DWDM: the solution is cheaper than the carrier by 30-50% (Enterprise class)

Something has changed in the optics market over the past two years. Now you can buy your own DWDM units, put them in a rack in the data center. And getting it all is cheaper than traditional carrier solutions.
Who needs exactly:
- If you have a DWDM / CWDM transport network implemented before 2012.
- If you need to increase the capacity of your transport network and / or connect new branches, and you just calculate the budget.
- If at the same time you have a metro network (not transcontinental, but inside the city and its suburbs).
- If you have overloaded optical channels or soon they will be.
A few years ago, a number of major DWDM vendors announced that equipment would evolve into a more Enterprise-friendly side (more compact, more cost effective, with greater bandwidth). Now it happened, but the forms of such "friendly" are different.
In this post, I will explain why it’s time to switch to Enterprise hardware, and review devices from several top vendors: Huawei, ADVA, Ciena.
Likbez
Big companies connect their points with optics. Almost all oil and gas has its own transport network, in many banks, in the energy sector, in stock exchanges, large-scale machine building, transport companies, etc.
First, “dark” optics are laid to connect objects. This is a simple fiber that can be fed into a digital signal. Extremely simplifying, there is light - one, no light - zero. Usually in the laid cable there is not one conductor, but several: packs of 12–32–64 lines.
The transport ability of dark optics is very quickly exhausted, so you need to "paint" the line. This requires optical seals, they are also DWDM devices. DWDM not only “colors” the signal, but also multiplexes several signals into one, that is, it “packs” several carriers into one optical core due to the ability to work at different wavelengths. In addition to the physical compression itself, the equipment also uses OTN technology to multiplex several low-speed streams into one high-speed stream. For our educational program, the principle itself is not important, but it is important that this is a special shamanic magic of physics and technology.
Further, large companies make a fault-tolerant network at the L1 level. As a rule, on a linear signal we make channel redundancy: the first optical signal goes along the usual (shortest) path, the second through an independent optical line or ring topology transits through nodes (a “triangle” as a simple case of a decentralized network) to point existed independent routes. We also usually install 1 + 1 traffic duplication kits. This is important for creating full redundancy and the possibility of creating a disaster-proof solution at the transport network level.
So what about the new equipment? What are his opportunities?
First, high throughput. In more detail - a little later, and here's why.
Traffic in companies is growing - this is an obvious trend.
If you still think that on 80 lines of 800 Gbit / s optics for developing companies is a lot, then something is wrong. As a rule, now you need more bandwidth for different tasks and transit traffic.
Figure 1. The evolution of bandwidth in data centers
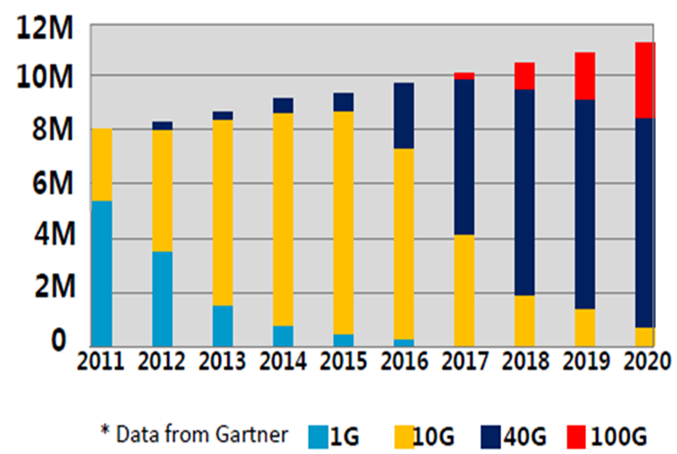
This graph shows the constant growth of transmitted data streams in modern data centers. And the greater part of the traffic takes at speeds of 100 Gbit / s.
Secondly, the cost. Until 2015, the cost of 100 Gbit / s per line was more expensive than 10 times 10 Gbit / s. Everyone was fascinated by bundles of fibers, but now vendors have made equipment where 200 Gbit / s may be cheaper than 20 times 10, and even cheaper than 10 times 10.
Thirdly, the size. The old camera was put in a cross, and the new Enterprise - in the server. This is not a stand for the office, as it was before, not a stand for an attic, but a piece of hardware that should be located in a data center with cold and hot corridors. And the modules are now not 300 mm deep, but 600 mm for server racks.
We turn directly to the review of Enterprise-equipment.
Let's start with Huawei. He can accommodate six boards for two units; each of which can produce 400 Gbit / s per line.
Fig.2. Sample Huawei Enterprise Equipment

general information | • Chassis 2RU 600mm (D) * 442mm (W) * 86.1mm (H) • Hot swap • 6 slots • Up to 400 Gbps per slot • 1 + 1 AC / HVDC power supplies • Ventilation units 2 + 1 air flow "Front to back" |
Interfaces | • Client interfaces: 100GE; 40GE; 10GE; FC16G; FC32G. • Linear: 100G QPSK / 200G 16QAM Programmable |
Data protection | • Support LLDP, AES256 encryption |
Control | • SNMP / MML / U2000 / RESTful / CLI / NETCONF / Corba / WebLCT |
And that's what ADVA has.
Fig. 3. Sample TeraFlex ADVA-FSP 3000 Enterprise Equipment

