How the search for applications on Google Play works. Abstract
The article discusses some features of the application search in the Google Play store.
Google rarely discusses its search technologies publicly, but in 2013 at the Google I / O conference 2013 it said that it affects the ranking of applications in the Google Play store.
Our team made a summary of this presentation with their comments and examples from practice. Video in English at the link , data management help guide for Google Play .
Google Play is a store where mobile apps, books, music, movies are available.

The claimed development vector is personalization of the store. Google Play aims to display in the store the content that is interesting to a particular user. Based on past experience, preferences, context of use and recommendations of friends.
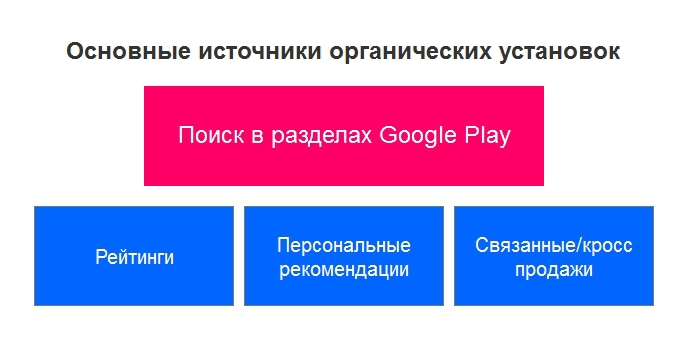
This concept combines several scenarios when a user finds and discovers new applications on Google Play:
1.1. Ratings (lists) of applications on Google Play (Top free, Top paid, Best sellers, Top new free, Top new paid, Gaining popularity).
1.2. Personal recommendations. Blocks with applications that Google Play generates based on the recommendations of your friends.
1.3. Connected / cross-selling. Blocks “More applications from the developer”, “Install with this application”, “Similar applications”.
Here we do not consider hand picks from the Google Play team, in slang called "featured".
Choosing the right category for the application is important. For example, a user using category browsing wants to find an alarm. He does not enter “alarm clock” in the search field, but goes to the category. In which? Instruments? Miscellaneous? Health and Fitness? If the user goes to the Miscellaneous section, and our application in the Tools section, he will not find it. Therefore, when choosing a category, it is advised to think the way the user thinks.
Many underestimate the second source of attitudes - the direct search. It can be divided into 2 categories.
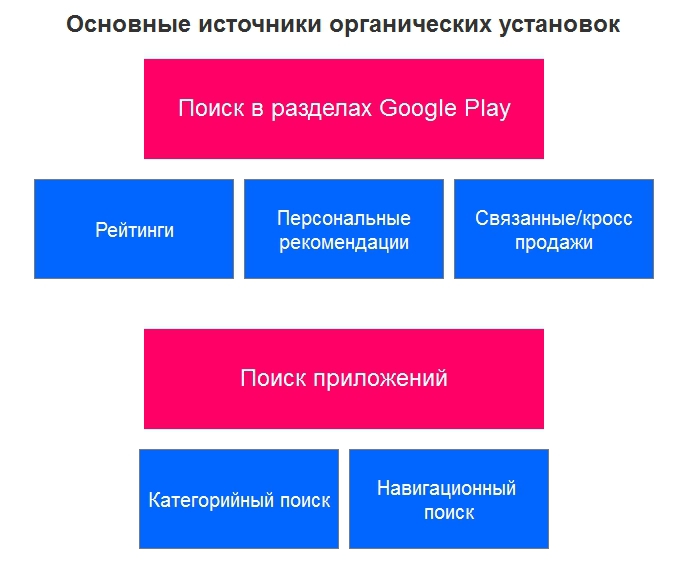
2.1. Category Search
When we know which category the application we want to find belongs to. For example, an application with recipes, reviews about restaurants in a particular city, free or multiplayer games.
The user enters the search category of the application that will solve his problem (for example, "meat recipes", "tours of Moscow").
2.2. Navigation search
In this case, we know exactly what we are looking for. For example, a friend told us about the application or we heard about it somewhere. We enter the name of this application and find it (for example, “engards birds ”,“ facebook messenger ”).
- Every day, 12% of active users return to the store and look for new applications.
- Within a week, 50% of all active users return to the store and look for new applications.
- Per month, users enter more than 6 million unique search phrases.
* Keep in mind that this is 2013 data.
A unique and creative name is encouraged. The name should say what this application is about.
The name significantly affects the visibility of the application when searching (affects ASO - App Store Optimization). Therefore, many developers try to put in the title the main keywords that users will enter when searching.

