in 2016, General Motors bought a startup called Cruise and began working on an autonomous taxi service in San Francisco. In 2017, Ford made a similar bet on Argo., and now the company is developing an autonomous taxi service project in Miami and Washington.

Volkswagen and Hyundai have struck a deal with startup Aurora , co-founded by Chris Urmson, a former Google self-driving project leader, to develop fully autonomous taxi services. Technology companies such as Uber and Zoox also plan to introduce autonomous taxi services.
Tesla Business Model
Tesla, meanwhile, is steadily pushing forward with its original strategy. For two years, Tesla has charged $ 3,000 from customers for a full self-drive package. But progress was slow. And this confused Tesla. Rejecting the old strategy is likely to require reimbursement of funds to customers who paid for the Self-Driving package, which was ultimately inconvenient and expensive. Instead, Tesla's decision was to change strategy.

“We already have all the opportunities for autopilot driving on highways,” Elon Musk said in January.
“Thus, now we can ride with an autopilot not only right along the highway, but also make turns to junctions and side roads.” Obviously, the driver must monitor the car so that it does not crash.
Last week, Tesla announced a reshuffle of the autopilot's pricing structure, which reflects this new, more generous definition of full self-driving. Previously, driver assistance functions were sold as part of the Tesla Advanced Autopilot level, which cost $ 5,000. Customers can pay an additional $ 3,000 for the Self Drive package. But people who have already paid for this package have not received any additional functionality. They were waiting for, well, "full driving", because a machine that can behave without human supervision.
The new pricing structure defines complete self-driving in different ways. For example, the ability to navigate interchanges on the freeway has been changed from Advanced Autopilot in the old pricing structure to Full self-driving in the new. Later this year, Tesla with the “Full Self-Driving” package will be able to “recognize traffic lights and stop signs and respond to them”, as well as perform “automatic driving through the city streets”.
Consequently, Tesla now seems to define “complete independent driving” as a system that can handle most of the road conditions under the supervision of a human driver. Tesla is still striving to improve the system so that - ultimately, it can work without human control. But at the same time, the new pricing structure makes things more comfortable for the user, since Tesla can now claim that customers have already received “full independent driving” features, such as the ability to stop at stop signs.
Tesla's strategy can cripple people
From a business strategy perspective, Tesla’s shift makes sense.
Remember the story of how early Google beta testers applied makeup or tinkered with their phones when they should have been following Google prototypes. It’s really hard for a person to pay attention to the road when driving in a car that basically moves by itself. The better the technology of self-driving, the easier it is for the mind to lose vigilance and the less likely it will be ready when intervention is required.
This dynamic had tragic consequences a year ago when a Uber car hit and killed a pedestrian in Tempe, Arizona. The video from the DVR shows how the safety driver looked down on his knees for several seconds before the accident. Records from Hulu show that at that time she was broadcasting a television show on her phone.
Leading car companies are taking a number of precautions to avoid a recurrence of this tragedy. Safety drivers undergo extensive training before they are allowed to get in the car. Some companies limit their drivers' opening hours. Many companies put two people in each car - one at the wheel and the other a navigator, making sure that the driver remains vigilant.
Tesla's plan is essentially to launch a large-scale project to test cars without drivers, using its customers as unpaid safety drivers. Drivers do not receive real training about the dangers of inattentive use of autopilot. Tesla does not limit the number of hours during which people can drive cars, and the company obviously does not hire someone to sit in the passenger seat.
Tesla takes several important precautions. Tesla’s car detects if the driver’s hands are on the steering wheel and issues a series of increasing warnings, which ultimately stops if the driver ignores them. Messages on the screen warn drivers of the dangers of inattentive driving.
Nevertheless, there is reason to doubt that these measures are sufficient to enable drivers to perform their tasks. And this problem will only be aggravated, as the autopilot begins to move along the interchanges on the freeway, turn and stop at traffic lights. If your car safely takes you home from work for 100 days in a row, you can naturally dull your vigilance a bit. But if the car makes a serious mistake during the 101st trip, you may not pay enough attention to intervening and preventing an accident. Just a few seconds of inattention, and you can skip the deadly mistake.
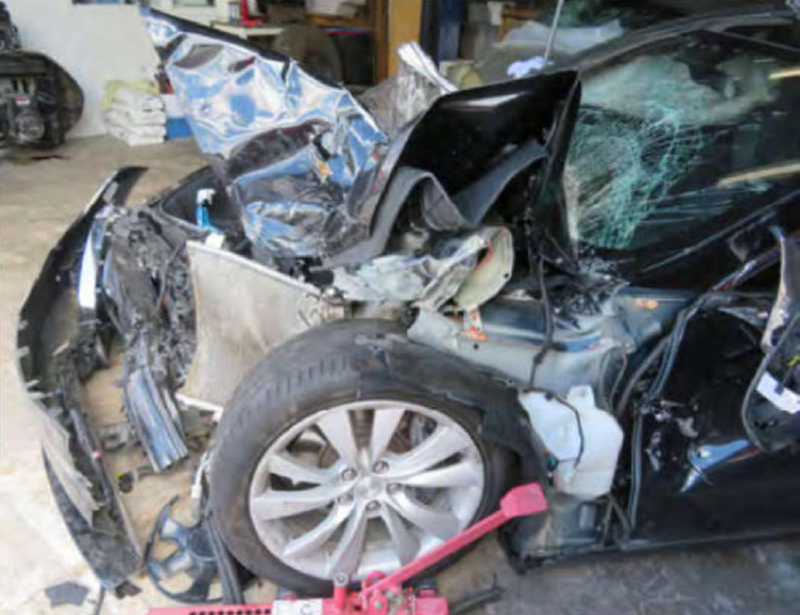

