Videoconferencing systems market review

Modern business communications are increasingly moving from personal meetings to remote methods of interaction, and this trend applies to all sectors of the economy. Modern technical solutions allow to provide high-quality communication (sound and video signal) and data exchange between a sufficiently large number of subscribers. An example of such solutions are video conferencing systems (video conferencing).
The main business advantages of video conferencing at the dawn of its formation were and still remain increasing the manageability of branches and subsidiaries, streamlining business processes and decision-making procedures, improving internal corporate communications and saving travel expenses.
History of VCS
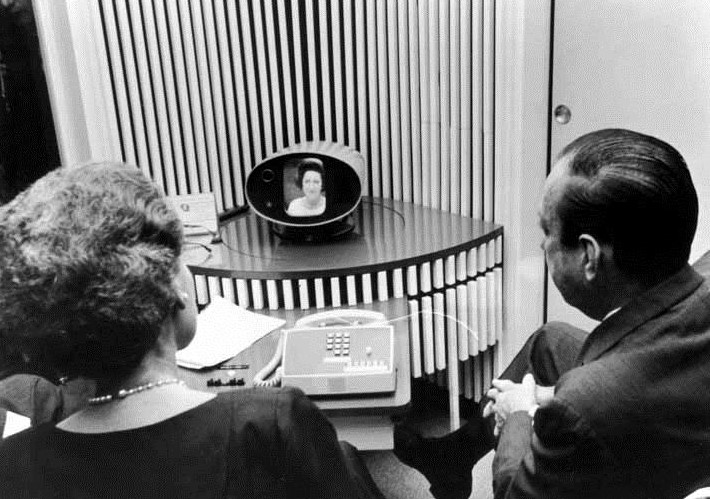

VKS appeared at the intersection of TV technology and data transmission in the 60s of the XX century. The first videophone (“picturephone”) was introduced in 1964 by AT & T. By the end of the 1970s, the first relatively full-fledged video conferencing systems appeared (Ericsson introduced the first videophone), which transmitted audio-visual information at a high enough level for that time.
In 1976, Network Voice Protocol (NVP) technology for packet data was introduced, which is an early example of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology. At this stage, the main technology of video conferencing was voice and image transmission over an analogue public switched telephone network (PSTN). At that time, VCS solutions were expensive and cumbersome, which limited their commercial use.
In 1981, a video protocol (PVP) was introduced, and in 1991, the first IBM-based PC videoconferencing solution. In 1990, the first international standard in the field of video conferencing was approved - H.320 to support video conferencing over ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network). During this period, the main technology of video conferencing was image compression, which helped to improve the quality and speed of image transmission using broadband access. When the updated CU-SeeMe (Internet video conferencing client), which was compatible with Windows, was released, video conferencing became available to any PC user.
A new round of development of the VKS received in the early 2000s. Video conferencing is divided into two main product lines - hardware and software. At the same time, Samsung released the first cellular videophone, and Skype and iChat introduced the direction of the software. In 2005, Lifesize introduced the first HD video conferencing solution.
At the beginning of the development of the corporate market of video conferencing, sessions between terminals of the video conferencing were carried out via ISDN lines. In the future, videoconferencing using IP networks (H.323 standard) has become increasingly common. Further development of technologies led to an avalanche-like growth of both technical solutions and equipment offered by manufacturers. And the introduction of 3G and 4G communication standards has opened up tremendous opportunities for the development of mobile solutions and cloud-based video conferencing.
Technology VCS
VCS systems are traditionally divided into hardware, software and cloud. Hardware solutions - "old-timers" among the systems of video conferencing. Their mandatory components include a codec, a means of displaying and reproducing sound, an MCU server (Multipoint Control Unit is a device for implementing multipoint video conferencing, where several subscribers participate). The advantages of these solutions include the use of a special room for video conferencing sessions, high quality video and sound transmission, including with low bandwidth, reliability and data security, compatibility with other vendors' equipment, etc. The disadvantages of hardware solutions are their high cost, and when upgrading the video conferencing system, you need to buy new equipment.
Software solutions assume the presence of server and client software, which is installed on the corresponding equipment up to smartphones. These solutions are characterized by relatively low cost compared to hardware, simplicity and low requirements for communication channels, a high degree of integration with other products, low requirements for the training of technical staff and no need to purchase new equipment. However, in this case, you can lose as a “picture” and the absence of the ability to connect several cameras to one client at once.
The most popular now are cloud solutions (Skype, etc.), which significantly reduce the cost of the entire VCS procedure, since The server with the software is located at the provider of the cloud solution, and simplifies the installation and configuration procedures. There are disadvantages to these solutions - the quality of the video image is not always high, the security level is inconclusive and there is a high dependence on external communication channels and servers.
In general, low-cost alternatives in the form of cloud services or client software installed on a PC or laptop are replacing expensive hardware solutions. The transition from hardware to software is more than logical: customers do not see the point in large-scale
World market of video conferencing systems
VCS technology is currently undergoing great changes. The segment is growing, above all, at the “everyday” level - in terms of cloud services (Skype, FaceTime, Google Hangouts, etc.), and video calls are being integrated into an increasing number of applications and services.
Analysts predict further growth of the market. According to a study by Transparency Market Research, the global market for video conferencing in 2016 was estimated at $ 5 billion. It is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 7.9% in 2018–2026, and the market will reach $ 10.5 billion by the end of the period. In the company Research and Markets, the volume of the global video conferencing market in 2017 was estimated at the same $ 5 billion, and the average annual growth rate in 2017–2025 was forecast at 8.6%. The increase in the number of implementations of video conferencing in medicine and education has increased worldwide demand for corporate video conferencing.
In September 2018, analyst firm Gartner introduced the Magic Quadrant of systems for corporate video communications. Cіsco, Zооm, Microsoft and LogMeIn were among the market leaders in Gartner (in 2017, the leaders were Cісco, Zооm and Microsoft). BlueJeans and Vidyo were ranked as “visionaries”, and Google and Adobe were ranked as “challengers”. Compared with the “magic quadrant-2017” in 2018, it was left by ZTE, West and Polycom.

