Technical aspects of Internet blocking in Russia. Problems and Prospects
Let's start right away with a disclaimer: below there will be no fundamentally political issues. Administrative and legal issues will also be circumvented as much as we can, in order not to completely pull out the technical part from the rest of the planes.
Internet blocking in Russia already exists - this is a reality with which we live and must live on. And if so, you need to understand how it is arranged technically, which the provider can and cannot. Philip Kulin ( schors ) began to collect information on this subject long ago, participated in regulatory work, and went to various meetings. As a result, now only Roskomnadzor knows more about it in Russia, but this is not certain. Under the cut a brief summary of the current state of affairs.
About the speaker: Philip Kulin ( schors ), General Director of Dense Forest LLC - a small Russian hoster, mainly engaged in shared-hosting.
Tangle of problems
It would seem that there are locks and there are. We don’t like them, but maybe there’s nothing wrong with them?
Collateral damage is the biggest blocking problem. The most vivid example illustrating this occurred in April 2018, when large blocks of IP addresses of cloud services were blocked, respectively, many services did not work and suffered great damage.
The volatility of regulations and practices that are constantly changing. A year ago, this story would have been completely different, and two years ago it would most likely contradict today's. In a year, everything will be different again. Today this is so, in a month - a little bit wrong, and in six months, not at all. You need to follow this, but you also need to have time to work.
Locks difficult to diagnose. If a resource has been blocked by the registry, this is the simplest case. In the cases that we consider further, it is quite difficult to distinguish a real block from technical problems. A vivid example - in October, Yandex dropped the DNS clock for five, during which time many managed to decide that it was a Roskomnadzor block. It is really difficult to determine exactly, but such situations have already happened, so people immediately think about blocking.
It is impossible to predict when they will block you and whether they will block you at all. You work quietly, and your work is suddenly over.
It’s absolutely impossible to calculate risks., because maybe some widget on the site will fall off, about which you have already forgotten, and maybe the whole business will be hit. A very good example of risk unpredictability is the case of Bitrix24. In March, they very quickly transferred their services to Amazon. In the same month, a document leaked to the network, which truth might have been a fake one, in which large Amazon subnets were registered. Nevertheless, Bitrix24 somehow reacted to it and avoided problems in April, when Amazon services were really blocked.
I assure you that most of you will be so unlucky! Such documents will not by chance flow into your hands. When your business ends, you will know this after the fact.
In simple cases, we know why your site was blocked. For example, the forum posted information that a court declared prohibited, but you did not have time to react. But communication with the supervisory authority has unacceptable terms - for example, a day. On the Internet during this time you can lose a fifth of the business.
All this leads to some hopelessness. It is possible to argue with irony over, for example, David Khomak and the blocking of Lurk. But it is quite another thing when it happens to you, as it happened to me once. The client specified the IP addresses of my servers at the domain that I did not manage - I am sitting, and the phone just doesn’t fall silent. Customers say that they are leaving, they demand a refund, but I can not do anything! And no one can help me with this. This is really a feeling of complete hopelessness.
Risk groups
Locks affect:
How locks work
First, we will briefly discuss how blocking occurs in order to understand the full picture.
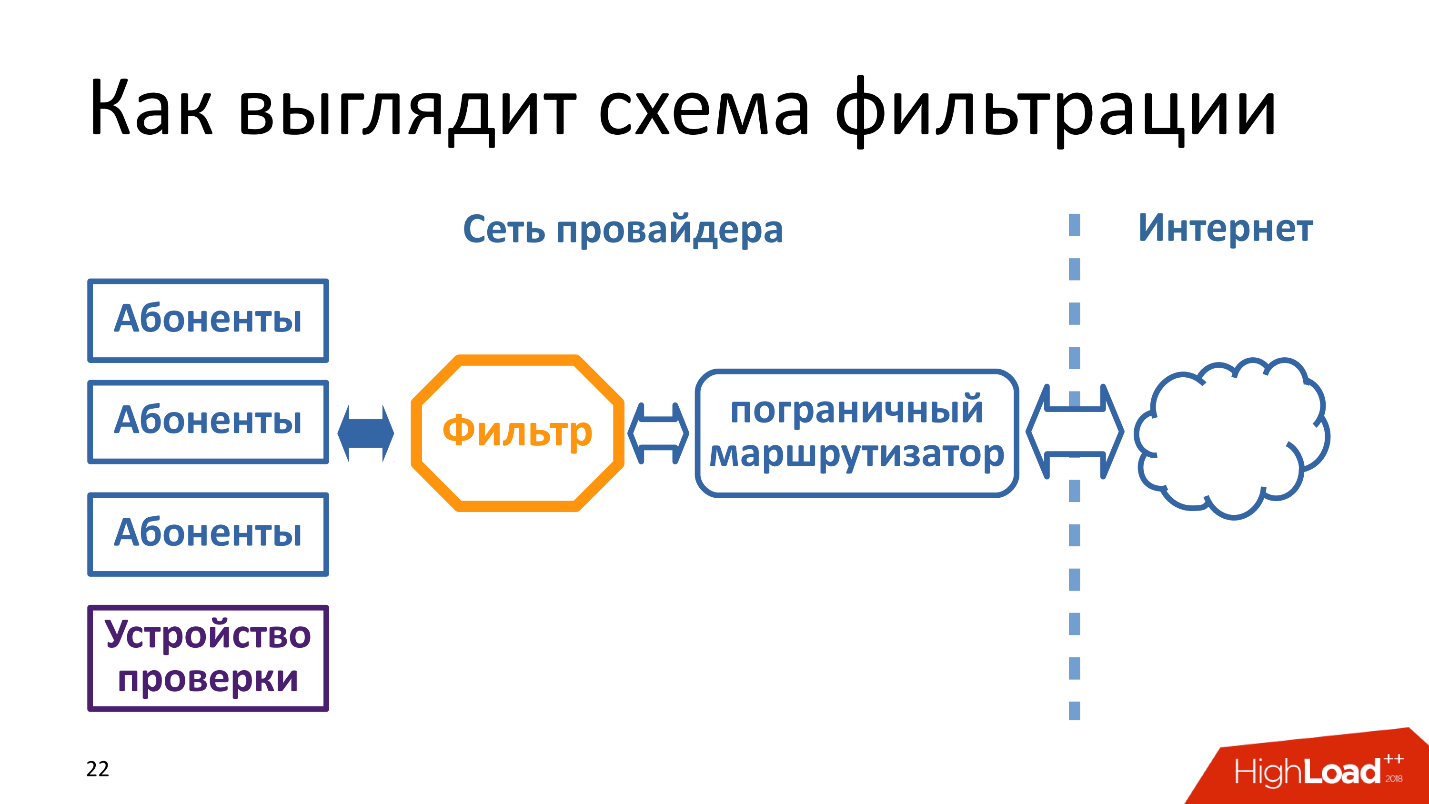
It is important to understand that traffic is filtered by each provider. That is, not somewhere on cross-border routers or a state filter, but each provider sets itself a filter between the Internet and subscribers in each of its subnets. In the diagram above, the verification device is next to subscribers, because it pretends to be a subscriber - this is important.