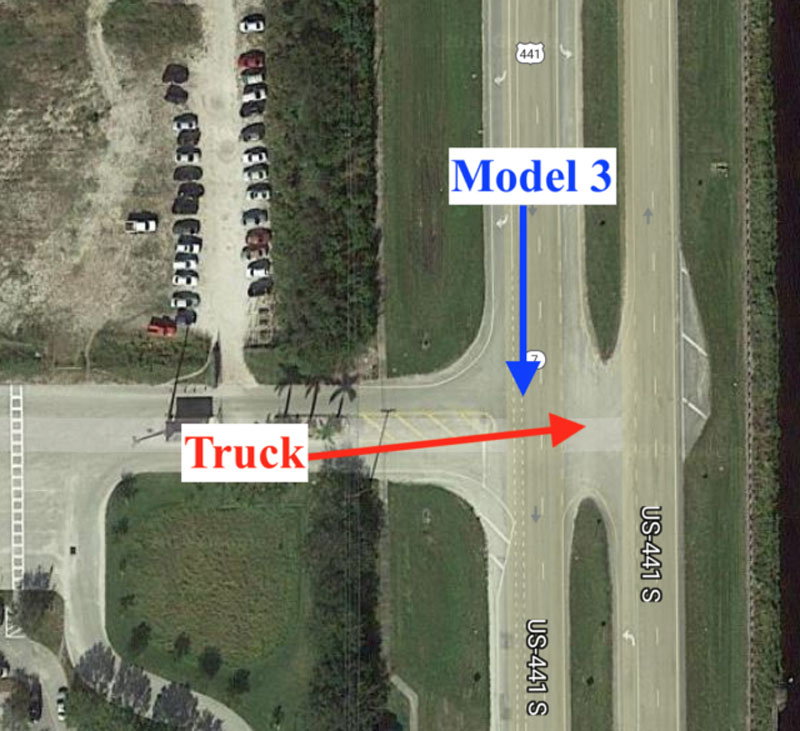
Tesla owner Walter Huang died in March 2018 after his Model X headed for the concrete lane at a speed of 70 mph. Low-contrast lanes forced the vehicle to leave its lane and go into the "mountain zone" - a triangular zone of the asphalt road that separated the lanes of the highway from the lane. If Juan did not expect Model X to make this particular mistake, it would be easy to assume that this was a stretch of the path that did not require his close attention.
Musk claims that the testing period will be quite short, because soon the technology will become much safer than the human driver. “When will we think that it is safe for complete independent driving? Probably closer to the end of the year, ”Musk said. But this seems like another of the overly optimistic forecasts. The lack of orientation sensors (lidars) will complicate autopilot driving. Lidar helps make sure that the car does not go straight into large obstacles, such as concrete partitions or other vehicles. Most recently, in October last year, the Autopilot still crashed into stopped cars.

Nevertheless, even with the lidar and many years ahead of Tesla, Weimo struggled to get work without a driver in the same metropolis. Tesla is working to achieve fully autonomous operation in a wide range of transport and weather conditions on different continents. It is very difficult to believe that this will happen in 2019.
