User support, or emergency computer help. How is it done and how much does it cost
Restoring computers to working places and resolving the problems of business users in the event of any incidents often resembles extinguishing fires - the response to failures and breakdowns should be as expeditious as possible. You can’t do without a special service. But it’s not so simple without numbers and examples to answer the question whether it is worth creating your own department or is it better to contact an outsourcer. I calculated how much the technical support for medium and large companies can cost.
I took up the article because I and my colleagues from Ontantaoften it is necessary to explain to potential customers how the cost of technical support for users is formed. The discussion of an adequate comparison of prices and the organization of the work of an IT outsourcer and its own IT service remains relevant, although the service is standard and well-known.
“User support” is the most typical task for both IT services of enterprises and IT outsourcing companies. Here we are talking about servicing an automated workstation (AWP) for each employee, which, in addition to a computer, can also include a printer, scanner, and other peripherals.
Readers who want to get acquainted with how the technical support processes of users are organized and which specialists are involved in these processes can look under the cat. We will proceed to examples of calculating the cost of technical support.
We offer calculation and comparison of the cost of the “User Support” services by our own IT service and with outsourcing in four options: with the number of users 200 people, and then with an increase in this number to 400, 1000 and 3000 users.
The table below shows the results of typical calculations, which shows how much you will have to spend on support for a different number of users.
The table shows the practical cost calculations prepared as part of the feasibility study for a number of customers. The cost of outsourcing also includes taxes and overhead costs of the company.
Note that in the version with its own IT service, the customer, with an increase in volumes, is forced to hire additional specialists to fit into the internal SLA. And an outsourcing company has the opportunity to increase the share (%) of employment of specialists of the necessary qualifications.
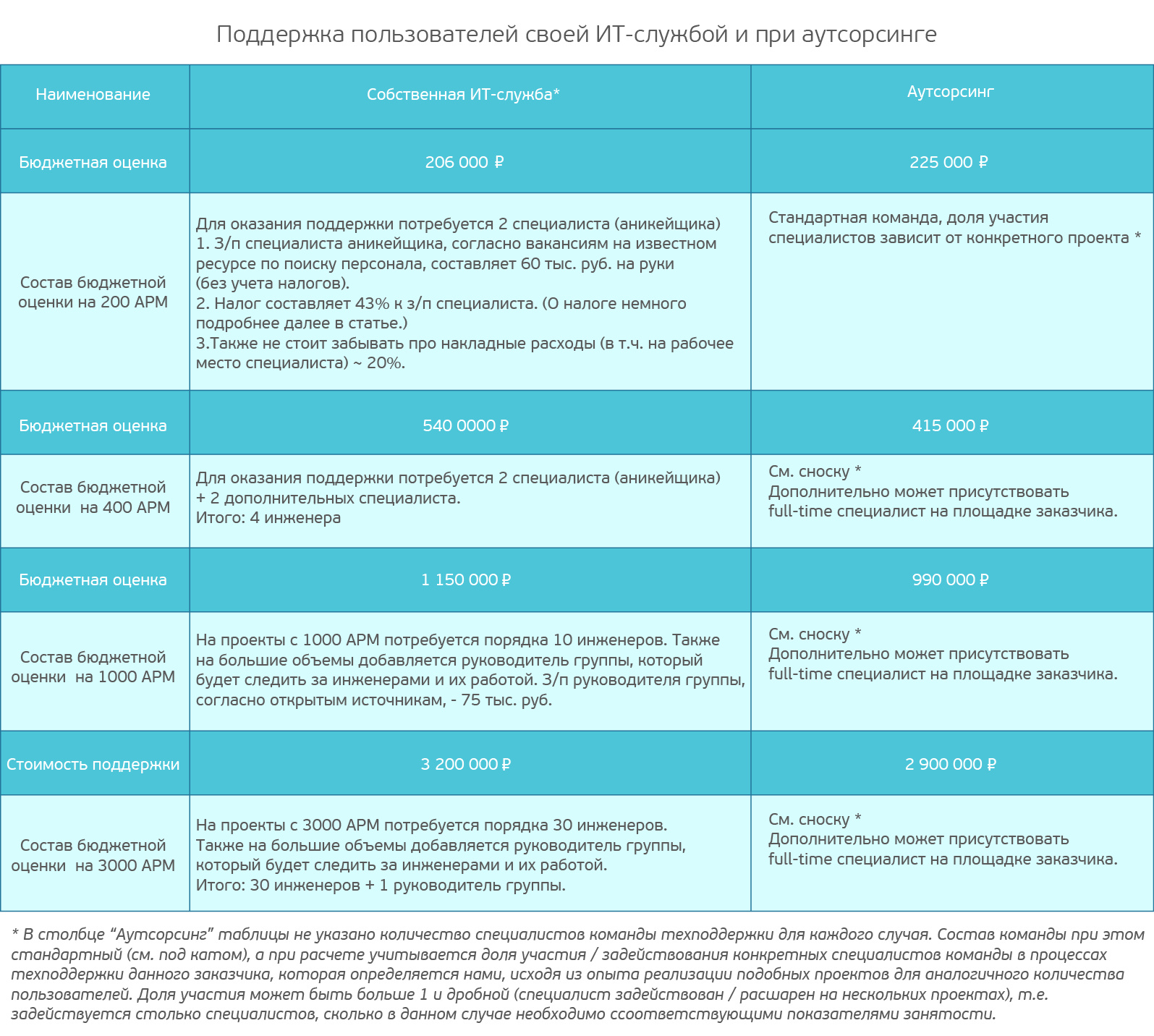

