Testing flash storage. Violin 6232 Series Flash Memory Array
We continue the topic begun in the articles " Testing flash storage. Theoretical part " and " Testing flash storage. IBM RamSan FlashSystem 820" . Today we will consider the capabilities of one of the most “mass” models of the Violin Memory company. The startup, founded by immigrants from Fusion-io , became a pioneer and spiritual leader in the ideology of building data storage systems based solely on flash memory. The Violin 6232 array was released in September 2011 and remained the flagship until the release of the 6264 model in August 2013.

We, as technical specialists, were more interested in the architecture of Violin Memory arrays, which is their distinctive feature and undoubted advantage over competitors. Each component is its own development of the company :
A system without a single point of failure where all components are duplicated. Where replacing components or updating the firmware not only does not require a shutdown, but also does not reduce performance: 4 controllers, lack of an internal cache, recording with full "strips", optimal algorithms for "garbage collection". This architecture allows you to get the highest performance, minimize delays and side effects (Write Cliff), ensures the availability of data level 99,9999 and eliminates the loss of performance with the possible failure of components. The rich, thoughtful control interface harmoniously adds the convenience of working with Violin equipment. Many technological advantages are provided through joint development with Toshiba, which is the company's main investor.
During testing, the following tasks were solved:
The test bench consists of a server connected via an FC factory with four 8Gb FC connections to the Violin 6232 storage system. The server and array characteristics are as follows: IBM 3630 M4 (7158-AC1) server ; Storage Violin Memory 6232
As an additional software on the test server installed Symantec Storage Foundation 6.1, which implements:
Flexible IO Tester (fio) version 2.1.4 utility is used to create a synthetic load (performing synthetic tests) on the storage system. For all synthetic tests, the following configuration parameters of the fio section [global] are used:
The following utilities are used to take performance indicators under synthetic load:
The performance indicators are taken during the test by the iostat, vxstat, vxdmpstat utilities with an interval of 5 s.
Testing consisted of 3 groups of tests. The tests were performed by creating a synthetic load using the fio program on a block device, which is a stripe logical volume with 8 disks stratification, 1MiB data block size created using Veritas Volume Manager or Native Linux LVM (in group 3 ) of 8 LUNs presented from the system under test.
1. With a long load on the recording at a certain point in time, significant degradation of the storage performance is recorded. A drop in performance is expected and is a feature of the SSD (Write Cliff) operation associated with the inclusion of Garbage Collection (GC) processes and the limited performance of the indicated processes. Disk array performance recorded during running GC processes can be considered as the maximum average disk array performance.
2. The block size with a long recording load does not affect the performance of the GC process. CG runs at about 600Mib / s.
3. The difference in the values of the maximum storage run time at peak performance, recorded during the first long test and subsequent equivalent test with a 4K block, is due to incomplete storage before testing.
4. The maximum operating time of the storage system at peak performance differs significantly with the 4K block and all other blocks, which is most likely due to the architectural optimization of the storage system for the indicated block (Violin storage always writes in full stripe 4K size using the flash configuration of RAID5 (4 + P) modules , stripe unit size 1K).
Record:
Reading:
Mixed Load (70/30 rw)
Minimum latency:
In general, the array made an impression of a full-fledged high-end device. We managed to get very good results, however, the impression was that the whole resource of the system was still not possible to choose. To create the load, one server was used with two processors, which were overloaded during the testing process. With high probability, we can say that we rather reached the limit of capabilities of a load server than a tested storage system. Separately, it should be noted:
PS The author is grateful to Pavel Katasonov, Yuri Rakitin, and all other company employees who participated in the preparation of this material.

We, as technical specialists, were more interested in the architecture of Violin Memory arrays, which is their distinctive feature and undoubted advantage over competitors. Each component is its own development of the company :
- Own flash modules (VIMM);
- Native VMOS operating system optimized for working with flash;
- Own patented RAID (vRAID), devoid of the disadvantages of standard RAID 5.6;
A system without a single point of failure where all components are duplicated. Where replacing components or updating the firmware not only does not require a shutdown, but also does not reduce performance: 4 controllers, lack of an internal cache, recording with full "strips", optimal algorithms for "garbage collection". This architecture allows you to get the highest performance, minimize delays and side effects (Write Cliff), ensures the availability of data level 99,9999 and eliminates the loss of performance with the possible failure of components. The rich, thoughtful control interface harmoniously adds the convenience of working with Violin equipment. Many technological advantages are provided through joint development with Toshiba, which is the company's main investor.