The application description is divided into 2 blocks. Short and basic description. The main message must be placed in a brief description.
A short description significantly affects the visibility of the application. When compiling the main description of the application, Google recommends using recommendations for website optimization for search engines (SEO).

Further we will talk about how to use the application page to make user experiences even brighter and not to fool them.
The screenshots should show exactly what the user sees after installing the application. It is important not to deceive expectations. If the screenshots and the application are different, there is a risk of a negative reaction.
The video can show users what the application is. Game developers say the video helps a lot to explain the contents of the game to users.
We made videos for our non-gaming applications, but this did not bring tangible effect on promotion. Video can be a nice addition when doing a review.
Of the minuses: the application interface can change, so the video will have to be redone every time. Often there is not enough time for corrections, so the interface on the video and the interface in the current version of the application can differ significantly!
Creating a video needs a budget. And when the video loses relevance in a month, this money is a pity.
On the application page, the user has the opportunity to evaluate the application and / or leave a review. For Google Play, a high score is a very serious signal.
Google Play ranks apps based on a number of factors. One of the main ones is the number of application installations. The more installations you have, the higher the app will appear in the store.
A feature of the search by application is that Google Play takes into account not only the number of downloads, but also how many people then deleted this application (statistics are available in the Google Play Developer Console). The fewer users uninstalled the application, the better it solves their problem. Which means it ranks higher.
Often on Google Play you can see how an application with a lower rating and fewer installations ranks higher than other applications that have a higher rating and more installations. In this case, such a factor as the ratio of installation and removal of the application is taken into account.