Source
When comparing your IT service and outsourcing with a volume of up to 200 AWPs, the cost of support will be more profitable for your own IT service. But with an increase in the staff of more than 400 AWPs, the cost of the services of an outsourcing company becomes more attractive than its IT service. With a further increase in jobs, outsourcing is gaining an advantage due to the non-linear increase in the number of involved support specialists for workstations and well-established support processes.
Above, we compared the cost of user support for the outsourcing model and the forces of our IT service. When choosing your option for implementing the service, here's another thing to consider.
The "User Support" service, as a rule, is paid per one supported workstation. If AWPs are serviced less, then monthly payment is reduced. This is beneficial for companies experiencing seasonal business fluctuations. Outsourcing flexibility example Ice Cream Aquamarine sells ice cream. Imagine that each tent has one AWP, one printer, cash desk and camera, and there are about 100 such tents in Moscow. Let the SLA be light: solution of the incident within 8 hours in 8x5 mode. In such circumstances, both the outsourcer and his IT department will need at least two employees. But when the “dead season” (fall-winter-spring) comes for the tent with ice cream and ice cream sales drop significantly, the company decides to reduce the number of mobile tents to 50.
Now one specialist of his own IT service will become underutilized and the customer will have to pay wages for about six months (with an average salary, including taxes, this is 80 thousand x 6 months = 0.5 million for a period of quiet business. at the same time, the outsourcing company will employ a low-load engineer on other projects, and the customer will only pay for the support of the remaining workstations.
Comparing the price of the services of an outsourcer and the costs of their own specialists, the customer often does not take into account taxes: “Why are you asking 55 thousand? I’ll hire an admin and will pay him 40 thousand. " At the same time, costs for own IT specialists include the following payments:
Total: 43% *
If you add these 43%, then most likely the prices will be comparable.
In addition to taxes, the list of costs for your own IT service will not be out of place to include recruiting, that is, the costs of finding employees, posting vacancies, interviews, etc.
* The figures are given for the case when the amount of payments to employees does not exceed the limit base for the calculation of insurance premiums established by the Government of the Russian Federation (for our calculations this is usually the case). Case study Just a few months ago I received a request to calculate the cost of supporting user jobs. The volumes were not very large - in the region of 200 users plus server and network equipment. I beautifully wrapped the calculation in a commercial offer and sent it to the customer.
Two days later, the customer said that he liked the composition of our team and the principles of work, but he completely disagreed with the cost of services. It turned out that the customer reasoned rather banally: “I pay about two thousand specialists about 80 thousand rubles a month - 40 each. And your proposal contains a figure almost twice as high. ”
We calculated and added to the cost of the customer’s specialists all taxes, and the figures were comparable. The customer appreciated that we can, if necessary, select the engineer with the necessary specialization, who would solve narrow-profile problems, as well as replace absent specialists (on vacation, on sick leave), and still chose outsourcing.
I repeat that the introduction of a centralized user support service in your company involves debugging business processes, creating a Service Desk, introducing an ITSM system, training specialists, maintaining a knowledge base, working with service partners, and organizing logistics for supplies.

