Penetration Testing Laboratory "Test lab v.7" through the eyes of hackers
A review article on the results of participation in the free pentest laboratory Test lab v.7, codenamed Achilles Heel. The article contains information on the preparation of the laboratory, a partial passage, as well as comments by the winners.

“Test lab v.7” is a corporate network of the virtual company “SecureSoft LLC” based on Windows and Linux. A virtual company specializes in software development and has some security flaws. Using the vulnerabilities found, participants are invited to penetrate the network and gain access to all SecureSoft LLC nodes, each of which contains a secret token (there are 10 of them).
The laboratory was launched on 05/01/2015 at 22:00 Moscow time and is available to this day. At the time of launch, about 1200 participants from different countries were registered. For the convenience of communication and problem solving, a forum was prepared in Russian and English. The actions of the participants could be seen on the Cyberattack world map.
The first to make a successful attack on all nodes of the laboratory was able to Omar Ganiev (Beched). After 6 days of intense attack, Omar took the last token, thus becoming the third time in a row the champion of the Test lab laboratories.
Attention. The section contains instructions on passing part of the laboratory.
A feature of all “Test lab” laboratories is their proximity to the real conditions of the corporate network and modeling of vectors and attack scenarios encountered in real life. This write-up describes the first tasks of the laboratory and the direction for passing the following. Before completing the tasks, we need to register on the laboratory website and make settings in the distribution kit, which we will use to perform the virtual network pentest. We recommend using the Kali Linux distribution. This is a specialized distribution designed for information security professionals and contains a large number of tools for penetration testing. After registering and connecting via VPN to the laboratory, the following information is available to us:
In the context of laboratories, penetration testing takes place in the GrayBox mode - when partial information about the attacked infrastructure is known. In this case, we have a network map with nodes and their roles indicated on it.
The first thing you need to do penetration testing with is information gathering. We use the popular port scan utility - nmap. After that, we manually check the information received, namely, we check the responses from connecting to open ports using telnet and look at the generated html pages code.
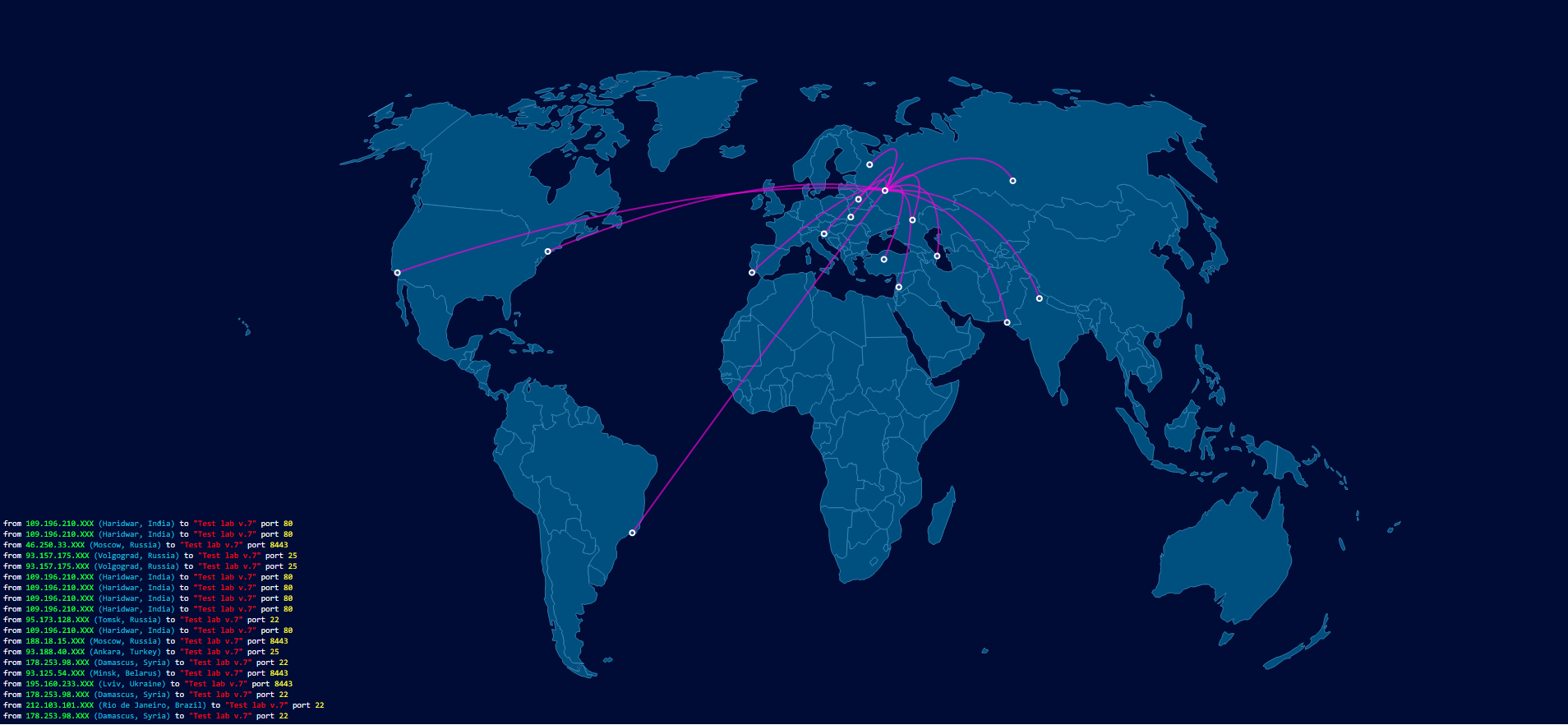
Specially for the launch of the 7th laboratory, a world map of attacks was implemented. Visualization of attacks allowed to see the geography of the participants. According to the data at the time of writing, experts from 63 countries and 194 cities took part in the laboratory. The largest number of participants was from Russia (322 IP), followed by the United States (64 IP) and closes the top three Ukraine (37 IP). Moscow is in the lead in the ranking of unique IPs by city (242 addresses), Kiev is in second place (25 addresses) and Petrozavodsk (18 addresses) in third place.
Full list of participating countries: Algeria, Andorra, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, China, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Egypt, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong (SAR), Hungary, India, Indonesia, Iran, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Korea South, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Mexico, Moldova, Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan , Panama, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Syria, Thailand, Turkey, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, United States, Uzbekistan, Zambia.
Work on the laboratory, as we have already adopted, is carried out in several stages:
1. Proposal and discussion of ideas for assignments.
2. Implementation of the poster version of the task, verification.
3. "Dopilivanie" to the final version.
4. Integration into a common scenario.
In order to avoid problems during the launch of the laboratory, the following must be taken into account when completing tasks:
- the fact that more than one participant completed the task simultaneously;
- not all participants are “white and fluffy”. It is necessary to exclude the possibility of vandalism or attempts to impede access to other participants.
In some cases, when the task requires full control over the system, but it is so interesting that you want to include it in the laboratory, you have to make some compromise. Then we try to minimize the risks. For example, provide a scenario for restricting access to a minimum number of participants at a time.
Of course, it is very interesting to watch attacks in real time, being "on the other side". In this laboratory, we did not use any intrusion detection systems, so the participants had no and no limitations in this regard. But, based on observations, the presence of such a system would reflect most of the attacks. Perhaps in the next lab we will include IDS / IPS workarounds.
Most port scans, brute force scans, directory scans, etc. was made public utilities with default settings: nmap scripting engine and DirBuster in User-Agent, for example. On one of the assignments, we left two options for passing, but the second also allowed others to be prevented - so we decided to see which option the participants would prefer. Unfortunately, as expected, vandalism began after some time :)
At first, we decided to play along and simulate the presence of an administrator who is trying to figure out what is happening and close the holes. About an hour they cut off the connections to the shells, removed them and interfered in every way, but without blocking the very possibility of exploitation. Then, nevertheless, I had to close the alternative option, because some unscrupulous participants constantly tried to remove the token itself, preventing others from completing this task - apparently, this lesson gave them more pleasure than going through the laboratory itself.
I hope the collective work of the authors of the article was not in vain and it turned out to be useful. I will be glad to consider all the wishes and comments in the PM. Have a nice day, everyone!

