About anti-spam techniques
Hello, Habr! According to a Symantec report released this summer, of the 704 billion emails sent in June, 353 billion (49.7%!) Were spam. Spam is harmful not only because of it, you have to rake up a bunch of useless advertising offers, among which the desired letter is easily lost. Bulk mailings are widely used by hackers.
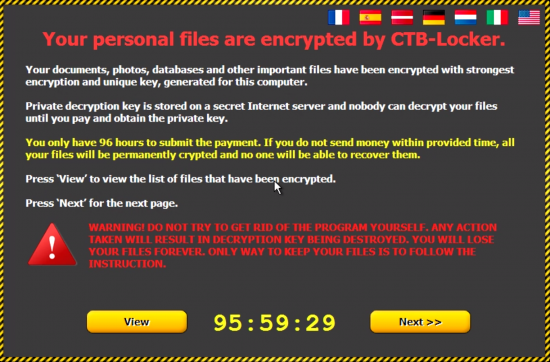
This summer, users all over the world received emails with fake return address update@microsoft.com, the text “Windows 10 Free Update” and the attached file Win10Installer.zip . After unpacking, the Ransomware virus (CTB-Locker variant) started encrypting files on the hard disk - in order to gain access to the data again, the victim had to pay a certain amount within 96 hours.
There are two main methods of protection. This is protection at the stage of receiving messages by the mail server and filtering mail after it is received.
The easiest way is to configure the mail client installed on the user's computer. Settings (in general, not rich) allow you to set filters and block unwanted messages by topic, sender address, or certain keywords. In our opinion, this is not the most effective way. In order to configure blocking by address or stop words, you still need to receive the first spam email, right? This method is only good in order to get rid of annoying mailing, which for some reason cannot be unsubscribed (this is rare, but it happens).
For corporate use, this method is not at all suitable. The Spam Defense service, which is used by Yandex.Mail, skips suspicious messages (for example, sent to too large a list of addresses), but puts them in the Spam folder. In addition, it checks emails sent from the user's address. Yandex does not guarantee that all suspicious emails will be recognized. “ If you think that you have received a spam email in the Inbox, select the email you need and click the“ This is spam! ”Button - the email will be moved to the Spam folder, and the necessary information will be sent to Spamoborona, ” the website reports .
Kaspersky Anti-Spam- a more advanced solution. The sender's IP address is checked against blacklisted DNSBL providers and services, the analysis takes into account sender authorization using the Sender Policy Framework ( SPF) technology , spammer URLs in the message body are analyzed using SURBL (Spam URI Realtime Block List), and signature and linguistic analysis is used.
First RBL Service(Realtime Blackhole List), which contained spam mailing list hosts, appeared in 1987. Checking mail is as follows: the mail server contacts DNSBL and checks for the presence of the IP address of the client from which the message was received. If the client IP address is listed, the server receives a response. Error 5xx is reported to the sender server and the message is not received.
It is alleged that the use of services based on RBL / DNSBL technology allows achieving spam filtering efficiency in 98-99.8% of cases. The drawback of DNSBL lists, apparently, is only one: quite legitimate mail servers can also get there by mistake if they transmitted spam sent through some computer inside their network.
However, according to testing data (which analyzes the effectiveness of the most popular anti-spam solutions), none of the emails that are not spam was mistakenly identified as spam.
We consider the solutions based on the use of DNSBL lists to be the most reliable. That is why the functionality of the SMTP gateway of the Traffic Inspector program also complements the RBL module.His work is based on checking the IP address of the received message in RBL services by sending DNS queries to them. The RBL module of the mail server at the time of receipt of the message requests the RBL service whether the IP address of the sender of the letter is “bad” and, based on the response, RBL accepts or rejects the letter.