A source
If the SLA is incomplete and below the KPI threshold, the outsourcer recalculates the monthly payment, reducing bills. For its IT service, the creation of a mechanism of material incentives and responsibility for failure to meet the requirements for the quality and efficiency of technical support is a difficult and sometimes simply unsolvable task.
In many cases, it’s “physically” difficult for the full-time IT staff to achieve an acceptable SLA. For example, small and medium-sized companies, as a rule, hire an IT specialist for a fixed fee. He is the “unit” that must maintain the equipment in working order. With such an employee, they do not sign an SLA to perform work - he simply does the work whenever possible.

Source
Case Study
An outsourcing company pays fines for violating an SLA. More precisely, the invoice amount is reduced by the size of the fine. In our practice, this rarely happens, and yet no one is safe from this.
Once we did not fulfill the SLA due to the fact that the regional partner at the “wrong time” decided to refuse to work under the contract. We had to quickly (during the day) look for a new partner. But during the search an incident happened - one user PC did not work. Our engineer arrived, performed the necessary work and restored the workstation, but with some violation of the SLA. At the end of the month, when the manager of our company allocated to the customer wrote a report, he made a recalculation in favor of the customer due to this violation of the SLA.
When choosing an outsourcing scheme, the customer relieves himself of the problems associated with the lack of specialists during the holidays and sick leave.

Source
Case study
A small travel company had an administrator on its staff who came to serve IT infrastructure by faith and truth. No one thought that one administrator in the office is a risk of being in a situation where the infrastructure is not working due to his unexpected dismissal, illness, or even planned leave. And so it happened. In the week when the administrator went to the hospital, the company had a failure on the automatic telephone exchange and several AWPs failed. By the time the replacement was found for the administrator, the company's downtime losses totaled hundreds of thousands of rubles.
Another point - the outsourcing company has accumulated competencies in the form of a knowledge base that reduces the time to resolve some incidents.
Possible increase in the cost of services. Under the current contract, it is difficult to raise the price, but when signing a new contract, it is possible. This probability can be reduced by choosing a contractor based on competitive procedures, the conditions of which, among other parameters, take into account the cost of services.
Transition period. The service provider needs to get comfortable with the customer’s IT infrastructure, debug the processes - this can take from several weeks to several months. The term depends on the experience of the outsourcing company and on the size of the customer company. In order to avoid disputes, write down an adequate transition period in the contract and, if possible, provide the outsourcer with the most complete information and funds for the provision of services (knowledge base, list and composition of supported equipment, etc.).
Information security issues. In order to guarantee customers compliance with information security requirements when rendering IT services, the service provider annually undergoes certification for compliance with the international standard ISO 27001. And the service provider should be ready, upon request, to familiarize the customer with the information security policy adopted by him.
This is the picture.
Count, analyze, choose. How to organize user support is up to you. And you have less “fires” in the IT infrastructure!