Testing methodology
During testing, the following tasks were solved:
- to study the process of degradation of storage performance with a long load on write (Write Cliff) and reading;
- to study the performance of Violin 6232 storage systems at various load profiles;
- study the effect of LUN block size on performance.
Testbed configuration
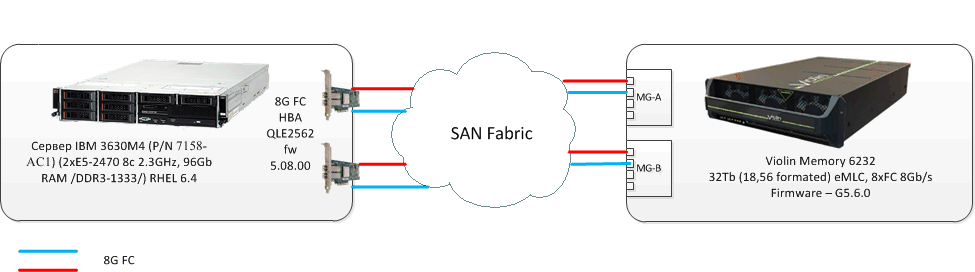 |
| Figure 1. Block diagram of the test bench |
The test bench consists of a server connected via an FC factory with four 8Gb FC connections to the Violin 6232 storage system. The server and array characteristics are as follows: IBM 3630 M4 (7158-AC1) server ; Storage Violin Memory 6232
As an additional software on the test server installed Symantec Storage Foundation 6.1, which implements:
- functionality of the logical volume manager (Veritas Volume Manager);
- functional of fault-tolerant connection to disk arrays (Dynamic Multi Pathing). (For tests of group 1 and 2. For tests of group 3, native Linux DMP is used)
See the tedious details and all sorts of smart words.
Settings have been made on the test server to reduce the latency of disk I / O:
On the storage system, the configuration settings for partitioning the disk space are performed: for all tests, 8 LUNs of the same volume are created. Their total volume covers the entire useful capacity of the disk array. For group 2 tests, the LUN block size is set to 512B, for group 3 tests, the LUN block size is set to 4KB. Created LUNs are presented to the test server.
- I / O scheduler changed from
cfqtonoopby assigning the noop value to the parameter/sys/<путь_к_устройству_Symantec_VxVM>/queue/scheduler - New parameter in
/etc/sysctl.confminimizing the size of the queue at the level of the logical volume manager Symantec:vxvm.vxio.vol_use_rq = 0; - the limit of simultaneous I / O requests to the device is increased to 1024 by assigning a value of 1024 to the parameter
/sys/<путь_к_устройству_Symantec_VxVM>/queue/nr_requests - disabled checking the possibility of merging I / O operations (iomerge) by assigning a value of 1 to the parameter
/sys/<путь_к_устройству_Symantec_VxVM>/queue/nomerges - increased queue size on FC adapters by adding an
/etc/modprobe.d/modprobe.confoption to the configuration fileql2xmaxqdepth=64 (options qla2xxx ql2xmaxqdepth=64);
On the storage system, the configuration settings for partitioning the disk space are performed: for all tests, 8 LUNs of the same volume are created. Their total volume covers the entire useful capacity of the disk array. For group 2 tests, the LUN block size is set to 512B, for group 3 tests, the LUN block size is set to 4KB. Created LUNs are presented to the test server.
Testing Software
Flexible IO Tester (fio) version 2.1.4 utility is used to create a synthetic load (performing synthetic tests) on the storage system. For all synthetic tests, the following configuration parameters of the fio section [global] are used:
- thread = 0
- direct = 1
- group_reporting = 1
- norandommap = 1
- time_based = 1
- randrepeat = 0
- ramp_time = 10
The following utilities are used to take performance indicators under synthetic load:
- iostat, which is part of the sysstat package version 9.0.4 with keys
txk; - vxstat, part of the Symantec Storage Foundation 6.1 with keys
svd; - vxdmpadm, part of the Symantec Storage Foundation 6.1 with keys
-q iostat; - fio version 2.1.4, to generate a summary report for each load profile.
The performance indicators are taken during the test by the iostat, vxstat, vxdmpstat utilities with an interval of 5 s.
Testing program.
Testing consisted of 3 groups of tests. The tests were performed by creating a synthetic load using the fio program on a block device, which is a stripe logical volume with 8 disks stratification, 1MiB data block size created using Veritas Volume Manager or Native Linux LVM (in group 3 ) of 8 LUNs presented from the system under test.