Filtering tools
Providers can buy filtered traffic from a superior provider. But there is a problem - buying traffic from a superior provider, the provider-buyer can not determine the technical problem or blocking. He has no tool, because he receives already cut traffic, and this does not affect his business very well.
Or you can use:
There are no rocket sets there, and the main problems are not about writing a program.
There are the following options for implementation.
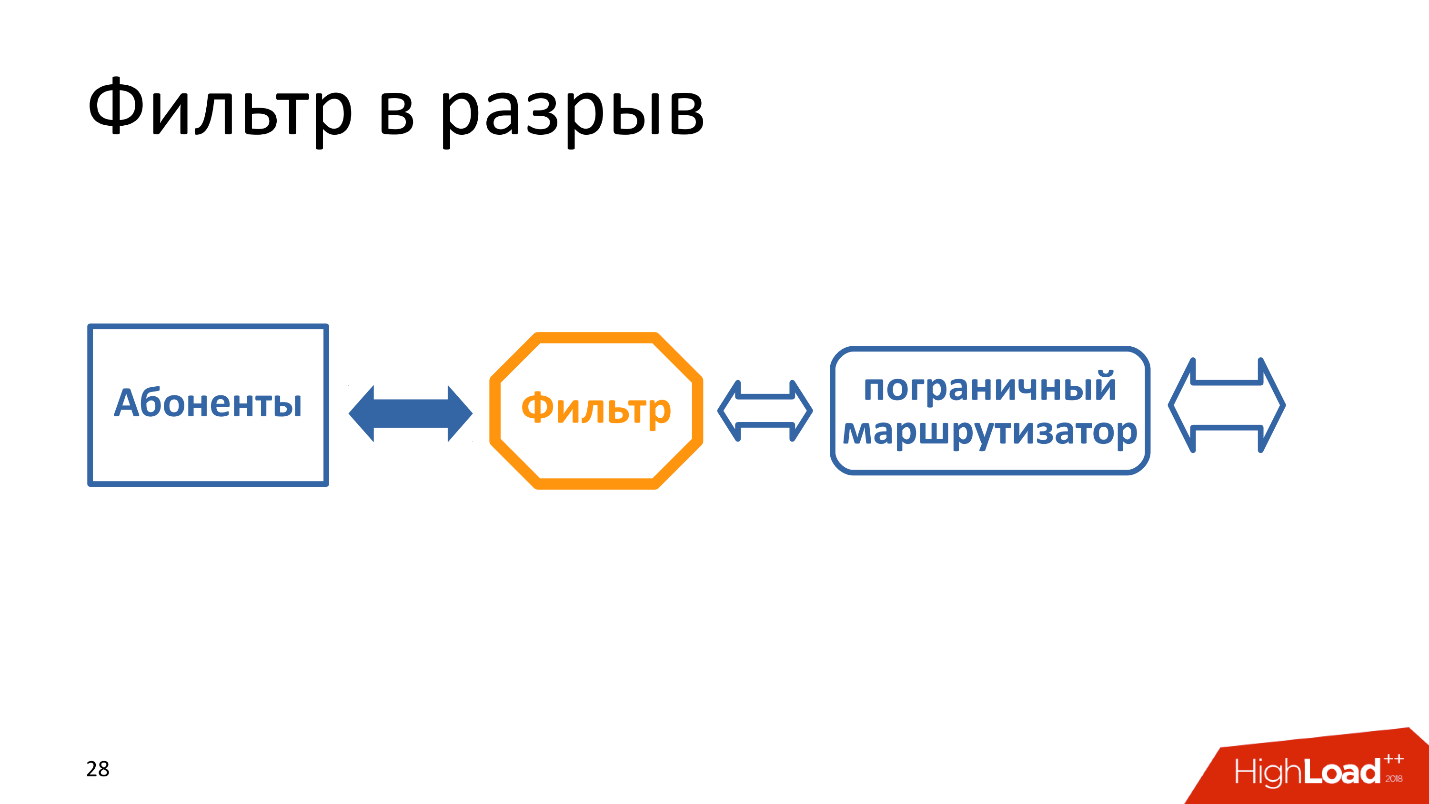
For example, you have a small channel of 100 Gbps, you put the filter in the gap.
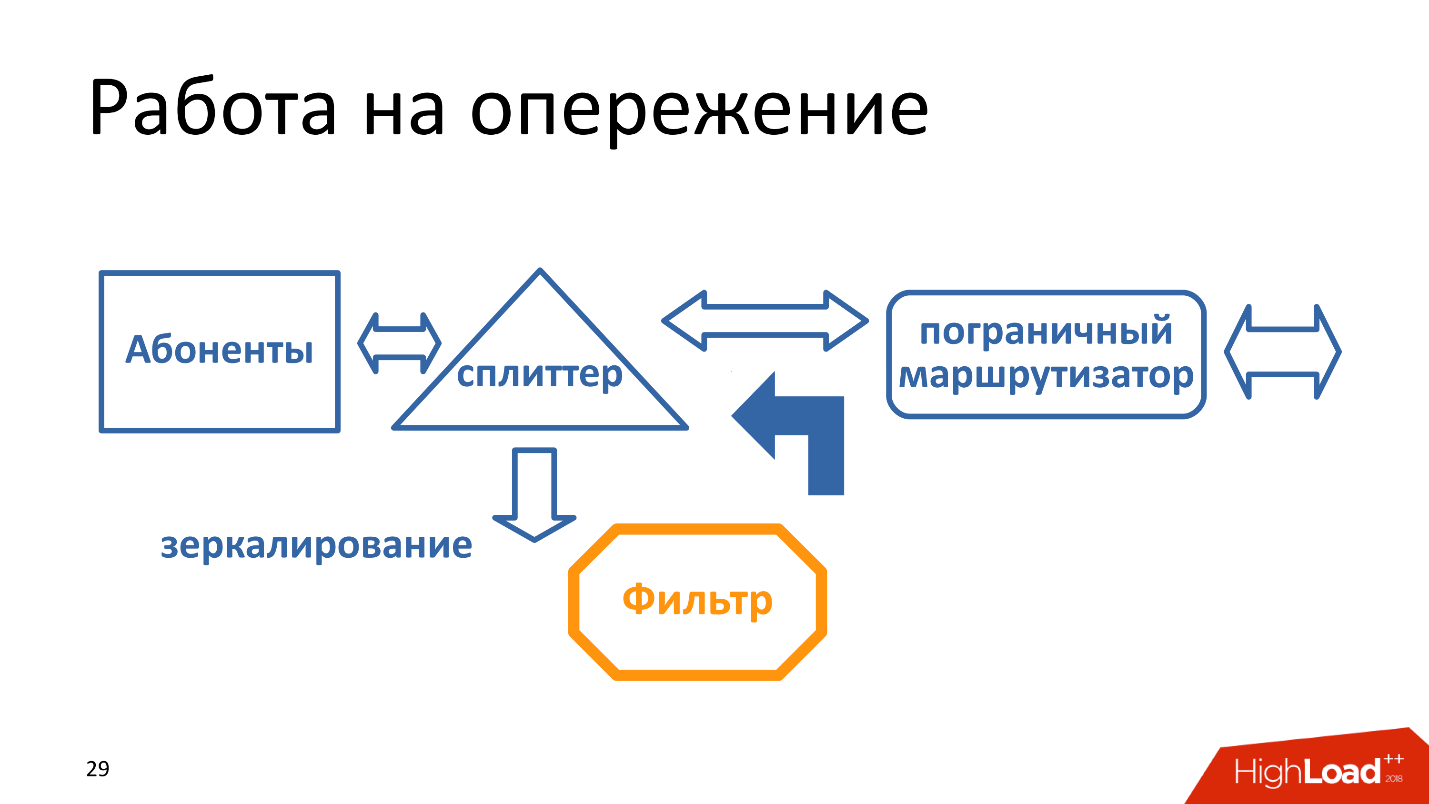
Some mirror traffic, but with traffic mirroring, the problem is that it works as if it is ahead of the curve. That is, the filter tries to respond faster than the normal response, respectively, if the filter began to slow down, - fines (remember, 50-100 thousand rubles).
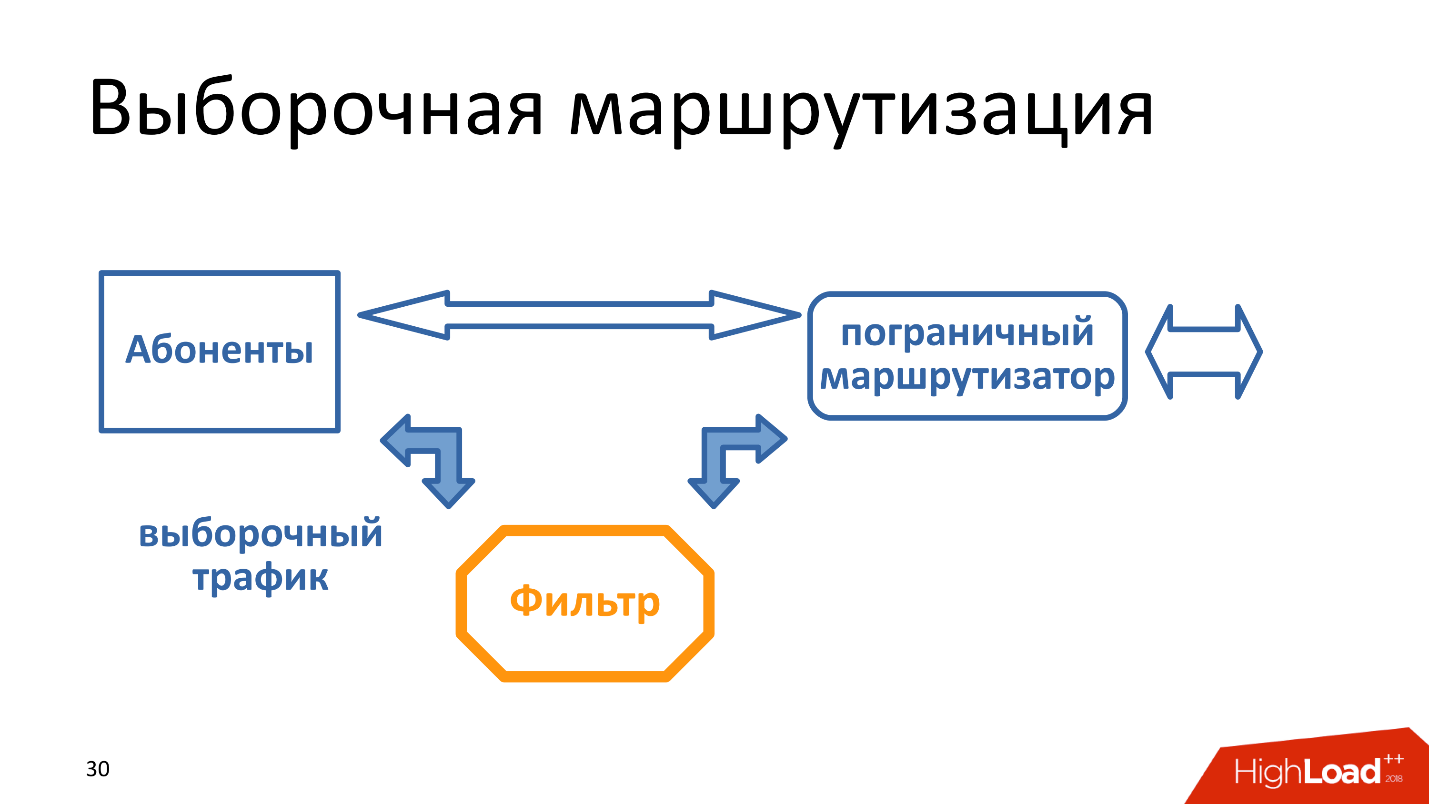
Selective routing - when traffic to IP addresses, among which there may be something from the “upload”, passes through a separate filter.
Unfortunately, there are no exact figures, but judging by indirect signs and tests, this is now the most common way to filter traffic.
Selective routing can be complemented by the fact that sets of IP addresses for filtering are aggregated in a big way. That is, it is not just several addresses that are blocked, but the entire network / 24 immediately hits the filter. Plus, large providers, for example, in MTS, have special security services that are specifically looking for IP blocks with risk, which also fall into filtering.
Selective routing can also be combined with DNS filtering . This is a popular method that Dom.ru uses, for example.
Let us examine in stages the problems that all this brings.
Decision on blocking
Roskomnadzor makes a decision - this immediately causes a problem associated, so to say, with the organization of a support service. In some cases, he must notify the site owner or host, but the addressee of the notification is not accurate (it is taken from public data, and not all support current addresses), notifications are lost, there is no public information .
Because of this, all sorts of bad things happen. The host or the site owner cannot control what requests are being sent to him, there is no public information. For example, Google has a database of websites with viruses, where you can register yourself as an autonomous system, somehow confirm that you are an autonomous system, and really see for yourself which sites in the opinion of Google in your autonomous system distribute “malware”. There is no such thing with locks - you expect only that the notification will reach you, and you will have time to read it in time.
The terms of interaction with Roskomnadzor are not respected, and on the whole, a bit strange, despite the fact that there are standards - to send a notification in 24 hours, to respond in 24 hours, to make a decision in 24 hours. When you receive a notification, and you say that you do not have such information and ask for clarification, you can get an answer in a few weeks. Or maybe you will be blocked, and then they will answer that you still have the information. I had such situations, but very few people sue - I don’t know such cases at all.
Again, if the notification came, you can not always understand what it is about. In most cases, Roskomnadzor normally describes what it means. But even in our practice of a micro-host, there were three cases when the description did not understand what information was involved. I did not even know what to write to the client - Roskomnadzor issues protocols and texts of the decision only by court, although they have such documents.
Time of application "unloading"
So, the decision was made, the provider downloaded the "upload" and then had to do something with it. There are two options for how fast: a day or immediately.
It is important that the day is set aside for locking the resource and unlocking, if suddenly a decision is made to unlock it. For many, this is done as a nightly upgrade to the switch From my experience: I took the notice at the wrong time, blocked the resource, decided the question, but wait a day until they unblock it. But business does not wait, losses appear.