A source

I took up the article because I and my colleagues from Ontantaoften it is necessary to explain to potential customers how the cost of technical support for users is formed. The discussion of an adequate comparison of prices and the organization of the work of an IT outsourcer and its own IT service remains relevant, although the service is standard and well-known.
“User support” is the most typical task for both IT services of enterprises and IT outsourcing companies. Here we are talking about servicing an automated workstation (AWP) for each employee, which, in addition to a computer, can also include a printer, scanner, and other peripherals.
Readers who want to get acquainted with how the technical support processes of users are organized and which specialists are involved in these processes can look under the cat. We will proceed to examples of calculating the cost of technical support.
How the user support service is organized
Source
In order to understand the cost structure and the methodology for calculating the final price, let's look at what elements and processes the technical support service of users usually consists of and which specialists implement it. So far, it doesn’t matter to us whether this is our own IT service or an outsourcing company.
In the minds of many, a support service is personified by an engineer (or several engineers), who, as the saying goes, "is both a Swiss, a reaper, and an arcade player." Ideally, it works 24 hours a day, is available through all communication channels and is ready to fix any problem in less than half an hour. Otherwise - “simple through your fault”!

Source
For small companies, the way it is. But if the number of jobs served goes to hundreds, then one engineer just can not do it. Here, a team of specialists armed with specialized software (ITSM) and involving a number of other components of the services, which will be discussed below, should take up the matter.
In general terms, the operation scheme is as follows:
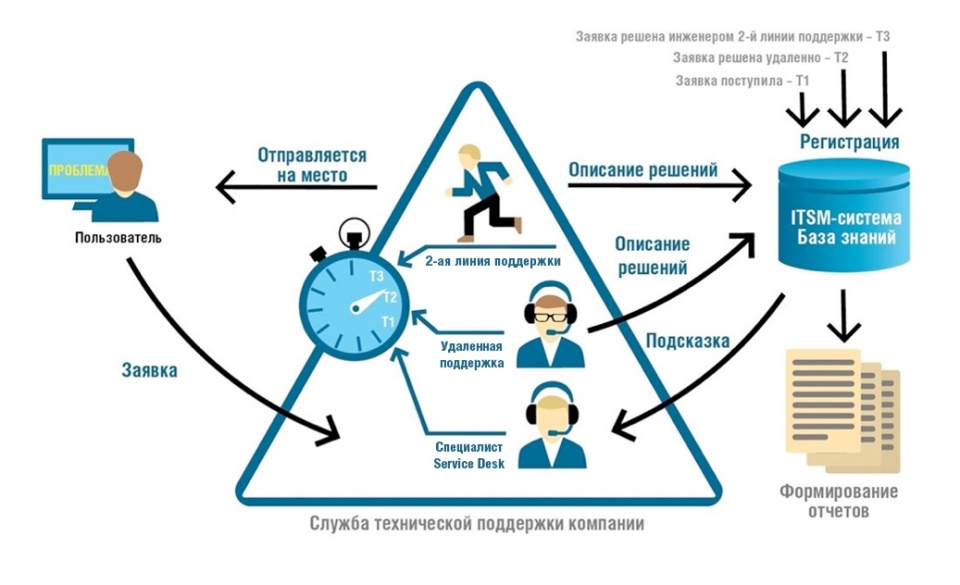
Service Desk is a single window for logging in user requests. Service Desk experts in 24x7 mode accept all incoming calls by mail, phone or via the web interface and record all applications in ITSM systems (IT Service Management, IT service management).
ITSM systems allow you to monitor the stages of work and adhere to the deadlines prescribed in the contract or regulation. Service Desk specialists - “first aid” in case of malfunctions in the workstation. They must understand the cause of the problem according to the user or diagnose it by connecting remotely to the workstation.
In response to a user’s request, a Service Desk specialist either gives the employee recommendations or remotely fixes the problem using the accumulated knowledge base (a list of typical calls).
 Source
Source
If the Service Desk specialist cannot solve the problem, then he redirects the request to the next line of “defense” - to the technical support engineers of the second line.
Engineers of the second support line, or anikeyshchiki, determine the next steps: to resolve the appeal remotely or to go to the place.
Service Desk and the second line form the “core” of the technical support process. The process may seem cumbersome, but when it is completed, it is a conveyor that operates in accordance with regulations that ensure the effectiveness of service delivery and SLA compliance.
What other specialists and resources are involved in the process of providing the “User Support” service?