Ask for details
When creating a test load, the following additional parameters of the fio program are used:
The test group consists of four tests that differ in the total LUN volume presented with the tested storage system, the size of the I / O block and the direction of the I / O (write or read):
Based on the test results, based on the data output by the vxstat team, charts are formed that combine the test results:
The analysis of the information obtained is carried out and conclusions are made about:
During testing, the following types of loads are investigated:
The test group consists of a set of tests, which is all possible combinations of the above types of load. In order to level the influence of service processes of storage (Garbage Collection) on test results, a pause between the tests is implemented equal to the ratio of the volume of information recorded during the test to the performance of service processes of storage (determined by the results of the first group of tests).
Based on the test results, based on the data output by fio software at the end of each test, the following graphs are generated for each combination of the following types of load: load profile, method of processing I / O operations, queue depths, combining tests with different values of the I / O block :
The analysis of the results is carried out, conclusions are made about the load characteristics of the disk array at latency <1ms.
The tests are carried out similarly to the tests of group 2, but only the synchronous I / O method is studied due to the limited testing time. At the end of each test, graphs are plotted showing the difference in% of the obtained performance indicators (iops, latency) from the indicators obtained during testing with a LUN block size of 512 bytes (test group 2). Conclusions are drawn about the effect of LUN block size on disk array performance.
Group 1: Tests that implement a long load of random write type with a change in the size of the block of input / output (I / O).
When creating a test load, the following additional parameters of the fio program are used:
- rw = randwrite
- blocksize = 4K
- numjobs = 64
- iodepth = 64
The test group consists of four tests that differ in the total LUN volume presented with the tested storage system, the size of the I / O block and the direction of the I / O (write or read):
- a write test performed on a fully labeled storage system — the total amount of presented LUNs is equal to the useful storage capacity, the test duration is 7.5 hours;
- tests for recording with a changing block size (4.32.1024K), performed on a fully labeled storage system, the duration of each test is 4.5 hours. The pause between tests is 2 hours.
Based on the test results, based on the data output by the vxstat team, charts are formed that combine the test results:
- IOPS as a function of time;
- Latency as a function of time.
The analysis of the information obtained is carried out and conclusions are made about:
- the presence of degradation of performance with prolonged load on the write and read;
- performance of service processes of storage systems (Garbage Collection), limiting the performance of a disk array for recording under long peak load;
- the degree of influence of the size of the I / O operations block on the performance of storage service processes;
- the amount of space reserved for storage for leveling service processes of storage.
Group 2: Disk array performance tests for different types of load, performed at the level of the block device created by the Symantec Volume Manager (VxVM) with a LUN block size of 512 bytes.
During testing, the following types of loads are investigated:
- load profiles (modifiable software parameters fio: randomrw, rwmixedread):
- random record 100%;
- random write 30%; random read 70%;
- random read 100%.
- block sizes: 1KB, 8KB, 16KB, 32KB, 64KB, 1MB (modifiable software parameter fio: blocksize);
- methods of processing input-output operations: synchronous, asynchronous (modifiable software parameter fio: ioengine);
- the number of processes that generate the load: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 160, 192 (modifiable software parameter fio: numjobs);
- queue depth (for asynchronous I / O operations): 32, 64 (modifiable software parameter fio: iodepth).
The test group consists of a set of tests, which is all possible combinations of the above types of load. In order to level the influence of service processes of storage (Garbage Collection) on test results, a pause between the tests is implemented equal to the ratio of the volume of information recorded during the test to the performance of service processes of storage (determined by the results of the first group of tests).
