About using character recognition camcorders on low-performance computing devices
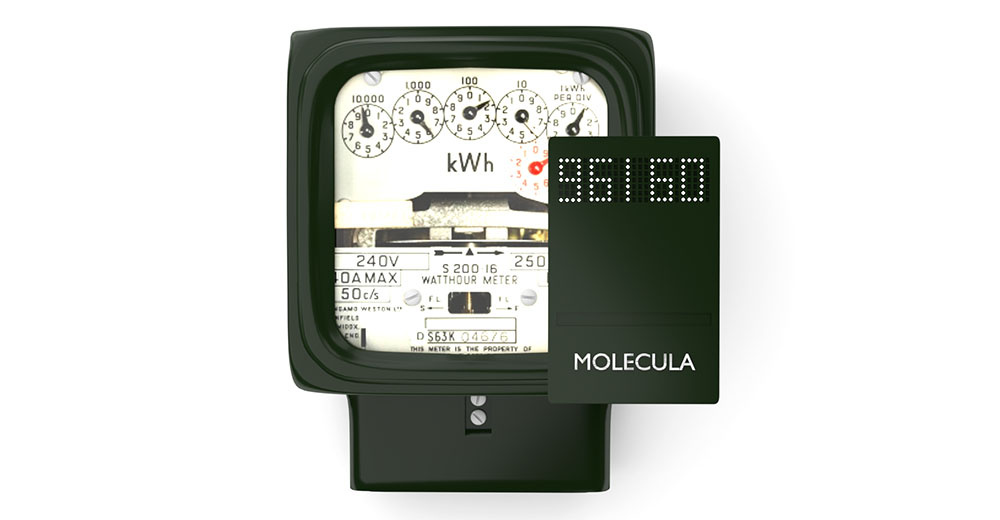
Earlier, the article talked about the development of a recognition method that allows optical recognition of characters from video on the fly. As evidence of the effectiveness of the new method, its implementation was used on a device that was not intended for this purpose - the microcontroller esp8266. During the discussion, the question arose: where can I use devices with recognition on board (reader)? Yes, and for less than $ 50. It is clear that in the same place where more expensive devices are used, but I would like to discuss other options. We hope for the help of readers in this matter. What do we see?
1. Reading of metering devices and measuring devices
To date, a clear trend has emerged in the issues of accounting and control over the use of various types of resources - electricity, gas, water and heat - the installation of “smart” meters. A smart meter is capable of transmitting measurement results, and the smartest is able to disconnect the consumer from electricity by a command “from above” in case of non-payment, and possibly for other reasons. The modern smart meter plays on the side of the supplier and leaves no freedom of choice for the consumer.
According to Ernst & Youngfifteen years of experience operating smart meters in Europe did not lead to unambiguous conclusions about their effectiveness, although everyone understands that there is something to it. The main effect is achieved by reducing the cost of taking readings, to a lesser extent reducing the stolen energy. A pilot project in our country showed much better results - a 37% reduction in losses in the Kaliningrad region, for example. The question remains, of course, how to remove the remaining 63%.
1.1. Considering that at an estimated cost of a domestic smart meter of $ 500, the payback period is 9 years, the following scheme seems to be interesting, which allows to reduce the payback period by at least four times:
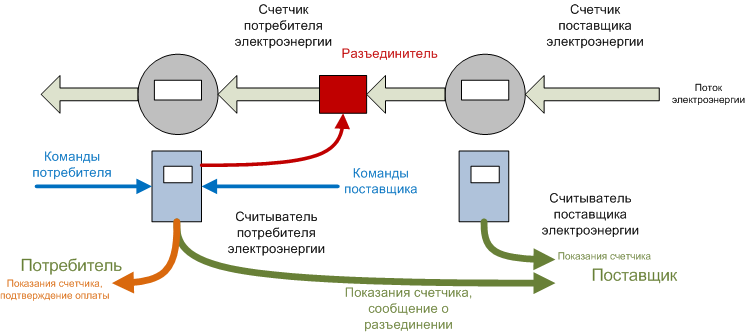
Reading is done through a reader, similar to that shown in the very first picture. The circuit contains two counters - a consumer counter that does not need to be changed and a duplicate supplier counter. The difficulty of synchronizing meter readings, as well as the awareness of continuous monitoring, significantly reduces the possibility of theft of electricity.
In addition to them, the scheme uses two optical readers with different functionality: the reader from the supplier’s counter can only transmit readings after a specified time interval, it does not accept commands and works like an AMR generation counter.
The consumer reader, in addition to directly reading the readings, can interact with the consumer and the supplier, as well as with the network disconnector. This reader can be in two states: 'blackout / disable / allow'. The switching of states is possible only during the payment period at the supplier’s command. If payment is made by the provider, the reader switches to the disabled state and the next switching of the state is possible only in the next payment period.
Disabling prohibition serves to prevent erroneous disconnections / connections (including from third parties). Deactivation can only occur in the reader state 'power off allowed'.
Thus, the consumer reader works like an AMI generation counter - the supplier receives from the reader the consumer counter and current disconnection information, and the reader receives commands and balance messages. At the same time, the consumer can also receive information on the readings of his counter and the status of the reader based on the commands.
