Harvard recorded an animation in the DNA of a living organism

The term "viral video" takes on new meaning in connection with an experiment conducted by scientists at Harvard Medical School. They managed to write digital information not just into synthesized genetic material, but into the genes of the living bacterium E. coli . This means that a living organism can act as a carrier of digital information and store files directly in DNA.
Scientists have long been experimenting with storing digital files in DNA, because this medium is great for digital information. After all, this is just a code in a quadruple number system: the genetic program is encoded with four nucleotides, which are denoted by the symbols A, G, C and T, and it holds a lot of information in a limited space.
DNA file writing experiments have been particularly successful in the last five years. In 2012, a Harvard group wrote a book of 53,000 words into a DNA synthesized macromolecule . The absolute record was set in March 2017, when 200 megabytes of information were recorded in DNA . Even Microsoft has connected to these scientific experiments: a year ago it became known that Microsoft ordered Twist Bioscience to synthesize 10 million DNA macromolecules with a specific nucleotide sequence. Interestingly, the manufacturer made the molecules, could not read the information recorded there, because it did not have a decryption key.
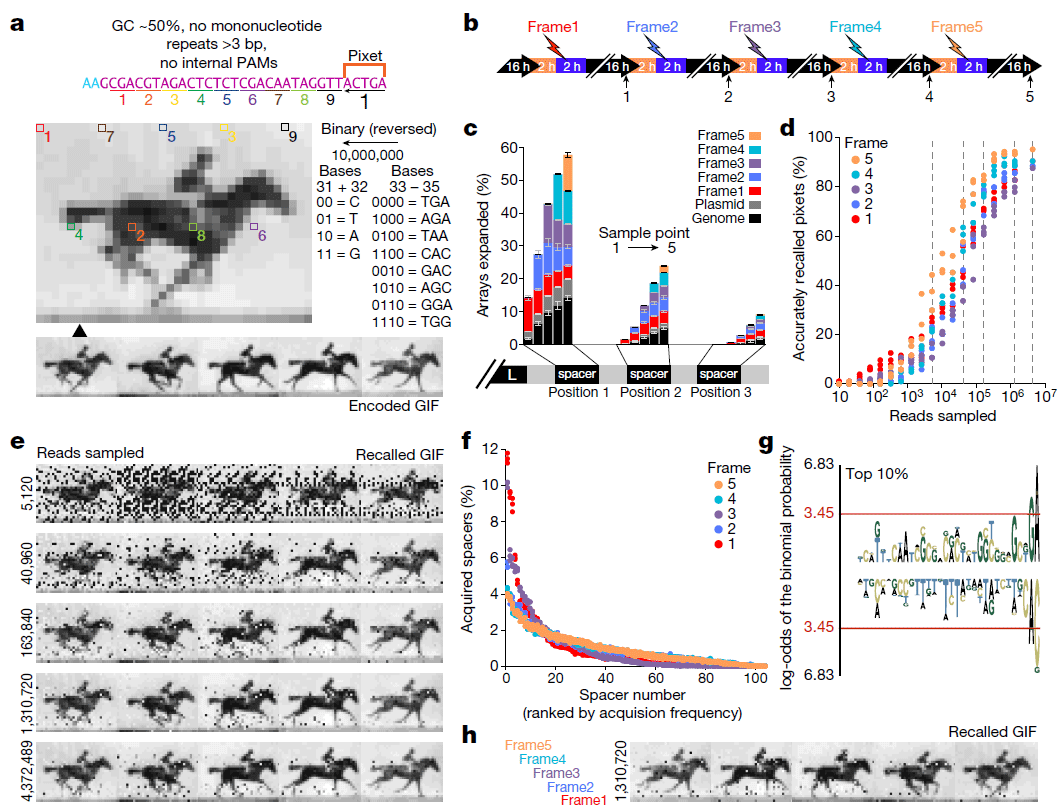
Until now, all experiments have been carried out mainly with synthesized DNA; never before have scientists succeeded in writing digital information to a living organism and then successfully reading it. This is a much more complex process, but researchers at Harvard did this using the CRISPR genome editing technique.
CRISPR (clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeats) is based on the mechanism of antivirus protection in the body. The immune system recognizes foreign viruses, captures a DNA fragment from them and places it in the signature database, which is stored in the bacterial genome. Scientists tricked the system by slipping fragments of their animated file, frame by frame, instead of viruses. The deceived immune system itself has composed the desired sequence from them.
