Features of the withdrawal of the site from "Minusinsk". How it was
If you are an advanced SEO-specialist and have brought out more than a dozen sites from under the Minusinsk algorithm, then perhaps more than half of this article will cause you emotions like “water”. However, if you have never encountered such a problem or simply encountered bits of information to solve it, here you will find a lot of interesting and useful things that will help you quickly solve this problem.
A little over a year ago, on 05/14/2015, Yandex launched the Minusinsk algorithm, aimed at identifying and "pessimizing" sites that use SEO links * for search promotion. SEO link is a link that affects search algorithms and can increase the site’s position.
Our company, one of many, received the so-called “letter of happiness”, the content of which was as follows:

We received such a letter, but since this is just a warning, we did not respond to it.
One evening, in February, after almost 9 months, on the internal service of our company, we found a site drop on most requests by 20 positions. Minusinsk in action. We started to plan how to solve this problem.
The main task was to get out of sanctions with minimal losses. Many administrators, frightened by the warning, took and deleted all links at once. We could do the same, however, a sharp decline in the link mass and the loss of high-quality links with high weight could lead to negative consequences when ranking a site in Google.
To begin with, it was necessary to collect the full reference mass. The collection was carried out both from downloads from search engines, and using separate services (majestic, ahrefs).
In total, about a million links were collected. They were sorted and cleaned of those that 100% could not get under the "Minusinsk" (links from our sites).
It turned out about 650 links, many of which were very old. The bulk was purchased on exchanges.
Then we began to analyze each link. About link analysis (good / bad) on the Internet you can find a lot of information. There are services that help determine the quality, however, they do not disclose their algorithms, which is why we decided to analyze all the links manually.
Links were evaluated by the following indicators:
I Basic
II Related
An interesting point is that about 200 links purchased through the sape.ru exchange were not in the Google index, which greatly facilitated our task. There are services that help determine the quality, but they do not disclose their algorithms, which is why we decided to analyze all the links manually.
In general, we have the following situation:

In principle, as expected. Most of the links were posted more than 5 years ago in automatic mode for "pennies" or free "runs". Donor performance has deteriorated over time.
Since more than half of the links were not indexed in Google, the risks after their removal are much lower, so we took up them first.
Links were removed by groups between updates. The repeated division of the groups turned out to be somewhat larger than in the screenshot above, so the process of solving the problem was delayed. In cases where the exchange did not allow the removal of the link directly through the system, it was necessary to contact the administrators.
There are a lot of communication methods, the following are the ones we used:
1. Feedback on the site . A very useful thing, but it does not always work, or it does not exist at all, or people respond for a very long time.
2. Contact information on the site. It happened that they turned out to be invalid, but in some cases they helped to get in touch. Separately, it is worth highlighting whois services that determine the contact information of the domain owner.
3. Domain registrars . With their help, you can contact the owner or representative of the domain. This was also used.
4. Communication through the host
5. Comments on the latest news
6. Standard mail . Many sites have standard mails of the form admin@site.ru, abuse@site.ru, webmaster@site.ru, info@site.ru are most often found, but there are others that are found in individual cases, such as support @ site. ru. We sent messages to them if there were no other options to contact. The option is not particularly effective, but also an option. We had no feedback at all.
7. Communication with web developers . Sometimes in the basements of many sites you can see the link and logo of the company that was developing this site. We contacted this company to get in touch with the owner of the site or simply solved this issue with them. In principle, if developers see that the site is about nothing and our link is located on some kind of left page, then removing it should not be a problem.

Imagine that the total number of administrators to contact was ~ 250. I had to write repeatedly, sometimes 3 or more letters for each of the methods listed above.
At first, we tried to remove all the links for free, and since we received a very small amount of feedback, we decided to try to offer the owners a certain amount.
It all started with $ 2. Feedback has increased and we removed some of the links for a fee. However, people began to come across who requested a much larger amount. At first, we scored on them, however, when almost three months passed, and we never got out of Minusinsk, we started paying for everything.
It is difficult to say how much was spent as a whole. There were several links, for the removal of which the administrators requested more than 1000 rubles, some were in the region of 500 rubles and the bulk of the cheap for $ 2.
1. Shoals with Yandex service. There were moments that some kind of link was in the interface, but it wasn’t in the unloading. All this was solved by communicating with technical support.
2. We removed some pages from Yandex search results through the url removal service in Yandex.Webmaster. You can delete a page with a link if it meets one of three conditions: the server returns 404, the page is not allowed to be indexed via robots.txt or using the noindex meta tag. We basically removed 404 each.

