Meet Spring Data MongoDB
Good day to all!
A new flow “Developer on the Spring Framework” started , “suddenly”, this course turned out to be very popular among new students, as well as those who have already learned how to use “regular” java and enterprise. So, if you are interested, come to us for open lessons , and, of course, share interesting materials on the subject.
Translation of the article Spring Data MongoDB Tutorial
Article author Anand Kumar
Let's go!
In the modern world it is very important to create and launch an application as soon as possible. Also, the application should be simple to develop and easy to maintain.
Spring is just such a framework that provides ease of integration with many other different frameworks, which makes it easy to develop an application using Spring. One such integration is Spring integration with MongoDB.

1. Introduction
In this lesson we will discuss the combination of the most famous java-framework "Spring" and the most famous NoSQL database management system (DBMS) "MongoDB". MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL DBMS that stores data in a JSON-like format.
Spring Data and MongoDB integration is provided by Spring to facilitate the interaction of both and the convenience of developers, eliminating the need to write multiple queries for insertion, update, and deletion.
The following are some of the features provided by the Spring Data MongoDB project:
The best way to understand any technology is to use it in practice, and this is exactly what we are going to do now.
Let's create a simple program to learn more about Spring Data MongoDB.
2. Technologies and tools
Let's look at the technologies and tools that we will use to create the program.
3. Project
Structure The structure of our project will look like the one shown below.

The project structure for the Spring Data MongoDB
Gradle project will have the structure shown above. In the case of pom.xml, the project structure will be slightly different.
4. Program
Under this program we will try to complete the following tasks.
Let's now analyze all the components of the program. First of all, we will start with the dependencies and jar files required for the program.
4.1 Gradle
We use Gradle for building as part of the program. The file
In the above file
The tag
The tag is
4.2 Configuration for MongoDB
To use the MongoDB configuration, we need to implement a class
Implementing the MongoConfig.java class
4.3 Model class
Now consider the model class. We use
Student Model Class
4.4 CRUD operations
To perform CRUD operations (abbr. From create, read, update, delete), such as saving, updating, deleting and retrieving data from MongoDB, we will use
Now let's look at the class
The MongoDBPOperations class that will be used to perform CRUD operations
The most important class of a Java program is the class that contains the method
4.5 Application
class The main class that contains the main method is the class
Application class for calling methods of the MongoDBPOperations class
Let's look step by step at the operations that are performed in the class
4.6 Launching the Program
Finally, let's now launch the program as a Java application. Right-click on Application.java -> Run as -> Java Application.
The following result will appear in the console.
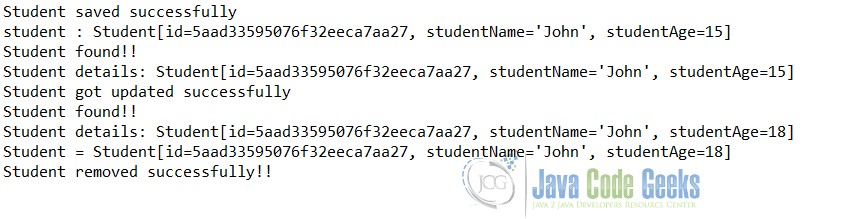
Console output after starting the program
Now let's comment out the command to delete the object. MongoDB will successfully store the data.
Also, let's comment out the line for deleting an object, as shown below.
Class application after commenting on removal methods
After making changes to the program, let's restart it. The following will appear in the console.
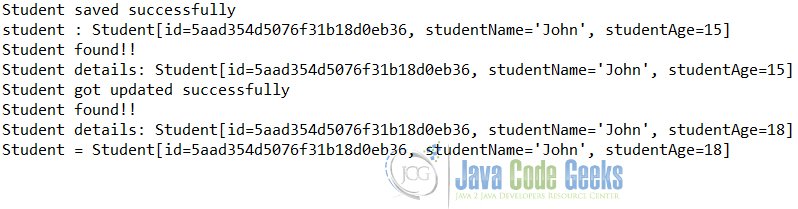
Console when a delete operation is commented out
As a result of commenting on the delete command, the MongoDB will store the data and, therefore, will look like the one below.
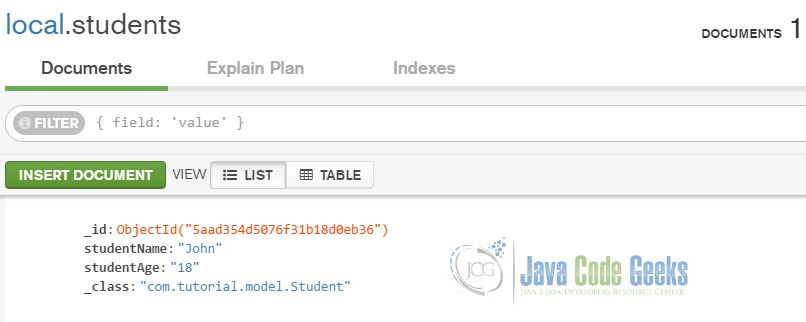
MongoDB output after executing the save and update command
5. Download the Eclipse project
You can download the entire source code of this example here
THE END
As always, we are waiting for questions and comments here or go to Yuri for an open lesson where you can not only listen, but also ask around .
A new flow “Developer on the Spring Framework” started , “suddenly”, this course turned out to be very popular among new students, as well as those who have already learned how to use “regular” java and enterprise. So, if you are interested, come to us for open lessons , and, of course, share interesting materials on the subject.
Translation of the article Spring Data MongoDB Tutorial
Article author Anand Kumar
Let's go!
In the modern world it is very important to create and launch an application as soon as possible. Also, the application should be simple to develop and easy to maintain.
Spring is just such a framework that provides ease of integration with many other different frameworks, which makes it easy to develop an application using Spring. One such integration is Spring integration with MongoDB.

