Production calendar and classifiers
In previous articles, I talked about how to take the first steps in the easla.com workflow system . Now it’s time to talk about how to set up a working calendar and store non-changing or rarely changing data in the system.

A work or production calendar is a unique tool for managing the work and days off of each organization. With its help, in easla.com it is possible to calculate time intervals not on calendar days, but on working days.
For example, in the process of task management, there is always the question of calculating the planned closing date of a task based on certain norms of time for its completion. In terms of calculating the planned date, the urgency of the task, the category of the task, the type of customer, and other criteria may appear, and as a result, the planned date and time of closing must be calculated in the task taking into account working hours, excluding weekends and holidays.
Or, a good example from the "IT" practice, when you need to take into account the parameter of the description of the level of service provided to calculate the planned date and time of the incident in working days and hours. The service states that the elimination time is, say, 8 hours, i.e. 480 minutes and it is necessary to calculate what the planned time for eliminating the incident on Friday 40 minutes before the end of the shortened working day on the eve of the weekend and Victory Day will be .
To do this without a working calendar is almost impossible!
At easla.comA work calendar is a set of rules that describe one or more days. Each rule must be valid for one year. The rules apply in the order they are placed, i.e. the first rule is the most important, and all the others following it, as it were, describe the exceptions to the first rule. Thus, in most cases, each organization will have at least three rules:
Of course, there are usually more rules: New Year's holidays, various holidays and holidays.
In working days and holidays it is necessary to indicate the working hours. They should be continuous non-overlapping time intervals. For example, a working day from 09:00 to 18:00 with a lunch break from 13:00 to 14:00 should be described in two time intervals: 09: 00-13: 00 and 14:00 to 18:00. Moreover, the time intervals must be located in the correct order.