The “magic quadrant” of Gartner for video conferencing systems as of August-2018
For its part, the research company IDC in a July study of 2018 called CSco and Microsoft as the market leaders for video conferencing. The major market players are Google, Zoom, BlueJeans, Vidyo, Avaya, Lifesize, Huawei and Polycom.

Key players in the VCS market as of July-2018 (IDC estimate)
According to MZA, in 2017, as in previous years, the market leaders in the VCS were the three largest suppliers of VCS endpoints - Cisco, Polycom and Huawei, in which accounting for more than 70% of revenues and almost 70% of the market. Despite the fact that the number of competitors in the market is growing rapidly, these "heavyweights" continue to dominate the market and actually increased their total share compared with 2016.

Market shares of key operators in the VKS endpoint market in 2017 (MZA estimate)
In its study, Frost & Sullivan highlights such trends in the global video conferencing market.
- Unified solutions. Users expect manufacturers to offer end-to-end video conferencing and collaboration solutions that will include the provision, monitoring, and management of all components — digital signatures, conference room solutions, software clients, projectors, and other peripherals.
- Great integration options. Video conferencing solutions will have all the great possibilities of integration and interaction with other electronic devices, applications and video conferencing systems.
- Cloud solutions VCS. Users will prefer these solutions due to lower costs, high scalability and ease of implementation.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology. With the help of big data and Internet-to-Things (IoT), AI technology can also be used in video conferencing. For example, using the Internet and an IoT device, you can automatically update and synchronize new functions to improve the quality of communication.
Product Overview
Their detailed characteristics can be found in the table of comparison of video conferencing products on ROI4CIO.
Cisco (Cisco Webex)