But now in the regulations very often the word “immediately” sounds , by verbal agreement this is the hour . But there is a verbal agreement today, but not tomorrow. Basically, the phrase “immediately” now concerns prosecutor’s decisions on extremism.
To understand how everything is filtered, you need to know what is inside the “unloading”. There is a list of XML records of one of four types by types of locks and solution details:
To make it clear what kind of numbers we are talking about, below is the statistics for January 22, 2019.
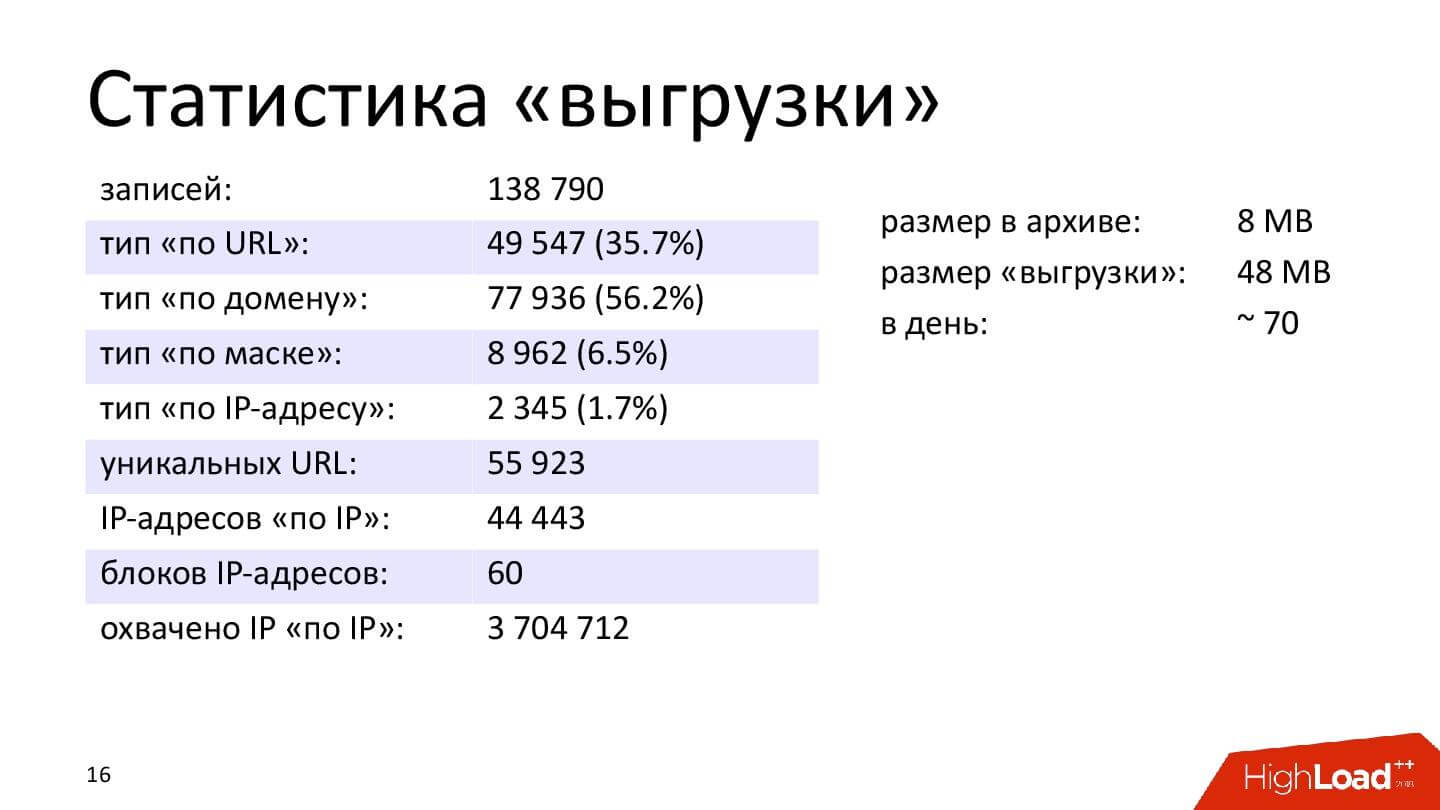
Important: only 139 thousand records, and the most popular type of blocking is blocking “by domain”. These are HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
Toxicity "unloading"
Before blocking a resource, the provider must parse the "unload". There are problems with this too. I specifically noted that “uploading” is not a registry, but a kind of technical document that is issued to the provider so that it can make decisions based on it. But despite this, the provider has to carry out a very large processing of "unloading".
For example, in the “unloading” there is redundancy , the records overlap each other. If you take a URL, it does not mean that there will be no blocking on the domain that is contained in this URL. Now there are not so many, though, a little more than three thousand.
The “upload” contains URLs with fragments (#) and sessions . This is generally terrible, because you need to understand how the test goes.
The provider must bring the “upload” into a normal form, because it contains incorrect URLs and domains. Mostly now there are only backslashes. There are gaps, but they are quickly removed, and for some reason, there is a special “love” for the backslash. Well, okay, with backward slashes, the question was decided, and if there is any plus sign? Therefore, there must always be monitoring, it is always necessary to do something.
Once again I draw your attention that the problem of the provider is our problem . What does the provider do? A motivation of 100 thousand rubles is a good motivation to make it so that if there is any problem at all, even with any hint of a problem, to cut it right away and then figure it out.
The urgency of “unloading” those IP addresses that are not “blocking by IP addresses”, but all others (blocking by domain, by URL, by mask) looks something like this.
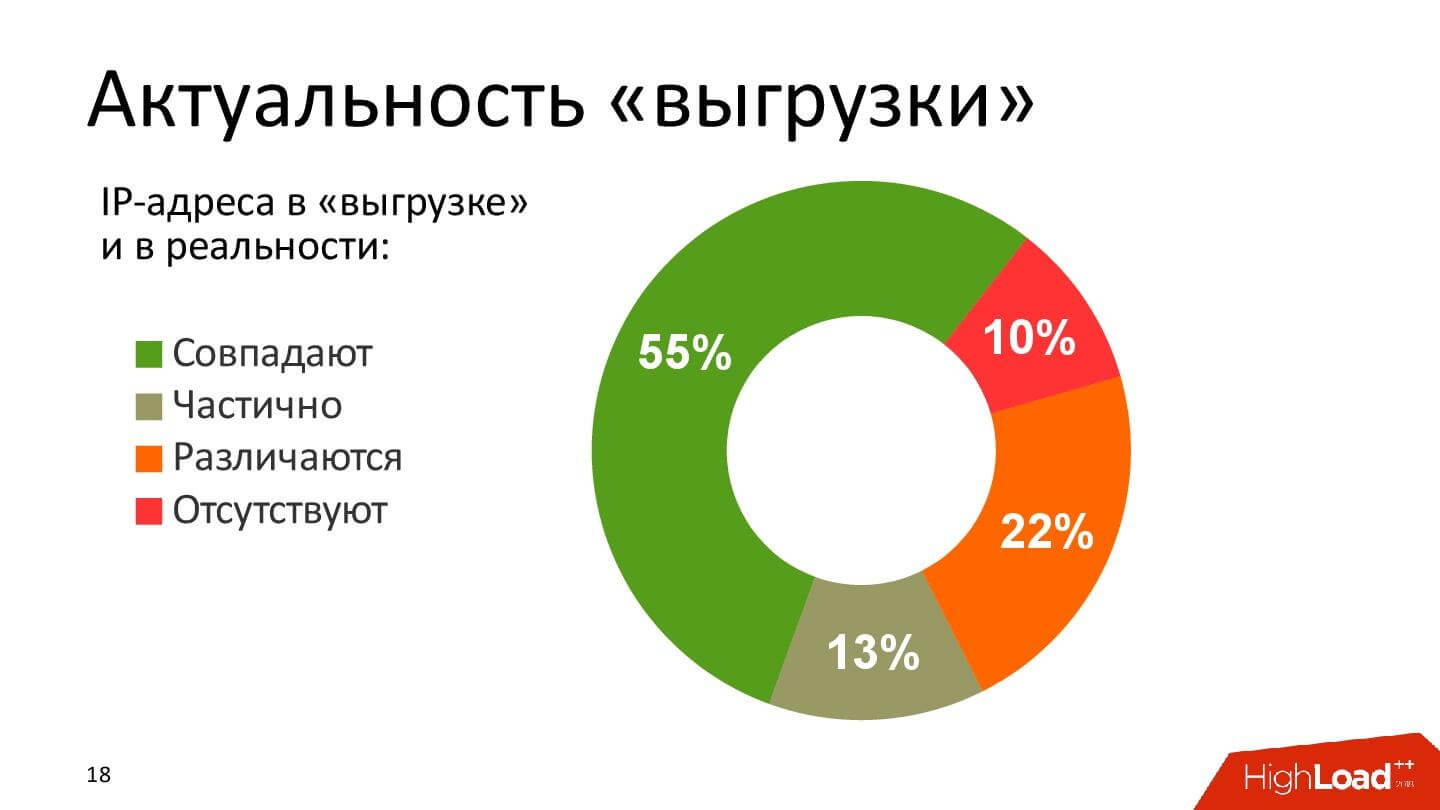
Just a little more than half of the time, and the rest is full stuffing.
Check locks
I'll start from the end.
I do not know how abroad, we have absolutely exactly the history of inspections. All locks are not done the way it is written, how to do them, but the way they are checked, because no one likes to pay fines, especially 100 thousand.
Prior to the registry of banned sites, there was a list of extremist materials of the Ministry of Justice (it still exists, it’s just now in the registry, and then it was separate) and prosecutor’s checks of blockings on this list. I am a micro-host and I managed to get into blocking my resources.
Existing types of checks:
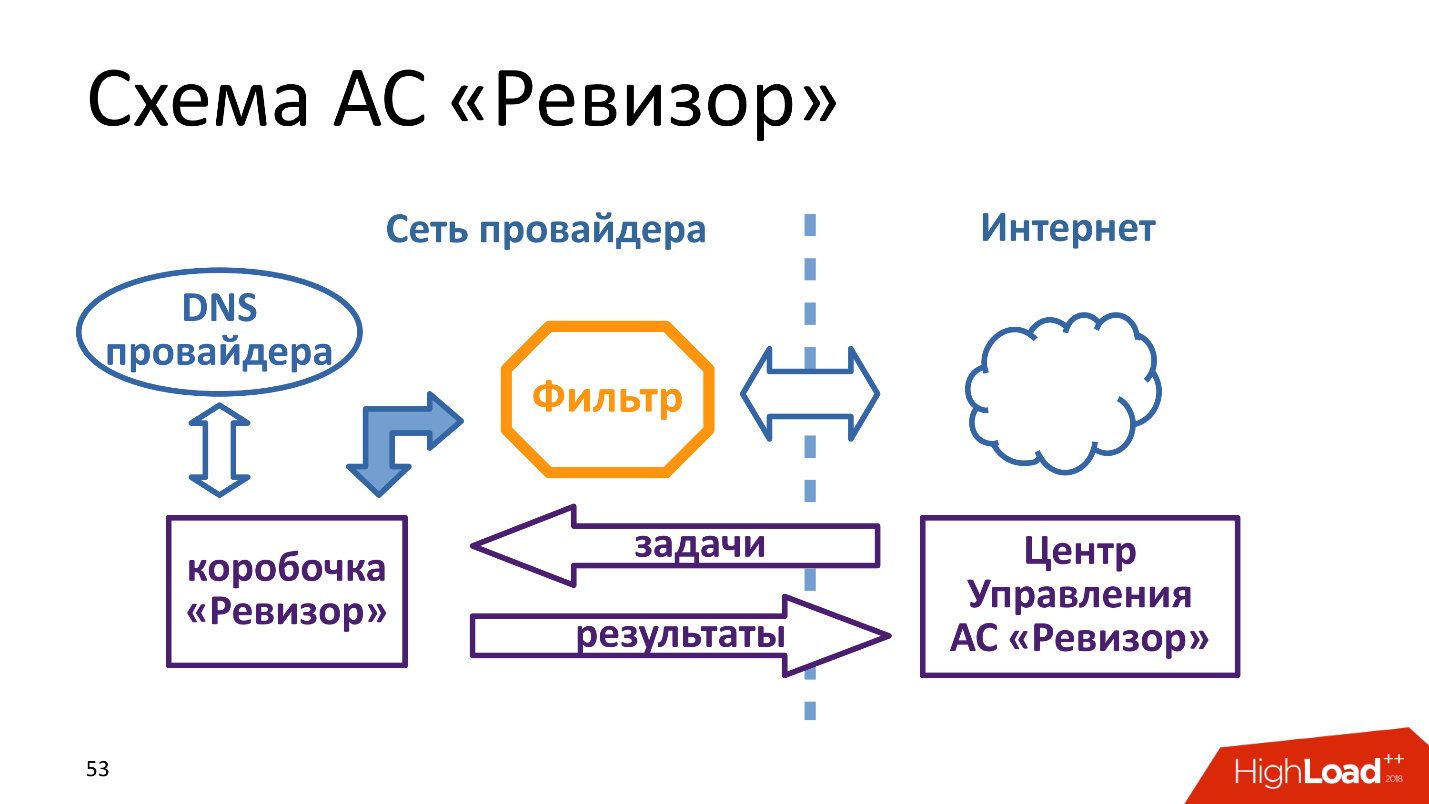
"Revizor" stands behind the filter and pretends to be a full subscriber. But the device itself does nothing, it receives tasks and gives answers to a certain control center, i.e. This is such a remote shell inside the network provider. It acts very similarly to RIPE Atlas .
The control center of an automated system is a true highload service, because we have 4,000 telecom operators, they do not have one network, but a box must be located in each network. That is, not each provider, but in each network of each provider . Accordingly, the control center has certain problems.
Question: Does the check itself have any problems? Of course have.
Verification problems
At SPEKTR-2017 (a forum under the auspices of Roskomnadzor itself), one of the heads of the FSUE of the main radio frequency center (HRDC), A. Veklich made a whole report on what technical problems there are with checking by the “Auditor” of providers.
Verification problems:
The method of work of the AU "Auditor"
In accordance with these problems, the method of work of the Auditor has been created.