A few words about the laboratory
“Test lab v.7” is a corporate network of the virtual company “SecureSoft LLC” based on Windows and Linux. A virtual company specializes in software development and has some security flaws. Using the vulnerabilities found, participants are invited to penetrate the network and gain access to all SecureSoft LLC nodes, each of which contains a secret token (there are 10 of them).
Timeline
The laboratory was launched on 05/01/2015 at 22:00 Moscow time and is available to this day. At the time of launch, about 1200 participants from different countries were registered. For the convenience of communication and problem solving, a forum was prepared in Russian and English. The actions of the participants could be seen on the Cyberattack world map.
The first to make a successful attack on all nodes of the laboratory was able to Omar Ganiev (Beched). After 6 days of intense attack, Omar took the last token, thus becoming the third time in a row the champion of the Test lab laboratories.
In this laboratory, as in the previous ones, I grumbled that I had to brutalize or guess a lot, but still made useful things again =). One of the most non-trivial tasks was to exploit vulnerabilities on the terminal server, where it was necessary to conduct DLL-hijacking bypassing the MSE antivirus. Also, despite the distracting false paths, the forum task stood out, in which it was necessary to exploit vulnerabilities by hand, and in which fuzzing dictionaries were brought in by default in Burp Suite. Other tasks are useful for developing standard skills and the ability to match different finds. Thanks to the organizers for the training site!Following Omar, after some time, participants of MERRON, DarkCat and AV1ct0r managed to collect all tokens. Despite the fact that the laboratory is considered completed, it does not lose its essence, namely, to give everyone an opportunity to consolidate the skills of a practical pentest, as well as get new ones. Given the complexity of the tasks, we prepared a partial passage through the laboratory.
Omar Ganiev (Beched), incsecurity.ru
Write-up
Attention. The section contains instructions on passing part of the laboratory.
A feature of all “Test lab” laboratories is their proximity to the real conditions of the corporate network and modeling of vectors and attack scenarios encountered in real life. This write-up describes the first tasks of the laboratory and the direction for passing the following. Before completing the tasks, we need to register on the laboratory website and make settings in the distribution kit, which we will use to perform the virtual network pentest. We recommend using the Kali Linux distribution. This is a specialized distribution designed for information security professionals and contains a large number of tools for penetration testing. After registering and connecting via VPN to the laboratory, the following information is available to us:
Initial Information
- Tested company network: SecureSoft LLC.
- Server's IP address: 192.168.101.5
- Network map