For recording, we chose one of the first in the history of animated images in the history of photography - a black horse moving on a white background, which was recorded at his farm in Palo Alto (California) by the English and American photographer Edward Maybridge in 1877. It was the world's first successful chronographic photography experience. Twenty years later, the Lumiere brothers will take over the experience and call it cinema.
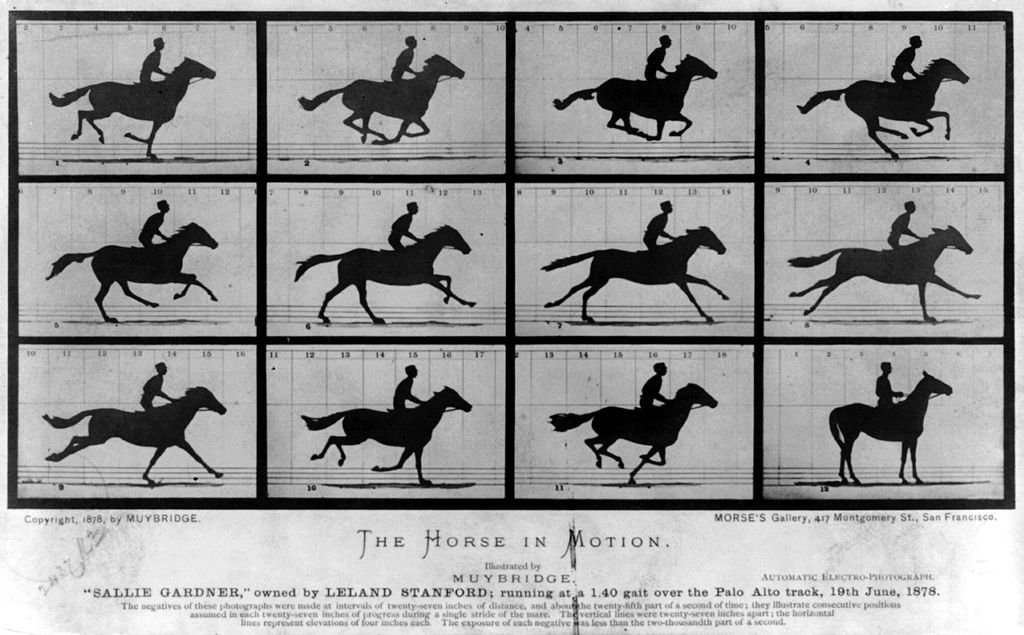
Maybridge's “Horse in Motion”
An animated file with a running horse of 36 × 26 pixels was recorded in DNA. Then, using the DNA sequencing technique, the researchers restored the animation with an accuracy of 90%.

The density of information in DNA is much higher than in flash memory or on magnetic media. About 1 zettabyte of files (10²¹ bytes) can be written in 1 gram of DNA, and the entire human genetic program fits in 1.6 GB . According to other estimates, if we calculate the total amount of information in the DNA of all human cells, then about 60 ST come out, and 99.9% of this information is the same for all.
The authors of the scientific work say that DNA is valuable not only as a carrier of existing information, but also as a means for recording biological processes in the body, which can then be read and decoded as log files from a server. For example, science does not know how cell development occurs at an early stage. Indeed, the whole diversity of human cells develops from exactly the same pluripotent stem cells. For unknown reasons, some of these cells turn into brain cells, others into internal organs, into blood cells, etc. The process of choosing the role and time when a "decision" is made about turning into a particular cell, as well as factors under the influence of which this decision is made, until it has been completely investigated by science. Maybe, "Digital" logs - a system for recording and storing information inside cells - will give a chronological record of cell development and help us understand the details of this process. But first, the system is checked on digital data.
It is curious that long before the development of molecular biology, Richard Feynman said about the recording of information in DNA: “Biology does not just write information, it does something with it,” he said in a 1959 lecture . That lecture prompted Dr. Leonard Adelman (one of the co-authors of the RSA encryption algorithm, where his last name is the letter A), to the first experiments on writing data to DNA. In 1994, he reported that molecular calculations were able to solve a mathematical problem from combinatorics.
Progress in bioinformatics is going at a crazy pace. The first sequencing of the human genome took several years and cost $ 3,000,000,000. The most optimists said that after 50-60 years, we could reduce the cost to $ 1,000. In fact, it took six years.
The scientific work was published on July 12, 2017 in the journal Nature (doi: 10.1038 / nature23017, pdf ).
