Commercial Website Security Survey

Our colleagues from SiteSecure conducted a study of the security of commercial sites in the .ru zone in the first quarter of 2015. Its results were very interesting, so we decided to publish them on our blog. The aim of the study is not only to determine the security status of sites in the .ru domain zone, but also the role of search engines in this.
Google and Yandex are still slowly identifying dangerous sites.
There is both good and bad news in this. The bad news for users is that they can reach dangerous or virus-infected sites without receiving the usual warning “This site is unsafe” from a search engine in a timely manner. The good news for site owners is that they can manage to respond and fix the problem faster than the site gets blacklisted by the search engine, but on one condition - if they themselves find the problem faster than the search engine does.
The share of sites where a security problem was detected, but the sites were not included in the black lists of search engines:

Our observation showed that Google and Yandex are still slowly and not fully detecting the presence of security problems and threats to users on the site. (In one of the following studies, we will check who is faster - traditional antiviruses or Google with Yandex). Compared to last year, Yandex has increased its capabilities - earlier it detected problems twice as often as Google, and now - already 2.5 times more often. However, it’s not enough for site owners to rely solely on diagnostics for Yandex and Google webmasters - when the search engine sends an alert about the problem, the site will already be blacklisted, and a significant part of the traffic to the site will be lost every hour or day until the solution problems will bring loss of leads, sales and site reputation.
It should be noted that the statistics on the graph were obtained during a one-time site scan, so we can not now reliably say how much time the site owners had to fix the problem before the sites were blacklisted by the search engine. We plan to find out in the course of our further research.
Summarizing, we can say the following that at the time of our site scan:
- Yandex has not yet found 30 to 65 percent of problems on sites
- Google has not yet found 50 to 85 percent of problems on sites
The main differences of the 2015 study.
After conducting the first site security research in early 2014, we decided to conduct research on a regular basis and deployed a permanent infrastructure for this, which is located in the Amazon cloud and represents a cluster of machines scalable to hundreds of servers, integrated by the RabbitMQ task manager and allowing monitoring several hundred thousand sites. For the first quarter of 2015, we collected and analyzed 2.5 million incident records discovered during continuous monitoring of more than 80,000 sites.
Additionally, especially for this study, we, together with the iTrack analytical data collection service, performed a one-time scan of 240 thousand sites with domains in the .ru zone registered by legal entities (presumably for commercial purposes).
Thus, in comparison with the previous study, we increased the number of sites being checked from 30,000 to more than 300,000, and also monitored part of the sites continuously for four months. Focusing on business sites is another difference from a study last year, in which sites were randomly selected from the domains in the .ru zone and could include personalized home pages and abandoned sites.
Summary of the 2014 study
According to a study conducted in October 2013 - January 2014, every seventh website in Runet is at risk of financial losses due to security problems. And if large market players solve the problem by hiring specialized specialists and using industrial monitoring and protection systems, the SMB sector for the most part simply does not think about solving such problems in advance, and is forced to respond to the fact of already incurred losses. The main results of the previous study:
- Sites on free CMS are infected 4 times more often than sites on paid
- Updating the CMS version reduces the risk of problems by 2 times
- Yandex blacklisted sites two 2 more often than Google
- The intersection of Google and Yandex blacklists is only 10%
- More than half of site owners were not aware of problems
- A third continued to spend money on website promotion
- 15% of businesses ceased to exist, and the owners of 10% of sites, as a result of infection, had to redo their site
After the publication of these data, we received many clarifying questions that we tried to take into account when finalizing the methodology and setting the task for the next study.
Key Findings of the 2015 Survey
To begin with, we give a brief summary of the main findings of the survey, which we thought were especially important to draw the attention of the audience.
The elimination of the identified problems requires considerable time - on average, the site is blacklisted for a week, which is equivalent to losing a quarter of the monthly revenue for an online business.
The average reaction time of a site owner or webmaster to a problem discovered by search engines and removing a site from the black list is 1 week. That is, the online business is experiencing a week of downtime, and the online store loses a quarter of its monthly revenue. And this is without taking into account the loss of funds invested in advertising (according to the results of a previous study, confirmed this time, about half of the owners of online businesses continued to invest in promoting a site that had security problems leading to blocking of the site by search engines).