Google PLay distinguishes when a user uninstalls an application immediately and when he does it over time (the so-called “long deletion”).
If the application was used and then later removed, Google Play does not consider this a negative factor. For example, the user has passed the game, and so that the application does not take up space on the phone, it is deleted.
The next important factor is user engagement. How much time a person spends in the application, how often he uses it, etc. This takes into account the category of needs that the application solves.
If this is an application with weather information, a few seconds in the application is enough to solve the user's task. For gaming applications, it can be minutes and hours. In the case of the game, the longer the user spends time in the application, the higher the involvement.
Therefore, Google Play does not say that one application is bad and the other is good. The task of the application and the category of needs are taken into account.
We had a new application, which due to the small number of installations had a very good installation / deletion ratio. The account went to hundreds of installations, the rating was 5.0 (again, due to the small number of installations). Given these indicators, Google Play on low-frequency queries gave this application higher than the rest, which had hundreds of thousands of installations. Then the indicators worsened, and the application went down in the list below.
Google Play also builds rankings based on other factors. It takes into account the preferences of users in a particular region and the type of devices from which the search is conducted (mobile phone or tablet).
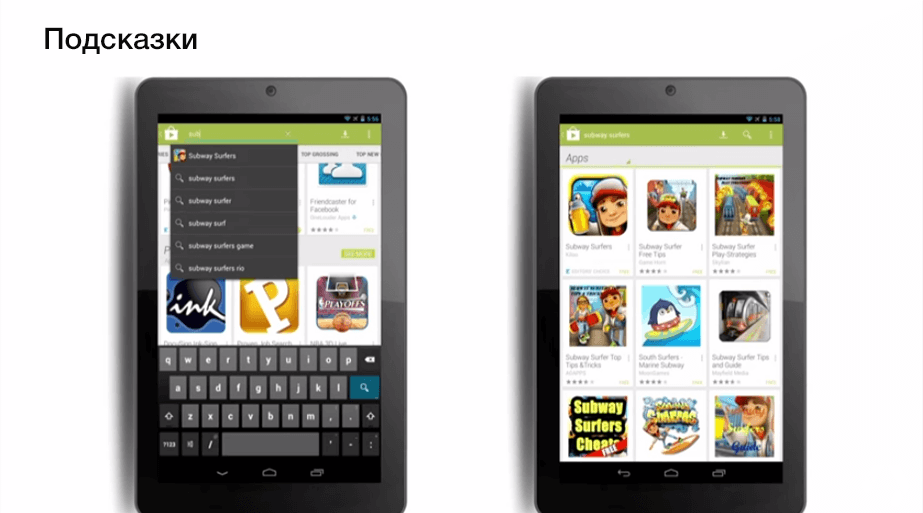
An important element in finding an application is the hint. When you enter part of a search phrase, Google Play tries to guess which category of application you want to find, or even a specific application. In the second case, the icon of this application can catch up on the hint.
When compiling a description of the application, these tips should be considered. They show the popularity of a particular search phrase.
Google reveals some factors affecting the ranking. Ratings are formed by country, category, type of device.
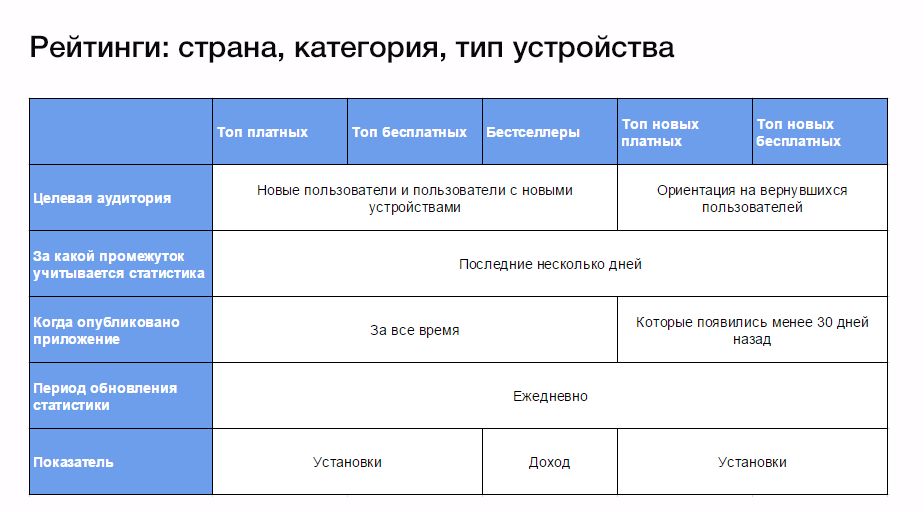
A brief description of each of the ratings in the certificate .
Different ratings are for different users. For example, Top Free and Top Paid are more suitable for new users or users with new devices. They need basic applications, they want to know what is most popular on Google Play. The ratings of Top New Paid and Top New Free are aimed at users who already have basic applications and want to find out what's new in the app store.
For paid applications, revenue is taken into account, for free - installs in a few days.
The goal of this section is to give users information about applications that are gaining popularity right now. All applications participate in this rating - new and old.
For each application, Google Play knows the projected growth rate of installations. And if at some point the installations become much larger than predicted, the application falls into this rating.
On the application page there are such blocks as “More applications from this developer”, “Similar applications”, “Install with this”.
For developers, the “More applications from this developer” block is valuable.
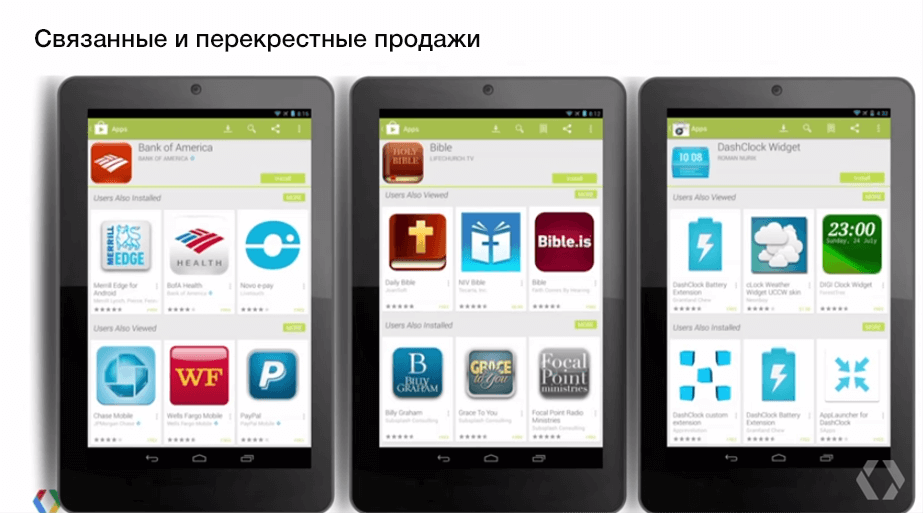
On our applications, we noticed that with the active promotion of one of them, the settings on the others in our account increase. On one of the projects was about 5% of the installations of the neighboring application.
Those. conditionally, if 1000 people installed Appendix A, then about 50 installations received Appendix B due to the traffic to Appendix A. Most likely, thanks to the “More applications from this developer” block and / or the developer’s Google Play page.
The same applies to the same applications on different platforms. If we actively promote Application A on the Android platform, then the installation for the same application on the iOS platform will increase.
“Similar applications” and “Install with this” are made for the convenience of users. For the owner of the application, this is, in fact, advertising competitors.
For a specific application, more than 80 factors are taken into account, and not all of them are related to Google Play. Signals from the Google search engine are also taken into account. All factors are not disclosed.
This is the homepage of two different users. As you can see, different applications are recommended to them. This is influenced by the past experience of these users (what applications they searched for, which pages they visited, etc.), the context of working with Google Play (if you are in New York, you will be offered an application with news from New York, not Tokyo ), your device, as well as reviews and ratings of friends.