Based on the test results, based on the data output by fio software at the end of each test, the following graphs are generated for each combination of the following types of load: load profile, method of processing I / O operations, queue depths, combining tests with different values of the I / O block :
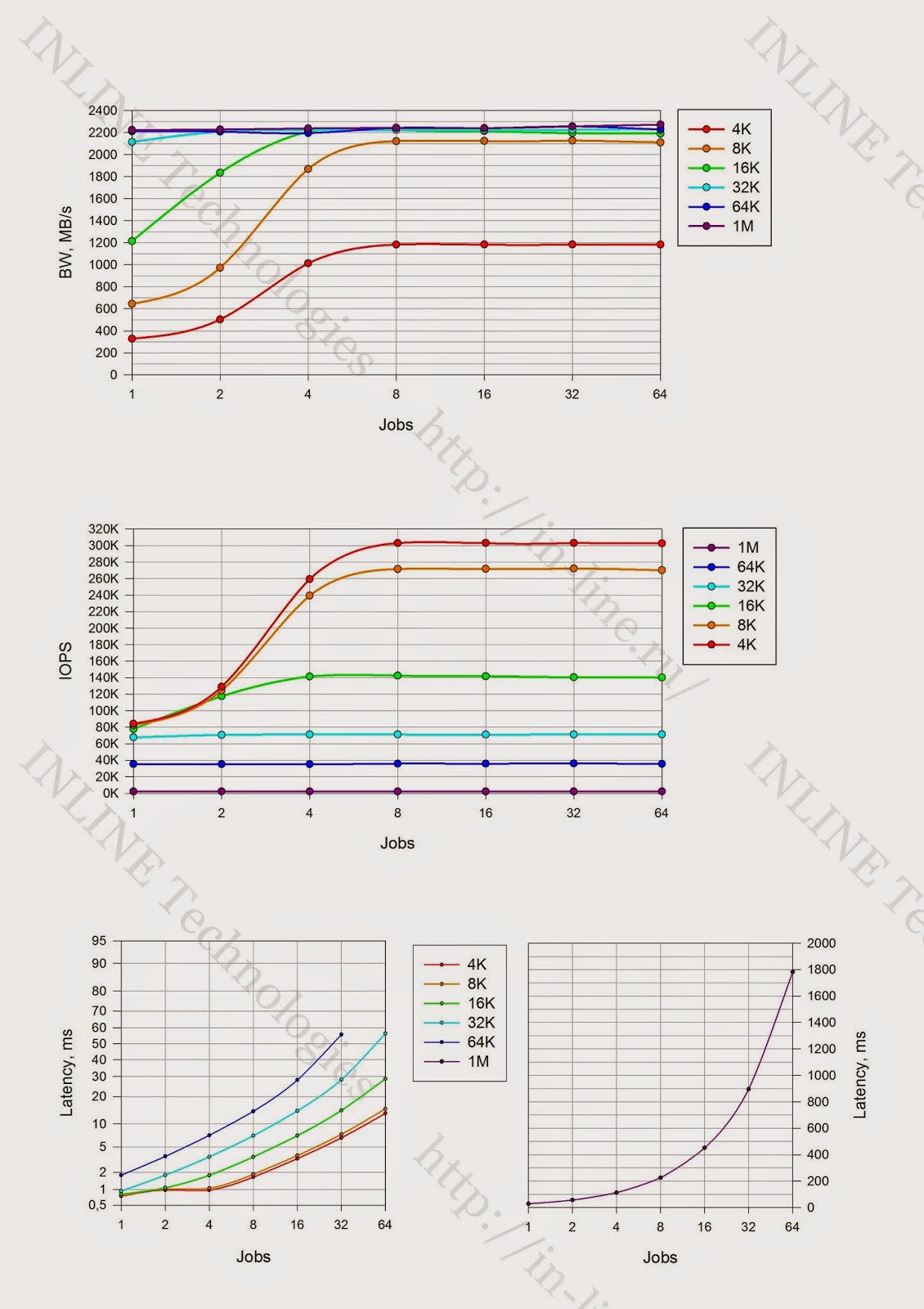
- IOPS - as a function of the number of processes generating a load;
- Bandwidth - as a function of the number of processes generating a load;
- Latency (clat) - as a function of the number of processes generating a load;
The analysis of the results is carried out, conclusions are made about the load characteristics of the disk array at latency <1ms.
Group 3: tests of disk array performance with synchronous I / O, different types of load, performed at the level of a block device created by Linux LVM, with a LUN block size of 4KiB.
The tests are carried out similarly to the tests of group 2, but only the synchronous I / O method is studied due to the limited testing time. At the end of each test, graphs are plotted showing the difference in% of the obtained performance indicators (iops, latency) from the indicators obtained during testing with a LUN block size of 512 bytes (test group 2). Conclusions are drawn about the effect of LUN block size on disk array performance.