Threat rating and situation with repeated and repeated infections
Based on the results of checking sites for infections, we compiled a popularity rating for infections of a certain type. Quite often (in more than 40% of cases) there are cases of repeated infection - double and triple. In this case, by multiple infection we mean the implementation of a dangerous object on a site that is different in the way of execution (for example, static link and mobile redirect, dynamic link and static link - different ways). It is worth noting that repeated cases of getting the site into the black lists are rare, especially with online stores. This is probably due to the increased importance that owners and administrators of commercial sites attach to protection after a site is blacklisted.
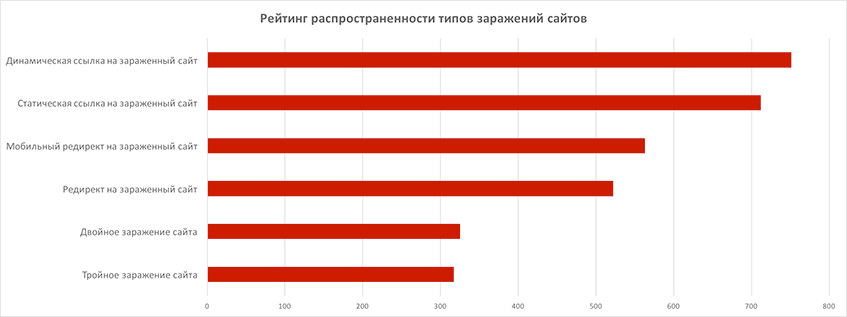
One treatment is not enough. Surveillance and prevention
Most of all the sites that fixed the detected security problems managed to get into the black lists of search engines, and then displayed therefrom. Site owners and administrators are most successful in combating links to infected sites. Almost half of all such incidents were eliminated before being detected by search engines. We attribute this to the fact that when promoting a site, tools are often used to control static external links, and dynamic external links are correctly detected by desktop antiviruses, and information about this gets to the owners of the sites. The most difficult to detect redirects, and only less than 10% of site owners could identify a mobile redirect on their own. This is because
The share of sites that fixed the problem before being detected by search engines:
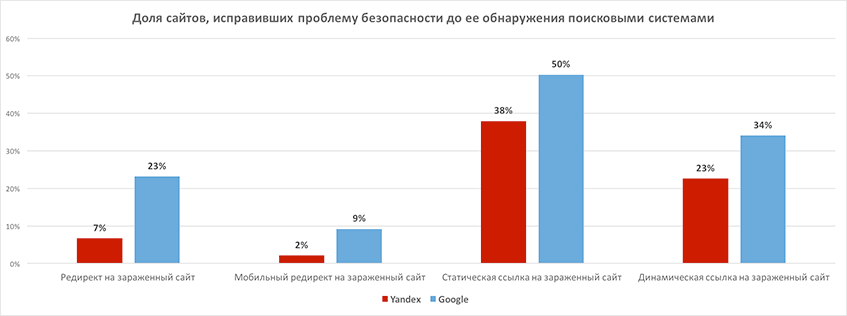
On the whole, this means that businesses that did not have sufficient funds to control the site’s security managed to suffer significant losses — on average, a week of downtime, as noted above, excluding traffic losses from redirects from the moment they appear on the site until the search engine detects it. If the owners of the sites and webmasters had the means of proactive diagnostics and prevention of sites, these losses could be avoided by using the slowness of search engines that we have discovered - the problem can be detected and fixed before the search robot visits the site and marks it as dangerous .
The impact of CMS type on security was not so great for business sites
In the last study, where randomly selected sites participated, we found a clear dependence - sites on free CMS were infected with viruses four times as many sites on commercial systems. Leaving only business sites in the sample, we found that the share of sites based on commercial CMS in blacklists is only half the share of sites on free CMS. Thus, commercial sites on free CMS “on average” can be called safer compared to all sites on free CMS in general.
In our opinion, many cases of hacking and infection of sites arise due to common security problems - weak passwords, uncontrolled access to the site code, attracting unverified freelancers and other web development system problems related to the overall security state of web development. With this we associate such a fact as the lack of clear leaders among paid and free CMS in terms of the number of problems. In general, the share of problem sites on the selected CMS corresponds to the share occupied by this CMS in the market.