1. Introduction
In this lesson we will discuss the combination of the most famous java-framework "Spring" and the most famous NoSQL database management system (DBMS) "MongoDB". MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL DBMS that stores data in a JSON-like format.
Spring Data and MongoDB integration is provided by Spring to facilitate the interaction of both and the convenience of developers, eliminating the need to write multiple queries for insertion, update, and deletion.
The following are some of the features provided by the Spring Data MongoDB project:
- Spring Data allows you to use both the @Configuration class and the XML configuration.
- The Data Access Spring exception hierarchy is used to translate the exception.
- Integrated mapping between a Java POJO and a MongoDB document.
- The MongoTemplate class, which simplifies the use of common MongoDB operations.
- In addition to MongoTemplate, you can use the MongoReader and MongoWriter classes for low-level mapping.
The best way to understand any technology is to use it in practice, and this is exactly what we are going to do now.
Let's create a simple program to learn more about Spring Data MongoDB.
2. Technologies and tools
Let's look at the technologies and tools that we will use to create the program.
- Eclispe Oxygen.2 Release (4.7.2)
- Java - version 9.0.4
- Gradle - 4.6
- MongoDB server - 3.6
- MongoCompass - 3.6
- SpringDataMongoDB - 2.0.5-RELEASE
3. Project
Structure The structure of our project will look like the one shown below.