A source
If an outsourcing company is engaged in IT support, then each customer interacts with a dedicated manager - a project manager who monitors the work of the services, prepares monthly reports for the customer and, in fact, is ready to resolve 24/7 issues of interaction between IT specialists and users. This role also exists in its own IT service, only it can be called differently.
This specialist performs the following functions:
If it is necessary to support the customer’s IT in the regions, and the outsourcer does not have branches there, he turns to service partners — small IT companies in the field with whom the outsourcer enters into an agreement on the same terms as with the customer, and sometimes for more "Hard." When organizing centralized user support, its own IT service can also work with service partners in the regions so as not to keep specialists that are not always busy. In this case, it is necessary to “build” partners on their own: to establish interaction processes and document management (contracts, acts, applications ...), make calculations, and resolve issues and problems arising in the course of interaction.
Technical support requires replacement equipment during the repair of a broken one, spare parts and consumables that need to be quickly delivered to places, including to the regions. To do this, we need well-organized logistics and storage facilities near service facilities (applies to both our own IT service and outsourcing company).

Source
I have listed the main components of the "User Support" service. A rather big list that should work as a single coordinated mechanism. These components, respectively, are included in the calculation of the cost of support.

Source
In order to understand the cost structure and the methodology for calculating the final price, let's look at what elements and processes the technical support service of users usually consists of and which specialists implement it. So far, it doesn’t matter to us whether this is our own IT service or an outsourcing company.
In the minds of many, a support service is personified by an engineer (or several engineers), who, as the saying goes, "is both a Swiss, a reaper, and an arcade player." Ideally, it works 24 hours a day, is available through all communication channels and is ready to fix any problem in less than half an hour. Otherwise - “simple through your fault”!

Source
For small companies, the way it is. But if the number of jobs served goes to hundreds, then one engineer just can not do it. Here, a team of specialists armed with specialized software (ITSM) and involving a number of other components of the services, which will be discussed below, should take up the matter.
In general terms, the operation scheme is as follows:

Who is who in this diagram?
Service Desk is a single window for logging in user requests. Service Desk experts in 24x7 mode accept all incoming calls by mail, phone or via the web interface and record all applications in ITSM systems (IT Service Management, IT service management).
ITSM systems allow you to monitor the stages of work and adhere to the deadlines prescribed in the contract or regulation. Service Desk specialists - “first aid” in case of malfunctions in the workstation. They must understand the cause of the problem according to the user or diagnose it by connecting remotely to the workstation.
In response to a user’s request, a Service Desk specialist either gives the employee recommendations or remotely fixes the problem using the accumulated knowledge base (a list of typical calls).

If the Service Desk specialist cannot solve the problem, then he redirects the request to the next line of “defense” - to the technical support engineers of the second line.
Engineers of the second support line, or anikeyshchiki, determine the next steps: to resolve the appeal remotely or to go to the place.
Service Desk and the second line form the “core” of the technical support process. The process may seem cumbersome, but when it is completed, it is a conveyor that operates in accordance with regulations that ensure the effectiveness of service delivery and SLA compliance.
What other specialists and resources are involved in the process of providing the “User Support” service?

A source
Project Manager
If an outsourcing company is engaged in IT support, then each customer interacts with a dedicated manager - a project manager who monitors the work of the services, prepares monthly reports for the customer and, in fact, is ready to resolve 24/7 issues of interaction between IT specialists and users. This role also exists in its own IT service, only it can be called differently.
Quality Service Specialist
This specialist performs the following functions:
- prepares terms of reference for adding a new customer to the ITSM system;
- at the request of specialists, Service Desk solves non-standard situations not described in the documentation;
- Based on reports received from the ITSM system, it analyzes SLA violations;
- according to the results of the analysis, it carries out corrective actions, changes in the documentation (regulations, instructions ...) or in the settings of the ITSM system. In their own IT service, this role can be performed, for example, by its head. In an outsourcing company, this is a separate position.
Service partners
If it is necessary to support the customer’s IT in the regions, and the outsourcer does not have branches there, he turns to service partners — small IT companies in the field with whom the outsourcer enters into an agreement on the same terms as with the customer, and sometimes for more "Hard." When organizing centralized user support, its own IT service can also work with service partners in the regions so as not to keep specialists that are not always busy. In this case, it is necessary to “build” partners on their own: to establish interaction processes and document management (contracts, acts, applications ...), make calculations, and resolve issues and problems arising in the course of interaction.
Ordering materials, delivery and storage
Technical support requires replacement equipment during the repair of a broken one, spare parts and consumables that need to be quickly delivered to places, including to the regions. To do this, we need well-organized logistics and storage facilities near service facilities (applies to both our own IT service and outsourcing company).