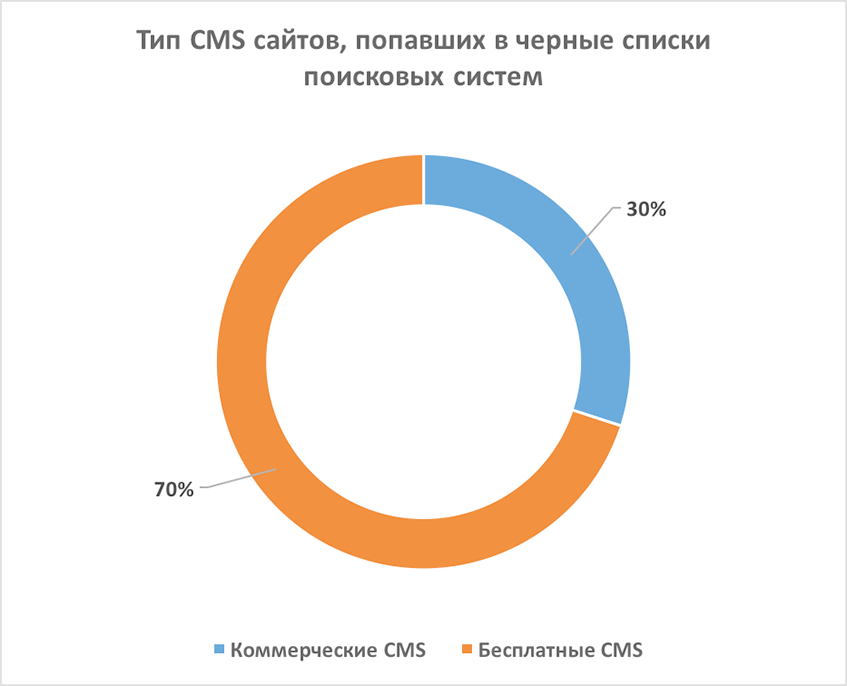
In relation to the graphs above, an explanation needs to be made: for technical reasons, we were not able to determine the CMS for some of the sites from the sample, so the data was obtained under the assumption that the CMS uncertainty error was randomly distributed. The list of sites does not include many well-known CMS, such as NetCat and Umi, because we show only the top common CMS found in the study, and this top generally matches the CMS popularity statistics published by iTrack.
Shares of various CMS on infected sites:

Internet business owners still lack awareness
Even having reduced the selection to commercial sites, we found in it sites that were blacklisted by search engines for a long time. So, among the sites of online stores, we found more than 300 incidents that were not resolved throughout the observation period (3 months). Most of them are mobile redirects, which can lead to losses from 25% to 40% of traffic, depending on the prevalence of mobile access to sites in a particular region of Russia. A similar picture was observed in the sample of sites in the zone .ru, included in the top 1 million sites registered on Alexa. However, there were practically no such sites among the Top-10,000 study group according to the Liveinternet counter, which we tend to associate with increased attention to site traffic from site owners participating in the ranking.
The main facts of the study 2015. Top 3 problems
- The most common and dangerous problem in our opinion is a redirect to external sites, including both a mobile and a regular redirect. In 90% of all cases of the presence of a redirect, we determined that it was a redirect to an infected site. Thus, it affects not only the Internet business, which loses traffic redirected to other sites, but also users who get to infected sites. And if the fact of the transition to the infected site is detected by the antivirus installed by the user, the reputation of the site that he wanted to go to initially will also suffer. Both mobile and ordinary redirects are not easily detectable, because how to correctly use the hiding techniques and, in addition, do not work for all IP addresses and types of mobile devices.
In our sample of more than 300,000 sites, Google identified less than 20% of the problems, and Yandex identified only 33% of the redirects that were installed on the sites at the time we crawled them. At the same time, if Yandex detects a malicious mobile redirect, in 100% of cases the site will be blacklisted.
We have already noted above that only about 10% of owners and administrators independently eliminated redirects before Google and Yandex detected them. - The second most common problem is dynamic links to infected sites. It is worth noting that in 100% of cases after the discovery of such a link, the site is blacklisted by Google (which means it will also be blocked in web browsers that use the Google SafeBrowsing API to identify insecure sites).
Dynamic links to infected sites were independently detected and eliminated by only 20-30% of all sites included in the study. - In third place in popularity is a static external link to an infected site. This type of problem turned out to be the easiest to identify and eliminate - from 40% to 50% of all sites were able to cope with the problem without waiting for it to be detected by search engines.
Statistics for the “Online Stores” slice.
A total of 2247 incidents were detected, affecting 5% of sites.