To facilitate the work with the calendar, special service functions are added that are added to easla.comas the end of each year approaches. Now, in 2016, in the section “All calendar rules”, the service team “Work calendar for 2016” is available. With its help, a typical working calendar is created with a working day from 09:00 to 18:00, a lunch break from 13:00 to 14:00 and all holidays, holidays and weekends!
A properly configured calendar allows you to use the special functions calendarDateAdd and calendarDateDiff and get accurately calculated dates in working days and hours with an accuracy of a second!
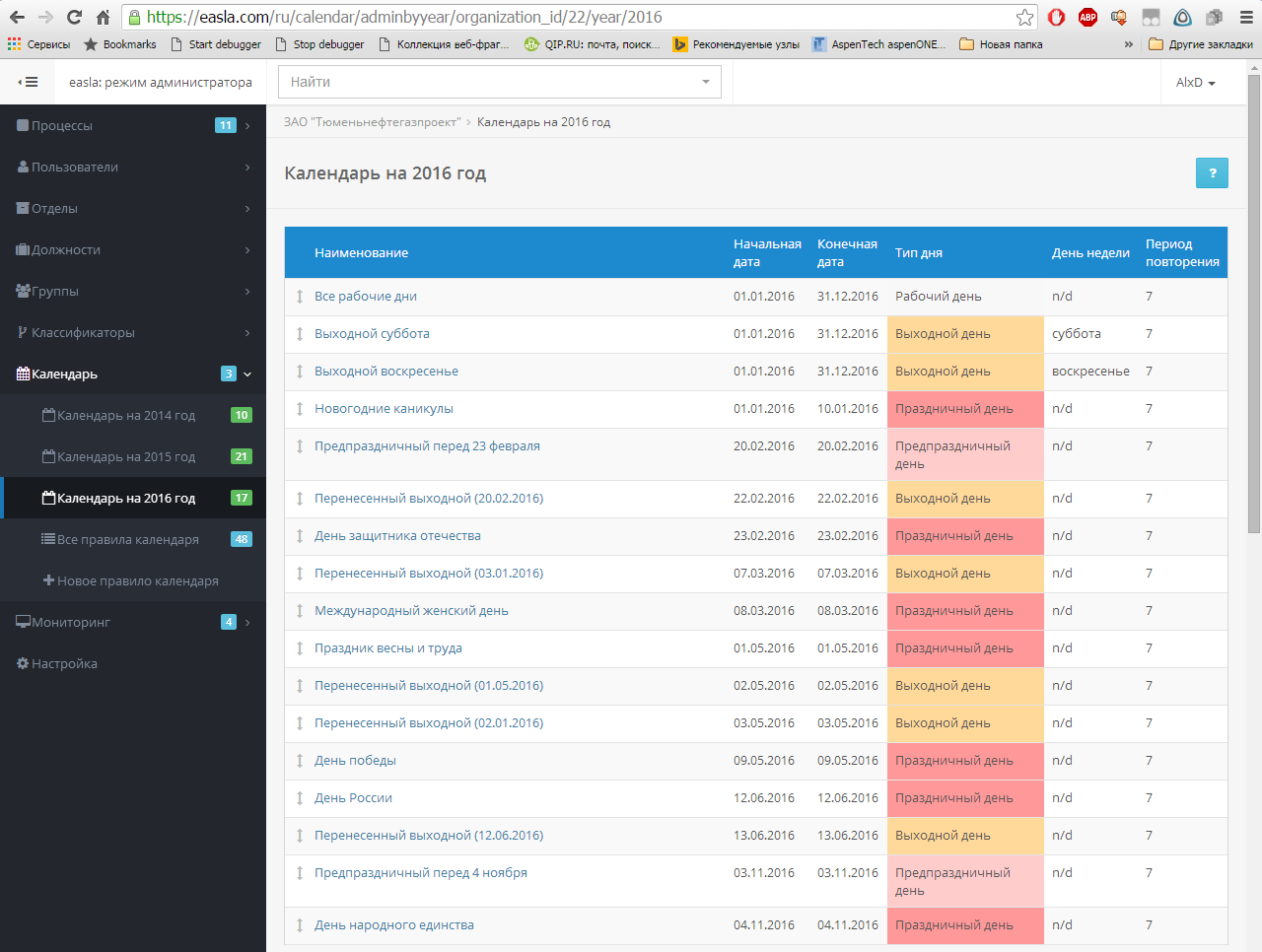
For administrator’s convenience, the calendar rules are displayed both in the form of a list:
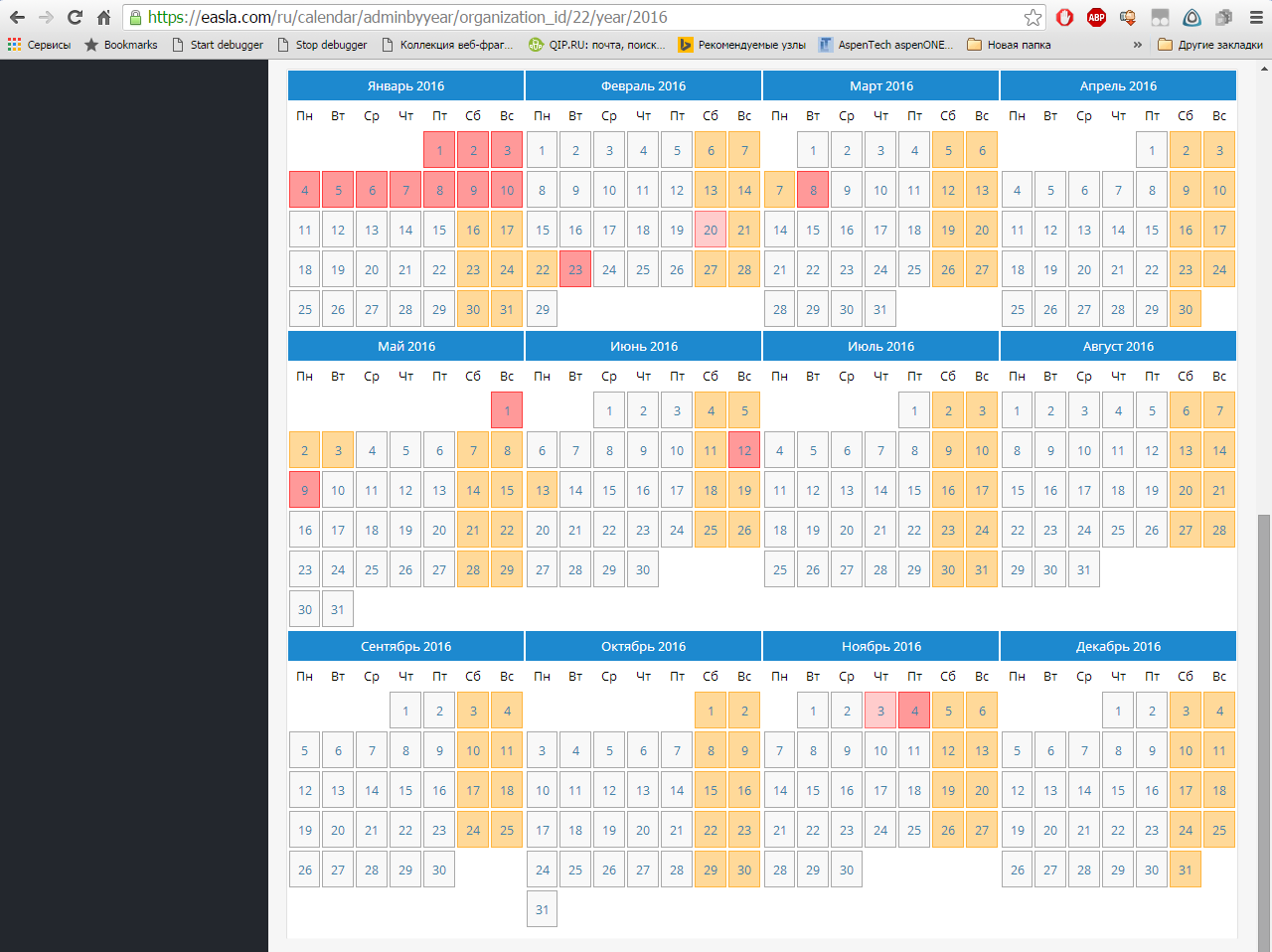
As well as the calendar form:
In each organization, when managing business processes, there is a need to decide on a set of different parameters that either do not change at all, or change extremely rarely. Such parameters are found in a variety of processes and can be attributed to them, for example:
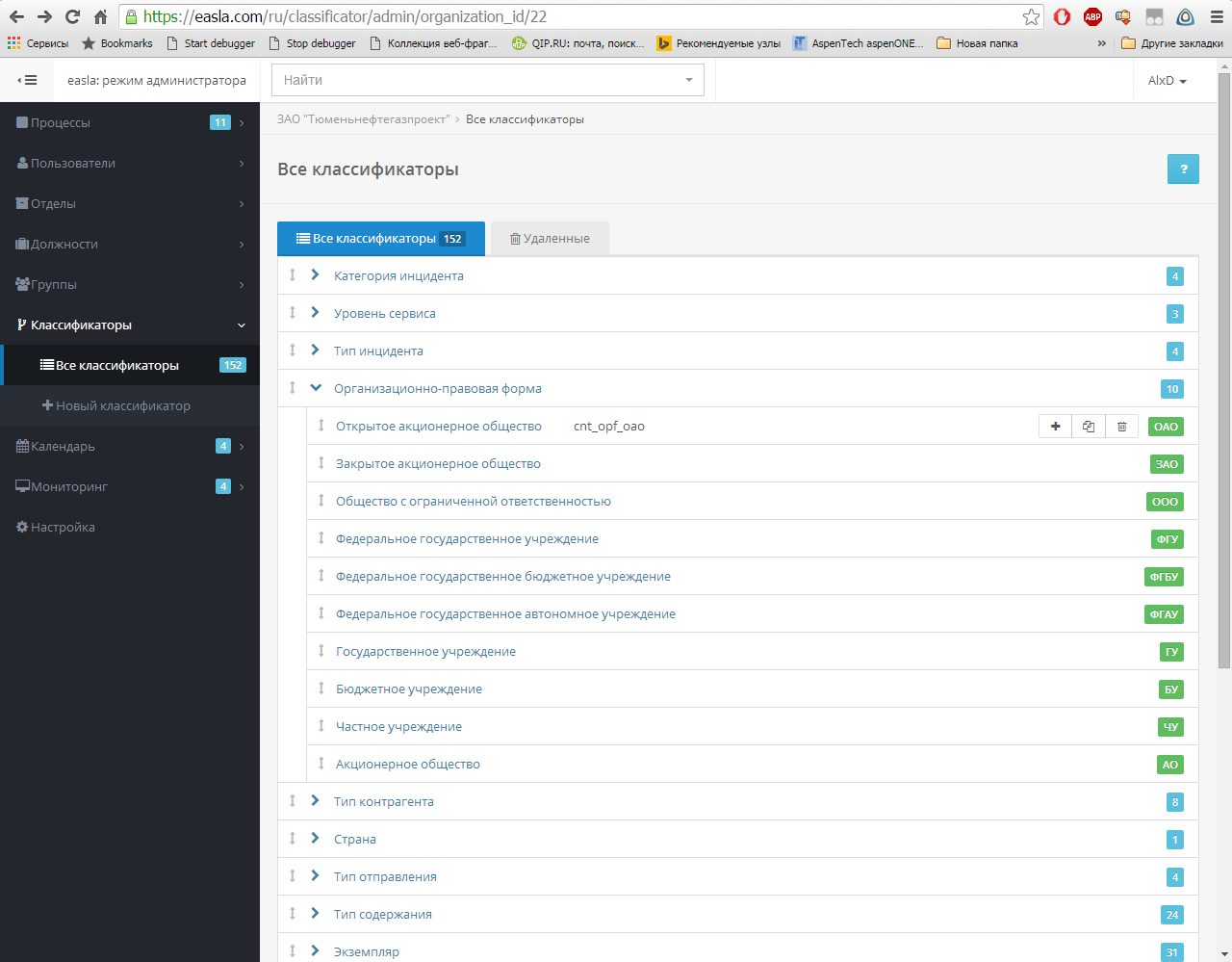
In easla.com, classifiers exist for storing such parameters. They are stored hierarchically. Only administrators can create, modify, and delete classifiers.