3. Re-indexation. We tried to use fast bots to quickly re-index deleted pages. Probably 3 services were tested, using all possible modes, but the result still turned out to be almost zero. Even boosted twitter accounts did not help speed up reindexing. Perhaps the reason is the quality of the pages where we sent the fastbot; maybe it's about the accounts, maybe something else. The main reason could not be identified.
However, Yandex does have a service called “page crawl,” with which the site owner can request quick reindexing. In correspondence with the webmaster, you can ask him to use this function, usually it is not difficult for a person.
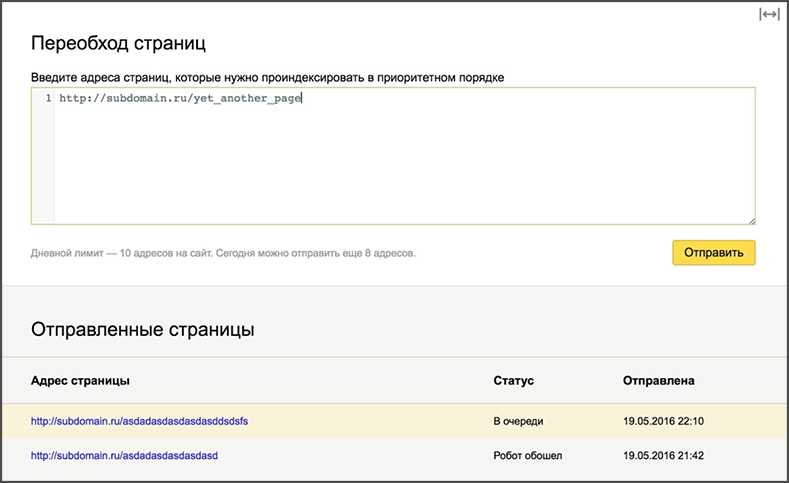
4. Minusinsk does not affect all keywords.
• website creation web studio (did not fall under Minusinsk)
• website in Vladimir (did not fall under Minusinsk)
• website promotion vladimir (did not fall under Minusinsk)
• website promotion in Vladimir (fell under Minusinsk)
Pay attention to the last two keys, which basically identical, but only on the last site lost ground.
There may be many reasons explaining this situation and perhaps we will analyze them in a separate article.
5. It is not necessary to delete all available links.
Here on such a site we found one of our links.

After a large number of attempts to contact the administrator, we did not receive any response. In general, the site shows that it was abandoned 5-6 years ago. We contacted those. support and explained to them the situation. In response, we received something like: "We can’t help you with anything, delete all links and sanctions will be eliminated." After countless attempts to contact the owner of this site, we began to gradually give up. And then we got out of Minusinsk.
The exit from the sanctions took place along with other sites that came under them at about the same time as our site.
At that time, we still had a certain number of purchased links. There were not many of them, from which we can conclude that the algorithm is possible, works by a certain percentage between the “natural” link mass and SEO links, or maybe those. support went to meet us, or maybe there’s just some limit to low-quality links, and we went down below it. There may be several reasons, and we are unlikely to ever find out the exact one.
It took about 3 months to remove the site from the sanctions of this algorithm.
The most important thing in solving this problem is to collect the full reference mass, using all the possible functionality.
Remember that tech. Support is always on your side and it is in its interests to help you resolve any issue, therefore it is necessary to conduct a dialogue with it.
The team of the VladVeb design studio ( http://vladwebstudio.ru/ ):
Sinitsyn Anton - Head of SEO Department
Nikov Serov - SMM / SEO Specialist
Sergey Petukhov - SEO Specialist
A little over a year ago, on 05/14/2015, Yandex launched the Minusinsk algorithm, aimed at identifying and "pessimizing" sites that use SEO links * for search promotion. SEO link is a link that affects search algorithms and can increase the site’s position.
Our company, one of many, received the so-called “letter of happiness”, the content of which was as follows:

We received such a letter, but since this is just a warning, we did not respond to it.
One evening, in February, after almost 9 months, on the internal service of our company, we found a site drop on most requests by 20 positions. Minusinsk in action. We started to plan how to solve this problem.
Sequencing
The main task was to get out of sanctions with minimal losses. Many administrators, frightened by the warning, took and deleted all links at once. We could do the same, however, a sharp decline in the link mass and the loss of high-quality links with high weight could lead to negative consequences when ranking a site in Google.
First stage. Collection and analysis of reference mass
To begin with, it was necessary to collect the full reference mass. The collection was carried out both from downloads from search engines, and using separate services (majestic, ahrefs).
In total, about a million links were collected. They were sorted and cleaned of those that 100% could not get under the "Minusinsk" (links from our sites).
It turned out about 650 links, many of which were very old. The bulk was purchased on exchanges.
Then we began to analyze each link. About link analysis (good / bad) on the Internet you can find a lot of information. There are services that help determine the quality, however, they do not disclose their algorithms, which is why we decided to analyze all the links manually.
Links were evaluated by the following indicators:
1) Google URL Indexing
2) Host characteristics
I Basic
- number of donors (unique IP)
- number of acceptors
- donor to acceptor ratio
II Related
- TIC
- Alexa Rank
- MCF (Majestic Citation Flow)
- MTF (Majestic Trust Flow)
- AUR (Ahrefs URL Rank)
- ADR (Ahrefs Domain Rank)
- Monthly traffic
3) Textual, human characteristics
- anchor and near-anchor text ((not) readability, speech, grammatical errors, etc.)
- page quality
- site quality
An interesting point is that about 200 links purchased through the sape.ru exchange were not in the Google index, which greatly facilitated our task. There are services that help determine the quality, but they do not disclose their algorithms, which is why we decided to analyze all the links manually.
In general, we have the following situation:

In principle, as expected. Most of the links were posted more than 5 years ago in automatic mode for "pennies" or free "runs". Donor performance has deteriorated over time.
Second phase. Gradual removal
Since more than half of the links were not indexed in Google, the risks after their removal are much lower, so we took up them first.
Links were removed by groups between updates. The repeated division of the groups turned out to be somewhat larger than in the screenshot above, so the process of solving the problem was delayed. In cases where the exchange did not allow the removal of the link directly through the system, it was necessary to contact the administrators.
There are a lot of communication methods, the following are the ones we used:
1. Feedback on the site . A very useful thing, but it does not always work, or it does not exist at all, or people respond for a very long time.
2. Contact information on the site. It happened that they turned out to be invalid, but in some cases they helped to get in touch. Separately, it is worth highlighting whois services that determine the contact information of the domain owner.
3. Domain registrars . With their help, you can contact the owner or representative of the domain. This was also used.
4. Communication through the host
5. Comments on the latest news
6. Standard mail . Many sites have standard mails of the form admin@site.ru, abuse@site.ru, webmaster@site.ru, info@site.ru are most often found, but there are others that are found in individual cases, such as support @ site. ru. We sent messages to them if there were no other options to contact. The option is not particularly effective, but also an option. We had no feedback at all.
7. Communication with web developers . Sometimes in the basements of many sites you can see the link and logo of the company that was developing this site. We contacted this company to get in touch with the owner of the site or simply solved this issue with them. In principle, if developers see that the site is about nothing and our link is located on some kind of left page, then removing it should not be a problem.

Imagine that the total number of administrators to contact was ~ 250. I had to write repeatedly, sometimes 3 or more letters for each of the methods listed above.
At first, we tried to remove all the links for free, and since we received a very small amount of feedback, we decided to try to offer the owners a certain amount.
It all started with $ 2. Feedback has increased and we removed some of the links for a fee. However, people began to come across who requested a much larger amount. At first, we scored on them, however, when almost three months passed, and we never got out of Minusinsk, we started paying for everything.
It is difficult to say how much was spent as a whole. There were several links, for the removal of which the administrators requested more than 1000 rubles, some were in the region of 500 rubles and the bulk of the cheap for $ 2.
A few interesting things discovered while working on this issue that may be useful to SEO specialists
1. Shoals with Yandex service. There were moments that some kind of link was in the interface, but it wasn’t in the unloading. All this was solved by communicating with technical support.
2. We removed some pages from Yandex search results through the url removal service in Yandex.Webmaster. You can delete a page with a link if it meets one of three conditions: the server returns 404, the page is not allowed to be indexed via robots.txt or using the noindex meta tag. We basically removed 404 each.

3. Re-indexation. We tried to use fast bots to quickly re-index deleted pages. Probably 3 services were tested, using all possible modes, but the result still turned out to be almost zero. Even boosted twitter accounts did not help speed up reindexing. Perhaps the reason is the quality of the pages where we sent the fastbot; maybe it's about the accounts, maybe something else. The main reason could not be identified.
However, Yandex does have a service called “page crawl,” with which the site owner can request quick reindexing. In correspondence with the webmaster, you can ask him to use this function, usually it is not difficult for a person.

4. Minusinsk does not affect all keywords.
• website creation web studio (did not fall under Minusinsk)
• website in Vladimir (did not fall under Minusinsk)
• website promotion vladimir (did not fall under Minusinsk)
• website promotion in Vladimir (fell under Minusinsk)
Pay attention to the last two keys, which basically identical, but only on the last site lost ground.
There may be many reasons explaining this situation and perhaps we will analyze them in a separate article.
5. It is not necessary to delete all available links.

Here on such a site we found one of our links.

After a large number of attempts to contact the administrator, we did not receive any response. In general, the site shows that it was abandoned 5-6 years ago. We contacted those. support and explained to them the situation. In response, we received something like: "We can’t help you with anything, delete all links and sanctions will be eliminated." After countless attempts to contact the owner of this site, we began to gradually give up. And then we got out of Minusinsk.
The exit from the sanctions took place along with other sites that came under them at about the same time as our site.
At that time, we still had a certain number of purchased links. There were not many of them, from which we can conclude that the algorithm is possible, works by a certain percentage between the “natural” link mass and SEO links, or maybe those. support went to meet us, or maybe there’s just some limit to low-quality links, and we went down below it. There may be several reasons, and we are unlikely to ever find out the exact one.
It took about 3 months to remove the site from the sanctions of this algorithm.
The most important thing in solving this problem is to collect the full reference mass, using all the possible functionality.
Remember that tech. Support is always on your side and it is in its interests to help you resolve any issue, therefore it is necessary to conduct a dialogue with it.
The team of the VladVeb design studio ( http://vladwebstudio.ru/ ):
Sinitsyn Anton - Head of SEO Department
Nikov Serov - SMM / SEO Specialist
Sergey Petukhov - SEO Specialist