And yes, your slide exhaustively illustrates this technique. I do not really understand how to live logically with this. For us, this all results in the fact that providers try to solve this problem somehow, and do it in a convenient way for themselves, and not always convenient for us.
Working without a technique, many providers have gained existential experience. In general, the whole method of blocking is an empirical way, which costs money, nerves, falls, even now, when a certain method is already well established.
There is an unofficial chat (which is remarkable - in Telegram, where else), where providers communicate with employees of the Radio Frequency Center. The most interesting thing is that there you can get real help, HRPC employees help providers solve their problems, and tell how the Auditor works. But this is all unofficial, there are no documents.
There is a Roskomnadzor standard on methods and methods for restricting access, which is registered with the Ministry of Justice. It specifically goes at the end, because it has the lowest priority. Providers do not act as written in the standard, but in the way the verification method works.
Methods of working with "unloading"
According to the standard and the accumulated experience, I will tell you how they work with “unloading”, that is, how our resources are blocked.
By URL :
Why is there generally a URL with an encrypted protocol is unclear, this is redundancy.
By Domain:
The standard really says that in the second case, blocking “by domain” cannot be blocked by IP address. But the provider, when it begins to knock down the filter, immediately includes another level, so as not to get a penalty. Such a story is not uncommon and naturally leads to additional damage to the business.
On the domain with a mask, theoretically, providers simply filter as a domain without an asterisk. Since, again, there are no checks, there are no problems either.
By IP address and a block of IP addresses , they are filtered as best they can - right on the border router sometimes.
We know that not only “evil” people are blocked, but also bona fide participants of the Internet . For example, when a person did not intend to keep prohibited information on his hosting, but did not read the letter or did not receive a notification.
The second group is foreign participants. They live in their legal field and do not violate the law. They can laugh, for example, at bribes, they see nothing wrong with that. For example, hosters do not even have the right to delete this information, because the laws do not apply to them. They are not evil people, but locks hit them.
Let's look at the problems, let's talk about DNS filtering, which is recommended by the standard.
First question: where is the DNS ? Indeed, forbidden information can be placed, but DNS represents a service that people need, specifically as a DNS, for example, IP addresses. If DNS is fake, everything is not very good, and it is not clear why.
The second point is the implementation of DNS interception . In fact, they intercept all traffic (they simply set up their own caching server — the most common practice), and accordingly the question of quality of service arises. For example, in my office I specifically made the Dom.ru bypass only for DNS, because it is impossible to work when you have to wait for a response from their DNS.
All this can be accelerated by creatingtheir system of substitution of answers . Then the provider must develop the system and maintain it. They also do this, but this is rare.
When distributing DNS request encryption technology (DNSCrypt, DoT, DoH), it is not known whether the type of DNS blocking will remain.
With domain filtering by mask, the problem is that the domains can be on different IP, so you have to scan the entire HTTP / HTTPS band. But what to do with the other protocols? You are scanning the entire band, and, for example, have banned only the Telegram by mask (by domain) - what to do about it? But there is still no verification !
The next very important point - by the way, is our future - what to do if on port 443: no SNI, SNI encrypted (ESNI), or other protocols in general, for example, QUIC, DNSCrypt, VPN, MTProto-proxy?
Large companies, such as Google, already support encrypted SNI, while Yandex has DNSCrypt on port 443. Now everyone decides this question in his own way. Some providers, especially mobile ones, if they cannot recognize traffic as HTTPS, simply cut it off. I can’t give exact statistics on this topic, but the approach itself does not inspire optimism.
Domain Resolving
Putting the filter on the entire band, for example, in 100 Gbps is unrealistic. Instead, providers take domains, their IP addresses, and already this traffic is scanned. This is done by large and small providers, mostly large ones, by the way.
In the norm it is not, but "you know!". "Auditor" checks on real addresses and on the fact that in the "unloading", that is, and so and so. Resolving is used because it is profitable for providers. It gives them the opportunity to filter all the same not 100 Gbps, but much less outgoing traffic.
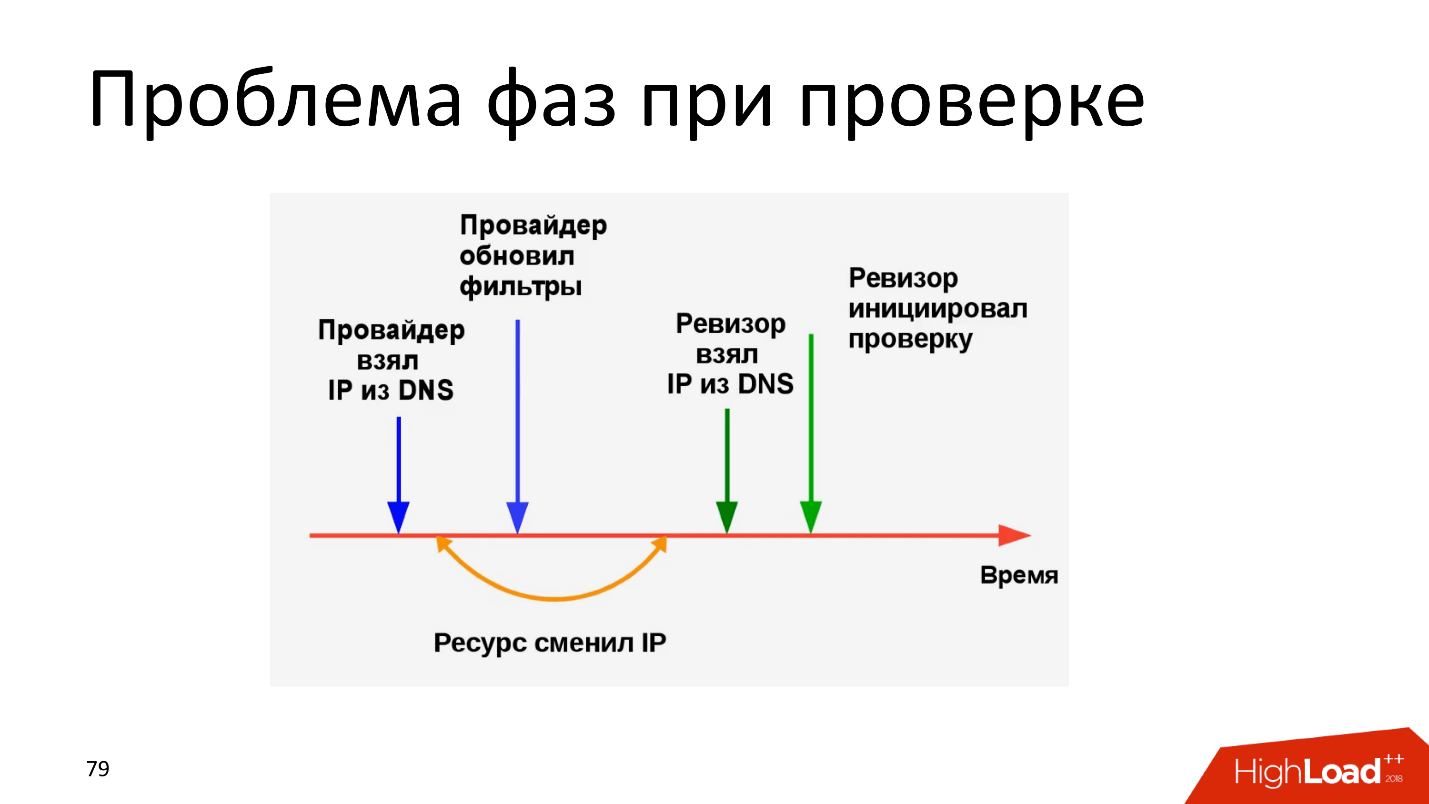
The problem of phases during verification has been known for a long time - everybody cries, injects and continues to do so. The provider took the IP, updated the filters, but before the “Auditor” was checked, the IP changed. The time for which the resource has changed IP (the yellow arrow on the diagram) can be measured in milliseconds, but this is enough for the provider to receive a fine.
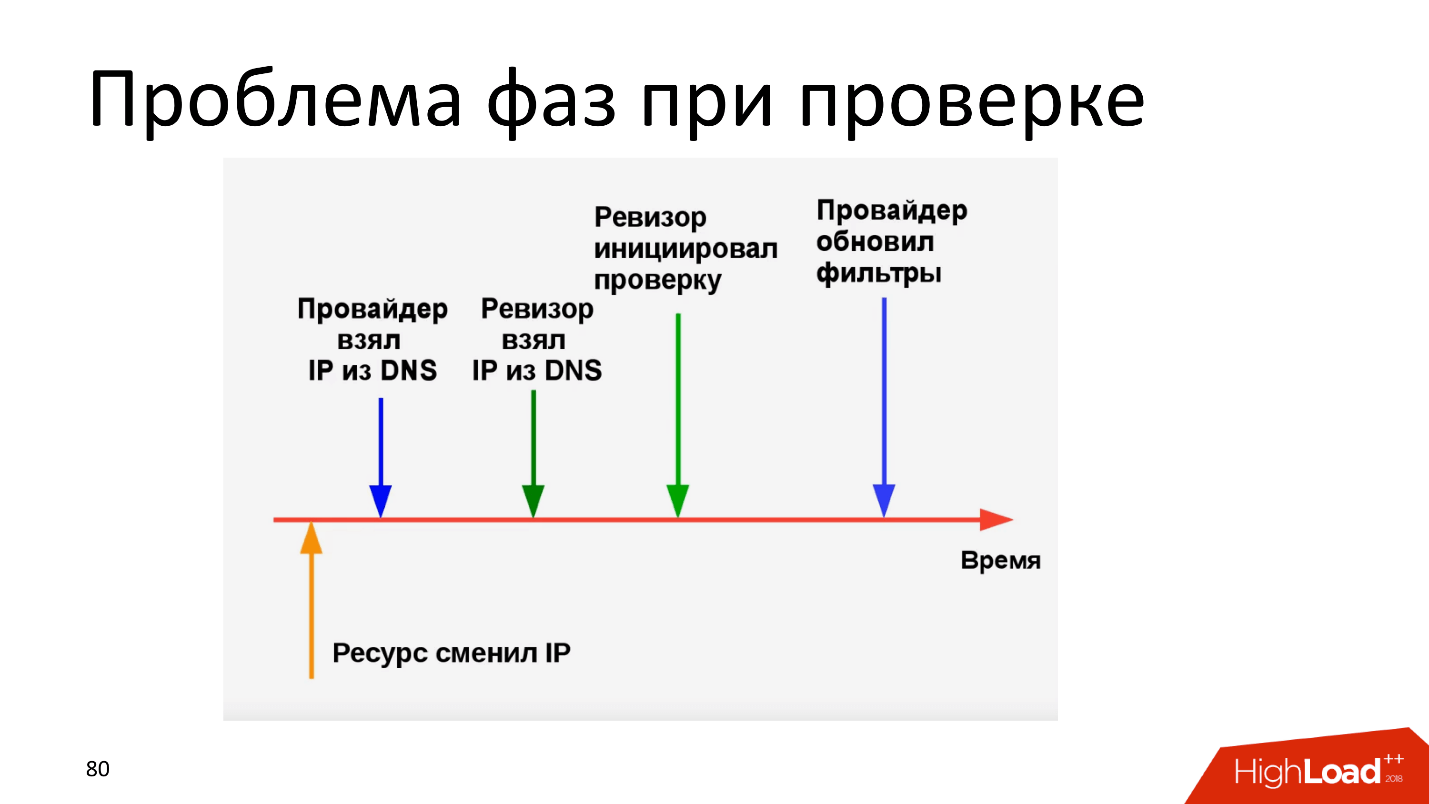
The second option: after changing the IP resource, the provider and the "Auditor" have the same IP, everything was done on time, only the provider updated the filters a millisecond later than the "Auditor" checked - with the corresponding damage. It is clear that the provider in such a situation will try to put so many straws that we may not like it.
There are still problems with rezolving:
About half a year ago, about a thousand domains escaped from blocking. And it is not known whether they did it on purpose or not. For example, LiveJournal for some reason discards all blocked journals to some CDN, which changes IP by 23 times a minute. Why do so, it is not very clear, but there is such a fact.
Foul Domains
The domain “foul” when it has expired registration, but it remains in the “unloading”, because, of course, no one is following this. The new owner of the domain gains control over the type of blocking that is in the “upload”. In the "upload" can be subdomains, and when you bought a domain, you get control over all subdomains.
I found about 200 “foul” domains in the “upload”, but in fact there are more of them. We do not know how many domains have already been bought by people who have decided to joke. Maybe they are not, maybe there is.
What does this lead to?