Test results
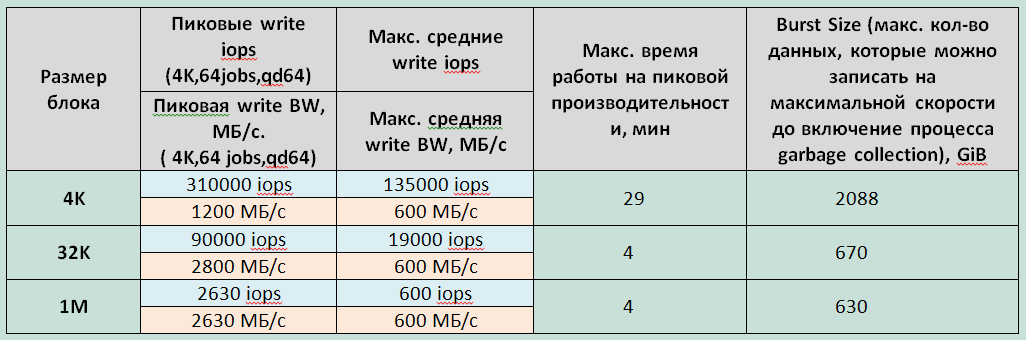
Group 1: Tests that implement a long load of random write type with a change in the size of the block of input / output (I / O).
1. With a long load on the recording at a certain point in time, significant degradation of the storage performance is recorded. A drop in performance is expected and is a feature of the SSD (Write Cliff) operation associated with the inclusion of Garbage Collection (GC) processes and the limited performance of the indicated processes. Disk array performance recorded during running GC processes can be considered as the maximum average disk array performance.
Graphs
2. The block size with a long recording load does not affect the performance of the GC process. CG runs at about 600Mib / s.
3. The difference in the values of the maximum storage run time at peak performance, recorded during the first long test and subsequent equivalent test with a 4K block, is due to incomplete storage before testing.
4. The maximum operating time of the storage system at peak performance differs significantly with the 4K block and all other blocks, which is most likely due to the architectural optimization of the storage system for the indicated block (Violin storage always writes in full stripe 4K size using the flash configuration of RAID5 (4 + P) modules , stripe unit size 1K).