Personalization is also subject to category pages.
The most reliable way to get on the Home Page is the recommendation of friends. Therefore, invite users to leave feedback about your application and click +1.
It seems to us that this is very valuable advice. Everyone wants to know how to get into the fichering from Google. But there is an easier way to get to the user on the main screen - this is the recommendation of his friends who are already using our application.
1. Adapt the application for tablets. In this case, the application will be available on Google Play for tablet users.
2. Google Play considers external links to the application, considering it a factor of trust. Therefore, ordering a review on the site about your application, ask to put a link to the application in the Google Play store.
3. Follow these mandatory rules:
- Do not create an application name that is close to an existing popular application. This leads to a deception of user expectations.
- Use country and device targeting deliberately, considering the audience of your application.
- Create the correct address for your application (the application link is formed with a parameter such as bundle).
4. The APK of your file should not weigh much. In addition to the fact that users try not to install heavy applications, these applications are also the first to be deleted if the user wants to clear the phone’s memory. Therefore, make the size of the APK file smaller.
5. Use viral mechanics to promote the application.
Of the 6 million unique phrases that users enter within a month, 50% have errors.
Very interesting statistics, actually. The fact is that now Google Play does not work with errors the way regular search works. The issuance of applications when entering a search phrase with an error and without is different.

We did not see cases on working with errors, but at the dawn of seo, when search engines did not work well with errors, some webmasters used this to get traffic.
The compendium did not address the localization of the application in different countries (and how to increase the visibility of the application due to this), work with user reviews, tips for writing descriptions and screenshots, etc. These and other factors also affect the ranking of the application on Google Play and the user's decision to download the application or not.
Google rarely discusses its search technologies publicly, but in 2013 at the Google I / O conference 2013 it said that it affects the ranking of applications in the Google Play store.
Our team made a summary of this presentation with their comments and examples from practice. Video in English at the link , data management help guide for Google Play .
Google Play is a store where mobile apps, books, music, movies are available.

The claimed development vector is personalization of the store. Google Play aims to display in the store the content that is interesting to a particular user. Based on past experience, preferences, context of use and recommendations of friends.
Allocate such main sources of organic plants
1. Search in Google Play sections
This concept combines several scenarios when a user finds and discovers new applications on Google Play:
1.1. Ratings (lists) of applications on Google Play (Top free, Top paid, Best sellers, Top new free, Top new paid, Gaining popularity).
1.2. Personal recommendations. Blocks with applications that Google Play generates based on the recommendations of your friends.
1.3. Connected / cross-selling. Blocks “More applications from the developer”, “Install with this application”, “Similar applications”.