Source
I have listed the main components of the "User Support" service. A rather big list that should work as a single coordinated mechanism. These components, respectively, are included in the calculation of the cost of support.
Calculation of user support costs
We offer calculation and comparison of the cost of the “User Support” services by our own IT service and with outsourcing in four options: with the number of users 200 people, and then with an increase in this number to 400, 1000 and 3000 users.
The table below shows the results of typical calculations, which shows how much you will have to spend on support for a different number of users.
The table shows the practical cost calculations prepared as part of the feasibility study for a number of customers. The cost of outsourcing also includes taxes and overhead costs of the company.
Note that in the version with its own IT service, the customer, with an increase in volumes, is forced to hire additional specialists to fit into the internal SLA. And an outsourcing company has the opportunity to increase the share (%) of employment of specialists of the necessary qualifications.


Source
When comparing your IT service and outsourcing with a volume of up to 200 AWPs, the cost of support will be more profitable for your own IT service. But with an increase in the staff of more than 400 AWPs, the cost of the services of an outsourcing company becomes more attractive than its IT service. With a further increase in jobs, outsourcing is gaining an advantage due to the non-linear increase in the number of involved support specialists for workstations and well-established support processes.
Important financial and non-financial aspects
Above, we compared the cost of user support for the outsourcing model and the forces of our IT service. When choosing your option for implementing the service, here's another thing to consider.
- An outsourcer can provide “price elasticity” - a proportional change in value when the number of supported users changes.
The "User Support" service, as a rule, is paid per one supported workstation. If AWPs are serviced less, then monthly payment is reduced. This is beneficial for companies experiencing seasonal business fluctuations. Outsourcing flexibility example Ice Cream Aquamarine sells ice cream. Imagine that each tent has one AWP, one printer, cash desk and camera, and there are about 100 such tents in Moscow. Let the SLA be light: solution of the incident within 8 hours in 8x5 mode. In such circumstances, both the outsourcer and his IT department will need at least two employees. But when the “dead season” (fall-winter-spring) comes for the tent with ice cream and ice cream sales drop significantly, the company decides to reduce the number of mobile tents to 50.
Now one specialist of his own IT service will become underutilized and the customer will have to pay wages for about six months (with an average salary, including taxes, this is 80 thousand x 6 months = 0.5 million for a period of quiet business. at the same time, the outsourcing company will employ a low-load engineer on other projects, and the customer will only pay for the support of the remaining workstations.
- Do not forget about taxes.
Comparing the price of the services of an outsourcer and the costs of their own specialists, the customer often does not take into account taxes: “Why are you asking 55 thousand? I’ll hire an admin and will pay him 40 thousand. " At the same time, costs for own IT specialists include the following payments:
- Personal income tax (PIT) - 13% *,
- Pension Fund of the Russian Federation (PFR) - 22% *,
- Social Insurance Fund (FSS) - 2.9% *,
- Compulsory Health Insurance Fund (MHIF) - 5.1% *.
Total: 43% *
If you add these 43%, then most likely the prices will be comparable.
In addition to taxes, the list of costs for your own IT service will not be out of place to include recruiting, that is, the costs of finding employees, posting vacancies, interviews, etc.
* The figures are given for the case when the amount of payments to employees does not exceed the limit base for the calculation of insurance premiums established by the Government of the Russian Federation (for our calculations this is usually the case). Case study Just a few months ago I received a request to calculate the cost of supporting user jobs. The volumes were not very large - in the region of 200 users plus server and network equipment. I beautifully wrapped the calculation in a commercial offer and sent it to the customer.
Two days later, the customer said that he liked the composition of our team and the principles of work, but he completely disagreed with the cost of services. It turned out that the customer reasoned rather banally: “I pay about two thousand specialists about 80 thousand rubles a month - 40 each. And your proposal contains a figure almost twice as high. ”
We calculated and added to the cost of the customer’s specialists all taxes, and the figures were comparable. The customer appreciated that we can, if necessary, select the engineer with the necessary specialization, who would solve narrow-profile problems, as well as replace absent specialists (on vacation, on sick leave), and still chose outsourcing.
- Outsourcing means that you get a finished result - a service according to a signed SLA.
I repeat that the introduction of a centralized user support service in your company involves debugging business processes, creating a Service Desk, introducing an ITSM system, training specialists, maintaining a knowledge base, working with service partners, and organizing logistics for supplies.