The picture crashes sites Yandex, VKontakte, Wikipedia. On the right is the MSK-IX chart, which MSK-IX itself denies and says that it was an internal failure. But for some reason, the internal failure exactly coincided with the DNS attack.
DNS attackThe reason was that someone bought a “rotten” domain, threw thousands of IP addresses there and started watering everything he wants, that is, throwing Yandex, VKontakte, etc. on these IP addresses. Someone played, and so it is still unknown who.
All, of course, puffed out their cheeks and said that this could not be. But despite this, on the graph on the right below, which shows the number of domains in the “upload”, it is clear that on June 5, 2017, Roskomnadzor carried out a thorough purge.
One of the targets of the attack was bank card payments. Banks do not recognize this, because then their shares will fall. But in fact, some banks did undergo DDoS, as a result of which they did not work with payment cards for the whole evening.
Do you think anyone did anything?
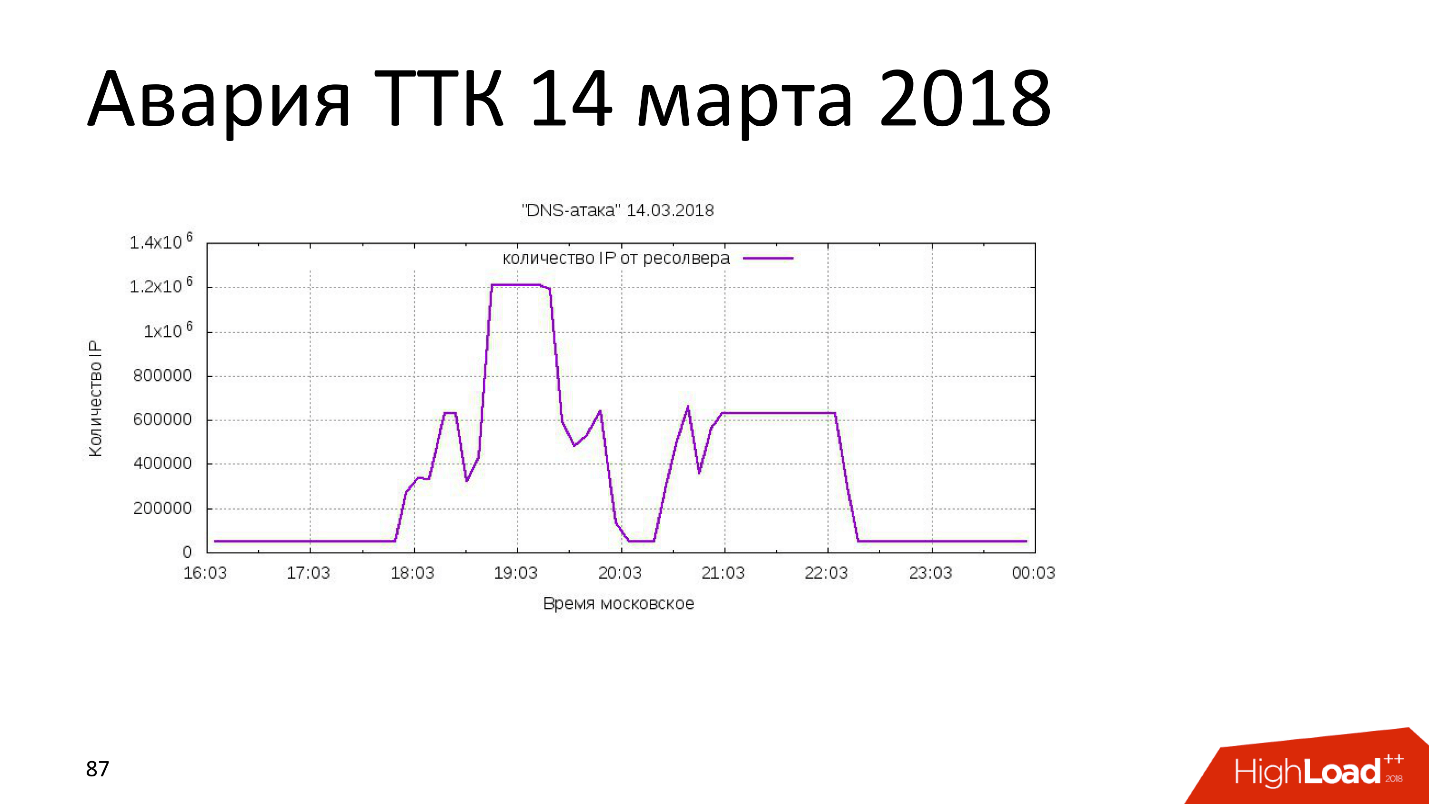
March 14, 2018: another attack vector, but also from “rotten” domains. Someone bought 4 domains, got control over 400 subdomains, and uploaded 4,000 IP addresses there. TransTeleCom, which, according to Roskomnadzor’s assurances, is doing fine, somewhere in 600 thousand, the table on the routers overflowed, and 20% of TTK networks throughout the country lay down.
Less than a year:

This is the rezolving schedule, that is, the IP addresses of the domains from the “upload”. On May 5, I say to Leonid Evdokimov: “But what if we don’t have a joke - would you write something Morse code on the chart?” In an hour he did it. By the numbers it is clear that we have calibrated for several thousands of IPs for my rezolving and for my time (I am constantly polling the domains) so that the peaks can be seen and began to write : DIGITAL RESISTANCE.
On the second chart there was a big inscription: “Truly Popov!”, Because it was Radio Day. I cite it, because it shows how Roskomnadzor has finally started cleaning domains. Where there is a step, there they have already found 2 domains, and 2 have not yet, but they brought the mind to some cleansing. At the time of generation, the “rotten” subdomains in the “unloading” inscription were about 4,000, and by November it was stable, that is, Roskomnadzor was conducting regular cleanings. But, unfortunately, by the time the article
came out, the number of domains had increased again - now there are 1538 of them. By the way, this is the only result of my activity in a few years - at least they started to do something!
By the way, about accidents and failures. The fact is that, for some reason, the equipment and filtering programs do not want to be marched: they are slowing down somewhere, failures and failures occur.. Slightly increases the load, and the quality of service becomes none. You can, for example, use a DNS attack - in the simple case the site will not fall, because everything is normally filtered, but the quality of its work for the user will be very low. We can say so, "semi-expensive" sites to reduce the quality of their work.
For example, last summer at Rostelecom in several regions, the filter for some reason gave out one chunk of the HTTP protocol incorrectly, and, accordingly, garbage was falling on the screen. The owner of the site Motobratan.ru was on vacation and said that he did not care. The site worked the whole weekend until on Monday morning the engineer came and repaired it.
ISP problems
There should be a good maintenance schedule in case:
But no, it's all fine. There is still a cheatcode here, but I'm afraid it will soon stop working. Providers in such cases, based on their existential experience, turn off the “Auditor”. If you turned off the Auditor, Roskomnadzor calls you, you say: “Oh, it is broken, now we fix it!” But you have a small amount of time between turning off the Auditor and Roskomnadzor’s call, and a little more to fix it. During this time, you can safely without any fines to carry out some preventive work.
Incidentally, when there was an accident at TTR, many simply turned off the filtering and the “Auditor”, just in case.
Fantasy
My favorite fantasy about what can be done with this is whitelists . But there is but:
The next option is the magic DPI , which the Chinese will sell to us now, and it will work. But miracles do not happen, the performance of the DPI is not at all magical. Secondly, when something complicated is filtered, you need to store states. But DPI is not rubber and, for example, can come under special attacks on DPI, which will just put it. Normal failures will naturally also. Who lived under the DPI in the closed Internet, knows that they are working so-so.
Another fantasy - let's make a single state DNS for rezolving , and everything will be fine.
And at the end of the entertainment question: is it possible to block Telegram?
I will answer in all seriousness, without irony: yes. You can block Telegram if you slightly change the regulatory framework, laws, put magical DPIs and neglect collateral damage . We see this in the example of Iran, in which thousands of sites are blocked, but Telegram is also relatively well blocked.
We hope this story has helped to form a general idea of the technical component of Internet blocking in Russia.
Some details can be found in the answers to the questions after the report, on Philip Kulin’s website , in the Telegram channel about Internet regulation in Russia @ usher2 and in the schors profile
Internet blocking in Russia already exists - this is a reality with which we live and must live on. And if so, you need to understand how it is arranged technically, which the provider can and cannot. Philip Kulin ( schors ) began to collect information on this subject long ago, participated in regulatory work, and went to various meetings. As a result, now only Roskomnadzor knows more about it in Russia, but this is not certain. Under the cut a brief summary of the current state of affairs.
About the speaker: Philip Kulin ( schors ), General Director of Dense Forest LLC - a small Russian hoster, mainly engaged in shared-hosting.
Tangle of problems
It would seem that there are locks and there are. We don’t like them, but maybe there’s nothing wrong with them?
In fact, locking is a solid tangle of problems.
Collateral damage is the biggest blocking problem. The most vivid example illustrating this occurred in April 2018, when large blocks of IP addresses of cloud services were blocked, respectively, many services did not work and suffered great damage.
The volatility of regulations and practices that are constantly changing. A year ago, this story would have been completely different, and two years ago it would most likely contradict today's. In a year, everything will be different again. Today this is so, in a month - a little bit wrong, and in six months, not at all. You need to follow this, but you also need to have time to work.
Locks difficult to diagnose. If a resource has been blocked by the registry, this is the simplest case. In the cases that we consider further, it is quite difficult to distinguish a real block from technical problems. A vivid example - in October, Yandex dropped the DNS clock for five, during which time many managed to decide that it was a Roskomnadzor block. It is really difficult to determine exactly, but such situations have already happened, so people immediately think about blocking.
It is impossible to predict when they will block you and whether they will block you at all. You work quietly, and your work is suddenly over.
It’s absolutely impossible to calculate risks., because maybe some widget on the site will fall off, about which you have already forgotten, and maybe the whole business will be hit. A very good example of risk unpredictability is the case of Bitrix24. In March, they very quickly transferred their services to Amazon. In the same month, a document leaked to the network, which truth might have been a fake one, in which large Amazon subnets were registered. Nevertheless, Bitrix24 somehow reacted to it and avoided problems in April, when Amazon services were really blocked.
I assure you that most of you will be so unlucky! Such documents will not by chance flow into your hands. When your business ends, you will know this after the fact.
In simple cases, we know why your site was blocked. For example, the forum posted information that a court declared prohibited, but you did not have time to react. But communication with the supervisory authority has unacceptable terms - for example, a day. On the Internet during this time you can lose a fifth of the business.
All this leads to some hopelessness. It is possible to argue with irony over, for example, David Khomak and the blocking of Lurk. But it is quite another thing when it happens to you, as it happened to me once. The client specified the IP addresses of my servers at the domain that I did not manage - I am sitting, and the phone just doesn’t fall silent. Customers say that they are leaving, they demand a refund, but I can not do anything! And no one can help me with this. This is really a feeling of complete hopelessness.
Risk groups
Locks affect:
- Site owners and services , which, including, may block by mistake. Or they may recognize some information as prohibited.
- Users of the lock service also apply. The fact that your site is blocked, concerns you in the first place. But there are people who used this site or service.
- Hosters and providers that are between two lights. Because they are required and working services, and the requirements of the supervisory authority, which faces fines. Let me remind you that fines from 50 to 100 thousand rubles for the protocol. For example, such protocols for a month can be many and the amounts are very substantial.
How locks work
First, we will briefly discuss how blocking occurs in order to understand the full picture.
- Federal executive authorities or the court decide to prohibit any information for some reason.
- Send information to Roskomnadzor, which must make an entry in the registry of prohibited sites.
- Then there are some internal procedures (there are too many of them - you can read a whole lecture), as a result of which Roskomnadzor may decide to block and enter the site into the so-called “upload” - a technical file that is sent to providers.
- Providers on this file implement the restriction.
- Check providers, which has been happening for two years automatically.