The reader allows you to make any meter multi-tariff, as it captures not only the readings of the meter, but also the time point of taking readings.
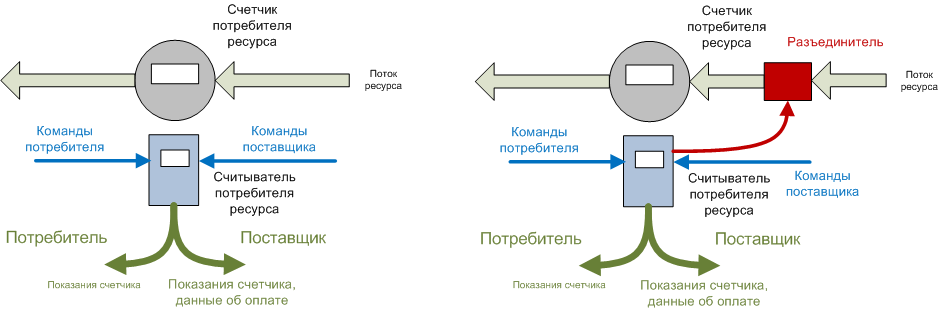
1.2. In addition, we should not forget about other types of resources - gas, water and heat. Since the theft of such resources is more difficult compared to electricity, simplified schemes can be used to take readings from metering devices.
1.3. Another example of the use of the device is the reading of the readings of measuring devices. For example, a large number of trading organizations use scales of various manufacturers, which are equipped with digital terminals that do not have outputs for communication with computers. When automating processes in such organizations, you can use the devices in question to read the necessary information.
2. Car license plate identification
Today, recognition of car numbers can be considered a trivial task. There are not only a large number of solutions that perform recognition on the server, but also cameras with recognition on board: Italian Tattile , Hungarian Arh , German Siemens , British Mav , Chinese HIKVision and Dahua , domestic Iris and many others.
Of course, there are a large number of applications in which cameras with the ability to recognize car numbers could find application. For instance:
2.1. Parking management. Currently, various occupancy sensors are used to track free parking spaces, mounted in the surface under the car or placed above it. Such sensors allow you to determine free / occupied space, but are not able to determine the number of the car that takes this place. Adding such an opportunity would offer customers new types of service, in addition to identifying a car at the entrance / exit:
- vehicle location message;
- booking a parking space with different time frames;
- escorting a car to a parking space with the help of dynamic signs
as well as it is done in an underground city in Finland;


* Freeze frames were made with the video above.
- the introduction of a differentiated payment, depending on the location of the
parking space ; - organization of the interface between the car and the parking lot, provided that the
phone number is linked to the car number; - receiving information about the amount of payment after vacating the seat and paying by card
tied to a phone tied to a car number;
2.2. Management of gas stations of the car. The ability to refuel without leaving the car (if there is a refueling tank) according to the scheme:
- Determining the number of the car drove up to the column;
- Checking the availability of necessary funds on a card tied to a phone tied to a car number;
- Request for confirmation of refueling;
- Gas station;
- Automatic payment;

* The basis for the image was taken from the resource init-e.ru.
2.3. Search for a stolen car. The low price of the device allows you to drastically increase the number of surveillance cameras with the possibility of recognition on board and build a citywide system for recording movement and / or parking with the desired number, model and color. For such a system, there is no need to transfer video or individual frames. All the necessary information is several tens of bytes, so you can establish a very fast data exchange.
2.4. An application in which it is necessary to read the readings of measuring devices and determine the number of the vehicle is the organization of automated weighing on public roads. In case of overload, the reader transmits the vehicle number to the server, which can send relevant information to other readers to monitor the movement of the overloaded car.
3. Infrastructure
In all the examples considered, only one side of the data collection systems was considered, namely, the reader. It is clear that this is only part of the system that collects data. This data needs to be transferred somewhere and somehow for processing, which implies a data receiver and a transmission channel. Thus, we get a structure consisting of a data source, two-way transmission channels and data receivers.
3.1. To transmit over the channel, various wireless (Bluetooth, WiFi, GSM, GPRS, LPWAN, ...) and wired (PLC, xDSL) technologies or their combinations are used. The choice of a specific architecture depends on the problem being solved. Since the amount of data transferred is small, the most convenient technology for long-distance transmission is LPWAN , which includeSwift , Sigfox , LoRaWAN , as well as technology based on cellular networks LTE-M and NB-IoT .
3.2. In most examples, the reader works with one data recipient - the server of the system, however, in data collection systems from metering devices the reader works with two recipients - the server of the system and the user. Moreover, for a user at a close distance, it is convenient to use channels with WiFi or Bluetooth for data transfer.
3.3. In the examples of parking and gas station management, it is easy to identify a car in the system, but communication with the car driver is necessary to organize feedback. For this, services of various levels are necessary at which it is possible to register communication between the vehicle number and the driver’s smartphone or to equip the vehicles directly with cellular communications. In this case, users registered on such services can send messages to each other on the car number, just as the system can send messages on violations and fines to the car number.
Thus, the existing infrastructure allows you to build new services to solve interesting applications.