In the context of laboratories, penetration testing takes place in the GrayBox mode - when partial information about the attacked infrastructure is known. In this case, we have a network map with nodes and their roles indicated on it.
The first thing you need to do penetration testing with is information gathering. We use the popular port scan utility - nmap. After that, we manually check the information received, namely, we check the responses from connecting to open ports using telnet and look at the generated html pages code.
Collection of information
Launching the nmap 192.168.101.5 utility gave the following information:
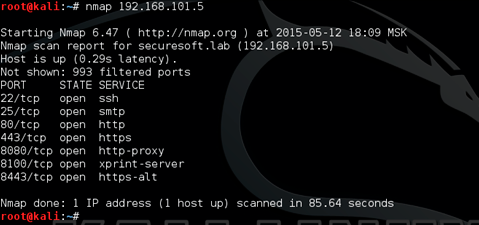
Open port 22 provides SSH access. For now, remember this.
The open 25th port of the mail server indicates that we can try to select passwords (BruteForce) at a sufficiently high speed (unlike web-bruteforce), Hydra is a good tool for bruteforce attacks. Checking the website on port 80 provided us with information about the account login rule used. In the source code of the web page you can find the e-mail of one of the employees of the company.

Open port 22 provides SSH access. For now, remember this.
The open 25th port of the mail server indicates that we can try to select passwords (BruteForce) at a sufficiently high speed (unlike web-bruteforce), Hydra is a good tool for bruteforce attacks. Checking the website on port 80 provided us with information about the account login rule used. In the source code of the web page you can find the e-mail of one of the employees of the company.