It is important to understand that traffic is filtered by each provider. That is, not somewhere on cross-border routers or a state filter, but each provider sets itself a filter between the Internet and subscribers in each of its subnets. In the diagram above, the verification device is next to subscribers, because it pretends to be a subscriber - this is important.
Filtering tools
Providers can buy filtered traffic from a superior provider. But there is a problem - buying traffic from a superior provider, the provider-buyer can not determine the technical problem or blocking. He has no tool, because he receives already cut traffic, and this does not affect his business very well.
Or you can use:
- special complex commercial solutions;
- open source open source solutions (currently there is only one such project);
- your "collective farm".
There are no rocket sets there, and the main problems are not about writing a program.
There are the following options for implementation.

For example, you have a small channel of 100 Gbps, you put the filter in the gap.

Some mirror traffic, but with traffic mirroring, the problem is that it works as if it is ahead of the curve. That is, the filter tries to respond faster than the normal response, respectively, if the filter began to slow down, - fines (remember, 50-100 thousand rubles).

Selective routing - when traffic to IP addresses, among which there may be something from the “upload”, passes through a separate filter.
Unfortunately, there are no exact figures, but judging by indirect signs and tests, this is now the most common way to filter traffic.
Selective routing can be complemented by the fact that sets of IP addresses for filtering are aggregated in a big way. That is, it is not just several addresses that are blocked, but the entire network / 24 immediately hits the filter. Plus, large providers, for example, in MTS, have special security services that are specifically looking for IP blocks with risk, which also fall into filtering.
Selective routing can also be combined with DNS filtering . This is a popular method that Dom.ru uses, for example.
Let us examine in stages the problems that all this brings.
Decision on blocking
Roskomnadzor makes a decision - this immediately causes a problem associated, so to say, with the organization of a support service. In some cases, he must notify the site owner or host, but the addressee of the notification is not accurate (it is taken from public data, and not all support current addresses), notifications are lost, there is no public information .
Because of this, all sorts of bad things happen. The host or the site owner cannot control what requests are being sent to him, there is no public information. For example, Google has a database of websites with viruses, where you can register yourself as an autonomous system, somehow confirm that you are an autonomous system, and really see for yourself which sites in the opinion of Google in your autonomous system distribute “malware”. There is no such thing with locks - you expect only that the notification will reach you, and you will have time to read it in time.
The terms of interaction with Roskomnadzor are not respected, and on the whole, a bit strange, despite the fact that there are standards - to send a notification in 24 hours, to respond in 24 hours, to make a decision in 24 hours. When you receive a notification, and you say that you do not have such information and ask for clarification, you can get an answer in a few weeks. Or maybe you will be blocked, and then they will answer that you still have the information. I had such situations, but very few people sue - I don’t know such cases at all.
Again, if the notification came, you can not always understand what it is about. In most cases, Roskomnadzor normally describes what it means. But even in our practice of a micro-host, there were three cases when the description did not understand what information was involved. I did not even know what to write to the client - Roskomnadzor issues protocols and texts of the decision only by court, although they have such documents.
Time of application "unloading"
So, the decision was made, the provider downloaded the "upload" and then had to do something with it. There are two options for how fast: a day or immediately.
It is important that the day is set aside for locking the resource and unlocking, if suddenly a decision is made to unlock it. For many, this is done as a nightly upgrade to the switch From my experience: I took the notice at the wrong time, blocked the resource, decided the question, but wait a day until they unblock it. But business does not wait, losses appear.
But now in the regulations very often the word “immediately” sounds , by verbal agreement this is the hour . But there is a verbal agreement today, but not tomorrow. Basically, the phrase “immediately” now concerns prosecutor’s decisions on extremism.
To understand how everything is filtered, you need to know what is inside the “unloading”. There is a list of XML records of one of four types by types of locks and solution details:
- URL (s) + domain + IP address (a);
- Domain + IP Address (s);
- Domain with mask (* .example.com) + IP address (a);
- IP-address (a) - it is clear, there is an address, and we block it completely.
To make it clear what kind of numbers we are talking about, below is the statistics for January 22, 2019.

Important: only 139 thousand records, and the most popular type of blocking is blocking “by domain”. These are HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
Toxicity "unloading"
Before blocking a resource, the provider must parse the "unload". There are problems with this too. I specifically noted that “uploading” is not a registry, but a kind of technical document that is issued to the provider so that it can make decisions based on it. But despite this, the provider has to carry out a very large processing of "unloading".
For example, in the “unloading” there is redundancy , the records overlap each other. If you take a URL, it does not mean that there will be no blocking on the domain that is contained in this URL. Now there are not so many, though, a little more than three thousand.
The “upload” contains URLs with fragments (#) and sessions . This is generally terrible, because you need to understand how the test goes.
The provider must bring the “upload” into a normal form, because it contains incorrect URLs and domains. Mostly now there are only backslashes. There are gaps, but they are quickly removed, and for some reason, there is a special “love” for the backslash. Well, okay, with backward slashes, the question was decided, and if there is any plus sign? Therefore, there must always be monitoring, it is always necessary to do something.
Once again I draw your attention that the problem of the provider is our problem . What does the provider do? A motivation of 100 thousand rubles is a good motivation to make it so that if there is any problem at all, even with any hint of a problem, to cut it right away and then figure it out.
The urgency of “unloading” those IP addresses that are not “blocking by IP addresses”, but all others (blocking by domain, by URL, by mask) looks something like this.

Just a little more than half of the time, and the rest is full stuffing.
Check locks
I'll start from the end.
The whole history of the implementation of locks in Russia is the history of checks on these locks.
I do not know how abroad, we have absolutely exactly the history of inspections. All locks are not done the way it is written, how to do them, but the way they are checked, because no one likes to pay fines, especially 100 thousand.
Prior to the registry of banned sites, there was a list of extremist materials of the Ministry of Justice (it still exists, it’s just now in the registry, and then it was separate) and prosecutor’s checks of blockings on this list. I am a micro-host and I managed to get into blocking my resources.
Existing types of checks:
- Field inspections (mainly the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the Federal Security Service and the Prosecutor’s Office) are rare, but there are some.
- AS “Revizor” is a favorite automated system that checks all providers.

"Revizor" stands behind the filter and pretends to be a full subscriber. But the device itself does nothing, it receives tasks and gives answers to a certain control center, i.e. This is such a remote shell inside the network provider. It acts very similarly to RIPE Atlas .
The control center of an automated system is a true highload service, because we have 4,000 telecom operators, they do not have one network, but a box must be located in each network. That is, not each provider, but in each network of each provider . Accordingly, the control center has certain problems.
Question: Does the check itself have any problems? Of course have.
Verification problems
At SPEKTR-2017 (a forum under the auspices of Roskomnadzor itself), one of the heads of the FSUE of the main radio frequency center (HRDC), A. Veklich made a whole report on what technical problems there are with checking by the “Auditor” of providers.
Verification problems:
- Does “Revizor” see this as a provider or resource filter? Maybe it was someone of you who found the “Auditor” database and all sites simply give a stub, similar to the provider stub.
- Block rate - for all types of blocking (for HTTPS, domain, IP-address), what is the indication that the resource is locked? For example, it is necessary to scan ports by IP address, this is a whole problem.
- Lock count for other protocols.
- How to check domain by mask ? Under the asterisk can be different IP-addresses, different domains. Can I put a filter on the whole strip? And to check what - selectively or some kind of hash to generate? I’ll say right away that there is a regulatory blocking, but nobody checks it.
The method of work of the AU "Auditor"
In accordance with these problems, the method of work of the Auditor has been created.