Chart and table
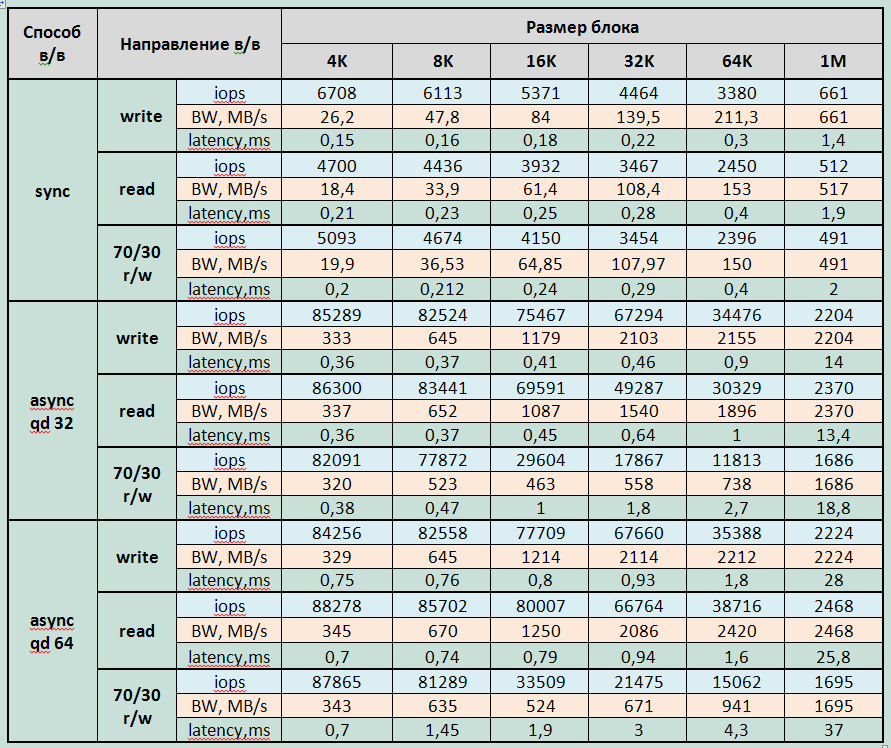
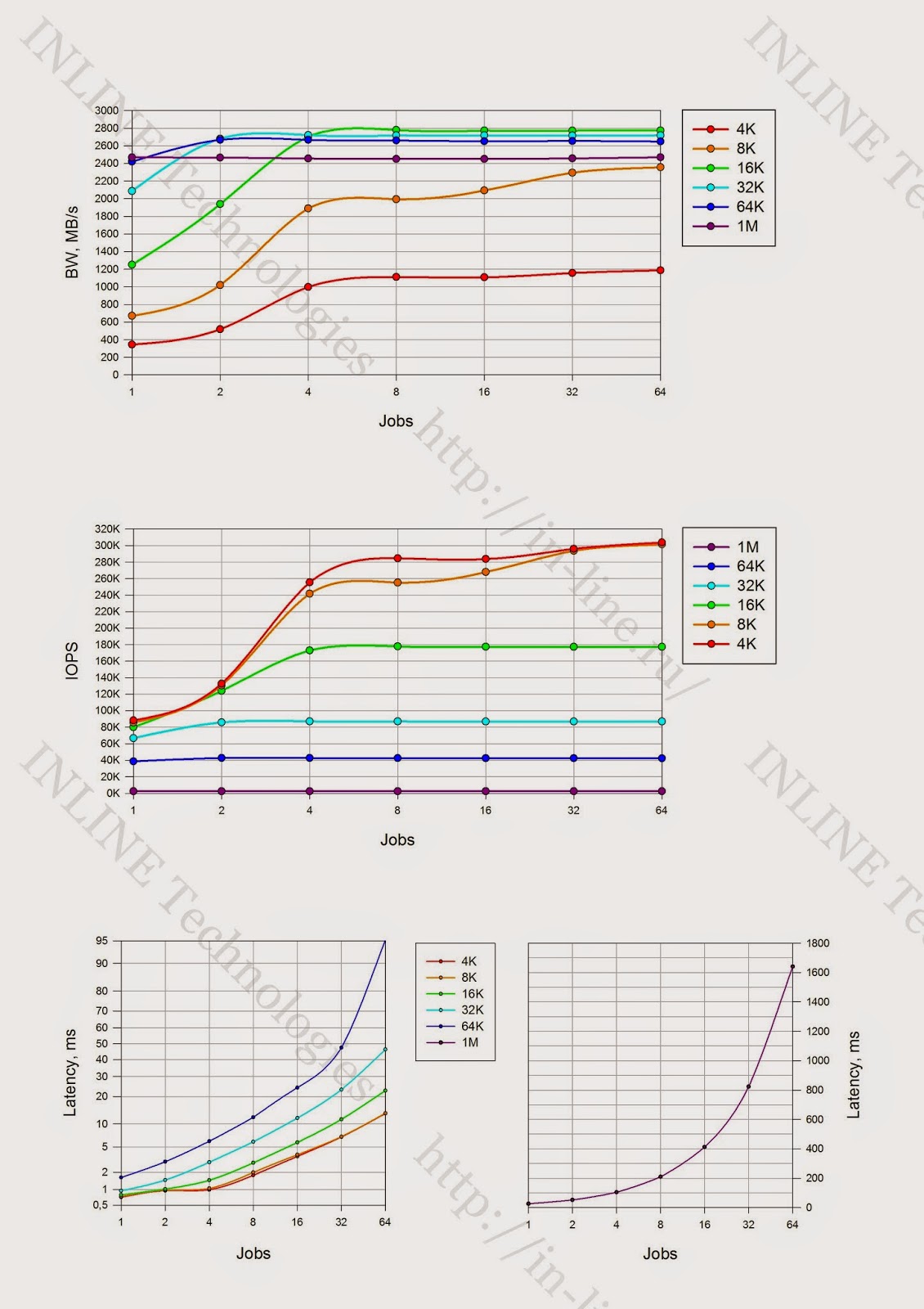
Group 2: Disk array performance tests for different types of load, performed at the level of the block device created by the Symantec Volume Manager (VxVM) with a LUN block size of 512 bytes.
Block device performance tables.
Block device performance graphs.
- Received approximately the same array performance for reading and writing.
- Failed to get manufacturer-declared read performance (maximum 500,000IOPS claimed).
- With mixed I / O, the array shows less performance than separately when writing and reading with almost any I / O profile.
- A significant decrease in performance is recorded with an 8K block on a mixed load profile with an increase in the number of input / output streams. (The reason for the discovered phenomenon is currently not clear).
Maximum latched performance parameters for Violin 6232
Record:
- 307000 IOPS at latency 0.8ms (4KB async qd32 block)
- Bandwidth: 2224MB / s for large blocks
Reading:
- 256000 IOPS at latency 0.7ms (4KB sync block);
- 300,000 IOPS at 6.7ms latency (4KB async qd 32 block);
- Bandwidth: 2750MB / s for medium blocks (16-32K).