We use the obtained information to attack
After checking the website on port 8100, we see that this is a web interface to the mail server on port 25. We will use this information later, but for now, we will select the password for the discovered account.
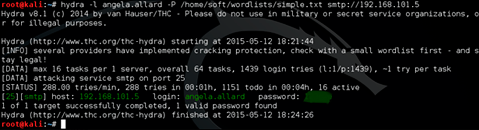
The found username and password provides access to the mail of the SecureSoft LLC employee angela.allard via the web interface.
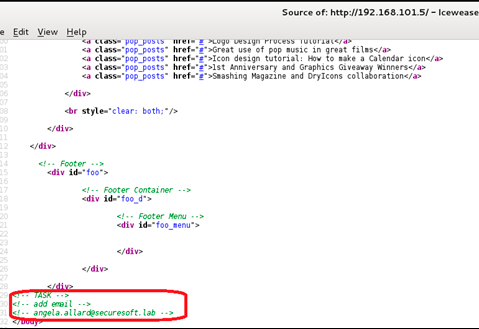
Looking through the mail angela.allard, we find a list of employees of SecureSoft LLC.
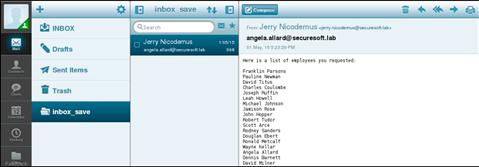
Now we have at our disposal a large list of company employees, which we will bring to the logic of creating account logins <name>. <name>.
We feed the resulting list to Hydra and ... And wait a bit. After some time, we get the password from the account pauline.newman. For the Bruteforce attack (password guessing), a dictionary was used consisting of the popular 2014 passwords found through a google request (it took 5 minutes to prepare the dictionary).
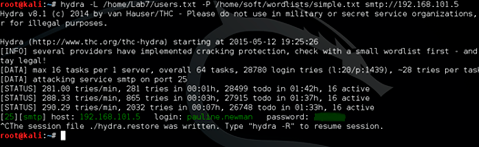
The post of the second employee provided us with more interesting information. Firstly, we received the coveted token from the Mail task, and secondly, we received additional information for going through the laboratory.
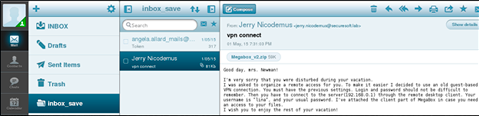

The found username and password provides access to the mail of the SecureSoft LLC employee angela.allard via the web interface.
Looking through the mail angela.allard, we find a list of employees of SecureSoft LLC.

Now we have at our disposal a large list of company employees, which we will bring to the logic of creating account logins <name>. <name>.
We feed the resulting list to Hydra and ... And wait a bit. After some time, we get the password from the account pauline.newman. For the Bruteforce attack (password guessing), a dictionary was used consisting of the popular 2014 passwords found through a google request (it took 5 minutes to prepare the dictionary).

The post of the second employee provided us with more interesting information. Firstly, we received the coveted token from the Mail task, and secondly, we received additional information for going through the laboratory.

We implement an additional attack vector
This is the introductory part of going through the laboratory, I hope it helps to understand the logic of the tasks and solve the rest of the tasks independently.As in real penetration testing, the attacker collects information about the attacked system in any possible and accessible places.
The resources that are intended for IT / IS personnel may turn out to be the most interesting - they may contain extremely critical information that will help to gain access to the entire network. An interesting resource is marked on the provided diagram - Admin Tools. Using nmap, we scan the range of ports 1-10000 of the resource we are interested in
.
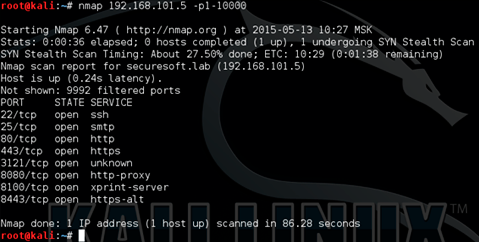
We see that some application is hanging on non-standard port 3121. Empirically, we determine that the Admin Tools website is launched there.
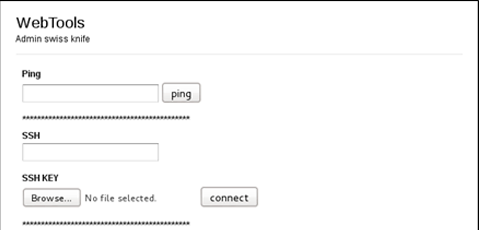
The functionality of this site turned out to be inoperative. It contained utilities that facilitate the work of the system administrator. On the tooltip of the submission form, an indication was found that the SSH key was being loaded, which suggested that this file might be located on this server. After studying the structure of the site and the html code, nothing useful was found, so it was decided to scan the site directories with the dirb utility.
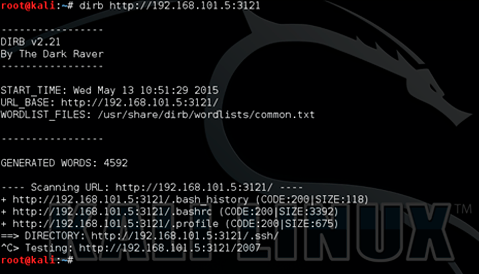
A .bash_history file has been detected. This file contains the history of commands that were executed in the console, for example, via SSH. The name of the SSH private key was found in this file - ssh_key.priv, which was immediately downloaded from the site.