The growth of Internet traffic and the transition to cloud services forced to increase the capacity and speed in the networks between the data center. Very many customers need to quickly develop the infrastructure, while maintaining simplicity and meeting the growing requirements for density and power. For these tasks, ADVA created a TeraFlex terminal. Now it is not on sale yet. It can transmit up to 600 Gbit / s at one wavelength and provide a total capacity of 3.6 Tbit / s over a pair of fibers.
Briefly about the FSP 3000 TeraFlex.
general information | • 1RU chassis • Hot swap • 3 slots for line cards; 1.2 Tbit / s per card • Up to 600 Gbit / s at one wavelength |
Interfaces | • 400GbE: FR4, DR4, SR8, LR8 and CWDM8 • 100GbE: LR4, CWDM4, ER4, SR4, AOC, DAC and third-party • 10GbE and 40GbE via FSP 3000 MicroMuxTM pluggable QSFP28 • FlexE support |
Data protection | • ADVA ConnectGuard encryption technology • Separation of network and secure domains • 600Gbit / s scaling |
Control | • Open Interfaces • Setup in SDN by YANG-model • JUNOS-like CLI • Support SNMP, REST, RESTCONF, NETCONF, SNMPv3 and WebGUI • Telemetry Transmission (gRPC) |
Easy operation | • Configure Zero Touch • Script support • Linux to download and run custom software • Simplified local settings |
Figure 4. Sample Waveserver Enterprise Equipment The Ciena

Waveserver is powerful and easy to use. To increase transport capacity and scalability, it uses Ciena WaveLogic 3 Extreme coherent optical processors. Provides high DCI bandwidth requirements for networks, saving space and energy costs. Easy to integrate and operate using programmable open APs.
physical characteristics | • 1U 44.45 mm (H) x 442 mm (W) x 553 mm (D) • Weight: 13.8 kg |
Standard Service | • Redundant / replaceable power system, fan assembly • Power options: AC or DC power • AC input range: 96 to 264 Vac. current • DC input range: -36 to -72 VDC. current • Power consumption: 600 W, standard |
Interfaces | • Client interfaces: 10 x QSFP + (40 x 10GbE; 8 x 40GbE + 8 x 10GbE); 4 x QSFP28 (4 x 100GbE); also supports various 10GbE / 40GbE / 100GbE client traffic from a single Waveserver • Linear: 200G (2 x 100 Gb / s; QPSK) 300G (2 x 150 Gb / s; 8QAM) 400G (2 x 200 Gb / s; 16QAM) |
Control | • CLI, SNMP, Websocket, REST API based on YANG models, NETCONF and gRPC |
Environmental characteristics | • Normal operating temperature: 0 ° C to + 40 ° C • Relative humidity at work: relative humidity 93% |
Figure 5. Sample Waveserver Ai Ciena Enterprise Equipment