Cisco is an American multinational company specializing in the development and sale of server, network and communication equipment. As a serious player in the VCS market, the company announced itself by acquiring in 2009 for $ 3 billion of the world leader in the video conferencing industry - the Tandberg company. Since then, the company has only strengthened its position - according to Gartner and IDC estimates, in 2018, Cісco is ranked among the leaders of the VCS market. Cisco products for video conferencing include Cisco Webex and Cisco Web Meeting Server.
Cisco Webex is a cloud service for web-conferences, with the number of participants up to 1000 people (with online broadcasts up to 100 thousand people). The product is paid, but there is a free trial period.
Cisco Webex users get the full range of services required for corporate video conferencing: multilingual interface, high-quality video and sound, text chat, end-to-end encryption, mobile applications on popular platforms, integration with office software, instant messengers and video conferencing vendors, remote access to desktop, keyboard and mouse, whiteboard (virtual collaboration board) and conducting participant surveys, recording meetings to a local computer or to the cloud, branding web meetings, integration with CRM systems, statistics and reports, etc. Cisco Webex is best suited for paid events and corporate training, for which the service provides for integration with training management systems.
The service is also represented in the Cisco Web Services Meetings Server server solution for implementation into the company's corporate IT infrastructure. The platform supports up to 96 simultaneous sessions in HD format. With it, you can connect to calls using a video call system in the meeting room, desktop video terminals, a mobile client, via a WebRTC compatible browser or Skype for Business.

Cisco Webex Service Dialog Box
Microsoft (Skype for Business)

Microsoft is one of the undisputed market leaders in video conferencing, as evidenced by Gartner and IDC estimates as of 2018. The history of Microsoft in the VCS market began not in 2011, after acquiring Skype for $ 8.5 billion. Until that time, the company was developing Microsoft Lync (and before it, Microsoft Communicator), but in April 2015, the company released a new version of Lync, renaming it Skype for Business with a Skype interface. However, Microsoft may soon close Skype for Business in favor of Microsoft Teams (part of Office 365).
Microsoft Teams is a corporate platform introduced at the end of 2016 and combining chat, meetings, notes and attachments, voice and video calls in the workspace. The platform is designed as a competitor to the Slack corporate solution. It works under iOS, Android and Windows 10 Mobile, as well as on computers running Windows and macOS.
Skype for Business differs from "home" Skype with expanded functionality and paid use. Skype is suitable for small company video calls, while Skype for Business with its paid options allows you to hold meetings for up to 250 participants and receive corporate-level security.
The set of Skype for Business features is quite similar to the functionality of analog cloud products - voice and video calls, messaging, accessibility on all popular desktop and mobile platforms (plus the ability to enter video calls through a browser without installing a software client), recording conversations, “sharing” desktop and collaborate on a virtual whiteboard. However, there is no way to brand video conferencing.
Owning a product to Microsoft gives Skype for Business all the benefits of integrating with the office products of the corporation - you can schedule a hangout in Outlook, and create it directly from Word and PowerPoint.
The server part - Skype for Business Server (introduced in 2015, the previous name is Microsoft Lync Server) allows you to get all the functionality of video conferencing based on your own servers and distribute users depending on their needs in communication media (split domain).

Skype for Business Dialog Box
Zoom (Zoom Meetings)

Zoom is a US company that provides remote conferencing services using cloud computing. In 2017-2018, Gartner recognized Zoom as the leader of the video conferencing market, and according to IDC, in 2018, the company was named a major player.
Zoom offers such solutions for video conferencing, online meetings and creating group chats - Video Webinar, Meetings and Conference Room. They are based on the use of cloud solutions on the SaaS model and hybrid solutions.
Zoom Meetings video conferencing has several tariff plans (if there is a “lightweight” free version), up to 200 people can participate in the sessions (up to 500 people for an additional fee), work on systems running Mac, Windows, Linux, Chromebook, iOS and Android, compatible with Outlook, Office 365 and Gmail. The service offers all the traditional options - encrypting video calls, collaborating on documents and a virtual board, polling, “sharing” control over the screen, statistics on participation in meetings, the possibility of branding meetings, as well as monitoring attentiveness of participants, video recording and audio decoding.

