How to get started with GitHub: quick start

Distributed version control systems (DVCS) are gradually replacing centralized ones. If you are not using one of them yet - it's time to try.
In this article, I will try to show how you can quickly start experimenting with git using github.com.
The article will not discuss the differences between different DVCS. Also, work with git will not be considered in detail, there are many good sources on this topic, which I will provide at the end of the article.
So, github.com is positioned as a web hosting service for projects using the git version control system, as well as a social network for developers. Users can create an unlimited number of repositories, for each of which a wiki, issue tracking system is provided, it is possible to conduct code review and much more. GitHub is currently the most popular service of its kind, overtaking Sourceforge and Google Code.
For open-souce projects, the use of the site is free. If you need to have private repositories, it is possible to switch to a paid tariff plan:

Let's start with registration. Follow the link github.com/signup/free and enter your data.
After registration, we get to the Dashboard of our account:

Now we do not have a single repository, and we can either create a new repository or fork from an existing foreign repository and maintain our own development branch. Then, if desired, you can offer your changes to the author of the original repository (Pull request).
But first, install git and configure it to work with the site.
If you are running Windows, download and install msysgit . This is the console version of git for Windows (hereinafter the story will be conducted on the example of this OS).
Instruction for MacOS X (eng)
Instruction for Linux (eng)
There should be no problems, just click Next everywhere. After installation, select Git Bash Explorer in the context menu:
or via Git Bash.lnk in the installation folder:

prescribed in the console their data and settings line breaks: By the way, I recommend to go through a good online course on using git from the console. The course takes several hours and provides the necessary basic skills. For those who prefer gui - for Windows there are several such tools for working with git. The two main ones are SmartGit (cross-platform) and TortoiseGit . Both are good, and which one to use is a matter of taste. I will describe working with TortoiseGit. For poppies, giu is also available.
git config --global user.name "ваше имя"
git config --global user.email "ваша почта"
git config --global core.autocrlf true
git config --global core.safecrlf true- official client from GitHub - in my opinion is still rather damp.
- GitX - I personally did not like
- GitBox - most follows the mac-way, I highly recommend trying it
Download the link code.google.com/p/tortoisegit/downloads/list . When installing everywhere click Next.
Now back to github and create a new repository. While on the Dashboard, click New Repository (https://github.com/repositories/new), enter the data and click Create Repository.
GitHub allows working with repositories in three ways: SSH, HTTP and Git Read-Only, respectively providing three types of links for our repository: In order to simply pick up the repository to the local machine, the internal git protocol (third link) is enough. This is the fastest and most effective way that provides read-only anonymous access. If we want to make changes to the github repository, we need to use HTTP or SSH.
1. git@github.com:habrauser/Hello-world.git
2. habrauser@github.com/habrauser/Hello-world.git
3. git://github.com/habrauser/Hello-world.git
Working on http does not cause any difficulties, at the right time, the account password on github is simply used.
To use SSH, we need to create a special key pair: public and private. The public one will be placed in the account settings on github, and the private one will be saved on the local machine.
To generate keys, you can use the ssh-keygen tool, which comes bundled with git (a description of this method can be found here ). We will use PuTTY (or rather, a small puttygen program included in its composition). PuTTY is a client for remote access, including using SSH.
Download the latest version from the official website (http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html). By the way, puttygen of the older version (2007) is part of TortoiseGit.
After installing PuTTY, run puttygen from the folder with the program installed:

click Generate, move the mouse cursor for a while to obtain random data necessary for the algorithm
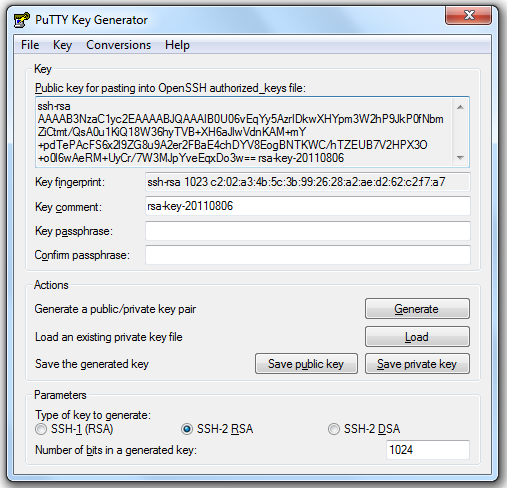
Enter the password that protects our private key in the Key passphrase field, enter the confirmation, click Save private key, save.
Next, copy the public key in OpenSSH format from the text area “Public key for pasting ...” and go to the settings of our account on github (Account Settings) in the SSH Public Keys section:

click Add another public Key, paste our public key:

click Add key. That's it, now we are ready to work with github on ssh. Let's try to pick up our empty rezitory on the local machine using TortioшseGit. In the explorer’s context menu, select Git Clone ...
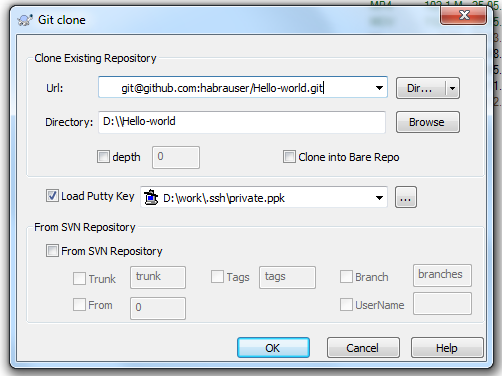
In the Url field, insert the SSH address of our repository, in the Load Putty Key field indicate the path to our private key, click OK.
Pageant will ask us for a password for the private key (then you won’t need to do this later)
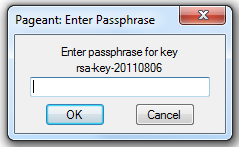
Pageant is an SSH authentication agent in PuTTY, it allows you to manage private keys.
His icon hangs in the tray:

The repository is successfully inclined to the local machine
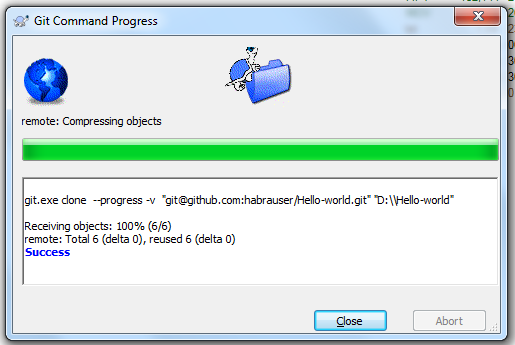
Now let's try changing the local repository and posting the changes to github. Add a README file to the local repository (a file called README is processed by github in a special way - its contents will be displayed as a description of the repository on the corresponding page)
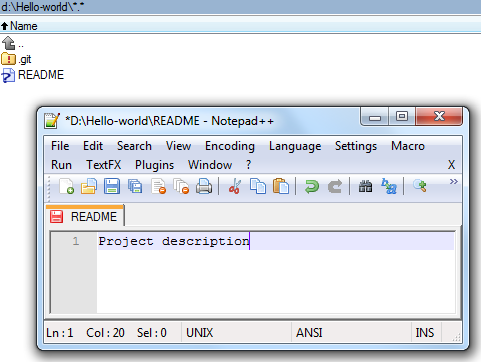
Submit changes to the local repository
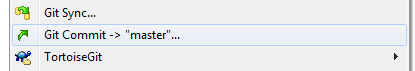