Now we have data for accessing the SecureSoft LLC internal network via port 22 using ssh. Also, in the ssh_key.priv file, you can find token for the Admin Tools task.
The resources that are intended for IT / IS personnel may turn out to be the most interesting - they may contain extremely critical information that will help to gain access to the entire network. An interesting resource is marked on the provided diagram - Admin Tools. Using nmap, we scan the range of ports 1-10000 of the resource we are interested in
.

We see that some application is hanging on non-standard port 3121. Empirically, we determine that the Admin Tools website is launched there.

The functionality of this site turned out to be inoperative. It contained utilities that facilitate the work of the system administrator. On the tooltip of the submission form, an indication was found that the SSH key was being loaded, which suggested that this file might be located on this server. After studying the structure of the site and the html code, nothing useful was found, so it was decided to scan the site directories with the dirb utility.

A .bash_history file has been detected. This file contains the history of commands that were executed in the console, for example, via SSH. The name of the SSH private key was found in this file - ssh_key.priv, which was immediately downloaded from the site.

Now we have data for accessing the SecureSoft LLC internal network via port 22 using ssh. Also, in the ssh_key.priv file, you can find token for the Admin Tools task.
Cyberattack world map

Specially for the launch of the 7th laboratory, a world map of attacks was implemented. Visualization of attacks allowed to see the geography of the participants. According to the data at the time of writing, experts from 63 countries and 194 cities took part in the laboratory. The largest number of participants was from Russia (322 IP), followed by the United States (64 IP) and closes the top three Ukraine (37 IP). Moscow is in the lead in the ranking of unique IPs by city (242 addresses), Kiev is in second place (25 addresses) and Petrozavodsk (18 addresses) in third place.
Full list of participating countries: Algeria, Andorra, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, China, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Egypt, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong (SAR), Hungary, India, Indonesia, Iran, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Korea South, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Mexico, Moldova, Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan , Panama, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Syria, Thailand, Turkey, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, United States, Uzbekistan, Zambia.
On the other side of the barricades. Organizer Comments
Work on the laboratory, as we have already adopted, is carried out in several stages:
1. Proposal and discussion of ideas for assignments.
2. Implementation of the poster version of the task, verification.
3. "Dopilivanie" to the final version.
4. Integration into a common scenario.
In order to avoid problems during the launch of the laboratory, the following must be taken into account when completing tasks:
- the fact that more than one participant completed the task simultaneously;
- not all participants are “white and fluffy”. It is necessary to exclude the possibility of vandalism or attempts to impede access to other participants.
In some cases, when the task requires full control over the system, but it is so interesting that you want to include it in the laboratory, you have to make some compromise. Then we try to minimize the risks. For example, provide a scenario for restricting access to a minimum number of participants at a time.
Of course, it is very interesting to watch attacks in real time, being "on the other side". In this laboratory, we did not use any intrusion detection systems, so the participants had no and no limitations in this regard. But, based on observations, the presence of such a system would reflect most of the attacks. Perhaps in the next lab we will include IDS / IPS workarounds.
Most port scans, brute force scans, directory scans, etc. was made public utilities with default settings: nmap scripting engine and DirBuster in User-Agent, for example. On one of the assignments, we left two options for passing, but the second also allowed others to be prevented - so we decided to see which option the participants would prefer. Unfortunately, as expected, vandalism began after some time :)
At first, we decided to play along and simulate the presence of an administrator who is trying to figure out what is happening and close the holes. About an hour they cut off the connections to the shells, removed them and interfered in every way, but without blocking the very possibility of exploitation. Then, nevertheless, I had to close the alternative option, because some unscrupulous participants constantly tried to remove the token itself, preventing others from completing this task - apparently, this lesson gave them more pleasure than going through the laboratory itself.
Comments of participants
Thank you very much for creating the laboratory. All tasks were interesting, although the solution to some was not obvious. I liked the task “ssh” the most: it was very exciting to try to understand what the vulnerability was. As a result, the laboratory is an excellent opportunity to gain new knowledge and put into practice existing knowledge.
Merron
I can say about the laboratory that it was very interesting, some tasks were very difficult. Since I like the web most of all, I would like to mention the task called “forum”, a rather interesting idea, and a very cool implementation) I want to wish good luck and development to the whole team, well, thank you very much for the laboratory, I will wait for the following laboratories.
Darkcat
I hope the collective work of the authors of the article was not in vain and it turned out to be useful. I will be glad to consider all the wishes and comments in the PM. Have a nice day, everyone!