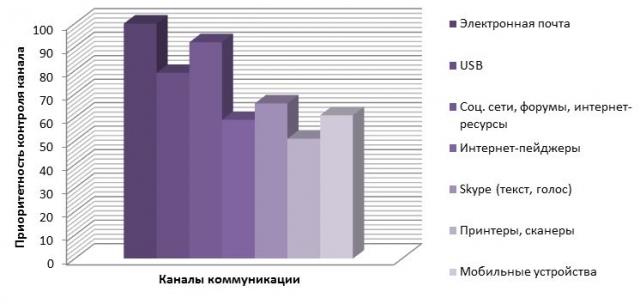
Mass mailing is also dangerous by the fact that in this way letters are sent directly or indirectly prompting the recipient to visit phishing sites. According to a survey by research firm MFI Soft, e-mail ranks first among potentially dangerous data leakage channels:
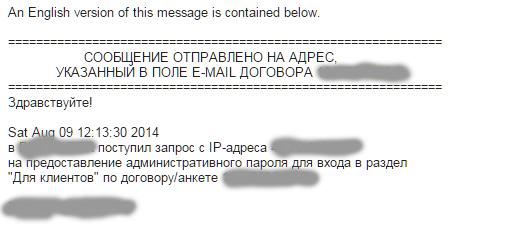
Fraudsters send out letters very similar to real ones on behalf of companies, services and social networks. In the text of the letter - a link to the site.
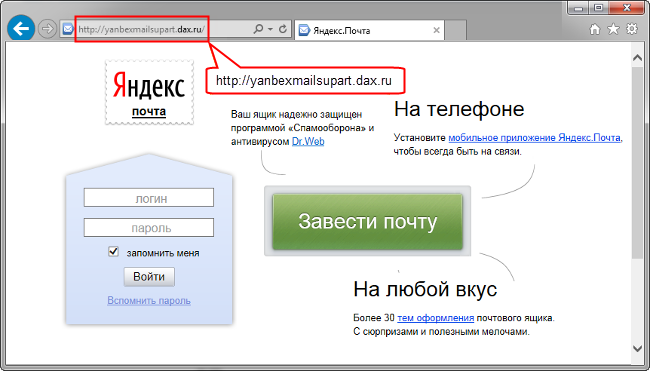
By clicking on this link, the user will be taken to a phishing page, and then, as they say, a technical matter: if he enters some personal data, they fall into the hands of scammers:
So online scammers can get sensitive user data: passwords from accounts, credit card numbers or PIN codes, and so on.
“ The most effective phishing attacks end in the success of the attackers in 45% of cases, and about 2% of emails received by Gmail are designed specifically to trick people into their passwords. Various network services send millions of such emails daily , ” according to Google.
One way to protect yourself from phishing sites is the Yandex.DNS service, which is available on Asus, D-Link, TP-Link, and ZyXEL routers. When you try to open a phishing site, Yandex.DNS stops downloading data and issues a warning to the user.
Most browsers also have the ability to block phishing sites. Chrome, Firefox and Safari use the Safe Browsing API technology, IE - Smart Screen.
An interesting system of protection against phishing "Protect" was released by Yandex a little more than a month ago. Protect monitors user actions and ensures that passwords are not entered on sites similar to well-known services. In addition, Protect technology includes checking all downloaded files. The Protect function protects the user's personal data when connected to an open Wi-Fi network in public places. Protect is integrated into the Yandex.Browser version for Windows and OS X. Chrome has a
functionally similar extension for Password Alert password checking , however, it only works on Google and Google Apps for Work accounts.
The Phishing Blocker phishing protection module in the Traffic Inspector uses the shareware Google Safe Browsing API project . Phishing Blocker checks URLs for threats on the Google-updated blacklist of potential phishing sites and pages. If the answer is yes, then the host or IP address is assigned to one of the previously created content categories. This prevents users from knowingly visiting fraudulent web resources.
Another possibility of Phishing Blocker is to assign a certain rating to a resource, which allows you to filter out unwanted content, allow access only to trusted content and receive reports on visited resources in accordance with the rating.
PS And how you fight against spam and phishing threats you, readers of Habr?

This summer, users all over the world received emails with fake return address update@microsoft.com, the text “Windows 10 Free Update” and the attached file Win10Installer.zip . After unpacking, the Ransomware virus (CTB-Locker variant) started encrypting files on the hard disk - in order to gain access to the data again, the victim had to pay a certain amount within 96 hours.
How to deal with spam?
There are two main methods of protection. This is protection at the stage of receiving messages by the mail server and filtering mail after it is received.
The easiest way is to configure the mail client installed on the user's computer. Settings (in general, not rich) allow you to set filters and block unwanted messages by topic, sender address, or certain keywords. In our opinion, this is not the most effective way. In order to configure blocking by address or stop words, you still need to receive the first spam email, right? This method is only good in order to get rid of annoying mailing, which for some reason cannot be unsubscribed (this is rare, but it happens).