- 247 online stores were in blacklists, 68 of them throughout the course of the study
- The average time a site spent in a blacklist is 1 week
- Repeated infections are rare but occur (3 cases out of 247)
- 243 sites had the usual redirect to an infected site (more than half of these sites Google or Yandex did not consider dangerous, although in fact they are dangerous)
- 372 sites had dynamic links to infected sites (At the time of our scan, Google did not manage to notice 75% of such sites, Yandex - only 60%)
- Over 50% do not have an SSL certificate
Top issues not resolved throughout the observation period
- Mobile redirect to another site (in 72% of cases - to an infected one)
- Dynamic links to an infected site
- Static redirect to an infected site
Top active issues for the entire observation period
- Dynamic link to an infected site
- Mobile redirect to an external site
- Normal redirect to an infected site
Statistics on the Top-10000 Liveinternet slice.
In total, 1166 incidents were detected, affecting 10% of sites.
Top active problems for the entire observation period:
- Dynamic link to an infected site
- Mobile redirect to an external site
- Static link to an infected site
Statistics on the slice “Sites in the .ru zone included in the Top 1 million Alexa sites”
A total of 3292 incidents were detected, affecting about 8% of all sites.
Sites were twice as likely to be blacklisted than online stores.
Top active problems for the entire observation period.
- Mobile redirect to an external site
- Static link to an infected site
- Dynamic link to an infected site
Summary statistics for all slices
Thus, in the course of the study, the presence of problems was revealed in 10% of sites from the LiveInternet list, in 8% of sites from the Alexa list and 5% of online stores. The proportion of sites with problems in this study decreased compared to the previous study because we eliminated the problems of blacklisting spam and focused only on the most dangerous problems that directly lead to loss of traffic, infection of users or loss of Internet reputation business. However, in the future we plan to reincorporate into the research problems related to spam mailing lists, as they, in some cases, can also lead to site downtime due to disconnection by the hosting provider, loss of leads and a decrease in conversion due to non-delivery of letters from confirmations of orders in online stores or sites,
Conclusions and recommendations.
Increasing the depth and duration of the observation, as well as narrowing the sample to sites that can be considered commercial, allowed us to refine and slightly adjust the results of the previous study. However, in general, we are observing the same, including alarming, trends regarding website security problems as a source of downtime and losses for online businesses.
Based on the results of a previous study of the security state of web development in studios, as well as the data of a study just conducted, we recommend that, regardless of the type of CMS system used, pay increased attention to basic security measures, such as regular password changes, rejection of insecure protocols such as FTP in favor of SSH, protection of access to the administration panel using an SSL certificate, and others, and we also recommend that dedicated experts in the field of response be trained security incidents - removing sites from blacklists, strengthening protection by configuring the CMS and server environments and other measures to counter hacking and infection of sites that cause Internet business to lose.
Research methodology
For the study, a sample of about 320,000 sites was specially created:
More than 80,000 sites for research in dynamics during the 1st quarter of 2015, of which:
- 36.750 online stores
- 37.233 Russian-language sites from the top 1 million Alexa sites
- Top 10.000 LiveInternet Rankings
About 240,000 sites of commercial firms, randomly selected from the total number of active (delegated) domain names in the .ru zone, registered with legal entities for a one-time scan, similar to the 2014 study.
During the study, the following parameters were observed:
- Type of CMS on which the site is made
- The presence of the site in the black lists of Google and Yandex
- The presence of redirects on the site (server and client) (mobile redirect to an external or infected site, search redirect);
- External links to infected sites (static or dynamic);
- Availability of SSL certificate;
- Errors in configuration;
Observation of 80,000 sites of the first part of the sample was carried out continuously during the quarter (all parameters were polled and values were recorded in a database, where all historical information about the change in parameters was accumulated with each scan). We applied various approaches to the analysis of historical data to this selection of sites to determine the correlations of the various events we discovered. The second part of the sample was scanned once and only statistical methods of analysis were applied to it.
Descriptions of the problems that we analyzed during the study:
- We defined a redirect to an infected site as automatic redirection of a regular browser user to a third-party site that has already been blacklisted by search engines
- We defined a mobile redirect as automatically redirecting a user of a mobile device to a third-party site that has already been blacklisted by search engines
- A static link to an infected site is a link directly registered in the code of the page on the web server.
- A dynamic link to an infected site is a link that occurs when a web page is displayed in the user's browser as a result of execution of, for example, Javascript code.
The site is an important asset of the company, both the success of the product or service being promoted and its attitude to the company as a whole depend on its work. If the site does not have proper control, it can be hacked at any time, both for personal gain and for many others, reputational risks can be quite high, which is completely unacceptable for business. Constant and professional monitoring of the integrity of the site, its components and their proper functioning and timely response to emerging security threats is required.
Research page and expert comments: https://sitesecure.ru/securityreport1q2015 .
