Roscosmos called the possible reasons for the loss of communication with the orbital observatory "Spectr-R"

In the morning of January 10, 2019, the Spektr-R space radio telescope stopped receiving commands from the Earth . The spacecraft developed by NPO Lavochkin is the space component of the international project Radioastron, which includes more than 40 ground-based radio telescopes and one orbital observatory.
Yesterday in the "Roskosmos" put forward the first version . The priority reason for the loss of communication with the telescope is harsh working conditions in orbit , said Alexander Bloshenko, adviser to the head of Roscosmos on science.
“We have not yet carried out a separate work on the analysis of these reasons. While it is early to do. In general, if we talk about this, a whole set of factors arising from the work in the orbit where it resides will be considered. The farthest point of its orbit is at a distance of about 350 thousand km, almost like a moon, ”explained Bloshenko. - There are a whole range of reasons. These can be temperature drops, radiation, accumulation of electrostatic charge ".

Artistic image of the space radio telescope "Spectr-R". Photo: IKI RAN / Lavochkin Scientific Association
The science adviser doubts that the cause could have been a collision with space junk, because in this case we would have lost the entire apparatus, but it is now fully operational, just does not contact.
Specialists of the Lavochkin Scientific and Production Association will continue their attempts to communicate with the satellite while it is working. There are chances of recovery, although the device has exceeded its service life.
"Spectr-R" exceeded the task and worked out the resource for a long time
The spacecraft was launched in 2011. Its warranty period is three years, and the original scientific program was designed for five years. That is, the device developed a resource and fulfilled the entire scientific program: “Different scientists will have a different view on the initial scientific problem of Radioastron,” sayshead of the research program of the Radioastron project, head of the laboratories of LPI and MIPT, corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences Yuri Kovalev. - Each scientist expected something of his own. I would say that today Radioastron has fulfilled and exceeded the tasks that Russian scientists and the world community have set for it. In some things we were able to achieve much more than expected, some things were unexpected for us, somewhere we were less fortunate. For example, the center of the Deva-A galaxy could be more transparent. We still hoped through the plasma in the center of the Virgin-A to see the shadow of the black hole. And the angular resolution was enough for us. But even before the launch of RadioAstron, we understood that we should be lucky from the point of view of radiation absorption. More precisely, his absence. Bad luck. But honestly speaking
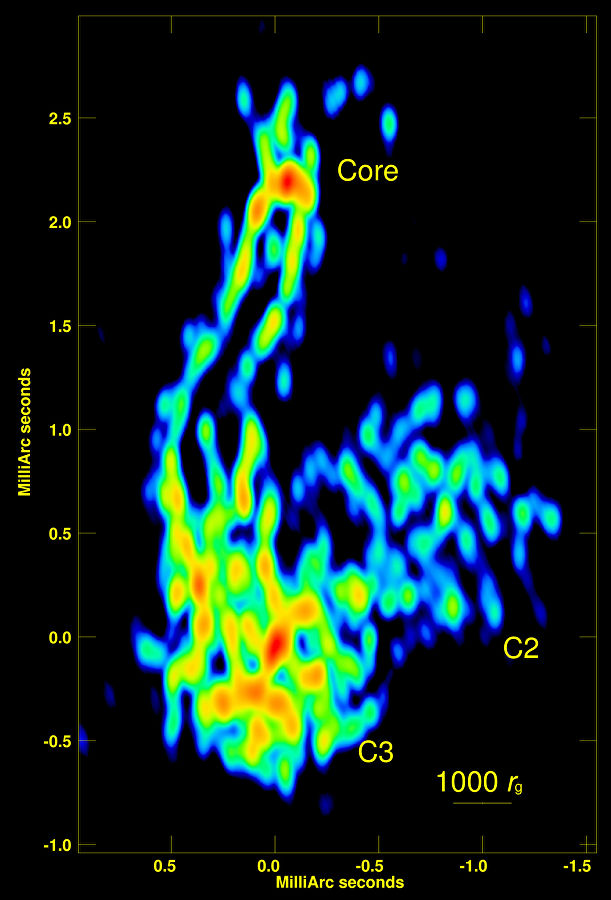
Emission in the Perseus A galaxy. Image: Radioastron
The next stage of space exploration will be the Millimetron project on shorter waves, which will allow you to look much deeper: “The center of our galaxy from Radioastron is hidden by scattering, because along the road from Earth to the center of the Galaxy, where the black hole weighing four million solar masses is located , a rather dense cloud is located. It scatters radio emission, so the center of the Galaxy for us looks like a lantern in a fog. If we use a short wavelength for research, this problem will not be. When we launched Radioastron, we thought that there was no chance to get around this restriction. However, after the launch, without waiting for it, they discovered a new scattering effect of radio waves, which will allow to solve a two-step problem: to determine the characteristics of the scattering parameters with high accuracy, and then, applying them to the obtained data, try to restore the original image of the object hidden behind the galactic fog. Processing this data is a very difficult task. We are still doing it. Let's go to short wavelengths with the “Millimetron” - we will see the center of the Galaxy relatively easily, ”says Yuri Kovalev.
The launch of a new space observatory is scheduled after 2024.