The project structure for the Spring Data MongoDB
Gradle project will have the structure shown above. In the case of pom.xml, the project structure will be slightly different.
4. Program
Under this program we will try to complete the following tasks.
- Saving an object in MongoDB
- Updating an object in MongoDB
- Deleting an object from MongoDB
- Getting all the objects from MongoDB
Let's now analyze all the components of the program. First of all, we will start with the dependencies and jar files required for the program.
4.1 Gradle
We use Gradle for building as part of the program. The file
build.gradlewill look like the one below.apply plugin: 'java'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile group: 'org.springframework.data', name: 'spring-data-mongodb', version: '2.0.5.RELEASE'
implementation 'com.google.guava:guava:23.0'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
}In the above file
build.gradle, the line apply plugin: 'java' tells you which plugin to install. In our case, this is a Java plugin. The tag
repositories{}reports the repository from which dependencies should be pulled. We have chosen mavenCentralto pull up dependent jar files. We can also use jcenter to pull the corresponding dependent jar files. The tag is
dependencies {}used to provide the necessary data about jar files that need to be pulled up for the project. 4.2 Configuration for MongoDB
To use the MongoDB configuration, we need to implement a class
AbstractMongoConfiguration. The class MongoConfig.javawill look like the one below. Here we use annotations instead of xml. But XML can also be used to customize the configuration.Implementing the MongoConfig.java class
package com.tutorial.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.config.AbstractMongoConfiguration;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
@ConfigurationpublicclassMongoConfigextendsAbstractMongoConfiguration{
@Overridepublic String getDatabaseName(){
return"local";
}
@Override@Beanpublic MongoClient mongoClient(){
returnnew MongoClient("127.0.0.1");
}
}@Configurationused to define a class MongoConfig.javaas a configuration class. @Beandefines bin MongoClient. 4.3 Model class
Now consider the model class. We use
student.javaas a class a model that contains attributes for the Student, such as Name and Age. The model class is Student.javaused to map the POJO to the MongoDB collection. Student Model Class
package com.tutorial.model;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
@Document(collection = "students")
publicclassStudent{
publicStudent(String studentName, int studentAge){
this.studentName = studentName;
this.studentAge = studentAge;
}
@Idprivate String id;
String studentName;
int studentAge;
public String getStudentName(){
return studentName;
}
publicvoidsetStudentName(String studentName){
this.studentName = studentName;
}
publicintgetStudentAge(){
return studentAge;
}
publicvoidsetStudentAge(int studentAge){
this.studentAge = studentAge;
}
@Overridepublic String toString(){
return String.format(
"Student[id=%s, studentName='%s',
studentAge="+studentAge+"]",
id, studentName);
}
}@Documentdefines the document. The property collection determines the collection that will be used for matching with the collection. All attributes that are referred to as part of the collection must be available in the POJO class. @Ididentifies the collection id. 4.4 CRUD operations
To perform CRUD operations (abbr. From create, read, update, delete), such as saving, updating, deleting and retrieving data from MongoDB, we will use
MongoOperations. Now let's look at the class
MongoDBPOperations.java. This class contains the implementation of all methods of CRUD operations. The MongoDBPOperations class that will be used to perform CRUD operations
package com.tutorial;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoOperations;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Criteria;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Query;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Update;
import com.tutorial.model.Student;
publicclassMongoDBPOperations{
publicvoidsaveStudent(MongoOperations mongoOperation, Student student){
mongoOperation.save(student);
System.out.println("Student saved successfully");
// student object got created with id.
System.out.println("student : " + student);
}
publicvoidsearchStudent(MongoOperations mongoOperation, String critera,String value){
// query to search student
Query searchStudent = new Query(Criteria.where(critera).is(value));
// find student based on the query
Student resultStudent = mongoOperation.findOne(searchStudent, Student.class);
System.out.println("Student found!!");
System.out.println("Student details: " + resultStudent);
}
publicvoidupdateStudent(MongoOperations mongoOperation, String critera,String value, String updateCriteria, String updateValue){
// query to search student
Query searchStudent = new Query(Criteria.where(critera).is(value));
mongoOperation.updateFirst(searchStudent, Update.update(updateCriteria, updateValue),
Student.class);
System.out.println("Student got updated successfully");
}
publicvoidgetAllStudent(MongoOperations mongoOperation){
List listStudent = mongoOperation.findAll(Student.class);
for(Student student:listStudent) {
System.out.println("Student = " + student);
}
}
publicvoidremoveStudent(MongoOperations mongoOperation, String critera,String value){
Query searchStudent = new Query(Criteria.where(critera).is(value));
mongoOperation.remove(searchStudent, Student.class);
System.out.println("Student removed successfully!! ");
}
}The most important class of a Java program is the class that contains the method
main. 4.5 Application
class The main class that contains the main method is the class
Application.java. We will use this class to call methods from the class MongoDBPOperations. Application class for calling methods of the MongoDBPOperations class
package com.tutorial;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoOperations;
import com.tutorial.config.MongoConfig;
import com.tutorial.model.Student;
publicclassApplication{
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
// For Annotation
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MongoConfig.class);
MongoOperations mongoOperation = (MongoOperations) ctx.getBean("mongoTemplate");
MongoDBPOperations ops = new MongoDBPOperations();
Student student = new Student("John", 15);
//save student
ops.saveStudent(mongoOperation, student);
// get student based on search criteria
ops.searchStudent(mongoOperation, "studentName", "John");
//update student based on criteria
ops.updateStudent(mongoOperation, "StudentName", "John", "studentAge", "18");
// get student based on search criteria
ops.searchStudent(mongoOperation, "studentName", "John");
// get all the students
ops.getAllStudent(mongoOperation);
//remove student based on criteria
ops.removeStudent(mongoOperation, "studentName", "John");
// get all the students
ops.getAllStudent(mongoOperation);
}
}Let's look step by step at the operations that are performed in the class
Application.java:- We create
ApplicationContext. This is due to the need to load the configuration. - In addition, an object was created
MongoOperationsfor loading the componentMongoTemplate. - The object
MongoDBOperationsprovides access to methods for performing various operationsMongoOperation. - In addition, a Student object is created with the name John and age 15.
- We call the
saveMethodclass methodMongoDBOperations, and pass the necessary parameters to save the object in the database. - Similarly, we call various methods
MongoDBOperationsone after another.
4.6 Launching the Program
Finally, let's now launch the program as a Java application. Right-click on Application.java -> Run as -> Java Application.
The following result will appear in the console.

Console output after starting the program
Now let's comment out the command to delete the object. MongoDB will successfully store the data.
Also, let's comment out the line for deleting an object, as shown below.
Class application after commenting on removal methods
package com.tutorial;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoOperations;
import com.tutorial.config.MongoConfig;
import com.tutorial.model.Student;
publicclassApplication{
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){
// For Annotation
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MongoConfig.class);
MongoOperations mongoOperation = (MongoOperations) ctx.getBean("mongoTemplate");
MongoDBPOperations ops = new MongoDBPOperations();
Student student = new Student("John", 15);
//save student
ops.saveStudent(mongoOperation, student);
// get student based on search criteria
ops.searchStudent(mongoOperation, "studentName", "John");
//update student based on criteria
ops.updateStudent(mongoOperation, "StudentName", "John", "studentAge", "18");
// get student based on search criteria
ops.searchStudent(mongoOperation, "studentName", "John");
// get all the students
ops.getAllStudent(mongoOperation);
//remove student based on criteria//ops.removeStudent(mongoOperation, "studentName", "John");// get all the students//ops.getAllStudent(mongoOperation);
}
}After making changes to the program, let's restart it. The following will appear in the console.

Console when a delete operation is commented out
As a result of commenting on the delete command, the MongoDB will store the data and, therefore, will look like the one below.

MongoDB output after executing the save and update command
5. Download the Eclipse project
You can download the entire source code of this example here
THE END
As always, we are waiting for questions and comments here or go to Yuri for an open lesson where you can not only listen, but also ask around .