Zoom Meeting Service Dialog
LogMeIn (GoToMeeting)

LogMeIn is a provider of SaaS solutions and remote communication cloud services for collaboration, IT infrastructure management and customer interaction. According to Gartner, in 2018, LogMeIn was among the leaders of the VCS market for introducing innovative services, in-depth analytics, speech and text transcription, and integration with smart assistants such as Amazon Alexa.
Among the key LogMeIn products for online meetings are GoToTraining, GoToMeeting, GoToConference and GoToWebinar and Join.me (freemium-service for online meetings and collaboration).
Let us dwell on the GoToMeeting service, which is designed for video conferencing and various online meetings with the number of participants up to 250 people (in the most expensive tariff plan). Like its many analogs, GoToMeeting is quite simple to use, works under Windows, Mac and Linux and all popular mobile platforms, and is compatible with MS Office and Google Calendar.
Also, the service, in which there are free and paid tariff plans, offers application sharing and work on documents, recording a meeting in the cloud or on a local computer with the ability to decrypt the recording, monitor attentiveness of participants, conduct polls, get statistics on meetings, “share” control above the keyboard and mouse and control of the screen, as well as the ability to brand online meetings.
LogMeIn is a provider of SaaS solutions and remote communication cloud services for collaboration, IT infrastructure management and customer interaction. According to Gartner, in 2018, LogMeIn was among the leaders of the VCS market for introducing innovative services, in-depth analytics, speech and text transcription, and integration with smart assistants such as Amazon Alexa.
Among the key LogMeIn products for online meetings are GoToTraining, GoToMeeting, GoToConference and GoToWebinar and Join.me (freemium-service for online meetings and collaboration).
Let us dwell on the GoToMeeting service, which is designed for video conferencing and various online meetings with the number of participants up to 250 people (in the most expensive tariff plan). Like its many analogs, GoToMeeting is quite simple to use, works under Windows, Mac and Linux and all popular mobile platforms, and is compatible with MS Office and Google Calendar.
Also, the service, in which there are free and paid tariff plans, offers application sharing and work on documents, recording a meeting in the cloud or on a local computer with the ability to decrypt the recording, monitor attentiveness of participants, conduct polls, get statistics on meetings, “share” control above the keyboard and mouse and control of the screen, as well as the ability to brand online meetings.
GoToMeeting service administration panel
Google (Hangouts)

In the 2018 IDC study, Google was named a major player in the VKS market. In the 2018 Magic Quadrant, Google is referred to as “Challengers,” which includes companies with operational excellence and a strong reputation.
Google online meeting solutions include Hangouts Meet and Hangouts Chat. Like many similar cloud products, Hangouts features ease of use, compatibility with any operating system and browser (correspondence is synchronized on all devices), etc. The advantages of Google products include their compatibility with other products of the corporation (Gmail, Google Drive, etc.) and automatic publication of the recording on YouTube.
In the enhanced corporate version of Hangouts (G Suite paid packages), users can record conversations and conduct live events that can be watched by up to 100 thousand people. Also, corporate users can participate in video calls even when there is no access to the Internet (by a special phone number with access through a PIN code). But you need to understand that the disadvantages of Hangouts are quite significant: there is no opportunity to conduct polls, receive statistics on sessions, hold paid webinars with integration with payment systems, brand video conferences and work together on a virtual whiteboard.
Hangouts Meet service settings panel
findings
VCS technologies are actively developing and improving, creating not only new business opportunities, but also new markets - telemedicine, conducting remote corporate training and distance learning.
The future development of video conferencing systems will continue existing trends: the prevalence of demand for cloud services and mobile solutions, the use of high-definition video and new video codecs, integration with other information systems, applications and services, the growth of demand for VaaS services (Video as a Service). The not so distant future of video conferencing is associated with the introduction of technologies of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), as well as the 4K standard, but so far there are many technical barriers associated with high-speed data transfer.
It should be noted that the majority of solutions presented on the VCS market in their categories have approximately the same functionality, which is naturally more in the paid versions and is curtailed in the free ones. In any case, you can see the differences in the proposed solutions for video conferencing in the comparative table.
Review author: Yuri Grigorenko, for ROI4CIO