For corporate use, this method is not at all suitable. The Spam Defense service, which is used by Yandex.Mail, skips suspicious messages (for example, sent to too large a list of addresses), but puts them in the Spam folder. In addition, it checks emails sent from the user's address. Yandex does not guarantee that all suspicious emails will be recognized. “ If you think that you have received a spam email in the Inbox, select the email you need and click the“ This is spam! ”Button - the email will be moved to the Spam folder, and the necessary information will be sent to Spamoborona, ” the website reports .
Kaspersky Anti-Spam- a more advanced solution. The sender's IP address is checked against blacklisted DNSBL providers and services, the analysis takes into account sender authorization using the Sender Policy Framework ( SPF) technology , spammer URLs in the message body are analyzed using SURBL (Spam URI Realtime Block List), and signature and linguistic analysis is used.
First RBL Service(Realtime Blackhole List), which contained spam mailing list hosts, appeared in 1987. Checking mail is as follows: the mail server contacts DNSBL and checks for the presence of the IP address of the client from which the message was received. If the client IP address is listed, the server receives a response. Error 5xx is reported to the sender server and the message is not received.
A large number of DNSBL lists can be found here .
It is alleged that the use of services based on RBL / DNSBL technology allows achieving spam filtering efficiency in 98-99.8% of cases. The drawback of DNSBL lists, apparently, is only one: quite legitimate mail servers can also get there by mistake if they transmitted spam sent through some computer inside their network.
However, according to testing data (which analyzes the effectiveness of the most popular anti-spam solutions), none of the emails that are not spam was mistakenly identified as spam.
We consider the solutions based on the use of DNSBL lists to be the most reliable. That is why the functionality of the SMTP gateway of the Traffic Inspector program also complements the RBL module.His work is based on checking the IP address of the received message in RBL services by sending DNS queries to them. The RBL module of the mail server at the time of receipt of the message requests the RBL service whether the IP address of the sender of the letter is “bad” and, based on the response, RBL accepts or rejects the letter.
Mass mailing is also dangerous by the fact that in this way letters are sent directly or indirectly prompting the recipient to visit phishing sites. According to a survey by research firm MFI Soft, e-mail ranks first among potentially dangerous data leakage channels:

Fraudsters send out letters very similar to real ones on behalf of companies, services and social networks. In the text of the letter - a link to the site.

By clicking on this link, the user will be taken to a phishing page, and then, as they say, a technical matter: if he enters some personal data, they fall into the hands of scammers:

So online scammers can get sensitive user data: passwords from accounts, credit card numbers or PIN codes, and so on.
“ The most effective phishing attacks end in the success of the attackers in 45% of cases, and about 2% of emails received by Gmail are designed specifically to trick people into their passwords. Various network services send millions of such emails daily , ” according to Google.
One way to protect yourself from phishing sites is the Yandex.DNS service, which is available on Asus, D-Link, TP-Link, and ZyXEL routers. When you try to open a phishing site, Yandex.DNS stops downloading data and issues a warning to the user.
Most browsers also have the ability to block phishing sites. Chrome, Firefox and Safari use the Safe Browsing API technology, IE - Smart Screen.
An interesting system of protection against phishing "Protect" was released by Yandex a little more than a month ago. Protect monitors user actions and ensures that passwords are not entered on sites similar to well-known services. In addition, Protect technology includes checking all downloaded files. The Protect function protects the user's personal data when connected to an open Wi-Fi network in public places. Protect is integrated into the Yandex.Browser version for Windows and OS X. Chrome has a
functionally similar extension for Password Alert password checking , however, it only works on Google and Google Apps for Work accounts.
A good overview of anti-phishing antivirus solutions can be found here .
The Phishing Blocker phishing protection module in the Traffic Inspector uses the shareware Google Safe Browsing API project . Phishing Blocker checks URLs for threats on the Google-updated blacklist of potential phishing sites and pages. If the answer is yes, then the host or IP address is assigned to one of the previously created content categories. This prevents users from knowingly visiting fraudulent web resources.
Another possibility of Phishing Blocker is to assign a certain rating to a resource, which allows you to filter out unwanted content, allow access only to trusted content and receive reports on visited resources in accordance with the rating.
PS And how you fight against spam and phishing threats you, readers of Habr?