and synchronize it with the repository on github:
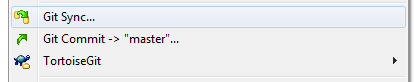
click Push
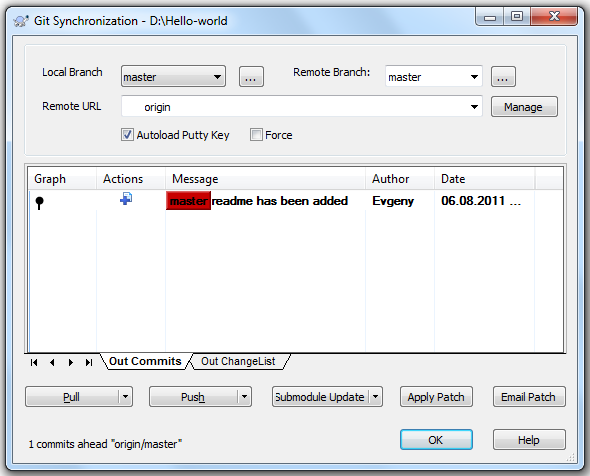
Now, going to the page of our repository, we see the following:
For each repository, the site offers a wiki:
as well as a simple issue tracking system: by the
way, for those who use Eclipse, there is a corresponding mylyn connector for github:
and an EGi plugin t:
The Explore GitHub link opens a directory of repositories where you can search by many other criteria, including programming languages, popularity, etc.
In summary, I want to say that if you are a novice developer planning to start using version control systems, or more experienced and looking at distributed VCS, but not knowing how to start, it makes sense to try git using such a wonderful tool like github.com.
useful links
To work with git:
code.google.com/p/msysgit git for windows
www.syntevo.com/smartgit/index.html SmartGit
code.google.com/p/tortoisegit TortoiseGit
http://www.chiark.greenend.org .uk / ~ sgtatham / putty / PuTTY
About git in Russian:
habrahabr.ru/blogs/Git/106912 “Successful branching model for git” - translation of a good English article
githowto.com interactive course on working with git from the console
habrahabr.ru/ blogs / Git / 106912 "Why git" + discussion
habrahabr.ru/blogs/development/68341 "Git for transitions from SVN" + discussion
habrahabr.ru/blogs/Git/75990 "Team work in git" + discussion
progit.org/book/en Russian translation of the book "Pro Git" (not fully translated)
habrahabr.ru/blogs/Git/123111 beginner cheat sheet
los-t.livejournal.com/tag/git%20guts post cycle " git internals »
lib.custis.ru/%D0%9B%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%81_%D0%A2%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%B2%D0%B0% D0% BB% D1% 8C% D0% B4% D1% 81_% D0% BE_GIT_% D0% BD% D0% B0_Google_Talks Linus Torvalds about git
habrahabr.ru/blogs/Git/80909 The Magic of Git book
About git in English:
the books
- progit.org/book Pro Git Book
- rutracker.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=2808582 book "Version Control with Git", 2009, O'Reilly
- book.git-scm.com Git Community Book
- rutracker.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=2808843 book “Pragmatic Version Control Using Git”, 2008, T. Swicegood
- rutracker.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=3239579 book “Pragmatic Guide to Git”, 2010, T. Swicegood. The described git version is 1.7.2.1. Book in the format of two-page spreads - problem / solution
- rutracker.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=900767 book "Git Internals"
- http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/~blynn/gitmagic/index.html book "Git Magic"
video
- rutracker.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=3520513 git video course. Pretty boring and with humor.
- www.youtube.com/watch?v=8dhZ9BXQgc4 git lecture by Randal Schwartz
- excess.org/article/2008/07/ogre-git-tutorial Git The Basics Tutorial video tutorial
other
- gitref.org reference for learning the most used commands
- ftp.newartisans.com/pub/git.from.bottom.up.pdf bottom-up instructions, i.e. from a low-level git device to high-level commands. The author claims that this way information is better perceived.
- ndpsoftware.com/git-cheatsheet.html nice cheatsheet
- whygitisbetterthanx.com git advantages over other VCS
- devcheatsheet.com/tag/git selection of cheatsheets