Here we do not consider hand picks from the Google Play team, in slang called "featured".
Choosing the right category for the application is important. For example, a user using category browsing wants to find an alarm. He does not enter “alarm clock” in the search field, but goes to the category. In which? Instruments? Miscellaneous? Health and Fitness? If the user goes to the Miscellaneous section, and our application in the Tools section, he will not find it. Therefore, when choosing a category, it is advised to think the way the user thinks.
2. Search for applications
Many underestimate the second source of attitudes - the direct search. It can be divided into 2 categories.
2.1. Category Search
When we know which category the application we want to find belongs to. For example, an application with recipes, reviews about restaurants in a particular city, free or multiplayer games.
The user enters the search category of the application that will solve his problem (for example, "meat recipes", "tours of Moscow").
2.2. Navigation search
In this case, we know exactly what we are looking for. For example, a friend told us about the application or we heard about it somewhere. We enter the name of this application and find it (for example, “engards birds ”,“ facebook messenger ”).

How important is application search:
- Every day, 12% of active users return to the store and look for new applications.
- Within a week, 50% of all active users return to the store and look for new applications.
- Per month, users enter more than 6 million unique search phrases.
* Keep in mind that this is 2013 data.
Anatomy of App Design on Google Play
1. Short and clear name of the application
A unique and creative name is encouraged. The name should say what this application is about.
The name significantly affects the visibility of the application when searching (affects ASO - App Store Optimization). Therefore, many developers try to put in the title the main keywords that users will enter when searching.

2. Bright and functional description
The application description is divided into 2 blocks. Short and basic description. The main message must be placed in a brief description.
A short description significantly affects the visibility of the application. When compiling the main description of the application, Google recommends using recommendations for website optimization for search engines (SEO).

Further we will talk about how to use the application page to make user experiences even brighter and not to fool them.
Actual screenshots
The screenshots should show exactly what the user sees after installing the application. It is important not to deceive expectations. If the screenshots and the application are different, there is a risk of a negative reaction.
Video clip
The video can show users what the application is. Game developers say the video helps a lot to explain the contents of the game to users.
We made videos for our non-gaming applications, but this did not bring tangible effect on promotion. Video can be a nice addition when doing a review.
Of the minuses: the application interface can change, so the video will have to be redone every time. Often there is not enough time for corrections, so the interface on the video and the interface in the current version of the application can differ significantly!
Creating a video needs a budget. And when the video loses relevance in a month, this money is a pity.
Reviews and Rating
On the application page, the user has the opportunity to evaluate the application and / or leave a review. For Google Play, a high score is a very serious signal.
The impact of statistics on application ranking
Google Play ranks apps based on a number of factors. One of the main ones is the number of application installations. The more installations you have, the higher the app will appear in the store.
A feature of the search by application is that Google Play takes into account not only the number of downloads, but also how many people then deleted this application (statistics are available in the Google Play Developer Console). The fewer users uninstalled the application, the better it solves their problem. Which means it ranks higher.
Often on Google Play you can see how an application with a lower rating and fewer installations ranks higher than other applications that have a higher rating and more installations. In this case, such a factor as the ratio of installation and removal of the application is taken into account.

Long removal
Google PLay distinguishes when a user uninstalls an application immediately and when he does it over time (the so-called “long deletion”).
If the application was used and then later removed, Google Play does not consider this a negative factor. For example, the user has passed the game, and so that the application does not take up space on the phone, it is deleted.
Engagement
The next important factor is user engagement. How much time a person spends in the application, how often he uses it, etc. This takes into account the category of needs that the application solves.
If this is an application with weather information, a few seconds in the application is enough to solve the user's task. For gaming applications, it can be minutes and hours. In the case of the game, the longer the user spends time in the application, the higher the involvement.
Therefore, Google Play does not say that one application is bad and the other is good. The task of the application and the category of needs are taken into account.
We had a new application, which due to the small number of installations had a very good installation / deletion ratio. The account went to hundreds of installations, the rating was 5.0 (again, due to the small number of installations). Given these indicators, Google Play on low-frequency queries gave this application higher than the rest, which had hundreds of thousands of installations. Then the indicators worsened, and the application went down in the list below.
Google Play also builds rankings based on other factors. It takes into account the preferences of users in a particular region and the type of devices from which the search is conducted (mobile phone or tablet).
Tips
An important element in finding an application is the hint. When you enter part of a search phrase, Google Play tries to guess which category of application you want to find, or even a specific application. In the second case, the icon of this application can catch up on the hint.
When compiling a description of the application, these tips should be considered. They show the popularity of a particular search phrase.