When creating a classifier, two required attributes must be specified: designation and name. In addition, each classifier has three additional attributes: first data, second data, third data. In essence, these are tags that allow you to store extra. information about the classifier. The most typical example for the use of tags is a list of forms of ownership, when the name of the classifier indicates the actual form of ownership, and in the tag - designation.
Classifier values can be used in attributes and scripts to describe the behavior of objects.
The processes described in previously published articles, one way or another, rely on classifiers. For example, the rules for sending outgoing letters, the type of content ( incoming and outgoing letters) and others.

The calendar
A work or production calendar is a unique tool for managing the work and days off of each organization. With its help, in easla.com it is possible to calculate time intervals not on calendar days, but on working days.
For example, in the process of task management, there is always the question of calculating the planned closing date of a task based on certain norms of time for its completion. In terms of calculating the planned date, the urgency of the task, the category of the task, the type of customer, and other criteria may appear, and as a result, the planned date and time of closing must be calculated in the task taking into account working hours, excluding weekends and holidays.
Or, a good example from the "IT" practice, when you need to take into account the parameter of the description of the level of service provided to calculate the planned date and time of the incident in working days and hours. The service states that the elimination time is, say, 8 hours, i.e. 480 minutes and it is necessary to calculate what the planned time for eliminating the incident on Friday 40 minutes before the end of the shortened working day on the eve of the weekend and Victory Day will be .
To do this without a working calendar is almost impossible!
At easla.comA work calendar is a set of rules that describe one or more days. Each rule must be valid for one year. The rules apply in the order they are placed, i.e. the first rule is the most important, and all the others following it, as it were, describe the exceptions to the first rule. Thus, in most cases, each organization will have at least three rules:
- All working days
- Weekend Saturday
- Weekend sunday
Of course, there are usually more rules: New Year's holidays, various holidays and holidays.
In working days and holidays it is necessary to indicate the working hours. They should be continuous non-overlapping time intervals. For example, a working day from 09:00 to 18:00 with a lunch break from 13:00 to 14:00 should be described in two time intervals: 09: 00-13: 00 and 14:00 to 18:00. Moreover, the time intervals must be located in the correct order.
To facilitate the work with the calendar, special service functions are added that are added to easla.comas the end of each year approaches. Now, in 2016, in the section “All calendar rules”, the service team “Work calendar for 2016” is available. With its help, a typical working calendar is created with a working day from 09:00 to 18:00, a lunch break from 13:00 to 14:00 and all holidays, holidays and weekends!
A properly configured calendar allows you to use the special functions calendarDateAdd and calendarDateDiff and get accurately calculated dates in working days and hours with an accuracy of a second!
For administrator’s convenience, the calendar rules are displayed both in the form of a list:

As well as the calendar form:

Classifiers
In each organization, when managing business processes, there is a need to decide on a set of different parameters that either do not change at all, or change extremely rarely. Such parameters are found in a variety of processes and can be attributed to them, for example:
- Incident category
- Service level
- Incident type
- Form of incorporation
- Counterparty Type
- Shipment Type
- Content Type
- Design stage
- Task category, etc.
In easla.com, classifiers exist for storing such parameters. They are stored hierarchically. Only administrators can create, modify, and delete classifiers.
When creating a classifier, two required attributes must be specified: designation and name. In addition, each classifier has three additional attributes: first data, second data, third data. In essence, these are tags that allow you to store extra. information about the classifier. The most typical example for the use of tags is a list of forms of ownership, when the name of the classifier indicates the actual form of ownership, and in the tag - designation.
Classifier values can be used in attributes and scripts to describe the behavior of objects.

The processes described in previously published articles, one way or another, rely on classifiers. For example, the rules for sending outgoing letters, the type of content ( incoming and outgoing letters) and others.