Mixed Load (70/30 rw)
- 256000 IOPS at latency 0.7ms (4KB sync block);
- 305000 IOPS with a latency of 6.7ms (4KB async qd 64 block);
- Bandwidth 2700MB / s for medium blocks (16-32K)
Minimum latency:
- When recording - 0.146ms for a block of 4K jobs = 1
- When reading - 0.21ms for a block of 4K jobs = 1
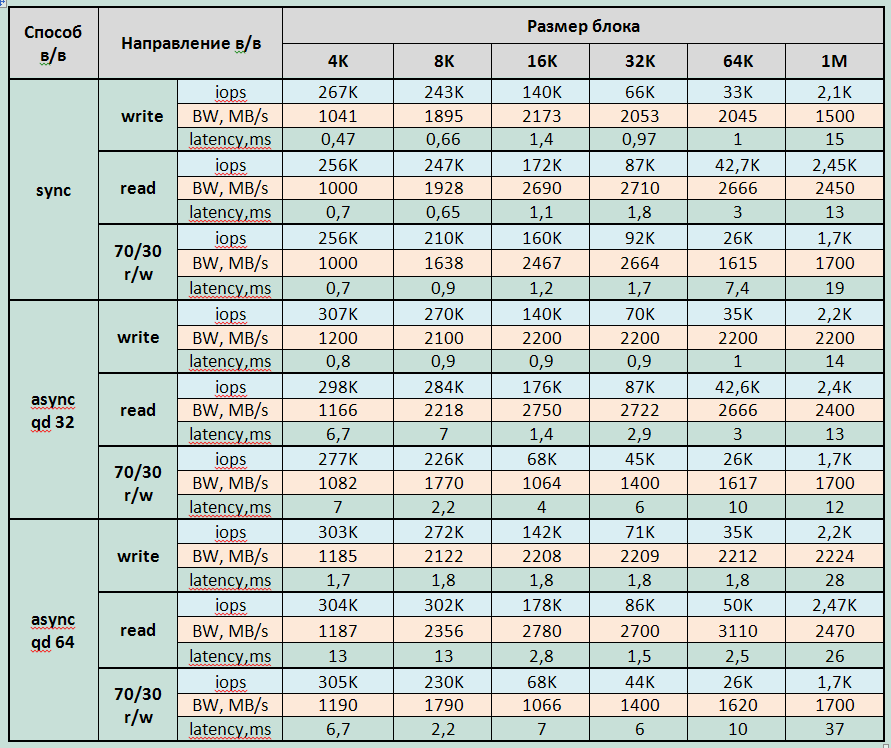
Group 3: tests of disk array performance with synchronous I / O, different types of load, performed at the level of a block device created by Linux LVM using a LUN block size of 4KiB.
Graphs
(All pictures are clickable)
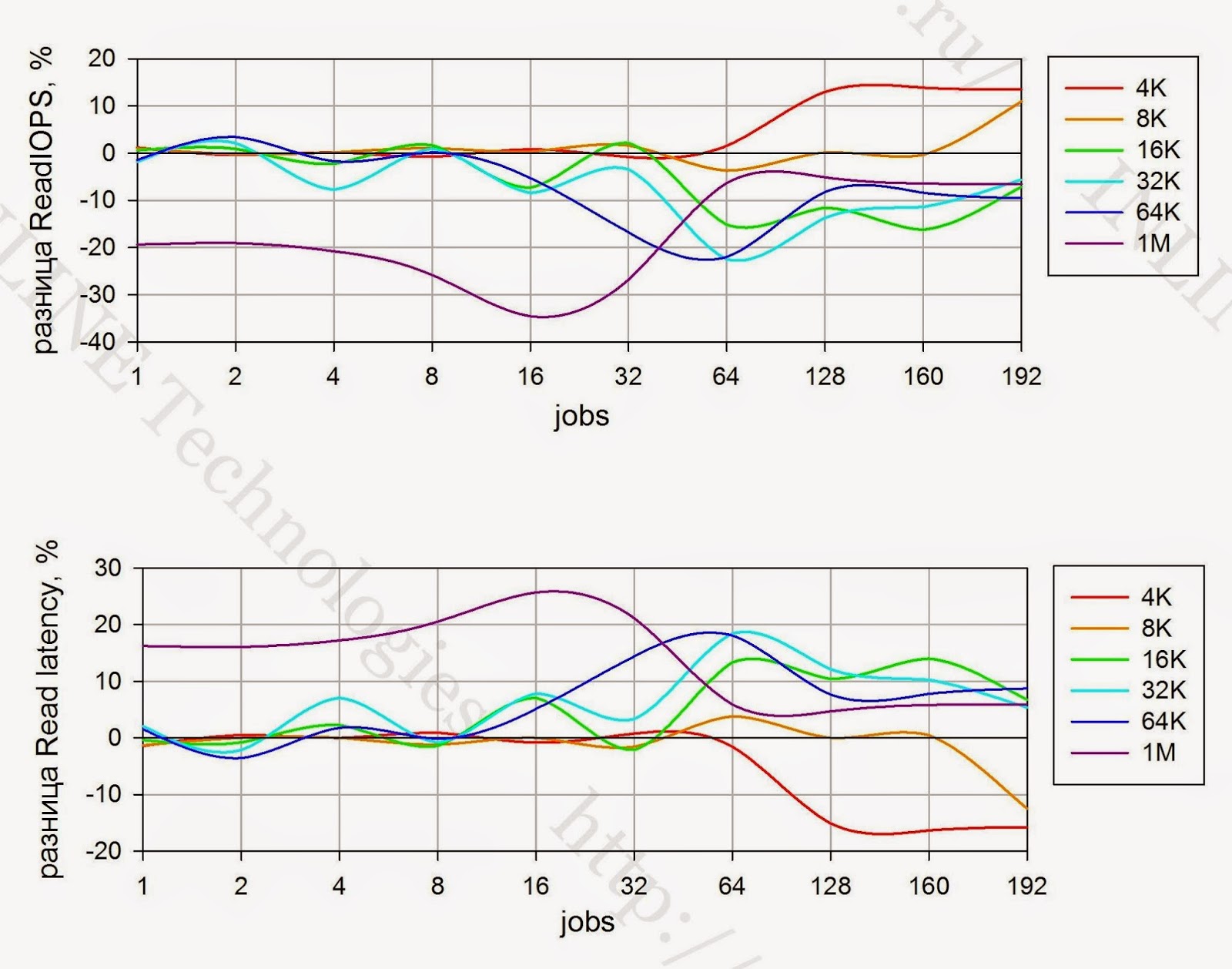 |
| The difference between IOPS and Latency between a device with a LUN block size of 4KB and 512B with random reading (indicators with a block size of LUN = 512B are taken as 0) |
 |
| Разница IOPS и Latency между устройством с размером блока LUN 4КБ и 512Б при случайной записи (показатели при размере блока LUN = 512Б приняты за 0) |
 |
| Разница IOPS и Latency между устройством с размером блока LUN 4КБ и 512Б при смешанной нагрузке (70/30 r/w)(показатели при размере блока LUN = 512Б приняты за 0) |
- Влияние размера блока LUN на производительность при количестве jobs до 64 отсутствует.
- При jobs > 64 на операциях записи наблюдается увеличение производительности до 20% по сравнению с размером блока LUN 512B
- При jobs > 64 на операциях чтения средними и большими блоками наблюдается уменьшение производительности до 10-15%
- With a mixed load of small and medium blocks (up to 32K), the array shows the same performance for both LUN block sizes. But with large blocks (64K and 1M), performance improves up to 50% when using the 4KiB LUN unit
conclusions
In general, the array made an impression of a full-fledged high-end device. We managed to get very good results, however, the impression was that the whole resource of the system was still not possible to choose. To create the load, one server was used with two processors, which were overloaded during the testing process. With high probability, we can say that we rather reached the limit of capabilities of a load server than a tested storage system. Separately, it should be noted:
- Очень хорошее отношение IOPS/занимаемоеместо в стойке (3U). Что в сравнении с традиционными дисковыми массивами, по сути, является конкурентным решением способным заменить набор шкафов High-End системы на несколько полок Violin при значимом увеличением производительности.
- Наличие Enterprise функционала, такого как Snapshot, может быть полезным для совмещения задач Test/Development и Production в рамках одной дисковой системы .
- Отсутствие penalty на запись при формирование RAID-5 (запись только полными stripe), приводит к лучшим результатам на операциях записи.
- The presence of 4 RAID-controllers and the lack of a cache (it is not needed in the SSD) guarantees stable performance in case of failures. On traditional, 2-controller Mid-range systems, when one controller fails, performance can sag 3-4 times, because controller failure turns off the entire write cache.
PS The author is grateful to Pavel Katasonov, Yuri Rakitin, and all other company employees who participated in the preparation of this material.