Physical dimensions | • 1U 44.45 mm (H) x 444 mm (W) x 584 mm (D) |
Weight | • 9.52 kg (without modules) • 14.92 kg (with three modules, without connectors) |
Capacity | • Support for three Waveserver plug-ins • Client: up to 24 QSFP28 with 100GbE or OTL4.4 (OTU4) clients • Line ports support the following speeds: 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 400 Gbps at 56 Gbaud or 100, 150, 200 Gbit / s at 35 Gbaud |
Maximum capacity | • 2.4 Tbit / s single Waveserver Ai chassis into one fiber • Provided for deployment in third-party linear systems |
Standard Equipment | • Backup / Replaceable Power Supply • Replaceable fan assembly |
Power options: AC or DC power | • AC input range: 100 to 264 V AC. current • DC input range: -40 to -72 VDC. current • Power consumption: 0.4 W / Gbps |
Control | • CLI, SNMP v2c, Blue Planet MCP • API: Websocket, RESTCONF, NETCONF, gRPC based on the OpenConfig, YANG, Streaming Telemetry and Declarative Configuration models • Underwater communication channel |
Security | • TACACS + • RADIUS |
Environmental characteristics | • Normal operating temperature: 0 ° C to +40 ° C • Normal humidity at work: from 5% to 85% |
A typical project for the transfer of 100 G between the three sites, calculated on the Enterprise Ciena equipment from Waveserver. Cost - up to $ 330 thousand in the GPL.
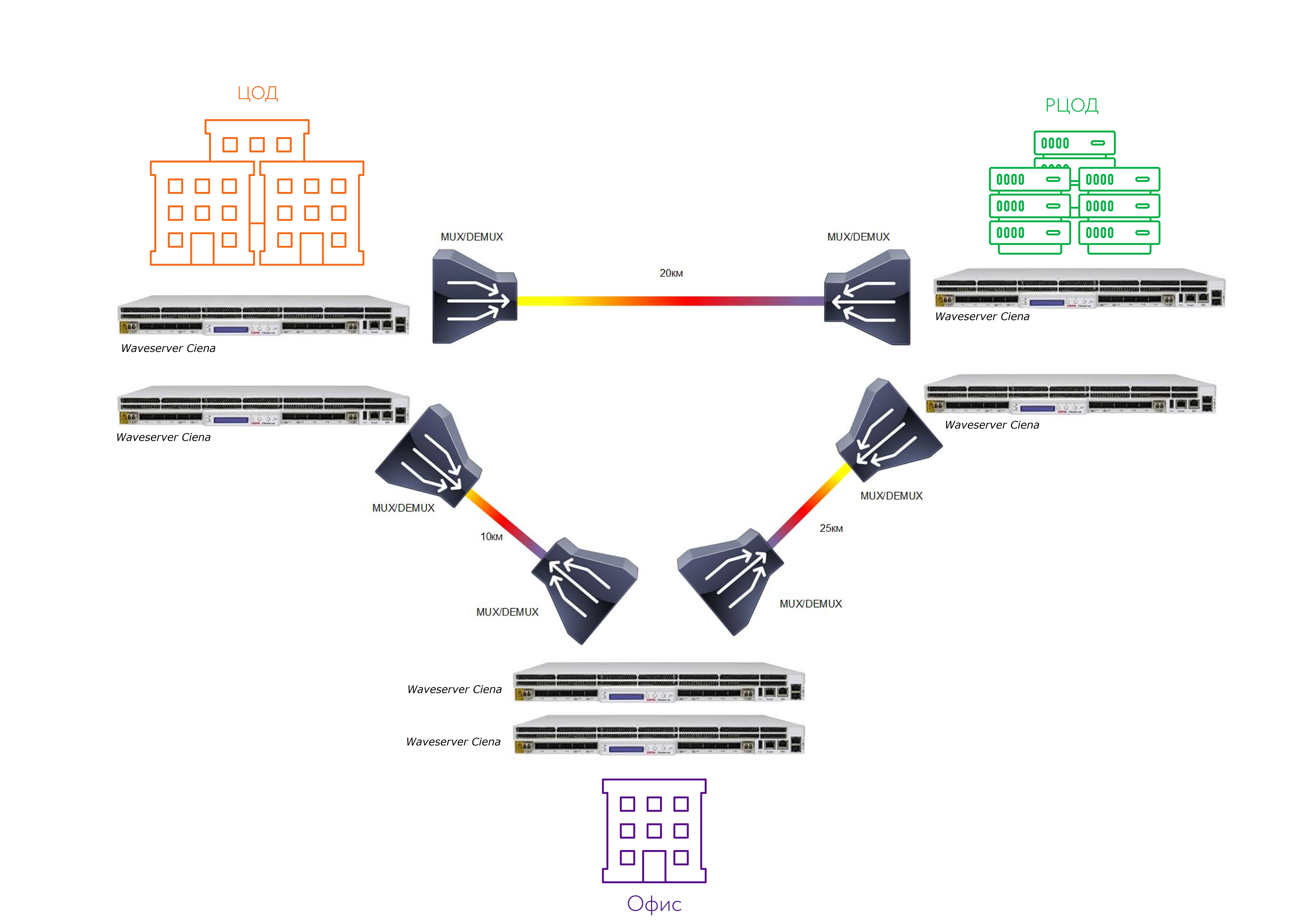
In general, this project as a standard is not particularly oriented, because each case is individual. WDM is an area where there are no typical things, in principle, due to the nature of networks and budgets. Therefore, if the topic is interesting, it is better to write a couple of lines in the mail. I will tell you what offers you can get from which vendor.
Links
- Post 2015 about banking WDM
- My mail for contacts and questions - VaVolkov@croc.ru