A source
- The outsourcer is legally and financially responsible for non-compliance with the SLA.
If the SLA is incomplete and below the KPI threshold, the outsourcer recalculates the monthly payment, reducing bills. For its IT service, the creation of a mechanism of material incentives and responsibility for failure to meet the requirements for the quality and efficiency of technical support is a difficult and sometimes simply unsolvable task.
In many cases, it’s “physically” difficult for the full-time IT staff to achieve an acceptable SLA. For example, small and medium-sized companies, as a rule, hire an IT specialist for a fixed fee. He is the “unit” that must maintain the equipment in working order. With such an employee, they do not sign an SLA to perform work - he simply does the work whenever possible.

Source
Case Study
An outsourcing company pays fines for violating an SLA. More precisely, the invoice amount is reduced by the size of the fine. In our practice, this rarely happens, and yet no one is safe from this.
Once we did not fulfill the SLA due to the fact that the regional partner at the “wrong time” decided to refuse to work under the contract. We had to quickly (during the day) look for a new partner. But during the search an incident happened - one user PC did not work. Our engineer arrived, performed the necessary work and restored the workstation, but with some violation of the SLA. At the end of the month, when the manager of our company allocated to the customer wrote a report, he made a recalculation in favor of the customer due to this violation of the SLA.
When choosing an outsourcing scheme, the customer relieves himself of the problems associated with the lack of specialists during the holidays and sick leave.

Source
Case study
A small travel company had an administrator on its staff who came to serve IT infrastructure by faith and truth. No one thought that one administrator in the office is a risk of being in a situation where the infrastructure is not working due to his unexpected dismissal, illness, or even planned leave. And so it happened. In the week when the administrator went to the hospital, the company had a failure on the automatic telephone exchange and several AWPs failed. By the time the replacement was found for the administrator, the company's downtime losses totaled hundreds of thousands of rubles.
Another point - the outsourcing company has accumulated competencies in the form of a knowledge base that reduces the time to resolve some incidents.
What other questions do companies care when they consider outsourcing?
Possible increase in the cost of services. Under the current contract, it is difficult to raise the price, but when signing a new contract, it is possible. This probability can be reduced by choosing a contractor based on competitive procedures, the conditions of which, among other parameters, take into account the cost of services.
Transition period. The service provider needs to get comfortable with the customer’s IT infrastructure, debug the processes - this can take from several weeks to several months. The term depends on the experience of the outsourcing company and on the size of the customer company. In order to avoid disputes, write down an adequate transition period in the contract and, if possible, provide the outsourcer with the most complete information and funds for the provision of services (knowledge base, list and composition of supported equipment, etc.).
Information security issues. In order to guarantee customers compliance with information security requirements when rendering IT services, the service provider annually undergoes certification for compliance with the international standard ISO 27001. And the service provider should be ready, upon request, to familiarize the customer with the information security policy adopted by him.
This is the picture.
Count, analyze, choose. How to organize user support is up to you. And you have less “fires” in the IT infrastructure!

A source