Rating table
Google reveals some factors affecting the ranking. Ratings are formed by country, category, type of device.

A brief description of each of the ratings in the certificate .
Different ratings are for different users. For example, Top Free and Top Paid are more suitable for new users or users with new devices. They need basic applications, they want to know what is most popular on Google Play. The ratings of Top New Paid and Top New Free are aimed at users who already have basic applications and want to find out what's new in the app store.
For paid applications, revenue is taken into account, for free - installs in a few days.
Gaining popularity
The goal of this section is to give users information about applications that are gaining popularity right now. All applications participate in this rating - new and old.
For each application, Google Play knows the projected growth rate of installations. And if at some point the installations become much larger than predicted, the application falls into this rating.
Bound and Cross-selling
On the application page there are such blocks as “More applications from this developer”, “Similar applications”, “Install with this”.
For developers, the “More applications from this developer” block is valuable.

On our applications, we noticed that with the active promotion of one of them, the settings on the others in our account increase. On one of the projects was about 5% of the installations of the neighboring application.
Those. conditionally, if 1000 people installed Appendix A, then about 50 installations received Appendix B due to the traffic to Appendix A. Most likely, thanks to the “More applications from this developer” block and / or the developer’s Google Play page.
The same applies to the same applications on different platforms. If we actively promote Application A on the Android platform, then the installation for the same application on the iOS platform will increase.
“Similar applications” and “Install with this” are made for the convenience of users. For the owner of the application, this is, in fact, advertising competitors.
External factors and how to get to the main page
For a specific application, more than 80 factors are taken into account, and not all of them are related to Google Play. Signals from the Google search engine are also taken into account. All factors are not disclosed.
The impact of recommendations
This is the homepage of two different users. As you can see, different applications are recommended to them. This is influenced by the past experience of these users (what applications they searched for, which pages they visited, etc.), the context of working with Google Play (if you are in New York, you will be offered an application with news from New York, not Tokyo ), your device, as well as reviews and ratings of friends.

Personalization is also subject to category pages.
The most reliable way to get on the Home Page is the recommendation of friends. Therefore, invite users to leave feedback about your application and click +1.
It seems to us that this is very valuable advice. Everyone wants to know how to get into the fichering from Google. But there is an easier way to get to the user on the main screen - this is the recommendation of his friends who are already using our application.
5 tips from the Google Play team after creating a quality app:
1. Adapt the application for tablets. In this case, the application will be available on Google Play for tablet users.
2. Google Play considers external links to the application, considering it a factor of trust. Therefore, ordering a review on the site about your application, ask to put a link to the application in the Google Play store.
3. Follow these mandatory rules:
- Do not create an application name that is close to an existing popular application. This leads to a deception of user expectations.
- Use country and device targeting deliberately, considering the audience of your application.
- Create the correct address for your application (the application link is formed with a parameter such as bundle).
4. The APK of your file should not weigh much. In addition to the fact that users try not to install heavy applications, these applications are also the first to be deleted if the user wants to clear the phone’s memory. Therefore, make the size of the APK file smaller.
5. Use viral mechanics to promote the application.
People are looking for errors
Of the 6 million unique phrases that users enter within a month, 50% have errors.
Very interesting statistics, actually. The fact is that now Google Play does not work with errors the way regular search works. The issuance of applications when entering a search phrase with an error and without is different.

We did not see cases on working with errors, but at the dawn of seo, when search engines did not work well with errors, some webmasters used this to get traffic.
The compendium did not address the localization of the application in different countries (and how to increase the visibility of the application due to this), work with user reviews, tips for writing descriptions and screenshots, etc. These and other factors also affect the ranking of the application on Google Play and the user's decision to download the application or not.