And yes, your slide exhaustively illustrates this technique. I do not really understand how to live logically with this. For us, this all results in the fact that providers try to solve this problem somehow, and do it in a convenient way for themselves, and not always convenient for us.
Working without a technique, many providers have gained existential experience. In general, the whole method of blocking is an empirical way, which costs money, nerves, falls, even now, when a certain method is already well established.
There is an unofficial chat (which is remarkable - in Telegram, where else), where providers communicate with employees of the Radio Frequency Center. The most interesting thing is that there you can get real help, HRPC employees help providers solve their problems, and tell how the Auditor works. But this is all unofficial, there are no documents.
There is a Roskomnadzor standard on methods and methods for restricting access, which is registered with the Ministry of Justice. It specifically goes at the end, because it has the lowest priority. Providers do not act as written in the standard, but in the way the verification method works.
Methods of working with "unloading"
According to the standard and the accumulated experience, I will tell you how they work with “unloading”, that is, how our resources are blocked.
By URL :
- If this is the usual HTTP protocol filter by headers.
- If the encrypted protocol is HTTPS - filter as "domain"
Why is there generally a URL with an encrypted protocol is unclear, this is redundancy.
By Domain:
- The usual HTTP protocol is a filter by the Host header.
- Encrypted HTTPS protocol - or DNS filter; or an SNI header filter (when an encrypted connection is established, an unencrypted header with a domain name is transmitted inside); or filter by IP address.
- It is recommended to block the rest of the protocols by IP-address, but since the “Auditor” does not check this, someone does it, someone does not.
The standard really says that in the second case, blocking “by domain” cannot be blocked by IP address. But the provider, when it begins to knock down the filter, immediately includes another level, so as not to get a penalty. Such a story is not uncommon and naturally leads to additional damage to the business.
On the domain with a mask, theoretically, providers simply filter as a domain without an asterisk. Since, again, there are no checks, there are no problems either.
By IP address and a block of IP addresses , they are filtered as best they can - right on the border router sometimes.
Bona fide members
We know that not only “evil” people are blocked, but also bona fide participants of the Internet . For example, when a person did not intend to keep prohibited information on his hosting, but did not read the letter or did not receive a notification.
The second group is foreign participants. They live in their legal field and do not violate the law. They can laugh, for example, at bribes, they see nothing wrong with that. For example, hosters do not even have the right to delete this information, because the laws do not apply to them. They are not evil people, but locks hit them.
Filtering problems
Let's look at the problems, let's talk about DNS filtering, which is recommended by the standard.
First question: where is the DNS ? Indeed, forbidden information can be placed, but DNS represents a service that people need, specifically as a DNS, for example, IP addresses. If DNS is fake, everything is not very good, and it is not clear why.
The second point is the implementation of DNS interception . In fact, they intercept all traffic (they simply set up their own caching server — the most common practice), and accordingly the question of quality of service arises. For example, in my office I specifically made the Dom.ru bypass only for DNS, because it is impossible to work when you have to wait for a response from their DNS.
All this can be accelerated by creatingtheir system of substitution of answers . Then the provider must develop the system and maintain it. They also do this, but this is rare.
When distributing DNS request encryption technology (DNSCrypt, DoT, DoH), it is not known whether the type of DNS blocking will remain.
With domain filtering by mask, the problem is that the domains can be on different IP, so you have to scan the entire HTTP / HTTPS band. But what to do with the other protocols? You are scanning the entire band, and, for example, have banned only the Telegram by mask (by domain) - what to do about it? But there is still no verification !
The next very important point - by the way, is our future - what to do if on port 443: no SNI, SNI encrypted (ESNI), or other protocols in general, for example, QUIC, DNSCrypt, VPN, MTProto-proxy?
Large companies, such as Google, already support encrypted SNI, while Yandex has DNSCrypt on port 443. Now everyone decides this question in his own way. Some providers, especially mobile ones, if they cannot recognize traffic as HTTPS, simply cut it off. I can’t give exact statistics on this topic, but the approach itself does not inspire optimism.
Domain Resolving
Putting the filter on the entire band, for example, in 100 Gbps is unrealistic. Instead, providers take domains, their IP addresses, and already this traffic is scanned. This is done by large and small providers, mostly large ones, by the way.
In the norm it is not, but "you know!". "Auditor" checks on real addresses and on the fact that in the "unloading", that is, and so and so. Resolving is used because it is profitable for providers. It gives them the opportunity to filter all the same not 100 Gbps, but much less outgoing traffic.

The problem of phases during verification has been known for a long time - everybody cries, injects and continues to do so. The provider took the IP, updated the filters, but before the “Auditor” was checked, the IP changed. The time for which the resource has changed IP (the yellow arrow on the diagram) can be measured in milliseconds, but this is enough for the provider to receive a fine.

The second option: after changing the IP resource, the provider and the "Auditor" have the same IP, everything was done on time, only the provider updated the filters a millisecond later than the "Auditor" checked - with the corresponding damage. It is clear that the provider in such a situation will try to put so many straws that we may not like it.
There are still problems with rezolving:
- balancing;
- geo-targeting;
- service migration, including intentional.
About half a year ago, about a thousand domains escaped from blocking. And it is not known whether they did it on purpose or not. For example, LiveJournal for some reason discards all blocked journals to some CDN, which changes IP by 23 times a minute. Why do so, it is not very clear, but there is such a fact.
Foul Domains
The domain “foul” when it has expired registration, but it remains in the “unloading”, because, of course, no one is following this. The new owner of the domain gains control over the type of blocking that is in the “upload”. In the "upload" can be subdomains, and when you bought a domain, you get control over all subdomains.
I found about 200 “foul” domains in the “upload”, but in fact there are more of them. We do not know how many domains have already been bought by people who have decided to joke. Maybe they are not, maybe there is.
What does this lead to?

The picture crashes sites Yandex, VKontakte, Wikipedia. On the right is the MSK-IX chart, which MSK-IX itself denies and says that it was an internal failure. But for some reason, the internal failure exactly coincided with the DNS attack.
DNS attackThe reason was that someone bought a “rotten” domain, threw thousands of IP addresses there and started watering everything he wants, that is, throwing Yandex, VKontakte, etc. on these IP addresses. Someone played, and so it is still unknown who.
All, of course, puffed out their cheeks and said that this could not be. But despite this, on the graph on the right below, which shows the number of domains in the “upload”, it is clear that on June 5, 2017, Roskomnadzor carried out a thorough purge.
One of the targets of the attack was bank card payments. Banks do not recognize this, because then their shares will fall. But in fact, some banks did undergo DDoS, as a result of which they did not work with payment cards for the whole evening.
Do you think anyone did anything?

March 14, 2018: another attack vector, but also from “rotten” domains. Someone bought 4 domains, got control over 400 subdomains, and uploaded 4,000 IP addresses there. TransTeleCom, which, according to Roskomnadzor’s assurances, is doing fine, somewhere in 600 thousand, the table on the routers overflowed, and 20% of TTK networks throughout the country lay down.
Less than a year:

This is the rezolving schedule, that is, the IP addresses of the domains from the “upload”. On May 5, I say to Leonid Evdokimov: “But what if we don’t have a joke - would you write something Morse code on the chart?” In an hour he did it. By the numbers it is clear that we have calibrated for several thousands of IPs for my rezolving and for my time (I am constantly polling the domains) so that the peaks can be seen and began to write : DIGITAL RESISTANCE.
On the second chart there was a big inscription: “Truly Popov!”, Because it was Radio Day. I cite it, because it shows how Roskomnadzor has finally started cleaning domains. Where there is a step, there they have already found 2 domains, and 2 have not yet, but they brought the mind to some cleansing. At the time of generation, the “rotten” subdomains in the “unloading” inscription were about 4,000, and by November it was stable, that is, Roskomnadzor was conducting regular cleanings. But, unfortunately, by the time the article
came out, the number of domains had increased again - now there are 1538 of them. By the way, this is the only result of my activity in a few years - at least they started to do something!
By the way, about accidents and failures. The fact is that, for some reason, the equipment and filtering programs do not want to be marched: they are slowing down somewhere, failures and failures occur.. Slightly increases the load, and the quality of service becomes none. You can, for example, use a DNS attack - in the simple case the site will not fall, because everything is normally filtered, but the quality of its work for the user will be very low. We can say so, "semi-expensive" sites to reduce the quality of their work.
For example, last summer at Rostelecom in several regions, the filter for some reason gave out one chunk of the HTTP protocol incorrectly, and, accordingly, garbage was falling on the screen. The owner of the site Motobratan.ru was on vacation and said that he did not care. The site worked the whole weekend until on Monday morning the engineer came and repaired it.
ISP problems
There should be a good maintenance schedule in case:
- unloading service does not work;
- there was an accident on the communication channels, the "unloading" is impossible to obtain;
- filters broke;
- filters on the prevention.
But no, it's all fine. There is still a cheatcode here, but I'm afraid it will soon stop working. Providers in such cases, based on their existential experience, turn off the “Auditor”. If you turned off the Auditor, Roskomnadzor calls you, you say: “Oh, it is broken, now we fix it!” But you have a small amount of time between turning off the Auditor and Roskomnadzor’s call, and a little more to fix it. During this time, you can safely without any fines to carry out some preventive work.
Incidentally, when there was an accident at TTR, many simply turned off the filtering and the “Auditor”, just in case.
Fantasy
My favorite fantasy about what can be done with this is whitelists . But there is but:
- Criteria for inclusion in the white lists.
- Interaction system - the support of Roskomnadzor is not very good, one can imagine what it will become.
- In the clouds, how to work - write a request for each virtual? For example, Kubernetes wants to create a node, and you write a request for adding it to the white list - hello Continuous Integration!
The next option is the magic DPI , which the Chinese will sell to us now, and it will work. But miracles do not happen, the performance of the DPI is not at all magical. Secondly, when something complicated is filtered, you need to store states. But DPI is not rubber and, for example, can come under special attacks on DPI, which will just put it. Normal failures will naturally also. Who lived under the DPI in the closed Internet, knows that they are working so-so.
Another fantasy - let's make a single state DNS for rezolving , and everything will be fine.
- This is a time consuming task, because the DNS is easy to do in an office, and not for public use.
- This does not solve the phase problem in the verification I mentioned above. This problem, in fact, will not be solved at all.
- I do not understand why to keep the state DNS, if it is easier to keep the "upload" relevant.
And at the end of the entertainment question: is it possible to block Telegram?
I will answer in all seriousness, without irony: yes. You can block Telegram if you slightly change the regulatory framework, laws, put magical DPIs and neglect collateral damage . We see this in the example of Iran, in which thousands of sites are blocked, but Telegram is also relatively well blocked.
We hope this story has helped to form a general idea of the technical component of Internet blocking in Russia.
Some details can be found in the answers to the questions after the report, on Philip Kulin’s website , in the Telegram channel about Internet regulation in Russia @ usher2 and in the schors profile
This article is based on one of the most interesting listeners of the HighLoad ++ 2018 report . Learning about new materials and open videos is convenient from the newsletter - it is infrequent, and only on business. For example, its recipients know for sure that the bid campaign for the April Saint HighLoad ++ is in full swing .
